Post-Project Review
(→Utilization of Post-Project Review) |
(→Lack of Framework) |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
Micro-article is a short article depicts topic and project description, where the main trait is that there are graphical representations of the key-learnings. Furthermore, Learning Histories are dense repoirts that provides more context or remarks of learnings obtained. Lastly, RECALL is an individual documentation methods where particpants addresses their personal learnings. It is important to emphasize that this is one out of several studies on how to conduct a post-project review. The tool contains high-flexibility considering how to use it, and is mainly depended on type of projects and how the organization operates regarding. | Micro-article is a short article depicts topic and project description, where the main trait is that there are graphical representations of the key-learnings. Furthermore, Learning Histories are dense repoirts that provides more context or remarks of learnings obtained. Lastly, RECALL is an individual documentation methods where particpants addresses their personal learnings. It is important to emphasize that this is one out of several studies on how to conduct a post-project review. The tool contains high-flexibility considering how to use it, and is mainly depended on type of projects and how the organization operates regarding. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Utilization of Post-Project Review=== | ||
| + | Previous section states that there are no fixed framework on how to conduct a post-project review. The purpose of the tool is to ensure knowledge-sharing between project-teams and increase efficiency and effectiveness of execution of future projects. Conducting a post-project review requires a foundation of criteria, that are considered before and during a project. A study conducted by Anbari et. al (2008), provides a detailed overview of measures to be applied during the processes of a project. The process groups are according to the PMBOK guide defined as following: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li> '''Initiation:''' Defining a new project or a new phase of an existing project, as well as obtaining authorization to initiate a phase | ||
| + | <li> '''Planning:''' Development of a scope statement that clarifies future decision-making in order to attain the objectives. | ||
| + | <li> '''Execution:''' The processes initiated in order to complete the work | ||
| + | <li> '''Controlling:''' The measures applied to maintain, review and regulate the progress | ||
| + | <li> '''Closing:''' Finalizing all activities and closing the project | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
====Initiation Process==== | ====Initiation Process==== | ||
Revision as of 17:55, 21 February 2018
When finalizing a project and providing a certain deliverable, a project manager does not necessarily know if the project can be considered a success. Thus, a methodology to gain tacit-knowledge can be done by using Post-Project Reviews. Post-Project Review is a tool to evaluate a project results in order to improve future projects methods and practises. It is a a process to analyze potential failures and successes, wherein a knowledge gained from it can be beneficial for future projects.
A project manager follows a set of interrelated actions in order to provide the desired deliverable, and do mainly follow the five categories know as Project Management Process Groups: Initiating, Planning, Executing, Monitoring/Controlling and Closing. Simultaneously, a successful application of Post-Project Review must follow these steps. If a project manager considers carefully analyses the different criteria for success or failure of a project, as well as applying strict quality management during the project; An easier application of Post-Project review can be assessed. Post-Project review are conducted by a small internal team after closing, and the two different types of assessing it are: Process-Based and Documentation-Based methods.
This article focuses on the method of applying Post-Project Review, based on research \& development and new product development-projects through publications from PMI and Project Managers. Furthermore, a case analysis regarding new-modern use of Post-Project Review conducted by PMI will be discussed.
Contents |
Big Idea
Post-Project Review to improve organizational learning
According to Von Zedtwitz (2002), Post-Project Review is a "formal review of a project examining the lessons that may be learned and used to the benefit of future projects". The purpose of the tool is to provide project managers a benchmark on the success and failure modes of a the project. The introduction of evaluation guidelines to an organization should lead to a more efficient way to manage projects as previous issues can be avoided, and safe solutions can be applied repeatedly. Furthermore, the experience from a project is documented in such a way that it is available for everybody to use it in future projects and not just linked to key employees who might not be present in the future.
The tool can be considered within the domain of uncertainty, as one of the four perspectives on how to do projects. Post-Project Review is a tool to acknowledge lessons learned from a project, and a method that emphasizes reflections. Application of the tool gives an additional possibility to adapt to other processes and increase people's competencies and awareness to issues.
