Managing habits in a project
(Created page with " == Abstract == Habits are a huge part of an individual's everyday life. According to Charles Duhigg 40 - 45% of what we do every day are controlled by habits and not actual ...") |
|||
| (97 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
| − | Habits are a huge part of an individual's everyday life. According to Charles Duhigg 40 - 45% of what we do every day are controlled by habits and not actual decisions. A projects most valuable resource is People. Understanding the theory and reason behind certain behavior of people is therefore vital. Geraldi, J is addressing the fact that the role of project managers is changing from a more technical and analytical role to a motivator and human behavior expert. | + | Habits are a huge part of an individual's everyday life. According to Charles Duhigg <ref name="Duhigg">An interview with Charles Duhigg, a reporter for The New York Times and author of The Power of Habit: Why We Do What We Do in Life and Business. https://hbr.org/2012/06/habits-why-we-do-what-we-do</ref> 40 - 45% of what we do every day are controlled by habits and not actual decisions. A projects most valuable resource is People. Understanding the theory and reason behind certain behavior of people is therefore vital. Geraldi, J <ref name="Geraldi">Geraldi, J., Thuesen, C., Oehmen, J. and Stingl, V. (2017). How to do projects. Nordhavn: Danish Standard Foundation. </ref> is addressing the fact that the role of project managers is changing from a more technical and analytical role to a motivator and human behavior expert. |
| − | This article will dive into how project managers can use the theory of habits to increase the efficiency in a project group. Charles Duhigg´s perception is that habits | + | This article will dive into how project managers can use the theory of habits to increase the efficiency in a project group. Charles Duhigg´s perception is that habits consist of a Cue, a routine and a reward which is the backbone of the tools and methods that project managers can implement in a project. The article will address why habits are important and what project managers can do to use them positively. Furthermore, tools such as Charles Duhiggs four steps and methods such as peer pressure and small wins will be elaborated on. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
== What are Habits == | == What are Habits == | ||
| + | Habits are controlling a huge part of the actions we perform during a regular day, from driving to work to brushing your teeth. | ||
| + | ''“A habit is defined as a motor or cognitive routine that, once it is triggered, completes itself without conscious supervision.”'' <ref>Bernacer J, Murillo JI. The Aristotelian conception of habit and its contribution to human neuroscience. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014;8:883. Published 2014 Nov 3. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2014.00883</ref>. Habits work as a factual template that helps us perform normal tasks without planning every little detail of execution. | ||
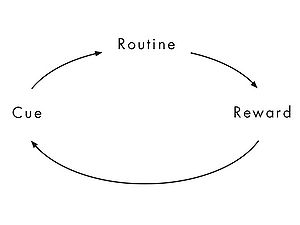
| + | Charles Duhigg explains that habits are extremely hard to remove but can be changed or overwritten with a new habit with less effort. To change these habits an understanding of how a habit is constructed is important. According to Charles Duhigg the habit consists of a three-step loop, The Habit Loop, the steps are respectively the cue, the routine, and reward. Each of these step is important to understand before trying to change a habit, and are shortly described. | ||
| + | [[File:HabitLoop.jpg|right|thumb|300px|The habit Loop <ref name="Duhigg" />]] | ||
=== Cue === | === Cue === | ||
| + | The Cue is what triggers a certain habit. Charles Duhigg<ref name="Duhigg" /> states that the majority of all cues can fit into one of the following five categories, A specific time, a location, an emotional state, specific people and preceding action. The cue tells the brain to perform a specific routine which is connected to exactly that cue. | ||
| + | |||
=== Routine === | === Routine === | ||
| + | The Routine follows right after the cue. A routine is an action that is performed on the brain's autopilot. The routine is the core of the actual habit. It is the cue that can be either good or bad, like sharing knowledge of an issue to your project manager or keeping it to yourself because you think it is someone else's responsibility. | ||
| + | |||
=== Reward === | === Reward === | ||
| − | + | The reward is the emotional state or satisfaction you get from performing the routine. It is also the way the brain decides if the routine is worth repeating. The reward is the reason why certain actions become habits. | |
== Why habits are important in projects == | == Why habits are important in projects == | ||
| + | As people are the main resource in projects it is important to make work enjoyable which also encourage efficiency. As stated by Geraldi, j <ref name="Geraldi"/>''“We do not hang up our emotions with our jackets outside the office! Managing people, with their own interests, feelings, ideas, and competencies is, therefore, a requirement, not an option. And, if done well, it can yield tremendous energy for the project and make days at work enjoyable.”'' This also suggests that in order to create a great environment, managing the individual is very important and can give great energy to the project. Habits help people to complete a specific task with very little mental effort. By introducing habits into project work the employees can use their energy and creative resources instead of regular day to day tasks. Or the habit itself can lead to a greater work life | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==The project manager's role== | ||
