McGregor's X & Y theory
(→References) |
(→Interpersonal relationship) |
||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
5. Without resolving problems or reestablishing trust, '''ending''' would be the final stage. | 5. Without resolving problems or reestablishing trust, '''ending''' would be the final stage. | ||
| + | <ref name="wikiinter"> | ||
===In relation to Project management === | ===In relation to Project management === | ||
Revision as of 16:17, 21 February 2021
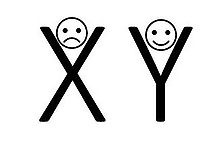
Douglas McGregor was a professor at Massachusetts Institute of Technology and developed in the 1960’s the two motivation theories X & Y, alongside the work of the American Psychologist Abraham Maslow. The theories described the two different manager styles, how the project manager believes his/her employees approach their work and how they are motivated.
Finding how the employees are motivated, is intriguing because a motivated co- worker is more likely to help the manager achieve the project objectives.
Theory X is based on the opinion that the employees does not want to work and must be externally motivated. The X illustrates the employee crossing arms in front of him/her and symbolizes “I do not want to work”.
The alternative approach is theory Y which are more recognizable in todays manager style. Here the manager believes the employees are motivated internally by work satisfaction and are encouraged without direct supervision. The Y describes an employee with open arms. “I am happy to work.”
These theories are not particular used in practice, but are however an interesting way of viewing the two different aspects of project management and employee motivation. The motivation topic is time accurate because of the continues aiming for self- actualization. To understand how a project manager can use motivation as a tool, it is essential to consider what motivates, and which factors that influence motivation such as relationships and the managers soft skills.
Contents |
Motivation theory
Motivation and Human Relation Movement
There are several different tools and theories that point out the importance of the human aspect in project management. The ability to motivate and the relationship between employees, teams and individuals are some of the regulars.
The importance of motivation related to work, started with the human relation movement. Motivation, social relation, and employee satisfaction was investigated in relation to factory productivity in the 1930s’. Here the workers were considered in terms of their psychology rather than as replaceable bricks. The movement realized that organizational structures and processes influenced worker behavior and motivation.
Elton Mayo was one of those who laid the foundation of the human relation movement and was especially interested in group effects on the behavior of individuals at work. He stressed the power of naturel groups, two-way communication, and high-quality leadership.[2] [3]
What motivates
In extend of the Human relation movement the Maslow hierarchy of needs was made, which laid the foundation for every human being and the universal needs of society. Humans have several needs, which follow the step of the pyramid where the basic needs at the bottom must be satisfied in some extent to be able to climb upwards. They are not fixed, but they are basic needs which influence our psychological and our tendency to growth, identity, and excellence. For individuals to complete their hierarchy, a portion of internal sensation must be met. The five steps that human motivation generally need according to Maslow are: physiological, safety, belonging and love, social needs, esteem, and self- actualization.[4] These applies for theory X and Y.
Theory X
Theory X is based upon that the manager tends to think that the workers are naturally unmotivated, avoids reasonability, must be controlled, needs supervision in every step, have no work ambition and do not like employment. To be sure the workers complete their task the manager often motivates with money or penalties, also referred to as a carrot-to-stick approach. To control staff performance, tangible results are used. An example of this is sales figures.
Usually this type of managing has an authoritarian style and a top- down approach. In this case the managers tend to micromanage people's work, which is often seen in process-driven workplaces. These types of workplaces are often huge organizations with a big number of employees and tight deadlines. [5] [1]
Theory Y
Theory Y describes the managers to have a positive opinion of their employees, which encourage to a more trust-based relationship. This means that the employees get more responsibility and are encouraged to a more open communication. The workers are assumed to be happy to work on their own initiative, to take ownership of their own work and requires less direction. In addition, they tend to approach the work as fulfilling and challenging, and solves problems creatively and imaginary. The workers are individualized and are going towards a higher level of self-actualization, which is also referred to in the Maslow hierarchy of needs. [6] [5]
The hierarchy is about how effort and motivation are correlated. This relates to the two theories, X & Y. Theory X describes motivation relative to the employees needs of financially safety. This need is one of the basic needs, and therefore the most effective incentive to make people work and demands less interpersonal effort. For obvious reasons, this need will always be important for the employees. This means that the employer will give you as a project manager or an employee, any other reason to keep on working in that specific firm, other than money.
