Project dashboard
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
A dashboard is a visual display of the most critical information and data which is needed to fulfill the objective of a specific job, project, or other tasks. A dashboard is configurable allowing for customization of data and the ability to choose how the data is displayed to e.g., include text, charts or graphs. Usually, a dashboard is linked to a database where it receives its information from. Thus, the more frequent the connected database is updated, the more up to date the dashboard is <ref> Stephen, Few, Information Dashboard Design, 2006, O'Reilly</ref>. | A dashboard is a visual display of the most critical information and data which is needed to fulfill the objective of a specific job, project, or other tasks. A dashboard is configurable allowing for customization of data and the ability to choose how the data is displayed to e.g., include text, charts or graphs. Usually, a dashboard is linked to a database where it receives its information from. Thus, the more frequent the connected database is updated, the more up to date the dashboard is <ref> Stephen, Few, Information Dashboard Design, 2006, O'Reilly</ref>. | ||
| + | ===Types of dashboard=== | ||
There are different types of dashboards which overall can be categorized as strategic, tactical and operational dashboards <ref>Rasmussen, N., Chen, C. Y., & Bansal, M, Business Dashboard. A Visual Catalog for Design and Deployment, 2012, Wiley & Sons</ref> | There are different types of dashboards which overall can be categorized as strategic, tactical and operational dashboards <ref>Rasmussen, N., Chen, C. Y., & Bansal, M, Business Dashboard. A Visual Catalog for Design and Deployment, 2012, Wiley & Sons</ref> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 26: | ||
Using Rasmussen et. al categorizations of dashboard then project dashboards would be categorized as a type of tactical dashboard. However, the choice of static or dynamic level should depend on the intention of the project dashboard. It is possible to create a dashboard which allows to monitor progress customized to the specific project and communicate this through the dashboard to project stakeholders. Once the project is closed, the data which has been gathered throughout the project can be used for evaluating results which furthermore can be used to improve future projects <ref>Rasmussen, N., Chen, C. Y., & Bansal, M, Business Dashboard. A Visual Catalog for Design and Deployment, 2012, Wiley & Sons</ref> <ref> Stephen, Few, Information Dashboard Design, 2006, O'Reilly</ref>. | Using Rasmussen et. al categorizations of dashboard then project dashboards would be categorized as a type of tactical dashboard. However, the choice of static or dynamic level should depend on the intention of the project dashboard. It is possible to create a dashboard which allows to monitor progress customized to the specific project and communicate this through the dashboard to project stakeholders. Once the project is closed, the data which has been gathered throughout the project can be used for evaluating results which furthermore can be used to improve future projects <ref>Rasmussen, N., Chen, C. Y., & Bansal, M, Business Dashboard. A Visual Catalog for Design and Deployment, 2012, Wiley & Sons</ref> <ref> Stephen, Few, Information Dashboard Design, 2006, O'Reilly</ref>. | ||
| + | ===Common benefits of dashboard=== | ||
The benefit of a dashboard will be subjective to the user and differentiate depending on the type of dashboard. However, some common benefits are following: | The benefit of a dashboard will be subjective to the user and differentiate depending on the type of dashboard. However, some common benefits are following: | ||
*'''Monitor performance and progress:''' By continuously monitoring the task at focus it will provide the users with information to analyze and evaluate of who and/or what went good or bad <ref> Pauwels, K. et al., Dashboards as a Service Why, What, How, and What Research Is Needed?, November 2009, Journal of Service Research, pp. 175-189</ref> | *'''Monitor performance and progress:''' By continuously monitoring the task at focus it will provide the users with information to analyze and evaluate of who and/or what went good or bad <ref> Pauwels, K. et al., Dashboards as a Service Why, What, How, and What Research Is Needed?, November 2009, Journal of Service Research, pp. 175-189</ref> | ||
| − | + | *'''Ability to make informed decisions:''' When having the necessary and correct information available, then informed decision making is possible and gut-feeling decision making can be limited <ref> Stephen, Few, Information Dashboard Design, 2006, O'Reilly</ref>. | |
| + | *'''Enhanced efficiency:''' It limits the time used for searching for information or reviewing a large number of reports to gain necessary information <ref> Pauwels, K. et al., Dashboards as a Service Why, What, How, and What Research Is Needed?, November 2009, Journal of Service Research, pp. 175-189</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Motivate employees and stakeholders:''' When seeing direct results of actions, it enhances a feeling of involvement and ownership with employees<ref> Pauwels, K. et al., Dashboards as a Service Why, What, How, and What Research Is Needed?, November 2009, Journal of Service Research, pp. 175-189</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Cost-efficient:''' Manual labor regarding searching and reporting process can be eliminated, as this is handled by the dashboard <ref> Pauwels, K. et al., Dashboards as a Service Why, What, How, and What Research Is Needed?, November 2009, Journal of Service Research, pp. 175-189</ref>. | ||
