Eisenhower Decision Matrix
(→Prioritisation of tasks (Big Idea)) |
(→Limitations) |
||
| (30 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | Created by ''s163822'' | ||
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
Prioritising work tasks as an individual or a team is crucial for ensuring success and avoiding stress. One popular method for doing this is the Eisenhower Decision Matrix. | Prioritising work tasks as an individual or a team is crucial for ensuring success and avoiding stress. One popular method for doing this is the Eisenhower Decision Matrix. | ||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
The concept of the Eisenhower Decision Matrix is to prioritise tasks based on their urgency and importance, by categorising them into four quadrants: "Q1: Urgent and Important," "Q2: Important but Not Urgent," "Q3: Urgent but Not Important," and "Q4: Not Urgent nor Important." <ref name="study"> '''Jyothi, N.S., Parkavi, A.''' (2016) ''A study on task management system.'' In: International Conference on Research Advances in Integrated Navigation Systems. Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers Inc. https://doi.org/10.1109/RAINS.2016.7764421 </ref> | The concept of the Eisenhower Decision Matrix is to prioritise tasks based on their urgency and importance, by categorising them into four quadrants: "Q1: Urgent and Important," "Q2: Important but Not Urgent," "Q3: Urgent but Not Important," and "Q4: Not Urgent nor Important." <ref name="study"> '''Jyothi, N.S., Parkavi, A.''' (2016) ''A study on task management system.'' In: International Conference on Research Advances in Integrated Navigation Systems. Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers Inc. https://doi.org/10.1109/RAINS.2016.7764421 </ref> | ||
| − | By analysing tasks in this manner, teams and individuals can concentrate their energy on the most important and urgent tasks while delegating or postponing the less important ones. In a normal workday this can be done very easily by simply numbering the tasks on your to-do list according to the quadrants in the matrix, and then | + | By analysing tasks in this manner, teams and individuals can concentrate their energy on the most important and urgent tasks while delegating or postponing the less important ones. In a normal workday this can be done very easily by simply numbering the tasks on your to-do list according to the quadrants in the matrix, and then you are ready to start scheduling, delegating, deleting and completing tasks, in agreement with their placement in the Eisenhower Decision Matrix. |
The Eisenhower Decision Matrix is a useful tool for project managers and team members, as it provides a clear framework for determining task priority and making informed decisions about allocating time and resources. | The Eisenhower Decision Matrix is a useful tool for project managers and team members, as it provides a clear framework for determining task priority and making informed decisions about allocating time and resources. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 12: | ||
== Prioritisation of tasks (Big Idea) == | == Prioritisation of tasks (Big Idea) == | ||
=== Time and task management === | === Time and task management === | ||
| − | Time and task management are essential skills that help individuals and organizations effectively prioritize and use their time to achieve their goals.<ref name="study" /> Effective time management involves planning and organizing tasks, setting goals and deadlines, and prioritizing activities to make the most of the available time. Task management, on the other hand, involves breaking down larger projects or goals into smaller, more manageable tasks and efficiently managing these tasks to ensure timely completion of the project. | + | Time and task management are essential skills that help individuals and organizations effectively prioritize and use their time to achieve their goals.<ref name="study" /> Effective time management involves planning and organizing tasks, setting goals and deadlines, and prioritizing activities to make the most of the available time. Task management, on the other hand, involves breaking down larger projects or goals into smaller, more manageable tasks and efficiently managing these tasks to ensure timely completion of the project([[Work breakdown structure (WBS)]]). |
Time and task management are critical in both personal and professional settings, as they help individuals manage their workload, reduce stress, and improve productivity. Effective time and task management skills can lead to better work-life balance, increased motivation, and improved overall well-being. | Time and task management are critical in both personal and professional settings, as they help individuals manage their workload, reduce stress, and improve productivity. Effective time and task management skills can lead to better work-life balance, increased motivation, and improved overall well-being. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
