Project governance framework
(→Transaction cost economics (Assessment role)) |
|||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
<ref name="TCE"> O. Williamson, (1998). Transaction cost economics: how it works; where it is headed. De Economist 146, 23–58. </ref> | <ref name="TCE"> O. Williamson, (1998). Transaction cost economics: how it works; where it is headed. De Economist 146, 23–58. </ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="biesenthal"/> | ||
====Stakeholder theory (Coordinating role)==== | ====Stakeholder theory (Coordinating role)==== | ||
| − | + | The stakeholder theory, being based on a socially oriented perspective, focuses on a larger group than just the shareholders and it challenges assumptions of the agency theory, that the shareholder interests are primal. It implies that the management of a company should take the interests of all stakeholders (e.g. employees, suppliers, customers, environment) into account and suggests that conflicts and different interests need to be balanced between organizational shareholders | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | According to this theory, project governance is necessary as a strategy for project teams to understand and respond to different stakeholder groups. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | <ref name="Stakeholder"> Donaldson, T., Preston, L.E., 1995. The stakeholder theory of the corporation: | ||
| + | concepts, evidence, and implications. Acad. Manag. Rev. 20, 65–91 </ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="biesenthal"/> | ||
| + | |||
====Stewardship theory (Strategic role)==== | ====Stewardship theory (Strategic role)==== | ||
*provides an alternative description of human behavior compared to agency theory and is rooted in psychology and sociology | *provides an alternative description of human behavior compared to agency theory and is rooted in psychology and sociology | ||
Revision as of 09:36, 21 February 2018
Contents |
Abstract
The PMI Guide on Project Management defines Project Governance as “the alignment of the project with stakeholders’ needs or objectives”. It is a critical function for the management of stakeholders and furthermore for the achievement of organizational objectives. Project governance provides the project managers and sponsors with a framework on how to make decisions to satisfy both stakeholder needs as well as organizational strategic objectives. [1] A guide by the Association of Project Management (APM) does not only consider single projects but aims to align the organization’s project portfolio to its goals. [2] A paper on a conceptual framework for project governance and the management of project management suggests that it has two key function. The first is to make decisions about which projects an organization should do and by this specify rights and responsibilities of project participants and define rules and procedures for making decisions in the projects. Secondly, project governance has an oversight and assurance function in order to support the organization’s strategy. [3] According to P. Renz, project governance closes the gap between corporate governance and the actual management of projects. It provides the project managers with more strategic and integrative solutions beyond standard project management methodologies and operationalizes the corporate governance strategy. There is not one single definition and approach for a framework that can be taken for each and every specific case. This article will define aspects of a framework, which are presented in the literature on project governance. While the APM bases its framework on adhering to different principles, P. Rentz defines a Project Governance Model based on general governance theories and resulting key responsibilities. This article will define elements of a framework for project governance from different perspectives. [4]
Definition and Background
What is project governance?
"Project governance is a process-oriented system by which projects are strategically directed, integratively managed, and holistically controlled, in an entrepreneurial and ethically reflected way, appropriate to the singular, time-wise limited, interdisciplinary, and complex context of projects." [4] It has an oversight function which is aligned with the organization's governance model. A project governance framework provides the project manager and team with structure, processes, decision-making models and tools for managing the project, while supporting and controlling the project for successful delivery. [1] This high-level structure helps an organization to align it projects and their objectives with the organizational strategy as well as monitoring their performance. [5] Different actors and activities contribute to project governance and when effectively executed, project governance ensures that projects are delivered efficiently and sustainable while being in line with with the organisation's objectives. It also includes instructions for the board and other major stakeholders on how relevant and reliable information are exchanged between them. Summarizing, project governance helps to:
- assure boards and executives that solid governance requirements are in place across all the past and ongoing projects in an organization
- optimize the project portfolio according to strategy
- avoid common mistakes and failures in project management resulting in insufficient performance
- improve the relationships with staff, customers and suppliers
- minimize risk originating from new projects
- while maximizing the benefits realized through projects
- assure a continuing development of the organization
Why is project governance needed?