| + | The role of a project manager is described in the PMBOK standard as ''"Project managers require the skills to identify, build, maintain, motivate, lead, and inspire project teams to achieve | ||
| + | high team performance and to meet the project’s objective."''<ref name = "PMBOK"/> | ||
| + | As a project manager, the development and the performance are very important, and the knowledge about the behavior of the team members are therefore crucial. | ||
| + | The process of developing a project team can be described in five different phases as described in PMBOK<ref name = "PMBOK"> Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide). Sixth Edition; 2017 </ref> | ||
| + | * Forming | ||
| + | * Storming | ||
| + | * Norming | ||
| + | * Performing | ||
| + | * Adjourning | ||
| + | In the two first phases, Forming and Storming, the team is not very coherent and the environment might be unproductive. It is the project manager's job to get the team through these two steps as quickly as possible to get to a last three phases, Norming, Performing and Adjourning where the project team starts to get used to new work habits and start working together in a productive way. To do that an adjustment of habits and behavior is needed. By knowing the theory behind habits, the project manager would be able to quickly understand and know how to change the bad habits of the project team members. The project manager has an overview of all the individuals in the team and the following tools will help the project manager to steer the project team in the same direction and complete the project successfully. | ||
| + | A strong team requires effective and motivated team members, which can be created by introducing new or changing old habits. Introducing new habits also mean that the team is going to make some changes to their daily routines. The project manager's role is, therefore, to act as a change agent for the entire team. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Tools to encourage change or adopt new habits== | ||
| + | Habits are a very personal matter and require a commitment to a change from the individual. There will always be someone who will have trouble changing a certain way of working or thinking. Charles Duhigg explains three different phenomena and habits, Peer pressure, small wins and blending new habits which can inspire and fuel people to do things that they are not used to. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Peer pressure ==== | ||
| + | Human Beings are inspired and affected by their surroundings and the people around them. Charles Duhigg <ref name="Duhigg Book"> Duhigg, C. (2013). The power of habit. London: Random House Books.</ref> explains how our social habit and peer pressure will encourage individuals to follow group expectations. This means that a project manager can use this social habit of following the majority to make a change to an entire project team and not only those who thrive on change. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Small wins ==== | ||
| + | Projects tend to focus on the large goal or the big win. According to Linda Rising and Mary Manns<ref>Rising, L. and Manns, M. (2019). All In on Small Wins. [online] ProjectManagement.com. Available at: https://www.projectmanagement.com/articles/298908/All-In-on-Small-Wins [Accessed 22 Feb. 2019.</ref> the big wins are not happening very often and can lead to people becoming discouraged and burned out. By keeping the focus on the big win there is no time to look at what already is accomplished and the steps taking towards that big win. Linda Rising and Mary Manns suggest to take time to celebrate all the small wins, the celebrations do not have to be big but show that a great step towards the big goal has been accomplished whether it is with a cake, an internal release or high fives. | ||
| + | As Charles Duhigg<ref name="Duhigg" /> also states ''“Small wins fuel transformation changes by leveraging tiny advantages into patterns that convince people that bigger achievements are within reach”.'' | ||
| + | The reason for this is that the reward gained from the success feeling drives the need for another one, and the possibility to feel that reward again. | ||
| + | Using this in a project would make it more clear that steps are taken towards the big goal. At the same time give the team members the feeling of contribution and value and by that increase the efficiency and create a team that strives for the next small win. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Blending new Habits between old ones ==== | ||
| + | A way to introduce completely new habits is to make the habits feel like some of the other good habits you have. As an example many people today is addicted to their phones and it has become a habit to check for updates regularly. Using the phone as a place to get project updates or keeping project information can, therefore, enhance project members focus on the project. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Understand and replace habits== | ||