=== Urgency vs. Importance === | === Urgency vs. Importance === | ||
| − | There are two terms that need to be defined and discussed, before the discussion of the Eisenhower Decision Matrix can begin: Urgency and importance. These two terms define any activity. Urgency means that the activity needs immediate attention and insists on action. <ref name="7habits" /> Urgent matters | + | There are two terms that need to be defined and discussed, before the discussion of the Eisenhower Decision Matrix can begin: Urgency and importance. These two terms define any activity. Urgency means that the activity needs immediate attention and insists on action. <ref name="7habits" /> Urgent matters act on us and make us feel this psychologically pressure. These matters are often popular with others, because they usually benefit others. But they are very seldom important. |
| − | On the contrary, importance is related to the outcome.<ref name="7habits" /> Important matters contribute to | + | On the contrary, importance is related to the outcome.<ref name="7habits" /> Important matters contribute to the highest priority goals and values. Often, more initiative and proactivity are needed for these important but non-urgent matters. For things to happen, we must take action and take advantage of the opportunity. We are easily distracted into attending to the urgent matters instead, if we do not have a clear understanding of what is important or what outcome we wish for. |
=== The Eisenhower Decision Matrix === | === The Eisenhower Decision Matrix === | ||
| − | [[File:EDM_1.png|thumb| | + | [[File:EDM_1.png|thumb|400px|The Eisenhower Decision Matrix (own figure, inspirations from <ref name="7habits" />]] |
| + | |||
Before starting prioritising tasks, one should have a clear goal in mind, either a personal goal or an organizational goal.<ref name="study" /> This is crucial to be able to evaluate the task's importance. | Before starting prioritising tasks, one should have a clear goal in mind, either a personal goal or an organizational goal.<ref name="study" /> This is crucial to be able to evaluate the task's importance. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 31: | ||
| − | '''Q1: Urgent and Important -''' | + | '''Q1: Urgent and Important -''' Tasks in quadrant 1 are both urgent and important. These tasks require immediate attention as well as they have a high impact on the personal or organizational goal. Therefore, these tasks are often defined as crises or problems. <ref name="7habits" /> |
| − | Tasks in quadrant 1 are both urgent and important. These tasks require immediate attention as well as they have a | + | |
| − | '''Q2: Important but Not Urgent -''' Tasks in quadrant 2 are important but not urgent. These are the tasks that contribute to | + | '''Q2: Important but Not Urgent -''' Tasks in quadrant 2 are important but not urgent. These are the tasks that contribute to the personal or organizational goal but are not urgent since they can be done at a later point in time. <ref name="7habits" /> |
| − | '''Q3: Urgent but Not Important -''' Tasks in quadrant 3 are urgent but not important. Since these tasks are urgent, they may appear to be in Q1, however their urgency is frequently determined by other | + | '''Q3: Urgent but Not Important -''' Tasks in quadrant 3 are urgent, but not important. Since these tasks are urgent, they may appear to be in Q1, however, their urgency is frequently determined by other peoples’ expectations and priorities, and will not contribute to your goals, therefore they are not important. <ref name="7habits" /> |
| − | '''Q4: Not Urgent nor Important -''' Tasks in quadrant 4 are not urgent | + | '''Q4: Not Urgent nor Important -''' Tasks in quadrant 4 are not urgent nor important. These are often categorized as distractions. |
| − | + | [[File:EDM_filled.png|thumb|350px|Examples of activities for each quadrant in the Eisenhower Decision Matrix (own figure, inspirations from <ref name="7habits" />]] | |
| − | + | Examples of activities belonging to each quadrant can be seen in the second figure. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | Highly effective people ought to spend most of their time in Q2, because these are the tasks that contribute to | + | Highly effective people ought to spend most of their time in Q2, because these are the tasks that contribute to their goal in their personal or professional life and will have a positive effect on them. <ref name="7habits" /> On the contrary, they should spend less or none of their time in Q3 and Q4, because these tasks are simply not important. |
| + | |||
| + | === How each quadrant affects individuals === | ||
| + | The time spent in each quadrant should be controlled and balanced in order to stay mentally healthy and effective. This means, that if someone spends too much time in certain quadrants, it can lead to an ineffective lifestyle or maybe even a mental breakdown. | ||
| + | |||
