Need-Based Theories of Motivation
(→Abstract) |
(→Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
=== Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs === | === Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs === | ||
| + | In the 1960 Abraham Maslow proposed that there are five stages of human needs that motivate our behaviour. These stages are psychological needs, safety needs, belonging needs, esteem needs and self-actualization needs which are described in more details in the figure below. His idea is that the lowest level needs must be met before a person strives to satisfy needs higher up in the hierarchy. Once a need is satisfied, it ceases to operate a source of motivation. | ||
| − | + | [[File:Maslow.png|center|600px|Maslow's hierachy of needs]] | |
| − | + | This theory identifies some needs which are an importation source of motivation for many people, but he argues that only one level is motivational at one time. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
=== Alderfer's ERG Theory === | === Alderfer's ERG Theory === | ||
Revision as of 15:24, 18 February 2018
Contents |
Abstract
A need is a requirement or necessity for survival and wellbeing. The basic premise of need theories is that people are motivated to obtain outcomes at work that satisfy their needs. Need theories suggest that to motivate a person to contribute valuable inputs to a job and perform at a high level, a manager must determine what needs the person is trying to satisfy at work and ensure that he og she receives outcomes that help to satisfy those needs in return for performing at a high level and helping the organisation achieve its goals.
This article looks at some of the need theories and how these are connected to each other. It states examples of what managers can do to help employees to satisfy the needs at work. Lastly the limitations are mentioned.
Big idea
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
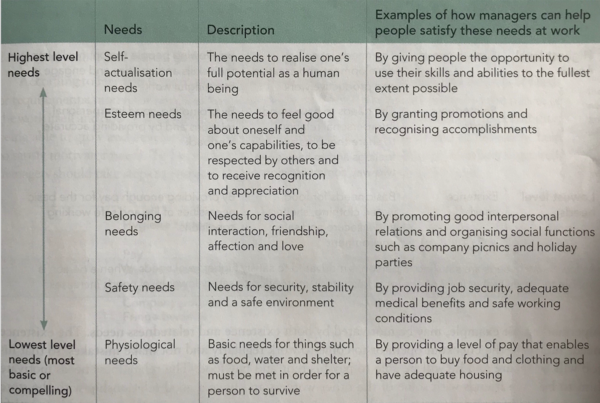
In the 1960 Abraham Maslow proposed that there are five stages of human needs that motivate our behaviour. These stages are psychological needs, safety needs, belonging needs, esteem needs and self-actualization needs which are described in more details in the figure below. His idea is that the lowest level needs must be met before a person strives to satisfy needs higher up in the hierarchy. Once a need is satisfied, it ceases to operate a source of motivation.
This theory identifies some needs which are an importation source of motivation for many people, but he argues that only one level is motivational at one time.
Alderfer's ERG Theory
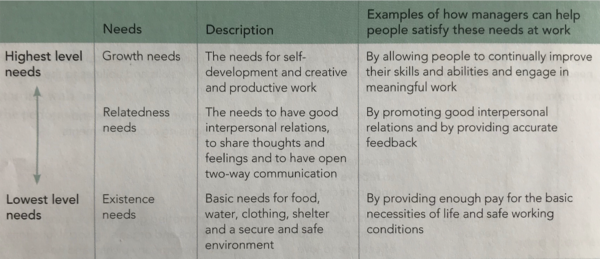
Clayton Alderfer observed that individual needs differ according to circumstances. They do not need to move in an order of progression.
Satisfaction-Progression
Frustration-Regression
McClelland's Need Theory
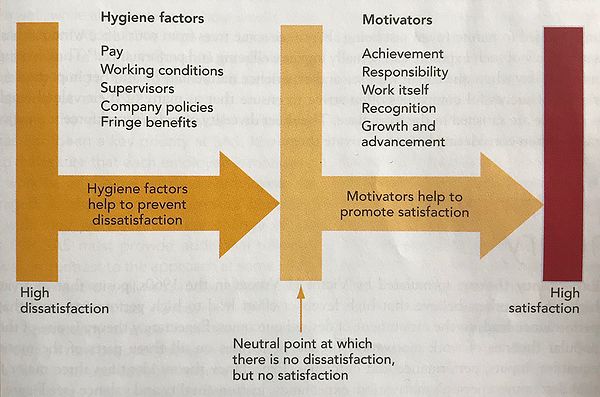
Herzberg's Motivation-Hygiene Theory
Comparison
Application
This section is in progress.
Limitations
This section is in progress.
Annotated bibliography
This section is in progress.
Di Waddell, Gareth R. Jones and Jennifer M. George (2013). Contemporary Management (3rd ed.).
https://wikispaces.psu.edu/display/PSYCH484/2.+Need+Theories