| + | The three methods, Peer pressure, small wins and blending new habits, can be used to engage people in the change that is desired. But in order to do that, it is important to identify the actual bad habit and experiment with how it could be changed. Charles Duhigg<ref name="Duhigg Book" /> provides a clear step by step guide to do this. There are four steps in this guide. | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Identify the routine | ||
| + | # Experimentation | ||
| + | # Isolate the cue | ||
| + | # Have a plan | ||
| + | |||
| + | These steps help to understand the full habit loop which is described in the section ''What is a habit''. '''The first step''' (Identify the routine) is to understand and identify what routine needs to change. A bad routine could be checking your Facebook regularly through the day. When the routine is determined an experimentation phase is entered. '''Step two''' (Experimentation) is to experiment with the rewards, a question can be asked, what are you craving since you are performing this routine. In regards to the facebook routine, you can experiment with finding someone around to have a quick talk, go get a coffee or to throw a ball up and down. After doing these things a list of the first three words should be written down. It can be anything from emotions to random words. After 10 to 15 minutes, see if you still have the urge to check your facebook. The craving might be that you are hungry or just tired of work and want to socialize for a minute. If you don't feel like checking Facebook after having a quick talk with someone, the craving might be to socialize or get your head away from work in a small period of time. | ||
| + | '''Step three''' (Isolate the cue) is to look at if there is a specific trigger of this routine. As mentioned in the section ''what is a habit'' the cue have five different categories. To locate the cue write down the answer to the following questions which is within these categories. | ||
| + | * Where are you? | ||
| + | * What time is it? | ||
| + | * What's your emotional state? | ||
| + | * Who else is around | ||
| + | * What actions preceded the urge? | ||
| + | By collecting these notes it will explain if it is at a certain time or certain emotional state which triggers the habit. | ||
| + | '''Step four''' (Have a plan) requires that you now know the entire habit loop of the habits you want to change, this has been accomplished in step one to three. This step is the planning step, and a plan has to be set in motion in order not to fall back to the old habit. In a project relation, the project manager would assist the individual through all the steps, and especially the planning of the new routine and help with not falling back to the old routine. This could be setting a timer on the phone to a certain time and the go socialize. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Completely new habits=== | ||
| + | When the need is to create a new habit, the cue, routine and the reward is not present yet. Therefore the project manager has to find a cue, determine the routine, and find a reward that encourages people. | ||
| + | Developing a new habit will make use of all the tools presented in this article. The Habit loop and the ability to implement the changes into a project team. The project manager has the responsibility to facilitate, plan and control the project teams behavior in order to make these habits stick. This implementation of a new habit might take time and require a lot of experimentation, especially in the reward area of the habit loop. The project manager might also discover that not the same reward works for every team member. Customization of a habit can be required in order to reach the routine which is desired for every team member. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Examples of productive Habits == | ||
| + | As every team is different the productivity habits needed might also vary. Some of the tools above describe how a project manager can use old habits or keystone habits to encourage the team to change behavior and adapt or change a certain habit. To use these tools it is important that the project manager is aware of the habit loop and is willing to spend time, to find the exact parts of the loop which would allow him to change the routine with a successful outcome. | ||
| + | [[File:HabitLoop2.png|right|thumb|450px|The habit Loop for celebrating small wins]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Celebrating small wins=== | ||
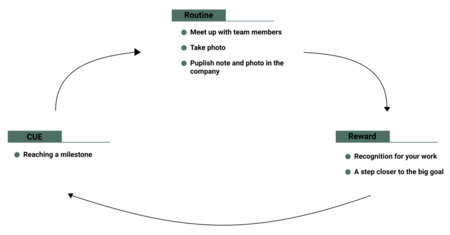
