The Triple Constraint in Project Management
(→The Three Constraints) |
(→Scope) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
===Scope=== | ===Scope=== | ||
| − | The scope is related to the work and deliverables necessary to complete the project successfully and the processes required to identify and define these. Project scope management is very important no matter which type of project. If the scope is not controlled and resources are used on tasks that are not a part of the scope it can be difficult to deliver a finished project that is on time and under budged. As stated by the PMBOK Guide (2017) scope management is primarily concerned with defining and controlling what is, and what is not included in the project<ref name="PMBOK"/>. Another important dimension in project scope management is how to be able to deal with and manage changes. During the project new demands can arrive naturally as the project evolve and stakeholders might have new and additional requests which changes the scope. The duration of each new task is critical to the successful completion of the final project | + | The scope is related to the work and deliverables necessary to complete the project successfully and the processes required to identify and define these. Project scope management is very important no matter which type of project. If the scope is not controlled and resources are used on tasks that are not a part of the scope it can be difficult to deliver a finished project that is on time and under budged. As stated by the PMBOK Guide (2017) scope management is primarily concerned with defining and controlling what is, and what is not included in the project<ref name="PMBOK"/>. Another important dimension in project scope management is how to be able to deal with and manage changes. During the project new demands can arrive naturally as the project evolve and stakeholders might have new and additional requests which changes the scope. The duration of each new task is critical to the successful completion of the final project <ref name="Westland"/>. How to cope with stakeholders and to only accommodate those changes that are necessary to achieve the project goals and deliverables are important as changing the scope can have great impact on the cost and schedule because of the interdependence in the Triplet Constraint. For example if we have a project where the goal is to built a two storey family house the scope is then determined by the goal. The idea is that if we know what to achieve, it it possible to find a way on how to do it \cite{Info_Tec_PM}. In other words, the scope is defined by the goal. When the scope is determined the schedule and budget can be determine as well and the work can begin. If the client then asks for additional features e.g a balcony or an extra storey this will not surprisingly require additional resources. Extra work load for the team due to increase of the project scope will result in time and cost increase according to the Triple Constraint (Figure 1). If the budget was fixed the only way to decrease the cost is to decrease the scope, meaning no additional features in this case \cite{Info_Tec_PM}. It could also be the time that was fixed meaning additional resources in terms of people would have to work on the project resulting in higher cost in order to meet the scope. Because the three constrains are interdependent a change in one of them will result in changes in the others. |
| + | |||
===Quality=== | ===Quality=== | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 10:37, 22 February 2019
Abstract
When managing a project several aspects constraints the project. These constraints are interdependent and the three key constraints form what has traditionally been known as the The Triple Constraint or The Iron Triangle. Some claim time, scope and cost (TCS) to be the key constraints others claim it is time, cost and quality (TCQ) [1] [2]. It is either way the project managers job to balance between the constraints to obtain trade-offs within a reasonable limit during the project's life cycle to obtain a successful project. The model implies that the project's successful completion is affected by the trade-offs performed and it is the project managers job to know how the constraints interrelate. The model however does not determine success [3]. The model has been widely used since the 1950s and the application and limitations have been discussed extensively [4]. Atkinson is one of the critics who claims the model is insufficient for determine the project success, because success rely on several additional factors and not only the three constraints [4]. Others are more positive, but in general it seem that many would like to modify the model to improve the interpretation [1]. Predominantly there seems to be a disagreement about whether scope or cost is the third constraint in the triangle. The aim of this paper is to explain the concept of the triplet constrain and it's application and limitations in project management and to reflect on the different perspectives.
Contents |
Introducing the Triple Constraint
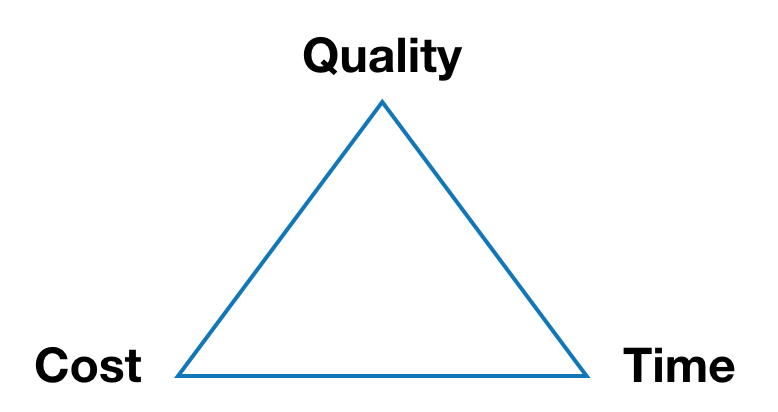
When managing a project there are several types of constraints e.g Cost, scope, schedule, resources and quality [5]. In fact the PMBOK guide has divided the chapters about project management into exactly these constraints and how to manage them in a project i.e project scope management, project schedule management and so forth [6]. These constraints are often interdependent of each other which is why it is important to balance the constraints against each other. According to ISO 12500 this means that a change in one constraint might affect the others [5]. In project management the three key constraints are often considered to be either time, cost and scope or time, cost and quality. These tree constraints either (TCS or TCQ) form what is known as The Triple Constraint or The Iron Triangle (Figure 1 and 2).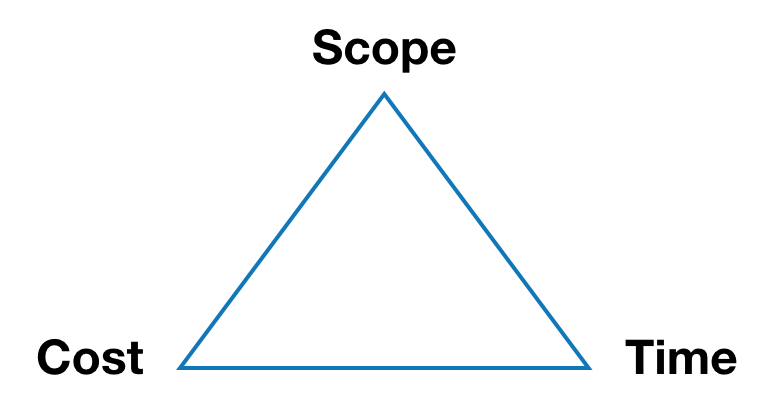
Whether taking basis in the Triplet Constraint model with time, cost and scope or time, cost and quality the time characterises the duration of the project and the scheduling and the cost addresses the budget and resources (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The scope denote the tasks required to fulfill the project's goals and this could also be the quality constrain which denote the quality criteria set for the project. If The triple constraint model formed by these three constraints can be used to evaluate projects. The model states that the success of a project is impacted by those three constraints. During the project's life cycle it is the project managers job to balance between the time, cost and scope/quality to obtain trade-offs within a reasonable limit to obtain a successful project. This model implies that the project quality or successfully completion is affected by the trade-offs performed and it is the project managers job to know how the three constraints interrelate. It is however not possible to use the model to actually determine success, which is why the model is often used wrongly [3]. Because of the mutual dependency between time, cost and scope/quality, a change in one of the constraints will affect the others making this model a useful tool in order to explain the effect or consequence of changes to project stakeholders.