| + | People who use the majority of their time and energy in Q1 will often experience stress, crisis management, and burnout. <ref name="7habits" /> Q1 can consume a person in a way, so if you focus on Q1 it continues to grow until there is no time left for the other quadrants. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other people tend to focus on Q3, thinking it is Q1, like mentioned before. People spending all their time in Q3 will often feel out of control and like they only have a short-term focus, crisis management, and feeling out of control. <ref name="7habits" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then there are some people who spend their time almost only in Q3 and Q4. These people live irresponsible lives since they never or rarely focus on important tasks. The effects may for instance lead to unemployment. <ref name="7habits" /> | ||
== Application == | == Application == | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:EDM_application.png|thumb|350px|The actions to take and in which order (own figure, inspirations from <ref name="7habits" />]] |
| − | + | It may seem like a lot of work to include this decision matrix in one’s everyday decision-making routine, however ones you know the Eisenhower Decision Matrix, it is very easy to incorporate it in a busy schedule. One would benefit from starting the day with putting the tasks in the EDM to get an overview before getting on to completing tasks. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | To use the EDM, you start by writing all your tasks on a list. Next you give every task a number, referring to which quadrant in the EDM the task belongs to. When this has been done, then you are ready to start scheduling, delegating, deleting, and completing tasks, in agreement with their placement in the EDM. In this process you should start at the end; quadrant 4, because deleting tasks is quickly done. Next is quadrant 3, since these are urgent tasks that need to de delegating and delt with as soon as possible. There next is quadrant 1, seeing as these are the urgent and important tasks, which you need to complete right away. Lastly it is quadrant 2, being the most important but not urgent tasks, which should be scheduled. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
== Limitations == | == Limitations == | ||
| − | + | [[File:Sung_2.png|thumb|350px|The Sung diagram (own figure, inspirations from <ref name="sung" />]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | According to studies, humans are quite skilled at recognising and completing tasks that are both important and urgent (Q1) as well as those that are neither important nor urgent (Q4). <ref name="illusion"> '''Kennedy, D.R., Porter, A.L.''' (2022). ''The Illusion of Urgency.'' In: American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, vol 86. American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy. https://doi.org/10.5688/ajpe8914 </ref> However, people struggle with prioritizing important tasks over those that are urgent or even just appear urgent. This phenomenon, where a task appears to be urgent but is not, is called the illusion of urgency. In Stephen Covey’s book , he redefines the EDM and defines tasks as; necessity (Q1), effectiveness (Q2), distraction (Q3) and waste (Q4). <ref name="illusion" /> Then when setting it up like a choice between effectiveness vs. distraction, the illusion of urgency vanishes and the value of the important tasks becomes clearer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | While the EDM is a great tool for task management, it also holds limitations. These limitations are mainly because the EDM only considers two factors: Urgency and Importance. How about those tasks that are both urgent and important, but could be delegated? For example, if you find a burst pipe in your basement, that would be both urgent and important. You could try to fix it yourself, however if you have the resources to hire a plumber to repair it, then it doesn’t require your time and therefore the task should be delegated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the article <ref name="sung" /> an alternative solution to the EDM is presented, it is called the Sung diagram. The Sung diagram does not only depend on two factors like the EDM, but it also takes a third factor into account, namely fitness. The fitness relates to whether the person is fit to complete the task. There are two aspects related to the decision on fitness: | ||
| + | * ''Capability:'' Is that person the most capable of completing this task? | ||
| + | * ''Ipseity:'' Does completing this task add to their ipseity (sense of self)? | ||
| + | With this extra factor/dimension the Sung diagram creates 8 possible actions to take. Those related to the fitness factor are "schedule", "do now", and "do next", and are further described in the article <ref name="sung" /> . | ||
== Annotated bibliography == | == Annotated bibliography == | ||
