Management with DISC profile analysis
(→Relevance & Application) |
(→Benefits) |
||
| Line 208: | Line 208: | ||
* Change management | * Change management | ||
| − | The questionaire is webbased and fast to anwer. It is provides consise, clear and simple profile analysis. It is a international tool and translated to many languages making it highly applicable for global companies. | + | The questionaire is webbased and fast to anwer. It is provides consise, clear and simple profile analysis. It is a international tool and translated to many languages making it highly applicable for global companies. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The key benefit of this process is that it results in improved teamwork, enhanced people skills and competencies, motivated employees, reduced staff turnover rates, and improved overall project performance. | ||
==Limitations== | ==Limitations== | ||
Revision as of 22:14, 27 February 2018
Contents |
Abstract
DISC (Dominance, Inducement, Submission, Compliance) analysis is a strategic tool for evaluating behavior often used internally in an organisation by managers to improve group dynamics and the well-being of the individual. DISC is a very simple and easy to use tool for improving relations, resolving conflicts, enhances motivation, and supports self-growth all by obtaining a better understanding of the individual’s personality. Misunderstandings happen daily and can lead to stress, unhappiness and low working effort. DISC was created by psychiatrist and professor William Moulton Marston, who believed all humans have psychological motives but they differ from human to human. The tool assesses the level of Dominance, Inducement, Submission, Compliance an individual possesses by referencing the norm.
[1].
Relevance & Application
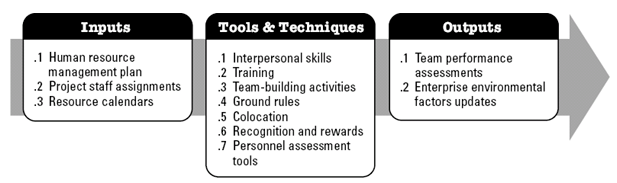
The relevance and application of the tool can be extremely broad. Whereever and whenever human interations take place synergies or tensions unfold. DISC analysis can be a tool for smoothing human relations is used right. At work the tool can be used by all levels of managers and employees working on a project, program or portfolio basis. For example a management team who know each ohers DISC profiles can communicate better, shorten the time of their meetings, and prevent misunderstandings when they have the knowledge of the individuals behavioral profile. On the other hand a manager can improve the wellbeing, communication and working effort of the team. Developing the project team is a process of improving competencies, interaction between team members and the environment. On the figure below the flow of inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs of developing project team are illustrated. Interpersonal skills, Recognition and rewards and Personnel assessment tools under Tools and Techniques all come into play with management with DISC profile analysis.
This article will be focussing on the usage of DISC behaviroal profile analysis as an operational tool for a project managers to improve the daily communication with the team.
Project managers should acquire skills to identify, build, maintain, motivate, lead, and inspire project teams to achieve high team performance and to meet the project's objectives. Teamwork is a critical factor for project success, and developing effective project teams is one of the primary responsibilities of the project manager. Project managers should create an environment that facilitates teamwork. Project managers should continually motivate their team by providing challenges and opportunities, by providing timely feedback and support as needed, and by recognizing and rewarding good performance. High team performance can be achieved by using open and effective communication, creating team building opportunities, developing trust among team members, managing conflicts in a constructive manner, and encouraging collaborative problem solving and decision making. The project manager should request management support and/or influence the appropriate stakeholders to acquire the resources needed to develop effective project teams.
Project managers operate in a global environment and work on projects characterized by cultural diversity. Team members often have diverse industry experience, know multiple languages, and sometimes operate in the “team language” that may be a different language or norm than their native one. The project management team should capitalize on cultural differences, focus on developing and sustaining the project team throughout the project life cycle, and promote working together interdependently in a climate of mutual trust. Developing the project team improves the people skills, technical competencies, and overall team environment and project performance. It requires clear, timely, effective, and efficient communication between team members throughout the life of the project. Objectives of developing a project team include, but are not limited to:
Improving knowledge and skills of team members to increase their ability to complete project deliverables, while lowering costs, reducing schedules, and improving quality; Improving feelings of trust and agreement among team members to raise morale, lower conflict, and increase team work; and Creating a dynamic, cohesive, and collaborative team culture to (1) improve individual and team productivity, team spirit, and cooperation and (2) allow cross training and mentoring between team members to share knowledge and expertise.
9.3.2. Develop Project Team: Tools and Techniques
9.3.2.1 Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal skills, sometimes known as “soft skills,” are behavioral competencies that include proficiencies such as communication skills, emotional intelligence, conflict resolution, negotiation, influence, team building, and group facilitation. These soft skills are valuable assets when developing the project team. For example, the project management team can use emotional intelligence to reduce tension and increase cooperation by identifying, assessing, and controlling the sentiments of project team members, anticipating their actions, acknowledging their concerns, and following up on their issues.