===Choosing key Performance indicators=== | ===Choosing key Performance indicators=== | ||
| − | + | To achieve the benefits as mentioned above it is crucial to establish the right KPIs for the individual dash-board. This is important, because “You cannot correct or improve something that cannot be effectively identified and measure.” (Kerzner, 2017, s. 1). Thus, it is imperative to establish an understanding of what are effective KPIs, within the context of the specific job, objective or others task the dashboard is to measure. For certain dashboards common KPIs such as time and cost can be sufficient. For other dash-boards customized metrics may be required (Kerzner, 2017). | |
| − | + | ||
| + | In general dashboards should be aligned with the company’s strategic and business goals (Lamptey & Fayek, 2012). Furthermore, dashboards should only include the necessary KPI which must be relevant and communicated in regard to the primary users of the dashboards. Occupying the limited space on the dashboard with wrong or unnecessary KPIs will lead to the dashboard becoming redundant (Few, 2006). | ||
| + | |||
===Visualization=== | ===Visualization=== | ||
Revision as of 17:23, 4 March 2022
Managing projects can be a complex task as there is a great deal of information and data which requires communication to various stakeholders. The larger the projects, the higher the complexity, thus making project management more difficult. Continuous progress reporting of projects gives project managers the benefit of having insight in the project and allows for informed decision making [1]. Project dashboard can be an efficient tool to communicate the most essential information for project stakeholders to improve project efficiency and allow for monitoring progress to determine the status of the project. [2].
A project dashboard is a visualization of central project data, which ideally includes key performance metrics which are customized to specific projects. These metrics should track performance and progress of the project such as deadlines, budget, deliveries, and other necessary insights into the project. To succeed with project management, it is imperative that project progress and performance is communicated, and project results are shared [3]. This should be done to encourage and motivate stakeholder of the project. Furthermore, the information is critical for project manager as without the necessary information the manager will face difficulty in managing the project. To gain most value of project dashboards it is imperative for project manager to have a fundamental grasp of the concept as a communication medium and be aware of who the receiver of the information and data is. Furthermore, a poorly visualized dashboard will result in a cluttered mess. Thus, a project dashboard should be well presented with necessary data to be an efficient mean of communication [4].
This article will focus on the digital dashboards and give an introduction to the general concept and of the tool. Hereafter, the article will focus on the application of dashboards for project management with an emphasis on their value as a communication tool and implementation of project dashboards are presented. Finally, common pitfalls and limitations of project dashboards are discussed.
Contents |
Dashboards as visual display
The following section will give an introduction to the general concept of dashboard. Followed by a description of the importance of choosing the right Key Performance Indicator (KPI) for the dashboard and how the information and data is visually displayed to enhance communication.
Concept of dashboard
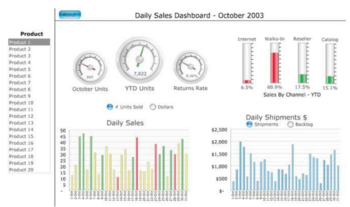
Few argues modern dashboards originate from Executive Information Systems from the 1980’s [6]. Whereas Krezner argues they have grown from decision support system in the 1970’s [7]. However, both claims that with the development of the internet in the late 90’s, and eventually business intelligence, allowed for development of digital dashboards. Furthermore, the introduction KPIs in the mid 90’s was introduced and became a common focus in a business-related context. The advanced in technology and the focus of KPIs allowed for the digital dashboards commonly used today [8] [9].
A dashboard is a visual display of the most critical information and data which is needed to fulfill the objective of a specific job, project, or other tasks. A dashboard is configurable allowing for customization of data and the ability to choose how the data is displayed to e.g., include text, charts or graphs. Usually, a dashboard is linked to a database where it receives its information from. Thus, the more frequent the connected database is updated, the more up to date the dashboard is [10].
Types of dashboard
There are different types of dashboards which overall can be categorized as strategic, tactical and operational dashboards [11]
Strategic dashboards are intended to secure organizational alignment of strategic objectives. Typically, these are used by managers and focus will be on high-level measures of performance. They are more static as they do not require frequent update to support the strategic purpose.