'''Stephen R. Covey''' (2013). ''The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: Powerful Lessons in Personal Change'' | '''Stephen R. Covey''' (2013). ''The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: Powerful Lessons in Personal Change'' | ||
| − | + | The main plot of this book is about how one can evolve personally to be able to become a highly effective person. Covey shares his knowledge and experience with great examples from both his personal and professional life. In relation to the topic of this wiki article, Covey explains in the chapter “Habit 3: Put First Things First” how his redefined version of the Eisenhower Decision Matrix(EDM) can be used, and how it can affect people's effectiveness and accomplishments. The book also provides some very good examples, for each quadrant of the EDM. | |
'''D.R Kennedy, A.L. Porter''' (2022). ''The Illusion of Urgency'' | '''D.R Kennedy, A.L. Porter''' (2022). ''The Illusion of Urgency'' | ||
| − | This article describes how the illusion of urgency can affect people's perception of urgency, and thereby also their | + | This article describes the importance of proper time and task management in an organization, and how people struggle to identify and prioritize importance from urgency. The article also defines the illusion of urgency, and how it can affect people's perception of urgency, and thereby also their prioritization of tasks. Further the paper also discusses some limitations of the EDM, which have not been mentioned in this wiki article. |
'''Hannah Bratterud et al.''' (2020). ''The Sung Diagram: Revitalizing the Eisenhower Matrix'' | '''Hannah Bratterud et al.''' (2020). ''The Sung Diagram: Revitalizing the Eisenhower Matrix'' | ||
| − | This paper addresses the limitation of the EDM and proposes an extension to the matrix, which | + | This paper addresses the limitation of the EDM and proposes an extension to the matrix, in which it introduces a third factor to the prioritizing process. Having these three factors should in some scenarios clarify some misleading suggestions that the EDM would otherwise make. The paper also provides an alternative diagram with the name The Sung Diagram, as well as a clear definition of the three factors and the eight possible actions to take accordingly. By reading this paper, one would be able to use the Sung diagram, which might be preferred in some case. |
| − | + | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 21:50, 9 May 2023
Created by s163822
Contents |
[edit] Abstract
Prioritising work tasks as an individual or a team is crucial for ensuring success and avoiding stress. One popular method for doing this is the Eisenhower Decision Matrix. Former president of the USA, Dwight D. Eisenhower, once said: "What is important is seldom urgent, and what is urgent is seldom important.[1] These are the words behind the concept of the Eisenhower Decision Matrix. Later on, Stephen Covey made the method popular in relation to time and task management by including the method in his book, The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People.[2]
The concept of the Eisenhower Decision Matrix is to prioritise tasks based on their urgency and importance, by categorising them into four quadrants: "Q1: Urgent and Important," "Q2: Important but Not Urgent," "Q3: Urgent but Not Important," and "Q4: Not Urgent nor Important." [3] By analysing tasks in this manner, teams and individuals can concentrate their energy on the most important and urgent tasks while delegating or postponing the less important ones. In a normal workday this can be done very easily by simply numbering the tasks on your to-do list according to the quadrants in the matrix, and then you are ready to start scheduling, delegating, deleting and completing tasks, in agreement with their placement in the Eisenhower Decision Matrix.
The Eisenhower Decision Matrix is a useful tool for project managers and team members, as it provides a clear framework for determining task priority and making informed decisions about allocating time and resources.
[edit] Prioritisation of tasks (Big Idea)
[edit] Time and task management
Time and task management are essential skills that help individuals and organizations effectively prioritize and use their time to achieve their goals.[3] Effective time management involves planning and organizing tasks, setting goals and deadlines, and prioritizing activities to make the most of the available time. Task management, on the other hand, involves breaking down larger projects or goals into smaller, more manageable tasks and efficiently managing these tasks to ensure timely completion of the project(Work breakdown structure (WBS)).
Time and task management are critical in both personal and professional settings, as they help individuals manage their workload, reduce stress, and improve productivity. Effective time and task management skills can lead to better work-life balance, increased motivation, and improved overall well-being.