The Three Constraints
As mentioned earlier are scope and quality very much debated. Some understand quality as a constraint others understand it as a success criteria for the finalized project. In the following is both scope and quality addressed as a constraint. The Triple Constraint is related to the definition of a project, but it is not as closely related as it was back when Atkinson (1999) wrote his article in 1999[4] . The international standard on project management define a project as: "A unique set of processes consisting of coordinated and controlled activities with start and end dates, performed to achieve project objectives" [5]. This relates to The Triplet Constraint in the way that the activities need a start and end date meaning time is a core element in projects. At the same time the activities performed have to be controlled and coordinated in order to meet the project objectives, and this is basically the scope of the project and/or the quality criteria. To perform the activities resources are needed and hereby the cost.
Time
The definite beginning and end date for projects is related to the temporary endeavor. As described earlier the time constraint includes the processes required to schedule the project activities and in relation to this supervise and monitor the progress to keep track of the schedule. Often does the projects have a specific start and then the end date is estimated by the project manager. It can however also be the opposite case where the end date is determined and then the job is to determine the date where the project has to begin. A project is often divided into many sub tasks and activities. These activities have to be defined and sequenced and a duration has to be estimated in order to estimate the total project duration. All this can be considered as project schedule management [6]. According to PMBOK Guide (2017) project schedule management includes the processes required to manage the timely completion of the project [6].
Cost
Normally projects cost money and the cost is related to the processes required to develop the budget and to monitor progress to control costs[5]. In order to complete the project within an approved budget project cost management is needed. Project cost management includes the processes involving estimation of costs so the budget can be determined. When the budget is determined the cost has to be controlled so the project can be completed within budget[6].
Scope
The scope is related to the work and deliverables necessary to complete the project successfully and the processes required to identify and define these. Project scope management is very important no matter which type of project. If the scope is not controlled and resources are used on tasks that are not a part of the scope it can be difficult to deliver a finished project that is on time and under budged. As stated by the PMBOK Guide (2017) scope management is primarily concerned with defining and controlling what is, and what is not included in the project[6]. Another important dimension in project scope management is how to be able to deal with and manage changes. During the project new demands can arrive naturally as the project evolve and stakeholders might have new and additional requests which changes the scope. The duration of each new task is critical to the successful completion of the final project [3]. How to cope with stakeholders and to only accommodate those changes that are necessary to achieve the project goals and deliverables are important as changing the scope can have great impact on the cost and schedule because of the interdependence in the Triplet Constraint. For example if we have a project where the goal is to built a two storey family house the scope is then determined by the goal. The idea is that if we know what to achieve, it it possible to find a way on how to do it \cite{Info_Tec_PM}. In other words, the scope is defined by the goal. When the scope is determined the schedule and budget can be determine as well and the work can begin. If the client then asks for additional features e.g a balcony or an extra storey this will not surprisingly require additional resources. Extra work load for the team due to increase of the project scope will result in time and cost increase according to the Triple Constraint (Figure 1). If the budget was fixed the only way to decrease the cost is to decrease the scope, meaning no additional features in this case \cite{Info_Tec_PM}. It could also be the time that was fixed meaning additional resources in terms of people would have to work on the project resulting in higher cost in order to meet the scope. Because the three constrains are interdependent a change in one of them will result in changes in the others.
Quality
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Van Wyngaard, C.J., Pretorius, J. H. C., Pretorius, L. Theory of the triple constraint – a conceptual review. IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, 13:1991–1997, (2012).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Pollack, J., Helm, J., and Adler, D. What is the iron triangle, and how has it changed? International Journal of Managing Projects in Business, 11(2):527–547, 2018, (2018).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Westland, J. The triple Constraint in Project Management: Time, Scope Cost. [Online] https://www.projectmanager.com/blog/triple-constraint-project-management-time-scope-cost, Accessed: 02-16-2019, (2018)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Atkinson, R. Project Management: Cost, Time and Quality, Two Best Guesses and a Phenomenon, it's Time to Accept Other Success Criteria. International Journal of ProjectManagement, 17(6):337–342,(1999).
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Danish Standards DS/ISO 21500:2013 - Guidance on Project Management. Danish Standards, 2. edition, (2013)
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 A Guide to Project Management Body of Knowledge Project Management Institute, 6.edition,(2017)