Project viability assessment through Net Present Value (NPV)
(→References) |
(→Annotated Bibliography) |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
Revision as of 23:15, 19 February 2023
Contents |
Abstract
The Net Present Value (NPV) is a widely used financial metric in project management. Its purpose is to evaluate the profitability of a proposed project by aggregating the streams of costs and benefits into a single value. This makes for an effective indicator of identifying profitable projects when assessing multiple projects at a time. For a given project to be considered a profitable investment, its NPV must be larger than zero. [1]
Central to the calculation of the NPV is assigning varying weights, dependent on time, to the benefits and costs through the utilization of a so-called discount factor, which is calculated using a discount rate. The discount rate represents the rate of interest that is used to discount all future costs and benefits. [2] By incorporating this principle, the NPV accounts for and subscribes to the paradigm of the time value of money, referring to the idea that money has a different value at different points in time.[3]
This article explores central concepts connected to the calculation and application of NPV in the assessment of projects, programs, or portfolios. For demonstration purposes, an example of the calculation of an emulated project's NPV will be given. Moreover, the advantages and disadvantages of using NPV as an indicator of project profitability will be addressed.
NPV Formula
The net present value method or tool achieves comparability of all costs and benefits by discounting to the beginning of the investment period. The NPV is amongst the most frequent and sophisticated tools when it comes to assessing the probability of projects or investments. [4] The formula used to calculate the net present value is presented below:
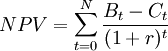
-
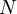 :The calculation period of the project in years.
:The calculation period of the project in years.
-
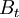 : The aggregated amount of benefits (both positive and negative) in year t
: The aggregated amount of benefits (both positive and negative) in year t
-
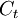 : The amount of investments costs in year t
: The amount of investments costs in year t
-
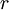 : The discount rate
: The discount rate
There are two inherent principles to the NPV as a tool. The first principle is the time value of money, which postulates that an uncertain Danish Crown tomorrow is less valuable than a Danish Crown today.
Time value of money
Brief explanation time value of money and how it relates to NPV
Discount rate
A succinct description of discount rate and it’s formula. Necessary to explain, to grasp the concept of NPV.
Financial Appraisal
Why do we make financial appraisals of projects, programs, and portfolios? Where do NPV fit?
Application and decision making
In the following paragraph, the application of NPV in regard to assessing the profitability of a project prior to commencing it will be outlined.
Example
A practical example on how to calculate the NPV of a construction project.
Advantages
Disadvantages
Annotated Bibliography
References
- ↑ Investopedia. (2023). Net Present Value (NPV): What It Means and Steps to Calculate It. Investopedia, 1–8. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/n/npv.asp
- ↑ Barfod, M. B., & Leleur, S. (2019). Decision Support and Strategic Assessment DTU Management Compendium.
- ↑ Gardner, N.D. 2004. The Time Value of Money: A Clarifying and Simplifying Approach. Journal of College Teaching & Learning (TLC). 1, 7 (Jul. 2004).
- ↑ Häcker, J., & Ernst, D. (2017). Financial Modeling. In Financial Modeling.