| + | As explained in the section ''Tools to change habits or implement new ones'' celebrating small wins can increase the productivity in a team. In this example, the habit loop of the habit that will perform this routine will be broken down. To find exactly the right reward will need some experimentation as mentioned before. The habit loop presented in this example will work a starting point, and can after experimentation be altered. The routine we want to implement in this case is a celebration on reaching a milestone. The routine could be that every person meets up to take a group photo and sign the milestone if it is depicted on some chart. The picture would be sent to the entire company together with an explanation of the milestone that has been reached. The great reward which is within every human is recognition and being apart of something, the statement would strive to provide this proud feeling as a reward for meeting the milestone. The cue for this is the reach of a milestone. In the picture on the right, the habit loop is visualized. The project managers job in this example is to ensure that every team member participation and the celebration is not skipped no matter how busy the project is. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Conclusion== | ||
| + | Habits and the human behavior of a project team is important to the project manager. Using the habit loop which consists of the Cue, Routine and the reward the project manager can understand the team's behavior. To facilitate a change in a project the use of general keystone habits which is triggered in peer pressure or small wins can be used to effectively change the entire team. If it is necessary the tools can be used to create new habits which could increase the efficiency or the regular work environment. To introduce new habits a good way is to blend the new habit between old habits. In this way, the change seems more familiar and the chance for the habit to stick is increased. The example at the end of the article gives an idea of how small wins together with the creation of a new habit can give great value to a project team. | ||
| + | ===Limitations=== | ||
| + | Habit creation and behavior, in general, is very different depending on the individual. The tools presented in this article will work as an outset to deeper understand why people behave the way they do. It is not easy to create a change in habits and it requires a lot of work from the individual. An important aspect of this is that the project manager is there to guide and assist the project team in this change or the acknowledgment of the need for a change. To do this the relationship between the project team and the project manager is very important. If the project team does not trust or believe in the project manager this issues will need to be addressed at first. Some of the tool given such as peer pressure and blending habits can easily result in the creation and spread of a new bad habit. The knowledge of habit creation can allow the project manager to stop these bad emerging routines before they become habits. | ||
| − | == | + | ==References== |
| + | <references /> | ||
| + | ==Anotated Bibliography== | ||
| + | ===Books=== | ||
| + | '''The power of habit by Charles Duhigg''' | ||
| + | This book provides a very general understanding of how habits are emerging and constructed using scientific evidence and real-world examples. Guidelines and advice to habit change are described in a simple manner. Charles Duhigg is a known author and a recipient of a Pulitzer for explanatory writing. | ||
| − | + | '''PMBOK''' | |
| + | PMBOK is the global standards for Project management. It is a very structured reference book for methods and tools used in project management. | ||
| − | + | '''Geraldi, J., Thuesen, C., Oehmen, J. and Stingl, V. (2017). How to do projects''' | |
| − | + | This book tries to provide information about project management so that managers can make their own recipe for good project management. The book is mainly used to provide evidence, that project managers are influence the behavior of a project team and the individuals. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Articles=== | ||
| + | '''Rising, L. and Manns, M. (2019). All In on Small Wins.''' | ||
| + | This article focus on why small wins are so important and why they important to celebrate instead of always looking to the big goal. Linda Rising is a specialist in change management and Mary Lynn Manns is a professor within management at the University of North Carolina. | ||
| − | + | '''Bernacer J, Murillo JI. The Aristotelian conception of habit and its contribution to human neuroscience.''' | |
| + | The article supports the definition of a habit an also links it to the scientific area of human neuroscience. Only a small part of the article is used, also due to the high complexity of the field of neuroscience. | ||
Latest revision as of 20:58, 4 March 2019
Contents |
[edit] Abstract
Habits are a huge part of an individual's everyday life. According to Charles Duhigg [1] 40 - 45% of what we do every day are controlled by habits and not actual decisions. A projects most valuable resource is People. Understanding the theory and reason behind certain behavior of people is therefore vital. Geraldi, J [2] is addressing the fact that the role of project managers is changing from a more technical and analytical role to a motivator and human behavior expert. This article will dive into how project managers can use the theory of habits to increase the efficiency in a project group. Charles Duhigg´s perception is that habits consist of a Cue, a routine and a reward which is the backbone of the tools and methods that project managers can implement in a project. The article will address why habits are important and what project managers can do to use them positively. Furthermore, tools such as Charles Duhiggs four steps and methods such as peer pressure and small wins will be elaborated on.