9.3.2.6 Recognition and Rewards
Part of the team development process involves recognizing and rewarding desirable behavior. The original plans concerning ways in which to reward people are developed during the Plan Human Resource Management process. It is important to recognize that a particular reward given to any individual will be effective only if it satisfies a need which is valued by that individual. Award decisions are made, formally or informally, during the process of managing the project team through project performance appraisals (Section 9.4.2.2). Cultural differences should be considered when determining recognition and rewards.
People are motivated if they feel they are valued in the organization and this value is demonstrated by the rewards given to them. Generally, money is viewed as a tangible aspect of any reward system, but intangible rewards could be equally or even more effective. Most project team members are motivated by an opportunity to grow, accomplish, and apply their professional skills to meet new challenges. A good strategy for project managers is to give the team recognition throughout the life cycle of the project rather than waiting until the project is completed.
9.3.2.7 Personnel Assessment Tools
Introduction
The DISC Model Theory
The DISC personality profile is strictly a measure of the individuals perception of themselves. All profiles are equally as good and it should not be considered as a test. The test results descripes some of the phsycological drivers which affects the behaviour.
The general rule: Different = Different and not Different = Wrong
In the following each of the four traits Dominance (D), Inducement (I), Submission (S) and Compliance (C) are considered. There exist different variations of the DISC letters such as Inducement/Influence, Submission/Steadiness, and Compliance/Conscientiousness. However, the overall interpretation is the same. [2] [3] [4]
Dominance (D)
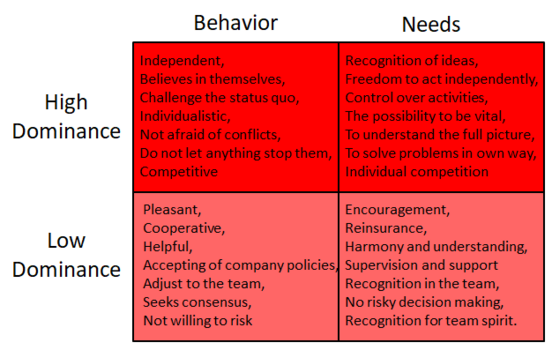
The behavioral trait of Dominance is characterized as seeing challenges and seeking to overcome them. People with a high D are characterized as confident, risk willing, determined, result oriented and demanding. They focus on shaping their surroundings to produce the outcome of the desired results. The people desires to have power and authority, take on challenges, get direct answers, have the liberty of no control and rules, make changes and new activities and the possibility of individual performance. The primary motive is taking control and be in charge and their major fear is losing control. They can be limited in lacking thoughts of others, being impatient, and lacking focus on quality.
Inducement (I)
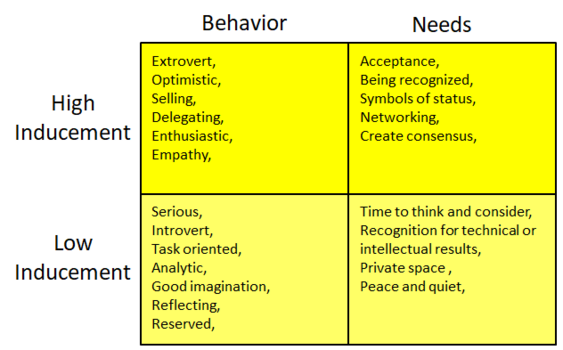
The trait of Inducement is perceived as extrovert and the aspiration of social interation with others. People with a high level of Inducement seek friendly and favorable environments where they can have an impact in collaboration with others. In addition, they will try to influence and convince others. They focus on creating results by convincing and including others in a team work. The characteristics are optimistic, creating confidence, emotional appealing, involving themselves in others, extrovert, enthusiastic, charming, and open. Furthermore, desires are to be popular, being the center of attention, being praised, group activities, having positive relations, and having the freedom of no control or details focus. The primary motive is to receive recognition from others and they fear social rejection. Their limitations are being impulsive, unorganised, over promising under delivering, and lacking of follow through.
Submission (S)
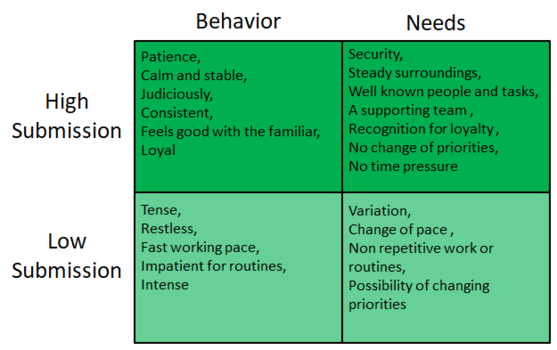
Profiles with a high Submission score seeks to conserve the surrounding working environment and keeping it stabile. They focus on solving tasks in collaboration with others. The characteristics are judiciously, reliable, collaboration oriented, patient and listing, loyal, caring for the group, and accepting. The desires are authentic appreciation, collaboration, using known methods and procedures in their work, stability, and time when nessesary to adapt to changes. The primary motive is stability and they fear changes and unexpected events. The limitations are putting others needs first and resistance against positive changes.