Tactical dashboards are used to monitors progress in key project or initiatives, which are aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives. Tactical dashboards have an analytical purpose and therefore require more context data to reach a higher level of detail to thoroughly breakdown the data. They are also used to monitoring progress and should enable the user to identify areas to investigate, to support and which corresponding actions are required. Tactical dashboards are likewise more static, where the data is not constantly changing, as this will make it difficult for the user to perform the required analysis.
Operational dashboards are more dynamic. When monitoring operations real-time or as frequent updated data as possible will enable the users of the dashboard to maintain status awareness of operations and take necessary action as fast as possible when needed.
Using Rasmussen et. al categorizations of dashboard then project dashboards would be categorized as a type of tactical dashboard. However, the choice of static or dynamic level should depend on the intention of the project dashboard. It is possible to create a dashboard which allows to monitor progress customized to the specific project and communicate this through the dashboard to project stakeholders. Once the project is closed, the data which has been gathered throughout the project can be used for evaluating results which furthermore can be used to improve future projects [12] [13].
Common benefits of dashboard
The benefit of a dashboard will be subjective to the user and differentiate depending on the type of dashboard. However, some common benefits are following:
- Monitor performance and progress: By continuously monitoring the task at focus it will provide the users with information to analyze and evaluate of who and/or what went good or bad [14]
- Ability to make informed decisions: When having the necessary and correct information available, then informed decision making is possible and gut-feeling decision making can be limited [15].
- Enhanced efficiency: It limits the time used for searching for information or reviewing a large number of reports to gain necessary information [16].
- Motivate employees and stakeholders: When seeing direct results of actions, it enhances a feeling of involvement and ownership with employees[17].
- Cost-efficient: Manual labor regarding searching and reporting process can be eliminated, as this is handled by the dashboard [18].
Choosing key Performance indicators
To achieve the benefits as mentioned above it is crucial to establish the right KPIs for the individual dash-board. This is important, because “You cannot correct or improve something that cannot be effectively identified and measure.” (Kerzner, 2017, s. 1). Thus, it is imperative to establish an understanding of what are effective KPIs, within the context of the specific job, objective or others task the dashboard is to measure. For certain dashboards common KPIs such as time and cost can be sufficient. For other dash-boards customized metrics may be required (Kerzner, 2017).
In general dashboards should be aligned with the company’s strategic and business goals (Lamptey & Fayek, 2012). Furthermore, dashboards should only include the necessary KPI which must be relevant and communicated in regard to the primary users of the dashboards. Occupying the limited space on the dashboard with wrong or unnecessary KPIs will lead to the dashboard becoming redundant (Few, 2006).
Visualization
-The visualization of the project dashboard is essential -Should be able to be viewed with a glance. Psychological aspect of seeing a color e.g., traffic light indicators [19]. For instance, having a dashboard monitor a risk, quality, cost etc. By using a color from a traffic light the viewers will just by a glance have an indication of the project metrics status. When the dashboard shows red the viewer will by a quick glance be aware of the status and take necessary action. By showing green, the receiver will be aware of status as under control.
Dashboards for project management
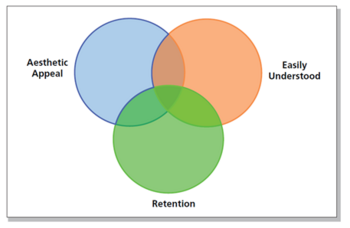
Project dashboards differentiate from typical business dashboards by having to be updated more frequently. Harold Kerzner argues that dashboards for project dashboards, regardless of the projects nature, should include following core attributes [21]:
- Aesthetic appearance: Creating a visualization, which is appealing to the viewer or users and make them engage in using the project dashboard
- Easily understood: The information and data displayed should be communicated clearly and should be easy to understand leaving little room for misinterpretations.
- Retention: The information and data should be remembered.
Depending on the nature of the project and the people involved, project dashboards have various different valuable functions. Following section will provide insight to some of the most important, but not limited to, functionalities. The important function which will be on focus for this article is:
- Communication of project objective
- Communication of project progress
- Cost-efficiency
Communication of project objective
ISO (DS/ISO 21500:2021) has defined project as “temporary endeavor to achieve one or more defined objectives” [22]. By this standard the success criteria for a project are to achieve the defined objective(s). Thus, the understanding of the project objective must be communicated clearly, and every stake-holder involved in the project must have a common understanding of the objective to perceive the project as a success. Another important point to emphasis is in projects (and especially in agile projects) the objective is changing, which further complicates the process of securing a common understanding of project objective.