[edit] What are Habits
Habits are controlling a huge part of the actions we perform during a regular day, from driving to work to brushing your teeth. “A habit is defined as a motor or cognitive routine that, once it is triggered, completes itself without conscious supervision.” [3]. Habits work as a factual template that helps us perform normal tasks without planning every little detail of execution. Charles Duhigg explains that habits are extremely hard to remove but can be changed or overwritten with a new habit with less effort. To change these habits an understanding of how a habit is constructed is important. According to Charles Duhigg the habit consists of a three-step loop, The Habit Loop, the steps are respectively the cue, the routine, and reward. Each of these step is important to understand before trying to change a habit, and are shortly described.
[edit] Cue
The Cue is what triggers a certain habit. Charles Duhigg[1] states that the majority of all cues can fit into one of the following five categories, A specific time, a location, an emotional state, specific people and preceding action. The cue tells the brain to perform a specific routine which is connected to exactly that cue.
[edit] Routine
The Routine follows right after the cue. A routine is an action that is performed on the brain's autopilot. The routine is the core of the actual habit. It is the cue that can be either good or bad, like sharing knowledge of an issue to your project manager or keeping it to yourself because you think it is someone else's responsibility.
[edit] Reward
The reward is the emotional state or satisfaction you get from performing the routine. It is also the way the brain decides if the routine is worth repeating. The reward is the reason why certain actions become habits.
[edit] Why habits are important in projects
As people are the main resource in projects it is important to make work enjoyable which also encourage efficiency. As stated by Geraldi, j [2]“We do not hang up our emotions with our jackets outside the office! Managing people, with their own interests, feelings, ideas, and competencies is, therefore, a requirement, not an option. And, if done well, it can yield tremendous energy for the project and make days at work enjoyable.” This also suggests that in order to create a great environment, managing the individual is very important and can give great energy to the project. Habits help people to complete a specific task with very little mental effort. By introducing habits into project work the employees can use their energy and creative resources instead of regular day to day tasks. Or the habit itself can lead to a greater work life
[edit] The project manager's role
The role of a project manager is described in the PMBOK standard as "Project managers require the skills to identify, build, maintain, motivate, lead, and inspire project teams to achieve high team performance and to meet the project’s objective."[4] As a project manager, the development and the performance are very important, and the knowledge about the behavior of the team members are therefore crucial. The process of developing a project team can be described in five different phases as described in PMBOK[4]
- Forming
- Storming
- Norming
- Performing
- Adjourning
In the two first phases, Forming and Storming, the team is not very coherent and the environment might be unproductive. It is the project manager's job to get the team through these two steps as quickly as possible to get to a last three phases, Norming, Performing and Adjourning where the project team starts to get used to new work habits and start working together in a productive way. To do that an adjustment of habits and behavior is needed. By knowing the theory behind habits, the project manager would be able to quickly understand and know how to change the bad habits of the project team members. The project manager has an overview of all the individuals in the team and the following tools will help the project manager to steer the project team in the same direction and complete the project successfully. A strong team requires effective and motivated team members, which can be created by introducing new or changing old habits. Introducing new habits also mean that the team is going to make some changes to their daily routines. The project manager's role is, therefore, to act as a change agent for the entire team.
[edit] Tools to encourage change or adopt new habits
Habits are a very personal matter and require a commitment to a change from the individual. There will always be someone who will have trouble changing a certain way of working or thinking. Charles Duhigg explains three different phenomena and habits, Peer pressure, small wins and blending new habits which can inspire and fuel people to do things that they are not used to.
[edit] Peer pressure
Human Beings are inspired and affected by their surroundings and the people around them. Charles Duhigg [5] explains how our social habit and peer pressure will encourage individuals to follow group expectations. This means that a project manager can use this social habit of following the majority to make a change to an entire project team and not only those who thrive on change.