Whereas esteem and self- actualization is essential motivation tools in theory Y, where the project manager use these to drive their employees to achieve success, the more basic needs of physiological and safety needs are the only needs related to theory X. Working with theory Y will therefore demand a greater amount of effort. When managers follow the theory Y in a greater extent, it will create positive ripple effects on the associated team, group, and organization. [4] [7]
Interpersonal relationship
To be able to accomplish the need for belonging, love, acceptance, and social exchange relative to esteem and self- actualization, relationships are substantial. The concept of interpersonal relation, also called relationship science, demonstrates why relationships are meaningful. Interpersonal skills are useful to communicate and create a reliable relationship and personal growth. By using soft skill or development of interpersonal communication, it is possible to exchange feelings with the use of verbal or non- verbal messages. This competence leads to preferable qualities such as effective and good communication, decision-making, problem solving, optimism and teamwork.
There are several types of relationships that involves social associations, connections, or affiliations between two or more people. One of them are business relationship and relates to partnership, employer/ employee, contractors, costumers, and coworkers. These relationships are dynamic systems and continuously vary from start to end. Business relationships are to some extent different, and may include power and dominance.
A dominant relationship is when the relation has an unequal distribution of power, where one is dominant and the other are submissive. Dominant people can influence the behavior of others. Often, submissive people will follow given instructions without disagreement, or disagree at first and then follow instruction when pressed. This type of relations is often seen in hierarchical organizations and correlates with uneven distribution of power. If applied to McGregor's theory, this kind of relationships can be found in workplaces where the managers uses the Theory x in a greater extent.
Top- down management is an example of hierarchical organization where a group of people form a dominant hierarchy. In this case, submissive people will be beneficial because they cause less discussion and disagreement. This may save time, prevent inconsistent decisions, maintain the owner’s organization goals, and use those who have the most power to make important decisions. This can be beneficial in terms of organizational and decision-making efficiency, but the organization will not experience democracy and may leave out qualified workers with expertise on the field.
According to the German- born psychologist George Levinger, the natural relationships follows five stages; Acquaintance and acquaintanceship, buildup, continuation, deterioration, and ending. The five stages describe all types of relationships and can provide a valuable understanding of how a relationships occurs. [8]
1. The first step is based on the first impression and may lead to the next stage, if the two parts like each other or are an acquaintance or establish acquaintanceship.
2. At this stage the buildup of trust and care for each other is a key- point whether or not the interaction continues.
3. This phase is about mutual commitment and continuation of a long- term friendship in form of growth and trust.
4. If the communication and self-disclosure are absent at this stage, the relationship tend to deteriorate.
5. Without resolving problems or reestablishing trust, ending would be the final stage. Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
According to the British Standard: Managing successful Projects with Prince2, project management is "the planning, delegating, monotoring and control of all aspects of the projects, and the motivation of those involved, to achieve the project objectives within the performance targets.. " [9]
To do this it is important to be able to manage people. This can be done using soft skills, such as interpersonal competence. This type of proficiency can be used as a tool to avoid or solve conflicts and to achieve consensus with the project stakeholders. [10]
What is a successful project manager?
To be the most effective project manager, recent PMI (Project Management Institute) studies have shown that the skills needed are the combined competences seen in the PMI Talent triangle. Here it is not only the technical, strategic, or business aspects of management competence that are important, but also the knowledge and ability to guide, motivate and direct a team to achieve the project objectives. This type of competence is also seen in qualified leaders.
A reoccurring theme in every project is people. Dealing with people is not as elementary as dealing with logistics, numbers, graphs or programs. Therefore, the knowledge of peoples behavior is essential to be able to motivate and guide. To accomplish success, a project manager should have these abilities and strive to be a greater leader. This type of expertise also applies when working with project stakeholders, the project team and sponsors. Qualities and competences for a good project manager are managing relationships and conflicts by building trust, seeking consensus, being respectful, ethical, service minded, a problem solver and use this to build effective teams.[11]
Marcus Buckingham wrote in March 2005 the article “What Great Managers Do”, in the Harvard Business review magazine after researching managers in general and its top performers. He found out that there is one quality that separates great managers from the rest: “They discover what is unique about each person and then capitalize on it. Average managers play checkers, while great managers play chess.” The difference was that top performing managers treated the employees with the knowledge of each unique value and their abilities, rather than in checkers where the pieces moves at the same pace on parallel paths. It is a plan and a coordination behind every movement, but each employee is treated the exact same way. Top performing managers discover peoples uniqueness and likes to work with people. «Fine shadings of personality, though they may be invisible to some and frustrating to others, are crystal clear to and highly valued by great managers.”
Application
In a business case, leadership and management is about to get things done and achieve goals. To obtain the projects objectives, the skills and qualities of a good project manager is essential.