Time and task management are becoming more and more crucial in today's fast-paced society when we are continuously confronted with distractions and conflicting demands for our attention. With the right strategies and tools, individuals and organizations can optimize their time and accomplish more, all while maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
[edit] Urgency vs. Importance
There are two terms that need to be defined and discussed, before the discussion of the Eisenhower Decision Matrix can begin: Urgency and importance. These two terms define any activity. Urgency means that the activity needs immediate attention and insists on action. [2] Urgent matters act on us and make us feel this psychologically pressure. These matters are often popular with others, because they usually benefit others. But they are very seldom important.
On the contrary, importance is related to the outcome.[2] Important matters contribute to the highest priority goals and values. Often, more initiative and proactivity are needed for these important but non-urgent matters. For things to happen, we must take action and take advantage of the opportunity. We are easily distracted into attending to the urgent matters instead, if we do not have a clear understanding of what is important or what outcome we wish for.
[edit] The Eisenhower Decision Matrix
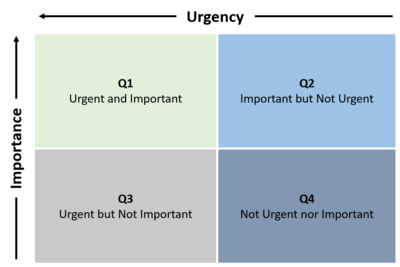
Before starting prioritising tasks, one should have a clear goal in mind, either a personal goal or an organizational goal.[3] This is crucial to be able to evaluate the task's importance.
The Eisenhower Decision Matrix (EDM) is a 2x2 matrix in which all tasks can be arranged by urgency and importance. The purpose of the EDM is to get an overview of all the tasks and to see how the tasks should be prioritised. The EDM consists of four quadrants, which now will be further described.
Q1: Urgent and Important - Tasks in quadrant 1 are both urgent and important. These tasks require immediate attention as well as they have a high impact on the personal or organizational goal. Therefore, these tasks are often defined as crises or problems. [2]
Q2: Important but Not Urgent - Tasks in quadrant 2 are important but not urgent. These are the tasks that contribute to the personal or organizational goal but are not urgent since they can be done at a later point in time. [2]
Q3: Urgent but Not Important - Tasks in quadrant 3 are urgent, but not important. Since these tasks are urgent, they may appear to be in Q1, however, their urgency is frequently determined by other peoples’ expectations and priorities, and will not contribute to your goals, therefore they are not important. [2]
Q4: Not Urgent nor Important - Tasks in quadrant 4 are not urgent nor important. These are often categorized as distractions.
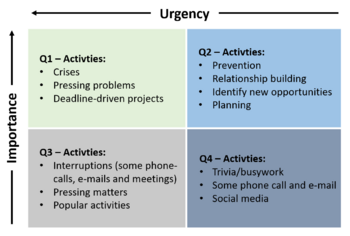
Examples of activities belonging to each quadrant can be seen in the second figure.
Highly effective people ought to spend most of their time in Q2, because these are the tasks that contribute to their goal in their personal or professional life and will have a positive effect on them. [2] On the contrary, they should spend less or none of their time in Q3 and Q4, because these tasks are simply not important.
[edit] How each quadrant affects individuals
The time spent in each quadrant should be controlled and balanced in order to stay mentally healthy and effective. This means, that if someone spends too much time in certain quadrants, it can lead to an ineffective lifestyle or maybe even a mental breakdown.
People who use the majority of their time and energy in Q1 will often experience stress, crisis management, and burnout. [2] Q1 can consume a person in a way, so if you focus on Q1 it continues to grow until there is no time left for the other quadrants.
Other people tend to focus on Q3, thinking it is Q1, like mentioned before. People spending all their time in Q3 will often feel out of control and like they only have a short-term focus, crisis management, and feeling out of control. [2]
Then there are some people who spend their time almost only in Q3 and Q4. These people live irresponsible lives since they never or rarely focus on important tasks. The effects may for instance lead to unemployment. [2]
[edit] Application
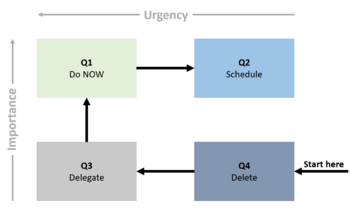
It may seem like a lot of work to include this decision matrix in one’s everyday decision-making routine, however ones you know the Eisenhower Decision Matrix, it is very easy to incorporate it in a busy schedule. One would benefit from starting the day with putting the tasks in the EDM to get an overview before getting on to completing tasks.