Compliance (C)
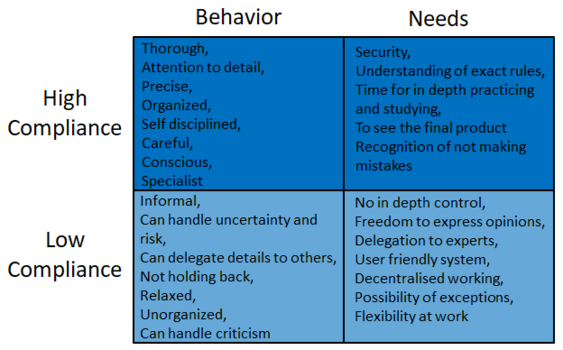
The triat of Compliance is considered the urge for formalities, rules and structure. The behavioral characteristics are seeking to work within established rules and guidelines to ensure high quality and aqurracy. People with a high level of Compliance focus on working under known conditions and to improve the quality of products and services. They are analytical and facts oriented and have awareness of standards and pay attention to details. Furthermore they are very consious, diplomatic, reliable and carefull, and can often be a bit reserved. The desires are being right, having complete overview, being praised for their tasks, limit risks, the possibility of leaning on authorities.
The primary motive is to ensure quality and aquarrcy and they fear mistakes, sloppy metholody, critism of their work and emotional situations. Limitations are very self critical, indeciceive, and lack of creativity.
Background
The history of the four quadrants DISC personality profile can be traced all the way back to Empodocles four elements of fire, earth, air and water in 450 B.C. Empodocles observed people seemed to behave in four different ways due to external environmental factors. 50 years later Hippocrates redefined these as four internal factors called the four temperaments: choleric, sanguine, phlegmatic, and melancholic. Many years later the theory was advanced further by Carl Jung. In 1921 Jung reconfirmed personality traits were internal and attributed the differences to how people think. Jung saw these four differences as: thinking, feeling, sensation and intuition. Today these are often used in Myers Briggs Personality Test (MBTI).
The DISC personality was manifested in 1928 when William Moulton Marston published his book with the title “Emotions of Normal People”. The main principles of DICS have its roots in the book. Marston believed people’s daily behavior stems from their predictable characteristics. The behavior was not only seen as internal but also influenced by the external environment. Marston defined the personality trait as: Dominance, Influence, Steadiness and Compliance. Based on Marston’s theory Walter Clark developed the DISC personality profile in 1940 which is widely used today.
Method of use
Goals of Management with DISC
As a manager using the DISC profile analysis tool it should be sought to:
- Understand own behavioural traits and tendensies and develop an understanding of how own behaviour affect others.
- Understand, respect and value the individual differences on the team.
- Develop strategies to improve cooperation.
- Improve effectiveness in operations by advancing the relations with team members.
The Analysis
A DISC personality profile is created by answering a questionaire about the person’s behavior in various situations. The answers are subjective as the individuals are considered being experts on themselves.
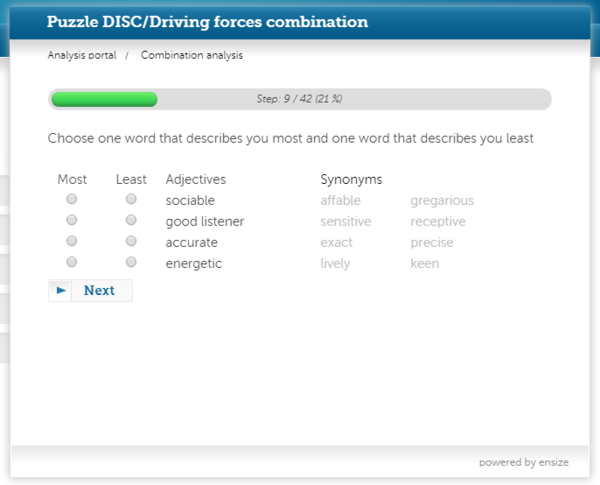
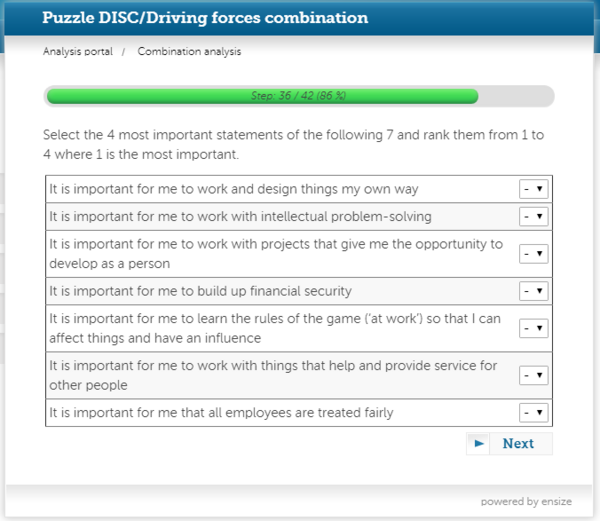
The analysis is based on self-reflecting. When completing the analysis, the participant should picture themselves in a normal work situation. The analysis takes 15-25 minutes and consists of two parts:
- The Most and Least option for a group of 4 adjectives. In totalt there is 28 words to be considered. The 4 adjectives are proposed as main words and if unsure synonyms are giving as help.
