Project Status Reporting
(→Relation to project management standards and literature) |
(→Best practices) |
||
| (79 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''Project Status Reporting''' (also known as ''Progress reporting'') involves the process of iteratively reporting the current status and progress of a project to relevant stakeholders. The reporting is conducted by the members of a project team by addressing whether or not the determined targets are being achieved.<ref name="Lock2007"> Lock, D. (2007). ''Project Management''(9th ed.) p.380-382,401-402. Burlington, VT: Gower. </ref><ref name="cdcp"> Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2006) ''Project Status Reporting'' https://www2.cdc.gov/cdcup/library/practices_guides/CDC_UP_Project_Status_Reporting_Practices_Guide.pdf</ref> | + | ''Developed by Anna Felicia Mai Lindström'' |
| + | |||
| + | '''Project Status Reporting''' (also known as ''Progress reporting'') involves the process of iteratively reporting the current status and progress of a project to relevant stakeholders. The reporting is conducted by the members of a project team by addressing whether or not the determined targets are being achieved.<ref name="Lock2007"> Lock, D. (2007). ''Project Management'' (9th ed.) p.380-382,401-402. Burlington, VT: Gower. </ref><ref name="cdcp"> Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2006) ''Project Status Reporting''. Available at https://www2.cdc.gov/cdcup/library/practices_guides/CDC_UP_Project_Status_Reporting_Practices_Guide.pdf [Retrieved 2021-02-18]</ref> | ||
== Summary == | == Summary == | ||
| − | '''Project Status Reporting''' is applied within project management to control and monitor progress of project deliverables. Project reporting involves the process of collecting day-to-day project information and distributing necessary updates to relevant stakeholders.<ref name="PMBOK"> Project Management Institute (2017) ''A guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK guide)''. 6th ed. Newton Square, PA: Project Management Institute.</ref><ref name="Lock2007" /> Performance measurements such as; time, cost, quality, accomplishments and risks, are being compared to the project plan and previous period, all along the project life cycle.<ref name="cdcp" /> This provides an understanding of whether or not, the project deliverables are being met within determined tolerances, which is of great importance in terms of managing uncertainties.<ref name="PMIRisk">Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). (2019). Standard for Risk Management in Portfolios, Programs, and Projects. Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). Retrieved from | + | '''Project Status Reporting''' is applied within project management to control and monitor progress of project deliverables. Project reporting involves the process of collecting day-to-day project information and distributing necessary updates to relevant stakeholders.<ref name="PMBOK"> Project Management Institute (2017) ''A guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK guide)''. 6th ed. Chapters: 4, 10 & 11. Newton Square, PA: Project Management Institute.</ref><ref name="Lock2007" /> Performance measurements such as; time, cost, quality, accomplishments and risks, are being compared to the project plan and previous period, all along the project life cycle.<ref name="cdcp" /> This provides an understanding of whether or not, the project deliverables are being met within determined tolerances, which is of great importance in terms of managing uncertainties.<ref name="PMIRisk">Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). (2019). ''Standard for Risk Management in Portfolios, Programs, and Projects''. Chapters: 4 & 7. Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). Retrieved from |
| − | https://app.knovel.com/hotlink/toc/id:kpSRMPPP01/standard-risk-management/standard-risk-management </ref> Continuous monitoring and reporting are regarded as main activities to highlight deviations in accordance to the project plan.<ref name="PRINCE2"> AXELOS, 2017. Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition, The Stationery Office Ltd, London. Available from: ProQuest Ebook Central. [18 February 2021].</ref> It enhances the possibilities to quicker discover deviating trends and responsiveness in terms of corrective actions.<ref | + | https://app.knovel.com/hotlink/toc/id:kpSRMPPP01/standard-risk-management/standard-risk-management </ref> Continuous monitoring and reporting are regarded as main activities to highlight deviations in accordance to the project plan.<ref name="PRINCE2"> AXELOS, 2017. Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition, Chapters: 10,12,17 & Appendix A. The Stationery Office Ltd, London. Available from: ProQuest Ebook Central. [18 February 2021].</ref> It enhances the possibilities to quicker discover deviating trends and responsiveness in terms of corrective actions.<ref name="PMIRisk" />The composition, format and frequency of the status reports are determined by the communication management approach, where communication format and frequency is defined in the initiation stage of the project.<ref name="PRINCE2" /> During the course of a project, the project manager is spending the majority of the time on communicating with its project team and relevant stakeholders.<ref name="PMBOK" /> Thus, effective communication is a key factor to maintain, in order to conduct and deliver successful project management.<ref name="cdcp" /><ref name="Swanson2014"> Swanson, S. A. (2014). ''Anatomy of an effective status report''. PM Network, 28(6), 52–61. Available at https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/anatomy-highly-effective-status-report-2198 [Retrieved 2021-02-16]</ref> On one hand, Project Status Reporting has an important function in terms of bridging the knowledge within the project network. On the other hand, it provides essential project updates a foundation to support managerial decision-making.<ref name="Swanson2014" /><ref name="PRINCE2" /> |
| − | + | ||
| + | Overall, this makes Project Status Reporting a powerful tool to support progress controlling, with a specific link to project management. However, if a project is a part of a portfolio or program, the level of progress control and reporting can be escalated into a larger context. That is, by creating a Portfolio Status Report to monitor and align progress of the individual projects, or a Program Status Report to control the included projects and portfolios. Here it is important to consider how to align the risk system within the project, portfolio and program hierarchy. Although, this article is focusing on the application on a project level, since this is the most detailed level where the status reports have to be produced. Thus, project specific deviations and accomplishments are identified on a lower level and later escalated upwards as a part controlling the project risk management network.<ref name="PRINCE2" /> | ||
== Big idea == | == Big idea == | ||
=== Concept of a Project Status Report === | === Concept of a Project Status Report === | ||
| − | Project Status Reporting | + | Project Status Reporting consists of a formal report which is updated consistently along the project lifecycle. The content of the reports involves critical aspects of the project, such as scope, scheduling, resources, cost and issues.<ref name="cdcp" /> The report is conducted by a member of a project team, either the project manager or another assigned team member. The frequency and framework specifications can vary, based on factors such as; project timeline, project size, complexity.<ref name="PRINCE2" /> However, reports are regularly being presented on a weekly basis and is an essential pillar of project communication.<ref name="Swanson2014" /> <ref name="cdcp" /> The reports are usually distributed through a roll-up process where reporting starts from the level of the team members and is being escalated to the project manager, and upwards in the project hierarchy. The reports are thereby being provided to all relevant stakeholders and decision-makers within the project network, to support decision-making. This could for instance include the steering committee, executive sponsors, customers, risk owners as well as all project staff members.<ref name="PRINCE2" /><ref name="Hayes2012" /> |