To use the EDM, you start by writing all your tasks on a list. Next you give every task a number, referring to which quadrant in the EDM the task belongs to. When this has been done, then you are ready to start scheduling, delegating, deleting, and completing tasks, in agreement with their placement in the EDM. In this process you should start at the end; quadrant 4, because deleting tasks is quickly done. Next is quadrant 3, since these are urgent tasks that need to de delegating and delt with as soon as possible. There next is quadrant 1, seeing as these are the urgent and important tasks, which you need to complete right away. Lastly it is quadrant 2, being the most important but not urgent tasks, which should be scheduled.
[edit] Limitations
According to studies, humans are quite skilled at recognising and completing tasks that are both important and urgent (Q1) as well as those that are neither important nor urgent (Q4). [4] However, people struggle with prioritizing important tasks over those that are urgent or even just appear urgent. This phenomenon, where a task appears to be urgent but is not, is called the illusion of urgency. In Stephen Covey’s book , he redefines the EDM and defines tasks as; necessity (Q1), effectiveness (Q2), distraction (Q3) and waste (Q4). [4] Then when setting it up like a choice between effectiveness vs. distraction, the illusion of urgency vanishes and the value of the important tasks becomes clearer.
While the EDM is a great tool for task management, it also holds limitations. These limitations are mainly because the EDM only considers two factors: Urgency and Importance. How about those tasks that are both urgent and important, but could be delegated? For example, if you find a burst pipe in your basement, that would be both urgent and important. You could try to fix it yourself, however if you have the resources to hire a plumber to repair it, then it doesn’t require your time and therefore the task should be delegated.
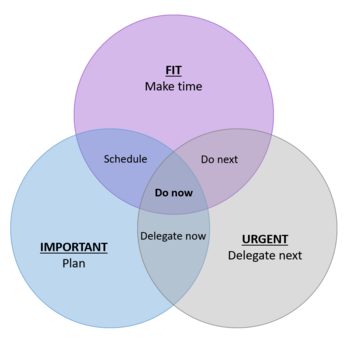
In the article [1] an alternative solution to the EDM is presented, it is called the Sung diagram. The Sung diagram does not only depend on two factors like the EDM, but it also takes a third factor into account, namely fitness. The fitness relates to whether the person is fit to complete the task. There are two aspects related to the decision on fitness:
- Capability: Is that person the most capable of completing this task?
- Ipseity: Does completing this task add to their ipseity (sense of self)?
With this extra factor/dimension the Sung diagram creates 8 possible actions to take. Those related to the fitness factor are "schedule", "do now", and "do next", and are further described in the article [1] .
[edit] Annotated bibliography
Stephen R. Covey (2013). The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: Powerful Lessons in Personal Change
The main plot of this book is about how one can evolve personally to be able to become a highly effective person. Covey shares his knowledge and experience with great examples from both his personal and professional life. In relation to the topic of this wiki article, Covey explains in the chapter “Habit 3: Put First Things First” how his redefined version of the Eisenhower Decision Matrix(EDM) can be used, and how it can affect people's effectiveness and accomplishments. The book also provides some very good examples, for each quadrant of the EDM.
D.R Kennedy, A.L. Porter (2022). The Illusion of Urgency
This article describes the importance of proper time and task management in an organization, and how people struggle to identify and prioritize importance from urgency. The article also defines the illusion of urgency, and how it can affect people's perception of urgency, and thereby also their prioritization of tasks. Further the paper also discusses some limitations of the EDM, which have not been mentioned in this wiki article.
Hannah Bratterud et al. (2020). The Sung Diagram: Revitalizing the Eisenhower Matrix
This paper addresses the limitation of the EDM and proposes an extension to the matrix, in which it introduces a third factor to the prioritizing process. