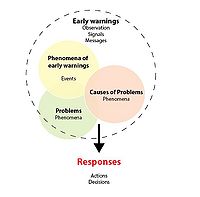
Early warning signals in project management
(→Theory of weak signals) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
=== Theory of weak signals === | === Theory of weak signals === | ||
| − | Many author have different interpretation and definition for a weak signal. The first who mentioned the weak signal concept was Igor Ansoff in 1975 and later on was supported by Nikander (2002). Ansoff stated that strategic events do not came up from nowhere; it is possible to predict their manifestation by the benefit of signs, which are named weak signals. A weak signal was defined by Ansoff, 1984 as “…imprecise early indications about impending impactful events…all that is known is that some threats and opportunities will undoubtedly arise, but their shape and nature and source are not yet known” | + | Many author have different interpretation and definition for a weak signal. The first who mentioned the weak signal concept was Igor Ansoff in 1975 and later on was supported by Nikander (2002). Ansoff stated that strategic events do not came up from nowhere; it is possible to predict their manifestation by the benefit of signs, which are named weak signals. A weak signal was defined by Ansoff, 1984 as ''“…imprecise early indications about impending impactful events…all that is known is that some threats and opportunities will undoubtedly arise, but their shape and nature and source are not yet known”'' |
| − | Later on, this definition was supported by Nikanders’s who defined early warning sign as “observation, a signal, a message or some other item that is or can be seen as an expression, an indication, a proof, or a sign of the existence of some future or incipient positive or negative | + | |
| + | Later on, this definition was supported by Nikanders’s who defined early warning sign as ''“observation, a signal, a message or some other item that is or can be seen as an expression, an indication, a proof, or a sign of the existence of some future or incipient positive or negative issue''” | ||
The main purpose of the authors was the improvement in the strategic planning methods, which are not perfect enough. According to them, when companies operates in uncertain environments requires paying specific attention to weak signals before making any strategic decisions. (Igor. Ansoff & McDonnell, 1990) | The main purpose of the authors was the improvement in the strategic planning methods, which are not perfect enough. According to them, when companies operates in uncertain environments requires paying specific attention to weak signals before making any strategic decisions. (Igor. Ansoff & McDonnell, 1990) | ||
===Levels and groups of early warnings=== | ===Levels and groups of early warnings=== | ||
| + | |||
According with Ansoff (1990), level of information have two stages (strong signals and weak signals): | According with Ansoff (1990), level of information have two stages (strong signals and weak signals): | ||
The progressivity of weak signals to get stronger during the time and turn into strong ones. | The progressivity of weak signals to get stronger during the time and turn into strong ones. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 42: | ||
Weak signals can be classified depending of the sources of data, quality of arguments and future impacts; including moreover feeling signals, uncertain signals or precise signals. | Weak signals can be classified depending of the sources of data, quality of arguments and future impacts; including moreover feeling signals, uncertain signals or precise signals. | ||
| − | + | *The '''feeling signals''' report that something is going to happen. Directly, is connected with the project manager who can have different feelings about things than the other managers, and take different decisions. The human perception varies depending on the person. Normally, this kind of signal are not reported due the missing strong arguments. | |
| − | + | *The '''uncertain signals''' indicates changes in the work environment, sources are anonymous but is possible to find good reasons about the matter. | |
| − | + | *The '''almost certain''' signal, are less uncertain but still there are issue measuring and calculated changes and consequences. | |
| − | + | *The '''exact signals''', signals with enough evidences of their occurrence. | |
Revision as of 22:21, 17 September 2015
Contents |
Abstract
Despite the use of numerous methods and tools for ensuring the success of the development in the project management, still a large number of construction projects experience failure or critical situations. During the front-end stage project, a constant uncertainty last in all critical decisions and corrective actions to reduce possible undesirable impacts to the project.
Identify early warning signal in the early stage is important for the project success, since more time will be available to take corrective actions before negative consequences and problems occur.
An early weak signal can be a missing project information, lack of documentation or the typical wrong scheduling of activities and allocating workers. Due the level of uncertainty at this stage is not easy to identify early warning signs of potential problems that can arise during the development of the project. Nevertheless, select the right approaches for indicate the signals will aid the managers to take right decisions. Furthermore, weak signals can became stronger if they consider at the time of detection at early stages and anticipating problems.
The article explain the importance of early warning signals, compare with the theory of weak signals by Igor Ansoff (1975) and complemented by Nikander’s (2002) and enumerate the typical barriers to identify it.
Introduction
The thought of early warning signal is a wide-ranging concept. It can be apply to any area where it is crucial obtain indications as soon as possible of any project progress that in the future can be undesirable and change the characteristics of the project prior development.
Early warning signals are direct consequences of a critical slowing down of the project development.
Theory of weak signals
Many author have different interpretation and definition for a weak signal. The first who mentioned the weak signal concept was Igor Ansoff in 1975 and later on was supported by Nikander (2002). Ansoff stated that strategic events do not came up from nowhere; it is possible to predict their manifestation by the benefit of signs, which are named weak signals. A weak signal was defined by Ansoff, 1984 as “…imprecise early indications about impending impactful events…all that is known is that some threats and opportunities will undoubtedly arise, but their shape and nature and source are not yet known”
Later on, this definition was supported by Nikanders’s who defined early warning sign as “observation, a signal, a message or some other item that is or can be seen as an expression, an indication, a proof, or a sign of the existence of some future or incipient positive or negative issue” The main purpose of the authors was the improvement in the strategic planning methods, which are not perfect enough. According to them, when companies operates in uncertain environments requires paying specific attention to weak signals before making any strategic decisions. (Igor. Ansoff & McDonnell, 1990)
Levels and groups of early warnings
According with Ansoff (1990), level of information have two stages (strong signals and weak signals): The progressivity of weak signals to get stronger during the time and turn into strong ones.
Weak signals can be classified depending of the sources of data, quality of arguments and future impacts; including moreover feeling signals, uncertain signals or precise signals.
- The feeling signals report that something is going to happen. Directly, is connected with the project manager who can have different feelings about things than the other managers, and take different decisions. The human perception varies depending on the person. Normally, this kind of signal are not reported due the missing strong arguments.
- The uncertain signals indicates changes in the work environment, sources are anonymous but is possible to find good reasons about the matter.
- The almost certain signal, are less uncertain but still there are issue measuring and calculated changes and consequences.
- The exact signals, signals with enough evidences of their occurrence.