=== Characteristics of a Project Status Report === | === Characteristics of a Project Status Report === | ||
| Line 17: | Line 20: | ||
In literature there are various approaches presented on how project status and progress can be reported. However, there are some main characteristics and elements of which the report should contain. The status reports can either be produced for internal purposes and distribution to the company management or externally to a client or customer. The internal version is providing detailed information regarding task fulfilment, explanations and forecasts. This data is usually handled as confidential with restricted access. The status report which is distributed to the customers is derived from an edited version of the internal report, but more customised and on a higher level.<ref name="Lock2007" /> | In literature there are various approaches presented on how project status and progress can be reported. However, there are some main characteristics and elements of which the report should contain. The status reports can either be produced for internal purposes and distribution to the company management or externally to a client or customer. The internal version is providing detailed information regarding task fulfilment, explanations and forecasts. This data is usually handled as confidential with restricted access. The status report which is distributed to the customers is derived from an edited version of the internal report, but more customised and on a higher level.<ref name="Lock2007" /> | ||
| − | When it comes to generic characteristics of the Project Status Reports, there are some | + | When it comes to generic characteristics of the Project Status Reports, there are some recurring elements which are included in the format. The reported content is conducted in the same format repeatedly along the project lifecycle.<ref name="Hayes2012"> Hayes Munson, K. A. (2012). ''How do you know the status of your project?: Project monitoring and controlling''. Paper presented at PMI® Global Congress 2012—North America, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute.</ref> Thus, the input to the status reports includes information on updates and progress that has been made since the last report was conducted.<ref name="cdcp" /> Firstly, it consist of a general description of the project itself as well as document information. The main parts consist of a status summary and a review of key areas and milestones of the project. Additionally, it is provided a summary of project risk, issues as well as presentation of performance metrics.<ref name="PRINCE2" /> The output of the status report depends on whether or not the project status of activities and metrics are kept within project tolerances. If targets are being met, continue according to the project plan. Else, corrective actions are to be taken based on risk evaluation.<ref name="cdcp" /> Moreover, in ''Section 3- Application'' it is being elaborated on how to conduct a Project Status Report, based on activities related to the reporting format and elements. |
=== Why Project Status Reports are important for project managers === | === Why Project Status Reports are important for project managers === | ||
| Line 26: | Line 29: | ||
* '''Decision-making''': The reports have the purpose of supporting and facilitating project-related decision-making, by contributing with metrics and status on project progress. This enables the opportunity for stakeholders to constantly monitor that activates are within project tolerances, and else decide on corrective actions.<ref name="PRINCE2" /> | * '''Decision-making''': The reports have the purpose of supporting and facilitating project-related decision-making, by contributing with metrics and status on project progress. This enables the opportunity for stakeholders to constantly monitor that activates are within project tolerances, and else decide on corrective actions.<ref name="PRINCE2" /> | ||
| − | * '''Risk transparency''': Another main purpose involves identifying and capturing new risks within the project boundaries or | + | * '''Risk transparency''': Another main purpose involves identifying and capturing new risks within the project boundaries or highlighting changes within already discovered ones. These are being escalated through the status reports by sharing them with the stakeholders. This enhances the risk culture within the project organisation by enabling higher risk transparency, as well as increasing awareness about project uncertainties.<ref name="PMIRisk" /> |
=== Different types of Project Status Reports === | === Different types of Project Status Reports === | ||
| − | A Project Status Report can appear differently in terms of format and reporting frequency, based on determined communication management approach of a specific project. In addition, there are different types of status reports which can be conducted on different levels within the project hierarchy, in order to collect information on process specific progress. For instance, the PRINCE standard (AXELOS 2017) is addressing four different types of Project Status Reports, elaborated on below. These can all be used for progress reporting within the same project.<ref name="PRINCE2" /> | + | A Project Status Report can appear differently in terms of format and reporting frequency, based on determined communication management approach of a specific project. In addition, there are different types of status reports which can be conducted on different levels within the project hierarchy, in order to collect information on process specific progress. For instance, the PRINCE standard (AXELOS, 2017) is addressing four different types of Project Status Reports, elaborated on below. These can all be used for progress reporting within the same project.<ref name="PRINCE2" /> |
| − | * '''Checkpoint reports''': Checkpoint reports are reporting the current status of individual work packages and are produced on a project team-level. The formality and presentation of these reports can vary, with either being presented verbally or through a project log. The collected information can consist of task completion, potential time and budget deviations and KPIs. The reports are provided to the project manager, who is transferring the collected data and updating the project stage plan accordingly. | + | * '''Checkpoint reports''': ''Checkpoint reports'' are reporting the current status of individual work packages and are produced on a project team-level. The formality and presentation of these reports can vary, with either being presented verbally or through a project log. The collected information can consist of task completion, potential time and budget deviations and KPIs. The reports are provided to the project manager, who is transferring the collected data and updating the project stage plan accordingly. |
| − | * '''Highlight reports''': Highlight reports are based on collected data from the Checkpoint reports and provides a summary on updates and progress for the entire project. The reports are produced by the project manager and | + | * '''Highlight reports''': ''Highlight reports'' are based on collected data from the Checkpoint reports and provides a summary on updates and progress for the entire project. The reports are produced by the project manager and are distributed to relevant stakeholders to create project awareness. The reported content can for instance be presented through documents, e-mails, charts or Kanban boards. |
| − | * '''End Stage report''': The End Stage report is produced by the project manager at the end of each management phase to evaluate the overall progress and performance of the project. It is being presented to the project board and is used as a foundation for decision-making regarding the next stage of the project. That is, approving to move on, taking corrective actions or | + | * '''End Stage report''': ''The End Stage report'' is produced by the project manager at the end of each management phase to evaluate the overall progress and performance of the project. It is being presented to the project board and is used as a foundation for decision-making regarding the next stage of the project. That is, approving to move on, taking corrective actions or worst case- cancel the project. |
| − | * '''End project report''': The End project report is merely conducted in the end stage of a project, and not repeatedly throughout the project lifecycle. It is produced by the project manager and presented to the project board as a foundation for evaluation and closure of the project. The report finalises handover project ownership and provides a detailed update on task completion as well as potential learnings to future projects. | + | * '''End project report''': ''The End project report'' is merely conducted in the end stage of a project, and not repeatedly throughout the project lifecycle. It is produced by the project manager and presented to the project board as a foundation for evaluation and closure of the project. The report finalises handover project ownership and provides a detailed update on task completion as well as potential learnings to future projects. |
| − | The output of the | + | The output of the Project Status Reports are emphasising if the current progress is corresponding to the project stage plan. However, if any new or increased risks and issues have been highlighted, then additional corrective action need to be taken to mitigate the risk. The process of taking corrective actions is not included in the scope of Project Status Reports, but are instead escalated through an ''Issue report'', ''Exception report'' or a ''Lesson report''. <ref name="PRINCE2" /> |
== Application == | == Application == | ||
| − | In terms of the application context of a | + | In terms of the application context of a Project Status Report, it is important to tailor the format, reporting frequency and requirements to the determined project communication and risk management approach.<ref name="PRINCE2" /> When applied in the right context and frequency, the reports are providing an essential documented history of progress along the project timeline. This is useful in terms of looking back at specific events in the project as well as for evaluation and identification of success factors and issues to regard for future projects.<ref name="cdcp" /> |
=== Process of conducting a Project Status Report === | === Process of conducting a Project Status Report === | ||
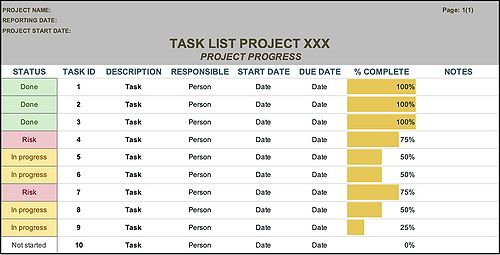
| + | [[File:Task List Template.jpg|500px|thumb|right|Figure 1: Task List (own figure based on Lock (2007)<ref name="Lock2007" />)]] | ||
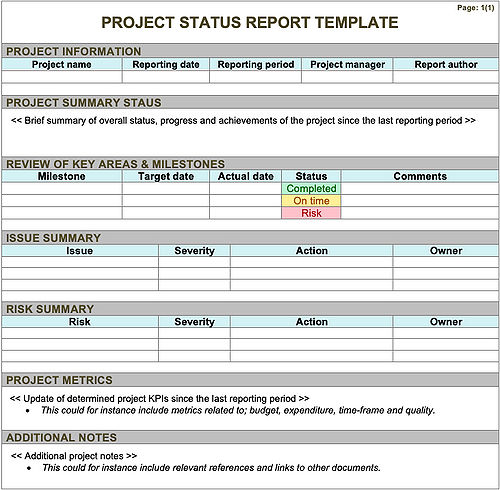
| + | [[File:Project Status Report Template .jpg|500px|thumb|right|Figure 2: Project Status Report Template (own figure based on <ref name="cdcp" />,<ref name="projectmanager"> ProjectManager. (2021) ''The ultimate guide to Project Status Reports''. Available at: https://www.projectmanager.com/status-report [Retrieved 2021-02-18]. </ref>, <ref name="templatelab"> TemplateLab. (2021) ''Benefits of Making a Status Report Template''. Available at: https://templatelab.com/status-report/#Benefits_of_Making_a_Status_Report_Template [Retrieved 2021-03-25]. </ref> and <ref name="microsoft"> Microsoft Office. (2021) ''Project Status Report (Time-less design)''. Available at: https://templates.office.com/en-us/project-status-report-timeless-design-tm02889890 [Retrieved 2021-03-25]. </ref>) ]] | ||
==== 1) Pre-phase ==== | ==== 1) Pre-phase ==== | ||
| − | Before being able to collect project progress data and conduct the status report itself, project-specific reporting guidelines | + | Before being able to collect project progress data and conduct the status report itself, project-specific reporting guidelines need to be defined. This is an important part of the initial phase of the project. The reporting process and delivery method is to be defined in the communication management approach as well as the project risk management strategy. In order to ensure an efficient communication flow and progress control, the stakeholders' actual need for different reporting metrics should be identified (as a part of the Stakeholder analysis).<ref name="cdcp" /> Furthermore, decisions have to be made regarding reporting frequency and formatting, in order to create a clear process in terms of reporting routines. In addition, roles and responsibilities need to be assigned within the project team in regard to who is responsible of; collecting respectively information, processing data, assuring reporting quality as well as distribution of reports to relevant stakeholders. Moreover, the distribution strategy needs to be determined, that is, delivery method and what presentation tools to use.<ref name="Lock2007" /><ref name="PRINCE2" /> |
| − | + | ||
==== 2) Collection of progress data ==== | ==== 2) Collection of progress data ==== | ||
| − | A method for data collection needs to be established in order to successfully provide objective information to write the | + | A method for data collection needs to be established in order to successfully provide objective information to write the Project Status Reports. The data collection can be done manually by team members through a progress log within a SharePoint or through utilisation of a project management software.<ref name="Pian2011">Piantanida, M., Cheli, E., & Lorenzi, M. (2011). Are you overwhelmed preparing too many reports? A smart approach to project reporting. Paper presented at PMI® Global Congress 2011—EMEA, Dublin, Leinster, Ireland. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute. </ref> The key participants in conducting the data collection need to undergo training to understand the routine and ensure high quality of the data. One way to analyse the status of the specific work packages and activities involve using a ''Task list'', as displayed in ''Figure 1''. The reported information is providing updates on; task status (completed/in progress/risk/not started), percentage of task completion, estimated time to task completion as well as additional comments and explanations. This is a method to keep the collection method as standardised and possible, to later be able to extract relevant information for the status reports.<ref name="Lock2007" /> |
==== 3) Elements of the report ==== | ==== 3) Elements of the report ==== | ||
| − | + | A generic template for a Project Status Report generally consists of the elements visualised in ''Figure 2''. Information is being filled in to the template accordingly. It is essential to keep the reporting brief and quickly get to the point. Especially, when giving an overview of the project summary status.<ref name="cdcp" /> | |
| − | A generic template for a Project Status Report | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
==== 4) Distribution ==== | ==== 4) Distribution ==== | ||
| − | The status reports are being provided to relevant stakeholders within the project according to the distribution method decided on in the communication management approach. It is of high importance that the correct information is clearly accessible for all the targeted stakeholders, in order to make well-founded decisions.<ref name="Swanson2014" /> The distribution and delivery methods are based on preferences from the different stakeholders as well as if the recipient is an internal or external | + | The status reports are being provided to relevant stakeholders within the project according to the distribution method decided on in the communication management approach. It is of high importance that the correct information is clearly accessible for all the targeted stakeholders, in order to make well-founded decisions.<ref name="Swanson2014" /> The distribution and delivery methods are based on preferences from the different stakeholders as well as if the recipient is an internal or external stakeholder of the organisation. In some cases distribution through email could be the most efficient one, while others prefer a shared document through the intranet or a visual Kanban board. This needs to be decided on in the initial communication strategy approach of the project.<ref name="PRINCE2" /> |
==== 5) Outputs and deliverables ==== | ==== 5) Outputs and deliverables ==== | ||
| − | The output is | + | The output of the Project Status Report is utilised by stakeholders as a foundation of decision-making and forecasting the future stages of the project. If work packages for the reported period are not kept within project tolerances, corrective actions are needed to be taken to mitigate the identified risks.<ref name="PMIRisk" /> In order to process risk, the identified issues and trend deviations are being escalated into ''Expectation reports''. In addition, ''Issue reports'' are being conducted, where an impact analysis is made and recommendations on how to proceed.<ref name="PRINCE2" /> |
==== 6) Evaluation ==== | ==== 6) Evaluation ==== | ||
| − | + | The last step involves evaluation of what needs to be done in order to move the project forward to the next period. In the end of a project a ''Lessons report'' can be conducted based on highlights from the project status documented history. Thereby, important learnings can be made on what worked well and not, which can be useful in future projects.<ref name="PRINCE2" /> | |
=== Best practices === | === Best practices === | ||
| − | In this section five best practices are presented on factors to consider in order to conduct an effective and successful | + | In this section five best practices are presented on factors to consider in order to conduct an effective and successful Project Status Report. The content has been compiled based on best practices from a report from the PRINCE2 standard (AXELOS 2017) and articles from Swanson (2014) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2006).<ref name="PRINCE2" /><ref name="Swanson2014" /><ref name="cdcp" /> They all are providing guidelines on how to best utilise the reporting tool within a project context and contributing with different aspects on similar success factors. |
* '''Simplify'''- When writing the status reports It is important to quickly get to the point and keep the information on a high level. One should aim to only point out the parameters which actually will contribute to higher project performance. All stakeholders should be able to easily extract the exact information which is relevant for their decision making, without being provided in-depth discussions about all specific work packages. | * '''Simplify'''- When writing the status reports It is important to quickly get to the point and keep the information on a high level. One should aim to only point out the parameters which actually will contribute to higher project performance. All stakeholders should be able to easily extract the exact information which is relevant for their decision making, without being provided in-depth discussions about all specific work packages. | ||
| − | * '''Verification'''- The information in the status reports is essential for decision-makers within the project | + | * '''Verification'''- The information in the status reports is essential for decision-makers within the project when it comes to knowing what actions to proceed with and which tasks to authorise. Therefore, it is important to verify with the stakeholders what project information, KPIs and elements they want the report to consist of to make well-founded decisions. Additionally, content and delivery method can be tailored based on different needs and communication preferences of the stakeholders, in order to achieve maximal effect. |
| − | * '''Consistency'''- The | + | * '''Consistency'''- The reporting format and distribution of the status reports must be kept consistent in order to achieve an effective communication of the reporting content. A standardised routine for processing of data, reporting structure and delivery method should be clearly established. That is, to achieve an objective view of the collected information and an efficient, uniform delivery to stakeholders. |
* '''Establish metrics'''- In order to monitor project status, metrics on how to actually measure progress needs to be defined. These KPIs are determined in the planning phase and updated throughout the course of the project as essential indicators on project health. | * '''Establish metrics'''- In order to monitor project status, metrics on how to actually measure progress needs to be defined. These KPIs are determined in the planning phase and updated throughout the course of the project as essential indicators on project health. | ||
| − | * '''Apply tools'''- There are various | + | * '''Apply tools'''- There are various project management tools which could be applied in order to facilitate the process of conducting efficient status reports. This is beneficial in terms of analysing and displaying larger data sets, by systematically analysing project metrics data to increase productivity. There are numerous reporting softwares which could be applied as well as visualisation tools such as Gantt charts, Kanban boards, Dashboards and wall charts. |
== Limitations == | == Limitations == | ||
=== Challenges in conducting a successful Project Status Report === | === Challenges in conducting a successful Project Status Report === | ||
| − | There are some main limitations to the Project Status Reports in “how” and what context the tool should be used. These limitations are important to be aware of in order to maximize utilisation of the tool. In terms of the risk aspect, the status reports are not considered as a sufficient tool in handling and | + | There are some main limitations to the Project Status Reports in “how” and what context the tool should be used. These limitations are important to be aware of in order to maximize utilisation of the tool. In terms of the risk aspect, the status reports are not considered as a sufficient tool in handling and mitigation of project risks. The scope of the tool merely lies in collecting information and monitoring progress of a project. Thus, issues are being identified, but does not provide a plan on how to actually take corrective actions.<ref name="PRINCE2" /> Here, the status reports need to be complemented with other project management tools, such as issue reports or contingency plans. One of the main purposes with status reporting lies in improving the communication flow amongst the stakeholders. Although, one drawback of the status reports lies in the risk of substituting the regular day-to-day communication.<ref name="MIT2014"> Keil, M., Smith, H.J., Iacovou, C.L. & Thompson, R.L. 2014, "The Pitfalls of Project Status Reporting", MIT Sloan Management Review, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 57-64.</ref> The reports are limited to providing essential data to relevant stakeholders, but only at a certain delivery frequency. It is important to consider that some information is more urgent, and cannot wait to be escalated when the status reports are presented.<ref name="Swanson2014" /> Moreover, the quality of the status report is only as good as the quality of the information extracted from the data collection. Hence, misreporting is considered as a main limitation of project status reporting, where it is of high importance to set up clear method of how to conduct the data collection, to mitigate the risk.<ref name="MIT2014" /> |
=== Relation to project management standards and literature === | === Relation to project management standards and literature === | ||
| − | The | + | The Project Status Reports (or ''progress reports'') are addressed in several standards as a main tool to support project progress control and improve communication and risk management.<ref name="PRINCE2" /><ref name="PMIRisk" /><ref name="PMBOK" /> This article is providing an in-depth summary of the topic of a Project Status Report, with the aim to cover all areas from overall concept, application and limitations. On one hand this article relates to several standards within project management to contextualise its contribution and usefulness. On the other hand, it is supported by the views of various articles and books as main references, to fill the gaps in regard to elaborating on the actual application process and drawbacks of the tool. Thus, the full process of conducting the status reports is extended out of the scope of the standards to achieve a bigger picture. |
== Annotated Bibliography == | == Annotated Bibliography == | ||
| − | + | This section is providing suggestions on where additional information about Project Status Reporting can be found, in terms of further reading. It is referring to some of the key references of the article based on different approaches to the topic and how it is contextualised within project management. | |
| + | |||
| + | '''Lock, D. (2007). Project Management (9th ed.) p.380-382,401-402. Burlington, VT: Gower.''' | ||
| + | This book describes the full project lifecycle in detail as well as related project management tools. It addresses the topic of Project Status Reporting (Progress reporting) in a context of how to manage and monitor progress during the course of the project. Moreover, it is describing the concept of Project status reporting in a fundamental manner. Both in terms of how to collect reliable progress data, establishing reporting requirements as well as how to communicate the information in an efficient way. | ||
| − | AXELOS, 2017. Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition, The Stationery Office Ltd, London. Available from: ProQuest Ebook Central. [18 February 2021]. | + | '''AXELOS, 2017. Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition, The Stationery Office Ltd, London. Available from: ProQuest Ebook Central. [18 February 2021].''' |
| + | PRINCE2 is a well-known British standard for project management. The standard is addressing the process of project reporting and how it is used to monitor and control progress of a project. It is mainly being related to the project stages of controlling, managing uncertainties and communication management. In addition the progress reports are contextualised in an expanded view of program and portfolio management. It is providing an in-depth understanding of reporting requirements and a guide on how to implement the reporting into a project communication approach. | ||
| − | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2006) "Project Status Reporting" https://www2.cdc.gov/cdcup/library/practices_guides/CDC_UP_Project_Status_Reporting_Practices_Guide.pdf | + | '''Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2006) "Project Status Reporting" https://www2.cdc.gov/cdcup/library/practices_guides/CDC_UP_Project_Status_Reporting_Practices_Guide.pdf [18 February 2021].''' |
| + | The Centres for Disease Control and Prevention is a national public health institute in the U.S.A., mainly operating within the area of disease control and other challenges related to public health. The agency has collected a portfolio of documents related to project management, in order to facilitate and unify processes. This includes various practices, tools, theories, templates and checklists to support a project manager and project team. Project Status Reporting is included in this portfolio and is providing a clear overview of the topic and importance of project management. The main document consists of a brief and clear summary of the main concept, purpose and how to apply the tool, and is helpful to get an overall understanding of the big idea. Moreover, there are other related documents in terms of a template and checklist with advice on how to utilise the reporting to improve project performance. | ||
| − | Swanson, S. A. (2014). Anatomy of an effective status report. PM Network, 28(6), 52–61. | + | '''Swanson, S. A. (2014). Anatomy of an effective status report. PM Network, 28(6), 52–61.''' |
| + | This article is published through Project Management Institute’s (PMI) network for publications. The paper is addressing various best practices and fallbacks related to conducting Project Status Reports, rather than explaining the concept itself. This perspective is important to include, in order to understand the context of which the tool is being applied as well as its limitations. Thus, it is good to get an overview of real challenges and improvements suggestions, which have appeared during actual application of the tool. | ||
| − | Keil, M., Smith, H.J., Iacovou, C.L. & Thompson, R.L. 2014, "The Pitfalls of Project Status Reporting", MIT Sloan Management Review, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 57-64. | + | '''Keil, M., Smith, H.J., Iacovou, C.L. & Thompson, R.L. 2014, "The Pitfalls of Project Status Reporting", MIT Sloan Management Review, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 57-64.''' |
| + | This article is addressing common drawbacks of the Project Status Reports and how to overcome these limitations. It is providing a self-assessment for a project manager to apply to see how vulnerable one is to misreporting. Moreover, the challenges are being contextualised with providing in-depth cases from the Affordable Care Act health care reform in the U.S.A. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:14, 27 February 2021
Developed by Anna Felicia Mai Lindström
Project Status Reporting (also known as Progress reporting) involves the process of iteratively reporting the current status and progress of a project to relevant stakeholders. The reporting is conducted by the members of a project team by addressing whether or not the determined targets are being achieved.[1][2]
Contents |
[edit] Summary
Project Status Reporting is applied within project management to control and monitor progress of project deliverables. Project reporting involves the process of collecting day-to-day project information and distributing necessary updates to relevant stakeholders.[3][1] Performance measurements such as; time, cost, quality, accomplishments and risks, are being compared to the project plan and previous period, all along the project life cycle.[2] This provides an understanding of whether or not, the project deliverables are being met within determined tolerances, which is of great importance in terms of managing uncertainties.[4] Continuous monitoring and reporting are regarded as main activities to highlight deviations in accordance to the project plan.[5] It enhances the possibilities to quicker discover deviating trends and responsiveness in terms of corrective actions.[4]The composition, format and frequency of the status reports are determined by the communication management approach, where communication format and frequency is defined in the initiation stage of the project.[5] During the course of a project, the project manager is spending the majority of the time on communicating with its project team and relevant stakeholders.[3] Thus, effective communication is a key factor to maintain, in order to conduct and deliver successful project management.[2][6] On one hand, Project Status Reporting has an important function in terms of bridging the knowledge within the project network. On the other hand, it provides essential project updates a foundation to support managerial decision-making.[6][5]
Overall, this makes Project Status Reporting a powerful tool to support progress controlling, with a specific link to project management. However, if a project is a part of a portfolio or program, the level of progress control and reporting can be escalated into a larger context. That is, by creating a Portfolio Status Report to monitor and align progress of the individual projects, or a Program Status Report to control the included projects and portfolios. Here it is important to consider how to align the risk system within the project, portfolio and program hierarchy. Although, this article is focusing on the application on a project level, since this is the most detailed level where the status reports have to be produced. Thus, project specific deviations and accomplishments are identified on a lower level and later escalated upwards as a part controlling the project risk management network.[5]
[edit] Big idea
[edit] Concept of a Project Status Report
Project Status Reporting consists of a formal report which is updated consistently along the project lifecycle. The content of the reports involves critical aspects of the project, such as scope, scheduling, resources, cost and issues.[2] The report is conducted by a member of a project team, either the project manager or another assigned team member. The frequency and framework specifications can vary, based on factors such as; project timeline, project size, complexity.[5] However, reports are regularly being presented on a weekly basis and is an essential pillar of project communication.[6] [2] The reports are usually distributed through a roll-up process where reporting starts from the level of the team members and is being escalated to the project manager, and upwards in the project hierarchy. The reports are thereby being provided to all relevant stakeholders and decision-makers within the project network, to support decision-making. This could for instance include the steering committee, executive sponsors, customers, risk owners as well as all project staff members.[5][7]
[edit] Characteristics of a Project Status Report
In literature there are various approaches presented on how project status and progress can be reported. However, there are some main characteristics and elements of which the report should contain. The status reports can either be produced for internal purposes and distribution to the company management or externally to a client or customer. The internal version is providing detailed information regarding task fulfilment, explanations and forecasts. This data is usually handled as confidential with restricted access. The status report which is distributed to the customers is derived from an edited version of the internal report, but more customised and on a higher level.[1]
When it comes to generic characteristics of the Project Status Reports, there are some recurring elements which are included in the format. The reported content is conducted in the same format repeatedly along the project lifecycle.[7] Thus, the input to the status reports includes information on updates and progress that has been made since the last report was conducted.[2] Firstly, it consist of a general description of the project itself as well as document information. The main parts consist of a status summary and a review of key areas and milestones of the project. Additionally, it is provided a summary of project risk, issues as well as presentation of performance metrics.[5] The output of the status report depends on whether or not the project status of activities and metrics are kept within project tolerances. If targets are being met, continue according to the project plan. Else, corrective actions are to be taken based on risk evaluation.[2] Moreover, in Section 3- Application it is being elaborated on how to conduct a Project Status Report, based on activities related to the reporting format and elements.
[edit] Why Project Status Reports are important for project managers
The concept of conducting consistent Project Status Reports is deeply embedded within several areas of project management. However, the main purpose and objectives are related to the steps of continuous progress controlling, risk reduction and communication management within a project. If the project status is not monitored on a regular basis, there is a risk of losing control of the course and target of the progress.[5] Nonetheless, the main purposes of conducting efficient project status reporting corresponds to the following areas:
- Communication: It aims to improve the communication flow across the project network, by distributing necessary status updates to relevant stakeholders. Establishing an effective communication management approach is essential for project success, in terms steering the project in the right direction in accordance to the project plan and objectives.[6]
- Decision-making: The reports have the purpose of supporting and facilitating project-related decision-making, by contributing with metrics and status on project progress. This enables the opportunity for stakeholders to constantly monitor that activates are within project tolerances, and else decide on corrective actions.[5]
- Risk transparency: Another main purpose involves identifying and capturing new risks within the project boundaries or highlighting changes within already discovered ones. These are being escalated through the status reports by sharing them with the stakeholders. This enhances the risk culture within the project organisation by enabling higher risk transparency, as well as increasing awareness about project uncertainties.[4]
[edit] Different types of Project Status Reports
A Project Status Report can appear differently in terms of format and reporting frequency, based on determined communication management approach of a specific project. In addition, there are different types of status reports which can be conducted on different levels within the project hierarchy, in order to collect information on process specific progress. For instance, the PRINCE standard (AXELOS, 2017) is addressing four different types of Project Status Reports, elaborated on below. These can all be used for progress reporting within the same project.[5]
- Checkpoint reports: Checkpoint reports are reporting the current status of individual work packages and are produced on a project team-level. The formality and presentation of these reports can vary, with either being presented verbally or through a project log. The collected information can consist of task completion, potential time and budget deviations and KPIs. The reports are provided to the project manager, who is transferring the collected data and updating the project stage plan accordingly.
- Highlight reports: Highlight reports are based on collected data from the Checkpoint reports and provides a summary on updates and progress for the entire project. The reports are produced by the project manager and are distributed to relevant stakeholders to create project awareness. The reported content can for instance be presented through documents, e-mails, charts or Kanban boards.
- End Stage report: The End Stage report is produced by the project manager at the end of each management phase to evaluate the overall progress and performance of the project. It is being presented to the project board and is used as a foundation for decision-making regarding the next stage of the project. That is, approving to move on, taking corrective actions or worst case- cancel the project.
- End project report: The End project report is merely conducted in the end stage of a project, and not repeatedly throughout the project lifecycle. It is produced by the project manager and presented to the project board as a foundation for evaluation and closure of the project. The report finalises handover project ownership and provides a detailed update on task completion as well as potential learnings to future projects.