Post-Project Review is a tool that can be utilized in any type of project, and has clear benefits regarding gain of knowledge. The tool is a way for an organization to increase the tacit-knowledge sharing, as the knowledge shared are based on experiences and not facts. Considering the different types of projects conducted, the Post-project review is a method emphasized especially withing the domain of new product development and research and development projects. Product development is a time-consuming process, and the learning curve are depended on knowledge-sharing. According to Goffin et. al (2010), it is necessary to pass the knowledge of lessons learned between project teams in order to improve the performance of product development.
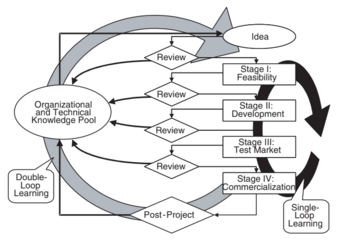
Von Zedvitz (2002) goes even further when defining what type on learnings that are generating when applying Post-Project Review, by stating that Post-Project Review focuses on the link between team-learning and organizational learning. The idea is that Post-Project Review do not only provide single-loop learning, but double-loop learning. Single-loop learning considers detection and corrections of mismatches between experience and a reference system \textit{without} questioning or altering the value of the system. However, double-loop learning considers the detected mismatch and implements measures to correct the reference-system.
Lack of Framework
Despite post-project review's purpose, there are no standardized framework provided on how to conduct it. The reason for that is that all organizations operates differently, and may have strategical aim that differs from other competitors. Thus, it is not possible to give a step-by-step description on how to apply the review %nor whom is responsible of conducting it.
There are different studies published that depicts their method of conducting a post-project review. Von Zedvitz published a study of recommended application of PPR given it is a R\&D-project. He devides post-project review in process-based and documentation-based methods. Process-based methods are the methods of acquiring the lesson learned from concluded projects, whereas the idea is to gather the project-team to answer four main questions:
- What was supposed to happen?
- What actually happened?
- Why were there differences?
- What can you learn from this experience?
Secondly, the document-based methods aim is to learn from the project experiences gathered. Documentation-based methods focus on aspects of experiences gathered from current project with knowledge gathered throughout the history of the organization. There are mainly three ways of documenting the lessons learned:
- Micro Articles
- Learning Histories
- RECALL
Micro-article is a short article depicts topic and project description, where the main trait is that there are graphical representations of the key-learnings. Furthermore, Learning Histories are dense repoirts that provides more context or remarks of learnings obtained. Lastly, RECALL is an individual documentation methods where particpants addresses their personal learnings. It is important to emphasize that this is one out of several studies on how to conduct a post-project review. The tool contains high-flexibility considering how to use it, and is mainly depended on type of projects and how the organization operates regarding.
Utilization of Post-Project Review
Previous section states that there are no fixed framework on how to conduct a post-project review. The purpose of the tool is to ensure knowledge-sharing between project-teams and increase efficiency and effectiveness of execution of future projects. Conducting a post-project review requires a foundation of criteria, that are considered before and during a project. A study conducted by Anbari et. al (2008), provides a detailed overview of measures to be applied during the processes of a project. The process groups are according to the PMBOK guide defined as following:
- Initiation: Defining a new project or a new phase of an existing project, as well as obtaining authorization to initiate a phase
- Planning: Development of a scope statement that clarifies future decision-making in order to attain the objectives.
- Execution: The processes initiated in order to complete the work
- Controlling: The measures applied to maintain, review and regulate the progress
- Closing: Finalizing all activities and closing the project
Initiation Process
When starting or pursuing a next phase of a project, a careful analysis of which criteria to measure against success or failure of a project should be conducted. Typically applied criteria are if project deliverable are given on-time within the budget, as well as it satisfies the different technical and legal specifications. These type of criteria are according Project Management Institute (PMI) considered the "triple constraints", as these criteria considers scope, time and cost. Projects considering triple constraints theory may be helpful for future project managers to determine the most effective approach to address a certain issue.
Planning Process
During the process of establishing the scope of the project and refining the objectives; It is according to Anbari (2008) recommended to use quality planning tools in order to ensure customer involvement with project team. Examples on quality planning tools are quality function deployment (QFD) which aids management to identify customer needs, wants expectations and translates it into a technical recommendation. Another tool is multi criteria decision-making to Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) that considers subjective values to different components and technical project deliverables. Utilization of quality management tools decreases the chances scope creep, cost overruns, specification gaps etc.