Project governance can support the successful outcome of a project in many ways. How to do project management is usually well defined within an organization and there are lots of information in- and externally on it. When it comes to more strategically problems, which are not covered within a project management framework, project managers are left without advice. The strategic and integrative nature of project governance bridges this so called "governance gap" and is going beyond standard project management methodologies. From a corporate level perspective, project governance helps to operationalize the strategy of an organization. It is linking corporate governance and strategy with the operational level, which is responsible for carrying out the projects. Through this, concerns on both levels are carried to the respective counterpart which brings them closer together. In a project oriented company, there is usually a asymmetry of information and knowledge between the project managers on the lower levels and governance boards on the upper level. Project governance overcomes this issue by being meaningful, value-adding link between project management and (corporate) governance. It institutionalizes a targeted information flow that enables the building of necessary knowledge. With this strategic orientation and a clear governance structure, it also handles multi-ownership of projects. [4]
Relation to Program, Portfolio and Corporate Governance
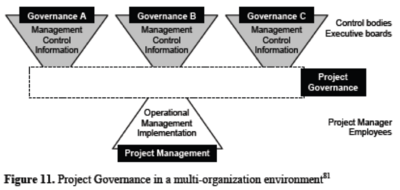
Project governance is not one single function as e.g. a project management office. It is rather an integrative and integrating element, which is related to various program, portfolio and corporate governance as well as management. It is a linking element between all of the above, aiming to resolve the governance gap between project governance at the operational level and corporate governance at the executive level (see picture). [5] According to the PMI standards on program and portfolio management, the governance functions on those levels have relatively similar goals for the respective levels. Common objectives shared by all of the above are e.g.:
- Monitoring and controlling activities
- Aligning projects, programs, portfolios with corporate strategy
- Standard communication procedures between different levels and components
- Approaches to decision-making
As each of the governance levels has relatively similar objectives, it can be considered as a top down structure, which has to be aligned starting from the big picture considered in corporate governance and going all the way down to the specific requirements for single projects. [1] [6] [7]
Theoretical Background: Governance Theories
As project governance originates from corporate governance, different organizational theories are considered to explain the theoretical background for the necessity of different elements and key responsibilities in project governance. Based on these theories critical elements for project governance are identified and will be further explained in the following chapters.
Agency Theory (Control role)
The agency theory analyses the relationship between two parties in an organization (a principal and an agent) and in general it implies that the principal faces difficulties in motivating the agent to work in a way the principal wants him to do. Because the agents need to be provided with a necessary level of decision-making authority by the principal, issues related to conflict of interest and moral hazard can arise due to asymmetric information. The fundamental assumption, this theory is based on, is that the agent is self-interested and will act opportunistically instead of just in the interest of the principal and that agents and principals may differ in their risk attitudes. The bottom line is, that agents need to get incentives, be monitored and controlled in some way.
In the context of project management and project governance, this theory is particularly used to identify a need for control between the owner and manager of a project.
Transaction cost economics (Assessment role)
The theory of transaction cost economics is about opportunistic behavior, which may be cause by organizational actions driven by self-interest and an ambition to minimize costs. It implies that companies adapt their governance structures in order to pay the lowest possible transaction costs. Between the buyer and seller of a good is a complex relationship and behavioral factors are also considered when choosing a transaction. In general it helps to understand governance in relation to procurement and organizational decision making.
In the context of this article, the theory can e.g. explain and describe the process of assessing and selecting contractors or suppliers within a project.
Stakeholder theory (Coordinating role)
The stakeholder theory, being based on a socially oriented perspective, focuses on a larger group than just the shareholders and it challenges assumptions of the agency theory, that the shareholder interests are primal. It implies that the management of a company should take the interests of all stakeholders (e.g. employees, suppliers, customers, environment) into account and suggests that conflicts and different interests need to be balanced between organizational shareholders
According to this theory, project governance is necessary as a strategy for project teams to understand and respond to different stakeholder groups.
Stewardship theory (Strategic role)
- provides an alternative description of human behavior compared to agency theory and is rooted in psychology and sociology
- assumes that not all human behavior is dictated by self-interest but that some organizational members (stewards) exhibit ‘pro-’ and collectivistic rather than individualistic and self-serving behavior
- steward believes that his or her value is increased and secured when the organization is performing well and thus tries to improve organizational performance
- In this context: Shareholders are best served by empowering project managers
Resource dependency theory (Linking role)
- offers valuable insights into the allocation, prioritization and facilitation of organizational resource
- suggests that organizational success depends on the organization's ability to control interdependent external and internal resources
- views resources as the main driver of an organization's governance structure
- Here: may help to understand the importance of allocating and prioritizing different resources that are often shared across project programs and portfolios
(03)
Institutional theory (Maintenance role)
- can help to understand governance in the context of social and cultural constraints imposed on organizations. Governance gets a maintenance role [in …] identifying with the societal expectations of organization.
Framework
Principles
Principles to follow in project according to the APM guide on project governance
Principles to follow in project according to the APM guide on project governance
- The board has overall responsibility for the governance of project management.
- The organisation differentiates between projects and non project-based activities.
- Roles and responsibilities for the governance of project management are defined clearly.
- Disciplined governance arrangements, supported by appropriate methods, resources and controls are applied throughout the project life cycle. Every project has a sponsor.
- There is a demonstrably coherent and supporting relationship between the overall business strategy and the project portfolio.
- All projects have an approved plan containing authorisation points at which the business case, inclusive of cost, benefits and risk is reviewed. Decisions made at authorisation points are recorded and communicated.
- Members of delegated authorisation bodies have sufficient representation, competence, authority and resources to enable them to make appropriate decisions.
- Project business cases are supported by relevant and realistic information that provides a reliable basis for making authorisation decisions.
- The board or its delegated agents decide when independent scrutiny of projects or project management systems is required and implement such assurance accordingly.
- There are clearly defined criteria for reporting project status and for the escalation of risks and issues to the levels required by the organisation.
- The organisation fosters a culture of improvement and of frank internal disclosure of project management information.