The output of the Project Status Reports are emphasising if the current progress is corresponding to the project stage plan. However, if any new or increased risks and issues have been highlighted, then additional corrective action need to be taken to mitigate the risk. The process of taking corrective actions is not included in the scope of Project Status Reports, but are instead escalated through an Issue report, Exception report or a Lesson report. [5]
[edit] Application
In terms of the application context of a Project Status Report, it is important to tailor the format, reporting frequency and requirements to the determined project communication and risk management approach.[5] When applied in the right context and frequency, the reports are providing an essential documented history of progress along the project timeline. This is useful in terms of looking back at specific events in the project as well as for evaluation and identification of success factors and issues to regard for future projects.[2]
[edit] Process of conducting a Project Status Report
[edit] 1) Pre-phase
Before being able to collect project progress data and conduct the status report itself, project-specific reporting guidelines need to be defined. This is an important part of the initial phase of the project. The reporting process and delivery method is to be defined in the communication management approach as well as the project risk management strategy. In order to ensure an efficient communication flow and progress control, the stakeholders' actual need for different reporting metrics should be identified (as a part of the Stakeholder analysis).[2] Furthermore, decisions have to be made regarding reporting frequency and formatting, in order to create a clear process in terms of reporting routines. In addition, roles and responsibilities need to be assigned within the project team in regard to who is responsible of; collecting respectively information, processing data, assuring reporting quality as well as distribution of reports to relevant stakeholders. Moreover, the distribution strategy needs to be determined, that is, delivery method and what presentation tools to use.[1][5]
[edit] 2) Collection of progress data
A method for data collection needs to be established in order to successfully provide objective information to write the Project Status Reports. The data collection can be done manually by team members through a progress log within a SharePoint or through utilisation of a project management software.[11] The key participants in conducting the data collection need to undergo training to understand the routine and ensure high quality of the data. One way to analyse the status of the specific work packages and activities involve using a Task list, as displayed in Figure 1. The reported information is providing updates on; task status (completed/in progress/risk/not started), percentage of task completion, estimated time to task completion as well as additional comments and explanations. This is a method to keep the collection method as standardised and possible, to later be able to extract relevant information for the status reports.[1]
[edit] 3) Elements of the report
A generic template for a Project Status Report generally consists of the elements visualised in Figure 2. Information is being filled in to the template accordingly. It is essential to keep the reporting brief and quickly get to the point. Especially, when giving an overview of the project summary status.[2]
[edit] 4) Distribution
The status reports are being provided to relevant stakeholders within the project according to the distribution method decided on in the communication management approach. It is of high importance that the correct information is clearly accessible for all the targeted stakeholders, in order to make well-founded decisions.[6] The distribution and delivery methods are based on preferences from the different stakeholders as well as if the recipient is an internal or external stakeholder of the organisation. In some cases distribution through email could be the most efficient one, while others prefer a shared document through the intranet or a visual Kanban board. This needs to be decided on in the initial communication strategy approach of the project.[5]
[edit] 5) Outputs and deliverables
The output of the Project Status Report is utilised by stakeholders as a foundation of decision-making and forecasting the future stages of the project. If work packages for the reported period are not kept within project tolerances, corrective actions are needed to be taken to mitigate the identified risks.[4] In order to process risk, the identified issues and trend deviations are being escalated into Expectation reports. In addition, Issue reports are being conducted, where an impact analysis is made and recommendations on how to proceed.[5]
[edit] 6) Evaluation
The last step involves evaluation of what needs to be done in order to move the project forward to the next period. In the end of a project a Lessons report can be conducted based on highlights from the project status documented history. Thereby, important learnings can be made on what worked well and not, which can be useful in future projects.[5]
[edit] Best practices
In this section five best practices are presented on factors to consider in order to conduct an effective and successful Project Status Report. The content has been compiled based on best practices from a report from the PRINCE2 standard (AXELOS 2017) and articles from Swanson (2014) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2006).[5][6][2] They all are providing guidelines on how to best utilise the reporting tool within a project context and contributing with different aspects on similar success factors.
- Simplify- When writing the status reports It is important to quickly get to the point and keep the information on a high level. One should aim to only point out the parameters which actually will contribute to higher project performance. All stakeholders should be able to easily extract the exact information which is relevant for their decision making, without being provided in-depth discussions about all specific work packages.
- Verification- The information in the status reports is essential for decision-makers within the project when it comes to knowing what actions to proceed with and which tasks to authorise. Therefore, it is important to verify with the stakeholders what project information, KPIs and elements they want the report to consist of to make well-founded decisions. Additionally, content and delivery method can be tailored based on different needs and communication preferences of the stakeholders, in order to achieve maximal effect.
- Consistency- The reporting format and distribution of the status reports must be kept consistent in order to achieve an effective communication of the reporting content. A standardised routine for processing of data, reporting structure and delivery method should be clearly established. That is, to achieve an objective view of the collected information and an efficient, uniform delivery to stakeholders.
- Establish metrics- In order to monitor project status, metrics on how to actually measure progress needs to be defined. These KPIs are determined in the planning phase and updated throughout the course of the project as essential indicators on project health.
- Apply tools- There are various project management tools which could be applied in order to facilitate the process of conducting efficient status reports. This is beneficial in terms of analysing and displaying larger data sets, by systematically analysing project metrics data to increase productivity. There are numerous reporting softwares which could be applied as well as visualisation tools such as Gantt charts, Kanban boards, Dashboards and wall charts.