When a project manager has the skills and ability to motivate employees, the managers own goals are more likely to be fulfilled. This means that both parts are rewarded. To understand what motivates people, it is important to understand what makes a person work towards a particular goal or result with a high level of commitment. This is because motivated employees are more productive and therefore more profitable.[12] Managers can therefore use McGregor's theory as a tool to understand the importance of motivation, and is therefore highly interesting in a project managers perspective.
Based on these two theories, the assumptions made about the team members or employees can have an influence on how they are managed. Based on evaluated circumstances, a project manager can also choose the most preferable method to fit the project by investigating the employees and work environment.
To be able to fulfill the project objectives a different way of using the theory X and Y is to create an optimal project team by handpicking the most suitable persons. Companies uses resources and effort into hiring people that fits the company by a thorough recruitment processes. There are several methods used to find the right candidates. Personality tests such as the Big five or ability tests like Korn Ferry are commonly used. This is to create a well functioning team that meets the companies preferable qualifications and standards to achieve successful projects. A project management team structure consist of people with defined roles and responsibilities that are able to maintain effective communication and to fulfill the main stakeholders interests and needs. The primary stakeholders are often the businesses, users- and suppliers.[13]
Limitations
Douglas McGregor was a professor at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, where he was a vocal advocate of the human relations approach. He studied heavily how our beliefs shape our behavior and thus how that behavior shapes the behavior of those around us. [14] Therefore it it reasonable to believe that he was more engaged in theory Y, which might explain why there is such a big contrast between the two theories. One can also assume that organizations and the work culture has changed over the past years, and that there is not that easy to divide the two manager styles and employee behavior, as it was done at the time when theory X and Y was developed.
Theory X and Y are two extremes on the scale, and are not necessarily the case for a specific situation. A combination of the two theories are often used rather than picking one over the other. The military is often associated with theory X. A particular reason for this is how the military works as a hierarchy, where the commanders rank indicates the degree of power over the soldiers. They are the one who are taking the decisions. The exact purpose of this is to obtain control and command by using highly constrained patterns with limited information. The strict rules have changed a bit, and a more modern way of doing this is the possibility of individual initiative. This can be in the form of individual judgement and action, within defined constraints. Mission command is an example of this, and this management concept are often used in modern military. This actively demonstrates that combining the two theories can be beneficial.[15]]] In relation to this, there are also different types and scales of projects, which makes it irrational to apply one theory over the other for all projects. In addition, McGregor based his theories on Maslow hierarchy of needs, which is not based on scientific proofs but rather "observations of humans' innate curiosity" [16] One can therefore argue that the human needs discovered by Maslow is not entirely accurate for all human beings.
Annotated Bibliography
PMI standards Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge 6th edition, by Project Management Institute, Inc 2017.
This book proves "detail about key concepts, emerging trends, considerations for tailoring the project management processes, and information on how tools and techniques are applied to projects. Project managers may use one or more methodologies to implement the project management processes outlined in the standard" The book is limited to project management do not include program-, and portfolio management.
British standards Managing successful Projects with Prince2 2017 edition, Published by TSO.
This book is made as a guidance to the use of the leading project management method PRINCE2. PRINCE stands for PRojects IN Controlled Environments, it is a well known method and widely used in the world. The method is established by experience from thousands of projects and countless project sponsors, project managers, - teams, academics, trainers and consultants. First edition of the book was made in 1996, this is the sixed edition from 2017.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 www.wikipedia.org, Theory X and Theory Y[1]
- ↑ www.wikipedia.org, Human relations movement[2]
- ↑ www.wikipedia.org, Elton Mayo[3]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 www.wikipedia.org, Maslow's hierarchy of needs[4]
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 www.mindtools.org, Theory X and Theory Y Understanding People's Motivations[5]
- ↑ www.hbr.org, Harvard Business Review, Beyond Theory Y by John J. Morse and Jay W. Lorsch, 1970 05[6]
- ↑ www.simplypsychology.org, Maslow [7]
- ↑ www.wikipedia.org, Interpersonal relationship [8]
- ↑ Managing successful Projects with Prince2 2017 edition, Published by TSO
- ↑ Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge 6th edition, by Project Management Institute, Inc 2017
- ↑ Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge 6th edition, by Project Management Institute, Inc 2017
- ↑ www.hbr.org, Harvard Business Review, What great managers do by Marcus Buckingham, 2005 03 [9]
- ↑ Managing successful Projects with Prince2 2017 edition, Published by TSO
- ↑ www.lucischart.com, Theory x vs theory y by Lucidchart Content Team https://www.lucidchart.com/blog/theory-x-vs-theory-y
- ↑ www.wikipedia.org, Theory X and Theory Y[10]
- ↑ www.wikipedia.org, Maslow's hierarchy of needs[11]