Resource Allocation in Project Management
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
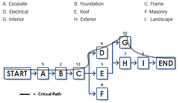
*1- A project activity network diagram | *1- A project activity network diagram | ||
| − | [[File:Activity-Network-Diagram-Example-Chart.png| | + | [[File:Activity-Network-Diagram-Example-Chart.png|thumb|alt=Figure 1 - Activity Network Diagram]] |
*2- | *2- | ||
Revision as of 16:07, 15 September 2016
Contents |
Introduction
In project management exists a tight connection between results and resources optimization. An inadequate planning of resource allocation might lead to a non-manageable or non-reasonable budget formulation.
Each organization must wisely allocate resources to avoid delays, rework, nonconformity and to ensure an overall company efficiency in the long run. All companies face the same dilemma at one point, how best allocate resources. Allocating resources to wrong ideas or projects that eventually fail will lead to wastage. On the other hand, not allocating resources in the right ones can lead to even greater opportunity costs. Under and over allocation are the main problems that arise in a non-planned resource allocation scenario.
Is critical to have a planned approach in RA to manage a project portfolio effectively. Being able to allocate the correct resources, in terms of skills and quantity, to the right ideas, projects and products should be the final goal of each project manager.
Resource Allocation
The process of assigning and managing assets in order to support an organization's strategic goals is called resource allocation. In project Management, is the scheduling of activities and resources required by those activities taking into consideration both the project time and the resource availability. It involves balancing competing commitments and priorities in order to determine the most effective course of action to best utilize a limited pool of resources and maximize the return on investment.
Core Resources
- Land: Natural resource required in production process, land, mineral, forest, oil and water resources.
- Labour: The aggregate of humans physical and mental effort used to generate goods and services. It is a primary factor in production. The labor force is determined by the adult population of a nation.
- Capital:Wealth in the form of money or assets, sign of the financial strength of an individual, organization, or nation, and assumed to be available for development or investment.
Allocation Decisions
The basic allocation decisions begin with the choice of what is going to fund the project, it is important to avoid allocating resource merely in terms of meeting milestones, but also in terms of timing and utilization of scarce resources. The challenge
Resource Allocation Problem
- Time Limited: Projects must be finished on an agreed time, using as few resources as possible.
- Resources Limited: Projects must be execute by not exceeding specific level of resource usage or general resource constraints.
- Resource Over-allocation: Assign more tasks than what resources can handle within the standard workweek time frame. A company with multiple projects and a limited pool of resources often risk to encounter this issue, this can lead to overtime and overspending on financial resources.
Resource Allocation Techniques
“The schedule produced for a project assumes that enough manpower and equipment is available to get the activities done as scheduled. This is not always the case, and in a large or complex project, it might not be obvious that a deficiency exists.” [1]
“Resources required by activities are unlimited, while some resources are highly limited in practice. In most real construction projects, scheduling without considering resource limitations may result in a non-credible schedule, since the start-ability of activities is affected by resource availability.” [2]
There are different solutions and techniques to tackle the problem of resource allocation, identify the right one for a specific business is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the procedure.
Resource Leveling
The aim of leveling resources is to minimize the variations in resource loading by "Shifting tasks within their slack allowances". [3]
The technique is applied to resolve conflicts and to create a smoother distribution of resources, determine the correct resource requirements to ensure availability at any given time and to schedule the activities in order to secure the smoothest achievable transition across usage levels.
In resource leveling resources should be assigned to those activities with:
- Minimum slack [4]
- Shortest duration
- Earlier start
- Most amount of successor tasks
- Highest resources requirement
Steps
- 1- A project activity network diagram
- 2-
- 3-
- 4-
Prioritize Projects
Linking Tasks
Leaving Breathing Room
Avoid "Putting out Fires" approach to PM
References
- ↑ The Associated General Contractors of America(AGC) (1976). The Use of CPM In Construction.
- ↑ Kim, Kyunghwan (2003). “A Resource-constrained CPM (RCPM) Scheduling and Control Technique with Multiple Calendars” - Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University PHD. Dissertation. https://theses.lib.vt.edu/theses/available/etd-06272003-143644/unrestricted/ETD.pdf.
- ↑ Schwalbe, Kathy (2007). Information Technology Project Management 5th Edition.
- ↑ Scheduling projects: How to determine the critical path using activity slack calculations? - http://www.pmknowledgecenter.com/dynamic_scheduling/baseline/scheduling-projects-how-determine-critical-path-using-activity-slack-calculations - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016