Executing Process
Considering that the quality management tools are applied by the management in the two first process groups, a solid foundation for Post-Project Review are provided as it gives a clear overview over the different criteria for successes and failures. Furthermore, the quality management tools aids a proper execution of the project as it clarifies the certain expectations the project customer and/or final user has to the deliverable.
Monitoring/Controlling Process
Given that the use of quality management tools were insufficient and were the cause of quality deficiencies; The recommendation is to use to quality improvement approaches. Examples on improvement approaches can be the Six Sigma method, seven-step method, benchmarking, quality audits etc. The idea behind these methods are to identify causes for quality deficiencies and analyze which measures to apply in order to meet customer expectations.
Closing Process
The last process is about providing the project deliverable. Usually, a deliverable are considered a success given that the tripe constraints are satisfied. Considering all the measures from previous processes are applied, a project manager will have a solid foundation to define the potential wrongdoings in the project. Thus, the remaining part of the review is to archive it in order to utilize the gained knowledge in future project.
Skepticism towards Post-Projects Review
Despite the tools purpose and benefits, experience via studies shows that the application of Post-Project Review lacks. The main reasons for this is that it is a time-consuming process, management's fear for failure and worsened social-relationship.
Project managers consider time as cost. Therefore, they tend to not perform a review of their project. According to Busby (1999), Project managers want to minimize cost allocated to their project in general, especially towards the end. They do not see the value for their own project if conducting Post-Project Review, as the benefits from the review are for the future projects and not the current one.
Furthermore, conducting a Post-Project Review means that the review-team might discover a flaw in the execution of the project. Experience shows that managers are afraid of being embarrassed or admitting their own wrongdoings. Thus, they prefer to pursue the next project rather than analyzing potential mistakes from the previous one.
Maintaining social relationship do usually matter for most people, and management are afraid of Post-Project Review being a platform to blame, criticize and recriminate each other.
Expectations
Considering the skepticism towards the tool, application of Post-Project Review is still to be standardized. The fundamental problem with it being widely used today is that organizational learning in connection with project work can be found contradictory towards each other considering their aims. An organization sets long-term goals wherein a project has a defined start and end-date. Thus, the responsibility of conducting Post-Project Review should be a program or portfolio manager. Conducting a successful Post-Project Review requires personnel that are willing to regularly capture experience directly after achieving a milestone. Secondly, the lessons learned should be performed graphically, by for instance drawing a time line that clearly depicts the occurrence of either positive or negative incidents. Furthermore, it is important to ensure a collective and interactive environment, wherein mutual understanding and respect are emphasized when conducting the review. Lastly, the review should be conducted by personnel that had an influence on the project; However, the debriefing are to be done by external and neutral moderators.
Application
As outlined in the abstract, the application of the Post-Project Review will be analyzed from a new-product development perspective. Previous section emphasized that the tool is yet to be standardized, and different organizations conducts it differently. Thus, one can not depict a certain framework of how to perform a Post-Project Review.
A recommendation of what measures to apply before conducting the review are given, however, how to apply the review after a project-end are yet to be defined. Before conducting the review it self, a project manager should apply the different measures in order to have a solid foundation of criteria for the review.
Post-Project Review in Product Development
Given the recommendations are applied during project-execution, a method to conduct Post-Project Review in a new-product development project can be applied. A study performed by Goffin suggests four focus areas to better leverage knowledge generation in an organization that strives for product development. The focus areas are following:
- Facilitation-method of PPR that stimulates and emphasizes tacit knowledge
- Foster individual learning
- Team members to act as knowledge brokers
- Project kick-off meetings as an opportunity to review
Facilitate PPRs to Stimulate Tacit Knowledge
When conducting the post-project review, an experienced facilitator should be hired. An experienced facilitator are able to successfully apply a stimulating environment, wherein the facilitator are able to guide the discussion and generate tacit-knowledge within the team and the organization. Experienced facilitators are known for using tools that make participants creative and motivated, thus, the ability for improved knowledge-sharing.
Foster Individual Learning
Project-managers developing new products must ensure that the team-members possesses motivation to strive for more learning. Knowledge may obtained in several ways. It can be direct project experience, mentoring, participation in communities of practice or even individual reflection. R\&D professionals need to be encourages to develop their expertise. By doing so, the team will have better base on executing the project, as well as more knowledge to share with the other teams.