[edit] Limitations
[edit] Challenges in conducting a successful Project Status Report
There are some main limitations to the Project Status Reports in “how” and what context the tool should be used. These limitations are important to be aware of in order to maximize utilisation of the tool. In terms of the risk aspect, the status reports are not considered as a sufficient tool in handling and mitigation of project risks. The scope of the tool merely lies in collecting information and monitoring progress of a project. Thus, issues are being identified, but does not provide a plan on how to actually take corrective actions.[5] Here, the status reports need to be complemented with other project management tools, such as issue reports or contingency plans. One of the main purposes with status reporting lies in improving the communication flow amongst the stakeholders. Although, one drawback of the status reports lies in the risk of substituting the regular day-to-day communication.[12] The reports are limited to providing essential data to relevant stakeholders, but only at a certain delivery frequency. It is important to consider that some information is more urgent, and cannot wait to be escalated when the status reports are presented.[6] Moreover, the quality of the status report is only as good as the quality of the information extracted from the data collection. Hence, misreporting is considered as a main limitation of project status reporting, where it is of high importance to set up clear method of how to conduct the data collection, to mitigate the risk.[12]
[edit] Relation to project management standards and literature
The Project Status Reports (or progress reports) are addressed in several standards as a main tool to support project progress control and improve communication and risk management.[5][4][3] This article is providing an in-depth summary of the topic of a Project Status Report, with the aim to cover all areas from overall concept, application and limitations. On one hand this article relates to several standards within project management to contextualise its contribution and usefulness. On the other hand, it is supported by the views of various articles and books as main references, to fill the gaps in regard to elaborating on the actual application process and drawbacks of the tool. Thus, the full process of conducting the status reports is extended out of the scope of the standards to achieve a bigger picture.
[edit] Annotated Bibliography
This section is providing suggestions on where additional information about Project Status Reporting can be found, in terms of further reading. It is referring to some of the key references of the article based on different approaches to the topic and how it is contextualised within project management.
Lock, D. (2007). Project Management (9th ed.) p.380-382,401-402. Burlington, VT: Gower. This book describes the full project lifecycle in detail as well as related project management tools. It addresses the topic of Project Status Reporting (Progress reporting) in a context of how to manage and monitor progress during the course of the project. Moreover, it is describing the concept of Project status reporting in a fundamental manner. Both in terms of how to collect reliable progress data, establishing reporting requirements as well as how to communicate the information in an efficient way.
AXELOS, 2017. Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition, The Stationery Office Ltd, London. Available from: ProQuest Ebook Central. [18 February 2021]. PRINCE2 is a well-known British standard for project management. The standard is addressing the process of project reporting and how it is used to monitor and control progress of a project. It is mainly being related to the project stages of controlling, managing uncertainties and communication management. In addition the progress reports are contextualised in an expanded view of program and portfolio management. It is providing an in-depth understanding of reporting requirements and a guide on how to implement the reporting into a project communication approach.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2006) "Project Status Reporting" https://www2.cdc.gov/cdcup/library/practices_guides/CDC_UP_Project_Status_Reporting_Practices_Guide.pdf [18 February 2021]. The Centres for Disease Control and Prevention is a national public health institute in the U.S.A., mainly operating within the area of disease control and other challenges related to public health. The agency has collected a portfolio of documents related to project management, in order to facilitate and unify processes. This includes various practices, tools, theories, templates and checklists to support a project manager and project team. Project Status Reporting is included in this portfolio and is providing a clear overview of the topic and importance of project management. The main document consists of a brief and clear summary of the main concept, purpose and how to apply the tool, and is helpful to get an overall understanding of the big idea. Moreover, there are other related documents in terms of a template and checklist with advice on how to utilise the reporting to improve project performance.
Swanson, S. A. (2014). Anatomy of an effective status report. PM Network, 28(6), 52–61. This article is published through Project Management Institute’s (PMI) network for publications. The paper is addressing various best practices and fallbacks related to conducting Project Status Reports, rather than explaining the concept itself. This perspective is important to include, in order to understand the context of which the tool is being applied as well as its limitations. Thus, it is good to get an overview of real challenges and improvements suggestions, which have appeared during actual application of the tool.
Keil, M., Smith, H.J., Iacovou, C.L. & Thompson, R.L. 2014, "The Pitfalls of Project Status Reporting", MIT Sloan Management Review, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 57-64. This article is addressing common drawbacks of the Project Status Reports and how to overcome these limitations. It is providing a self-assessment for a project manager to apply to see how vulnerable one is to misreporting. Moreover, the challenges are being contextualised with providing in-depth cases from the Affordable Care Act health care reform in the U.S.A.
[edit] References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Lock, D. (2007). Project Management (9th ed.) p.380-382,401-402. Burlington, VT: Gower.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2006) Project Status Reporting. Available at https://www2.cdc.gov/cdcup/library/practices_guides/CDC_UP_Project_Status_Reporting_Practices_Guide.pdf [Retrieved 2021-02-18]
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Project Management Institute (2017) A guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK guide). 6th ed. Chapters: 4, 10 & 11. Newton Square, PA: Project Management Institute.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). (2019). Standard for Risk Management in Portfolios, Programs, and Projects. Chapters: 4 & 7. Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). Retrieved from https://app.knovel.com/hotlink/toc/id:kpSRMPPP01/standard-risk-management/standard-risk-management
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 5.12 5.13 5.14 5.15 5.16 5.17 5.18 AXELOS, 2017. Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition, Chapters: 10,12,17 & Appendix A. The Stationery Office Ltd, London. Available from: ProQuest Ebook Central. [18 February 2021].
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Swanson, S. A. (2014). Anatomy of an effective status report. PM Network, 28(6), 52–61. Available at https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/anatomy-highly-effective-status-report-2198 [Retrieved 2021-02-16]
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Hayes Munson, K. A. (2012). How do you know the status of your project?: Project monitoring and controlling. Paper presented at PMI® Global Congress 2012—North America, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute.
- ↑ ProjectManager. (2021) The ultimate guide to Project Status Reports. Available at: https://www.projectmanager.com/status-report [Retrieved 2021-02-18].
- ↑ TemplateLab. (2021) Benefits of Making a Status Report Template. Available at: https://templatelab.com/status-report/#Benefits_of_Making_a_Status_Report_Template [Retrieved 2021-03-25].
- ↑ Microsoft Office. (2021) Project Status Report (Time-less design). Available at: https://templates.office.com/en-us/project-status-report-timeless-design-tm02889890 [Retrieved 2021-03-25].
- ↑ Piantanida, M., Cheli, E., & Lorenzi, M. (2011). Are you overwhelmed preparing too many reports? A smart approach to project reporting. Paper presented at PMI® Global Congress 2011—EMEA, Dublin, Leinster, Ireland. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Keil, M., Smith, H.J., Iacovou, C.L. & Thompson, R.L. 2014, "The Pitfalls of Project Status Reporting", MIT Sloan Management Review, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 57-64.