[edit] Small wins
Projects tend to focus on the large goal or the big win. According to Linda Rising and Mary Manns[6] the big wins are not happening very often and can lead to people becoming discouraged and burned out. By keeping the focus on the big win there is no time to look at what already is accomplished and the steps taking towards that big win. Linda Rising and Mary Manns suggest to take time to celebrate all the small wins, the celebrations do not have to be big but show that a great step towards the big goal has been accomplished whether it is with a cake, an internal release or high fives. As Charles Duhigg[1] also states “Small wins fuel transformation changes by leveraging tiny advantages into patterns that convince people that bigger achievements are within reach”. The reason for this is that the reward gained from the success feeling drives the need for another one, and the possibility to feel that reward again. Using this in a project would make it more clear that steps are taken towards the big goal. At the same time give the team members the feeling of contribution and value and by that increase the efficiency and create a team that strives for the next small win.
[edit] Blending new Habits between old ones
A way to introduce completely new habits is to make the habits feel like some of the other good habits you have. As an example many people today is addicted to their phones and it has become a habit to check for updates regularly. Using the phone as a place to get project updates or keeping project information can, therefore, enhance project members focus on the project.
[edit] Understand and replace habits
The three methods, Peer pressure, small wins and blending new habits, can be used to engage people in the change that is desired. But in order to do that, it is important to identify the actual bad habit and experiment with how it could be changed. Charles Duhigg[5] provides a clear step by step guide to do this. There are four steps in this guide.
- Identify the routine
- Experimentation
- Isolate the cue
- Have a plan
These steps help to understand the full habit loop which is described in the section What is a habit. The first step (Identify the routine) is to understand and identify what routine needs to change. A bad routine could be checking your Facebook regularly through the day. When the routine is determined an experimentation phase is entered. Step two (Experimentation) is to experiment with the rewards, a question can be asked, what are you craving since you are performing this routine. In regards to the facebook routine, you can experiment with finding someone around to have a quick talk, go get a coffee or to throw a ball up and down. After doing these things a list of the first three words should be written down. It can be anything from emotions to random words. After 10 to 15 minutes, see if you still have the urge to check your facebook. The craving might be that you are hungry or just tired of work and want to socialize for a minute. If you don't feel like checking Facebook after having a quick talk with someone, the craving might be to socialize or get your head away from work in a small period of time. Step three (Isolate the cue) is to look at if there is a specific trigger of this routine. As mentioned in the section what is a habit the cue have five different categories. To locate the cue write down the answer to the following questions which is within these categories.
- Where are you?
- What time is it?
- What's your emotional state?
- Who else is around
- What actions preceded the urge?
By collecting these notes it will explain if it is at a certain time or certain emotional state which triggers the habit. Step four (Have a plan) requires that you now know the entire habit loop of the habits you want to change, this has been accomplished in step one to three. This step is the planning step, and a plan has to be set in motion in order not to fall back to the old habit. In a project relation, the project manager would assist the individual through all the steps, and especially the planning of the new routine and help with not falling back to the old routine. This could be setting a timer on the phone to a certain time and the go socialize.
[edit] Completely new habits
When the need is to create a new habit, the cue, routine and the reward is not present yet. Therefore the project manager has to find a cue, determine the routine, and find a reward that encourages people. Developing a new habit will make use of all the tools presented in this article. The Habit loop and the ability to implement the changes into a project team. The project manager has the responsibility to facilitate, plan and control the project teams behavior in order to make these habits stick. This implementation of a new habit might take time and require a lot of experimentation, especially in the reward area of the habit loop. The project manager might also discover that not the same reward works for every team member. Customization of a habit can be required in order to reach the routine which is desired for every team member.
[edit] Examples of productive Habits
As every team is different the productivity habits needed might also vary. Some of the tools above describe how a project manager can use old habits or keystone habits to encourage the team to change behavior and adapt or change a certain habit. To use these tools it is important that the project manager is aware of the habit loop and is willing to spend time, to find the exact parts of the loop which would allow him to change the routine with a successful outcome.