- The Driving Forces Analysis part contains 6 questions with 7 statements each. The 4 most important statements in each question is ranked from 1 to 4 where 1 is most important
The individual options you choose are confidential and are not visible to anyone, it is only the combined results of these options that are presented in the personal report.
Results
The answers of the questions produces a profile report of the individual behavioral style, tendencies, needs, preferred environment and strategies useful for optimal behavior. Furthermore it also provides insights on the strength and weaknesses of the individual. The questions can for example ask in what way a person responds to challenges, influences others, working pace of comfortability and how rules and procedures are considered.
The DISC personality profile report evaluates the level of contribution of each of the four traits dominance, inducement, submission, and compliance. DISC can be considered as a “color palette of personality” where every person has their own unique blend. It is possible but highly unlikely to only have one of the four traits. Usually it is a combination for example a person can have dominance as the highest factor, influence as a secondary factor and steadiness as a third. The DISC personality profile shows how a person every day actions is affected, the preferences of various environments, the way of communication with others, response or avoidance to conflict.
This personality insight can be used by managers or team leaders in recruiting processes and provide them with a deeper knowledge of their team, group or colleagues. This knowledge is crucial for managers to support collaboration and communication. Proactive measures can be taken by managers to place people according to their preferences of environment to help them feel comfortable and empowered. When approaching people it can be done in a way that creates a positive response. It is widely believed in the community of psychologists that traits and situations are interactive. DISC can help managers adopting their responses based on the DICS profile of team members they are dealing with. This means managers should not always choose to use the behaviors that are the most comfortable for them, they should choose the behaviors that would be the most successful within the team.
Implementation of Results
When the manager believes to have the DISC theories underthe skin point 1) and 2) of the goals should come naturally. This section will therefore explore point 3) on how to develop strategies to improve cooperation. Questions to be asked are:
- How do the manager and the team members best communicate?
- How do the manager gain the trust of confidence of the team members?
- What concrete measures can the manager take in order to make the individual team members feel the most comfortable?
Assuming the manager already knows the DISC profile of the team members the task becomes What effective communication stategy can be utilized for the different DISC profiles. The following table provides an overview of how a manager should communicate with the team members of the four different behavioural profiles.
| Manager's Communication Strategy with Team Members DISC Profiles |
|---|
|
Dominance Profile
|
|
Inducement Profile
|
|
Submission Profile
|
|
Compliance Profile
|
When done aqurate the manager should be able to reach the goal 4) since team member relations are strengthen so the effectiveness in operations is increased.
Improve effectiveness in operations by advancing the relations with team members.
Benefits
As a personnel assessment tool DISC analysis provides project manager and team with knowledge about strengths and weaknesses. The manager can evaluate preferences of the team, on what grounds they make decisions and interact with people. There exist many tools for personel assessment. Such as Belbin's Team Roles and Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
Various tools are available such as attitudinal surveys, specific assessments, structured interviews, ability tests, and focus groups. These tools can provide improved understanding, trust, commitment, and communications among team members and facilitate more productive teams throughout the project.
The tool can be beneficial as a strategic tool on individual, team and organizational levels. It can be apllied on various needs of the company acspects of:
- Recruiting
- Individuel assesment
- Mangement development skills
- Talent spotting
- Optimization of teams and management groups
- Organizational development
- Change management
The questionaire is webbased and fast to anwer. It is provides consise, clear and simple profile analysis. It is a international tool and translated to many languages making it highly applicable for global companies.
The key benefit of this process is that it results in improved teamwork, enhanced people skills and competencies, motivated employees, reduced staff turnover rates, and improved overall project performance.
Limitations
Behaviour is flexible, dynamic, and depends on situations.
It does not measure all aspects of the personality It is subjective. What you think of yourselves is not always the reality or how you are perceived by others.
Different variations from company to company. Overall still the same
- ↑ Marston, W. M., (1928), Emotions of Normal People, Kegan Paul Trench Trubner And Company
- ↑ www.discprofile.com
- ↑ www.discinsights.com
- ↑ www.peoplekeys.com