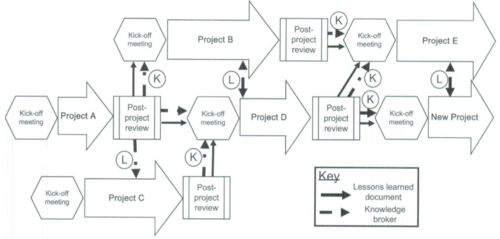
Designate Knowledge Brokers
Project personnel should emphasize members to transfer specific learning between each project. This method will make project-to-project learning more tangible. Furthermore, applying the method will ensure prevent knowledge-gaps in future projects.
Use Project Kick-Off Meetings
Considering the planning process, where the project scope and objectives are defined; It is recommended to have a kick-off meeting in order to ensure the correct motivation and mutual understanding of what the project has to deliver and understand the
An On-Going Process
The four main steps to perform in a product development project can be considered a reverse post-project review framework. The mission is to ensure that key-learning are to be shared between project-teams in order to aid future projects. The framework starts by having a kick-off meeting before executing a project, wherein a post-project review are conducted with an experienced facilitator after the end of project. Further on, knowledge brokers from the post-project review informs the kick-off meeting for the project.
Thus, the product-development post-project review framework can be considered an on-going evaluation that emphasizes tacit-knowledge. Organizations and projects are performed differently, but it is important that knowledge generated are done by failing. Therefore, it is important to have a work-environment that is not judgemental, but rather open.
Limitations
Responsibility of Post-Project Review
According to PMBOK guide, the responsibilities of a project manager is to ensure that the project led will generate value for the organization, and adapt to the many changes in the environment, competition and marketplace. A project is a temporary endeavour wherein the purpose is to provide a certain deliverable. A project is ended when deliverable is provided, however, it can also be deemed done if objectives can not be met. In cases where failure is obtained in a project, a Post-Project Review can provide the root-causes for it.
A post-project review generates better organizational learning, thus, one can argue that the main responsible manager of the review should be the managers initiating the projects. According to MSP (Managing Successful Programmes) framework, post-project review is an activity under the domain of program management, with the involvement of project-team members, project manager and external personnel. Incorporating all these members will according MSP capture successes and problem areas associated in the execution of the project.
Managing hurdle
Considering the theory of Von Zedvitz, a post-project review's objective is to ensure knowledge generation for future projects. However, despite the tool's purpose, utilization of post-project reviews lacks in organizations. As mentioned above, performing a post-project review requires personnel that are willing to invest time, having the right motivation, as well as the individual skills and the discipline. These abilities may be hard to require from personnel after a project-closeout.
Considering time
Allocating time and resources in the closing phase of a project, will as mentioned above, be regarded as more cost for the project. Considering that there are no fixed framework on conducting a post-project review, the program manager has to provide a method that makes the members willing to review the project despite the time it requires. Following the product-development framework is a possibility, as one can see that the review is implemented in an on-going program (figure 2).
Lack of motivation
Program managers need to use the necessary time to ensure better sharing of projects, either by performing the documentation themselves or allocating responsibility of the documentation to employees that can see the value of knowledge-sharing. A method of increasing motivation is to graphically show the long-term benefits that are obtained by performing such a review. Program managers goal is to ensure that projects provide deliverable that together will provide the program desired benefit.
According to M. Schindler project managers tend to have a weakness of admitting their wrongdoings. For the tool to be favorably performed, the mindset of the managers must change. A suggestion would be that program and portfolio managers apply measures, showing that failure can lead to success. Failure equals to success is a modern ideology that is becoming widely recognized in R\&D organizations, ever since Google X' CEO emphasized the many achievements they have reached with that mindset.
Requiring discipline and skills from personnel
It will require a committed, flexible and skilled workforce for post-project review to be successfully implemented in an organization. If the workforce has these qualities, the change towards improved performance will be significantly easier. Organizational change is often considered a long and challenging process.
Creating the framework
Given Schindlers concerns are considered by both program and project managers, it will be easier to implement a framework wherein post-project review are implemented. As understood from the application-section, creating a framework will require resources and time. However, a successful implementation may improve project execution and potentially make it easier for organization to obtain their vision.
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found