Communication of project progress
Cost-efficiency
Implementing Project Dashboards
Implementing project dashboards can be done by following these steps [23]:
- Needs assessment
- Selecting sufficient data/information input
- Choosing Key Performance indicators
- Selecting visuals
- Secure interaction of project dashboard with stakeholder
- Maintenance
It should be emphasized that the critical step of implementing project dashboard is the pre-work which is to be done before creating the project dashboards. The quality of the project dashboard is a direct result of the work, which has been made in the first phase.
Limitations of project dashboard
The benefits of dashboards which have been presented in this article, is what potentially can be obtained with the correct use of project dashboards. However, there are limitations. The following section will focus on the common pitfalls of using project dashboards and also the general limitations of project dash-boards.
Common pitfalls of project dashboards
- Misunderstanding the core concept of dashboard: Understanding the concept and value of a dashboard for project management is essential otherwise there is a risk of the dashboard being redundant.
- Insufficient or ineffective information overload
General limitations of project dashboards
- Creating and implementing a project dashboard is time consuming, therefor it is important to consider if time is spent efficiently creating a project dashboard or consider if other means of communication are more efficient.
- It is essential to take the context of the project into consideration. For small projects with a short life span and few stakeholders, it might be more efficient to have close verbal communication rather than using time on creating a project dashboard.
- Technological limitations.
Annotated Bibliography
References
- ↑ Lamptey, W. N., & Fayek, A., Developing a Project Status Dashboard for Construction, 2012, International Journal of Architecture, Engineering and Construction, pp. 112-120
- ↑ Harold, Kerzner, Project Management Metrics, KPIs, and Dashboards, 2017, Wiley & Sons
- ↑ American National Standard, ANSI/PMI 99-001-2004, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), 3rd Edition
- ↑ Stephen, Few, Information Dashboard Design, 2006, O'Reilly
- ↑ Stephen, Few, Information Dashboard Design, 2006, O'Reilly
- ↑ Stephen, Few, Information Dashboard Design, 2006, O'Reilly
- ↑ Harold, Kerzner, Project Management Metrics, KPIs, and Dashboards, 2017, Wiley & Sons
- ↑ Stephen, Few, Information Dashboard Design, 2006, O'Reilly
- ↑ Harold, Kerzner, Project Management Metrics, KPIs, and Dashboards, 2017, Wiley & Sons
- ↑ Stephen, Few, Information Dashboard Design, 2006, O'Reilly
- ↑ Rasmussen, N., Chen, C. Y., & Bansal, M, Business Dashboard. A Visual Catalog for Design and Deployment, 2012, Wiley & Sons
- ↑ Rasmussen, N., Chen, C. Y., & Bansal, M, Business Dashboard. A Visual Catalog for Design and Deployment, 2012, Wiley & Sons
- ↑ Stephen, Few, Information Dashboard Design, 2006, O'Reilly
- ↑ Pauwels, K. et al., Dashboards as a Service Why, What, How, and What Research Is Needed?, November 2009, Journal of Service Research, pp. 175-189
- ↑ Stephen, Few, Information Dashboard Design, 2006, O'Reilly
- ↑ Pauwels, K. et al., Dashboards as a Service Why, What, How, and What Research Is Needed?, November 2009, Journal of Service Research, pp. 175-189
- ↑ Pauwels, K. et al., Dashboards as a Service Why, What, How, and What Research Is Needed?, November 2009, Journal of Service Research, pp. 175-189
- ↑ Pauwels, K. et al., Dashboards as a Service Why, What, How, and What Research Is Needed?, November 2009, Journal of Service Research, pp. 175-189
- ↑ Harold, Kerzner, Project Management Metrics, KPIs, and Dashboards, 2017, Wiley & Sons
- ↑ Harold, Kerzner, Project Management Metrics, KPIs, and Dashboards, 2017, Wiley & Sons
- ↑ Harold, Kerzner, Project Management Metrics, KPIs, and Dashboards, 2017, Wiley & Sons
- ↑ DS/ISO 21500:2021, Project, programme and portfolio management - Context and concepts, 2021, Dansk Standard
- ↑ Harold, Kerzner, Project Management Metrics, KPIs, and Dashboards, 2017, Wiley & Sons