- Project stakeholders are engaged at a level that is commensurate with their importance to the organisation and in a manner that fosters trust.
- Projects are closed when they are no longer justified as part of the organisation’s portfolio.
Core Components
- Portfolio Direction:
This component seeks to ensure that all projects are identified within the one, sustainable portfolio. This portfolio should be evaluated and directed mindful of the organization’s aims, constraints, resources and capacity for change.
- Project sponsorship
This component seeks to ensure that project sponsorship is the effective link between the organisation’s senior executive body and the management of each project. The sponsoring role has decision making, directing and representational accountabilities.
- Project management capability
This component seeks to ensure that the teams responsible for projects are capable of achieving the objectives that are defined at project approval points and use that capability to improve governance and outcomes.
- Disclosure and reporting
This component seeks to ensure that the content of project reports will provide timely, relevant and reliable information that supports the organisation’s decision making processes, without fostering a culture of micro-management. A culture of open and honest disclosure is a key requirement for effective reporting and where internal or external pressures pose threats to this, the value of independent verification of information will be increased. As such threats often present themselves prior to major project approvals or when projects start, there is an opportunity for independent oversight and verification to help avoid serious difficulties. An internal risk and assurance function should plan checks even in the absence of specific threats. There is an opportunity for independent oversight and verification to improve project outcomes and learn lessons. External assurance can often reduce risks further and provide a check on internal risk and assurance functions
Modules
Different Modules in project management that address issues and principles of project governance (model according to P.S. Renz: Project Governance - Implementing Corporate Governance) and their objectives (+tasks, purposes) towards project governance including:
- Mission Management
- Integrity Management
- Extended Stakeholder Management
- Risk Management
- Audit Management
- Systems Management
- Key responsibilities of project governance:
- 1. System management, assuming the societal embedding role.
- a. System Management assures institutional embeddedness. It serves to analyze and understand the specific development context through a systemic perspective, laying the groundwork for defining a possible development project as well as creating the know-how to understand the interrelationships and context of a project once it is up and running.
- 2. Mission management, assuming the strategic direction and support role, as well as the control role.
- a. Mission Management combines a strategic, a support, and a control role. Based on a system understanding, mission management serves to identify the (strategic) mission for a project. It sets strategic objectives, outlines the fundamental implementation strategy, structure and – to a certain extent – the culture needed to achieve the project objectives or mission. Through mission management, the governance board further supports and controls the project along with the implementation of its mission.
- 3. Integrity management, assuming a role of normative guidance and as such lending support in downside issues.
- a. provides a normative foundation, firstly as a basis for certain other key responsibilities (for instance, for mission management, where defining the mission and ‘setting’ cultural elements involves normative reflections). Secondly, integrity management provides support for overcoming most of the summarized downsides of governance roles
- 4. Extended stakeholder management, covering the linking role, coordination role and partially the control role
- a. Extended Stakeholder Management comprises the linking between the project and possible stakeholders along with a coordination role. Furthermore, it takes on a negotiation role, in the case of possible dependency interlocks or deadlocks. Extended stakeholder management assures that all possible concerned parties are considered by the project, and are possibly involved in the governance of the project as well.
- 5. Risk management, contributing to the control role.
- 6. Audit management, also contributing to the control role.
- a. Risk Management and Audit Management, finally, are both classic key responsibilities in governance. They stem principally from the control role which governance is expected to exercise over its project to assure its conformance to rules and laws and to manage possible risks pro-actively.
- 1. System management, assuming the societal embedding role.
Key References
- Directing Change: APM Guide on Project governance
- Project Governance - Implementing Corporate Governance
- The management of project management: A conceptual framework for project governance
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Project Management Institute. (2004). A guide to the project management body of knowledge (PMBOK guide). Newtown Square, Pa: Project Management Institute.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 PM Governance Specific Interest Group. (2011) Directing Change: A Guide to Governance of Project Management. 2nd edition. Pa: APM
- ↑ E.G. Too, P. Weaver. The management of project management: A conceptual framework for project governance. International Journal of Project Management 32 (2014) p.1382–1394
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 P.S. Renz. Project Governance - Implementing Corporate Governance and Business Ethics in Nonprofit Organizations. Springer (2007)
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 C. Biesenthal & R. Wilden. Multi Level Project Governance: Trends and Opportunities. 2014
- ↑ Project Management Institute. (2008). The standard for Program Management. Newtown Square, Pa: Project Management Institute.
- ↑ Project Management Institute. (2008). The standard for Portfolio Management. Newtown Square, Pa: Project Management Institute.
- ↑ B.M. Mitnick. (1973). Fiduciary rationality and public policy: The theory of agency and some consequences. Paper presented at the 1973 Annual Meeting of the American Political Science Association, New Orleans, LA In Proceedings of the APSA, 1973
- ↑ O. Williamson, (1998). Transaction cost economics: how it works; where it is headed. De Economist 146, 23–58.
- ↑ Donaldson, T., Preston, L.E., 1995. The stakeholder theory of the corporation: concepts, evidence, and implications. Acad. Manag. Rev. 20, 65–91