[edit] Celebrating small wins
As explained in the section Tools to change habits or implement new ones celebrating small wins can increase the productivity in a team. In this example, the habit loop of the habit that will perform this routine will be broken down. To find exactly the right reward will need some experimentation as mentioned before. The habit loop presented in this example will work a starting point, and can after experimentation be altered. The routine we want to implement in this case is a celebration on reaching a milestone. The routine could be that every person meets up to take a group photo and sign the milestone if it is depicted on some chart. The picture would be sent to the entire company together with an explanation of the milestone that has been reached. The great reward which is within every human is recognition and being apart of something, the statement would strive to provide this proud feeling as a reward for meeting the milestone. The cue for this is the reach of a milestone. In the picture on the right, the habit loop is visualized. The project managers job in this example is to ensure that every team member participation and the celebration is not skipped no matter how busy the project is.
[edit] Conclusion
Habits and the human behavior of a project team is important to the project manager. Using the habit loop which consists of the Cue, Routine and the reward the project manager can understand the team's behavior. To facilitate a change in a project the use of general keystone habits which is triggered in peer pressure or small wins can be used to effectively change the entire team. If it is necessary the tools can be used to create new habits which could increase the efficiency or the regular work environment. To introduce new habits a good way is to blend the new habit between old habits. In this way, the change seems more familiar and the chance for the habit to stick is increased. The example at the end of the article gives an idea of how small wins together with the creation of a new habit can give great value to a project team.
[edit] Limitations
Habit creation and behavior, in general, is very different depending on the individual. The tools presented in this article will work as an outset to deeper understand why people behave the way they do. It is not easy to create a change in habits and it requires a lot of work from the individual. An important aspect of this is that the project manager is there to guide and assist the project team in this change or the acknowledgment of the need for a change. To do this the relationship between the project team and the project manager is very important. If the project team does not trust or believe in the project manager this issues will need to be addressed at first. Some of the tool given such as peer pressure and blending habits can easily result in the creation and spread of a new bad habit. The knowledge of habit creation can allow the project manager to stop these bad emerging routines before they become habits.
[edit] References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 An interview with Charles Duhigg, a reporter for The New York Times and author of The Power of Habit: Why We Do What We Do in Life and Business. https://hbr.org/2012/06/habits-why-we-do-what-we-do
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Geraldi, J., Thuesen, C., Oehmen, J. and Stingl, V. (2017). How to do projects. Nordhavn: Danish Standard Foundation.
- ↑ Bernacer J, Murillo JI. The Aristotelian conception of habit and its contribution to human neuroscience. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014;8:883. Published 2014 Nov 3. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2014.00883
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide). Sixth Edition; 2017
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Duhigg, C. (2013). The power of habit. London: Random House Books.
- ↑ Rising, L. and Manns, M. (2019). All In on Small Wins. [online] ProjectManagement.com. Available at: https://www.projectmanagement.com/articles/298908/All-In-on-Small-Wins [Accessed 22 Feb. 2019.
[edit] Anotated Bibliography
[edit] Books
The power of habit by Charles Duhigg This book provides a very general understanding of how habits are emerging and constructed using scientific evidence and real-world examples. Guidelines and advice to habit change are described in a simple manner. Charles Duhigg is a known author and a recipient of a Pulitzer for explanatory writing.
PMBOK PMBOK is the global standards for Project management. It is a very structured reference book for methods and tools used in project management.
Geraldi, J., Thuesen, C., Oehmen, J. and Stingl, V. (2017). How to do projects This book tries to provide information about project management so that managers can make their own recipe for good project management. The book is mainly used to provide evidence, that project managers are influence the behavior of a project team and the individuals.
[edit] Articles
Rising, L. and Manns, M. (2019). All In on Small Wins. This article focus on why small wins are so important and why they important to celebrate instead of always looking to the big goal. Linda Rising is a specialist in change management and Mary Lynn Manns is a professor within management at the University of North Carolina.
Bernacer J, Murillo JI. The Aristotelian conception of habit and its contribution to human neuroscience. The article supports the definition of a habit an also links it to the scientific area of human neuroscience. Only a small part of the article is used, also due to the high complexity of the field of neuroscience.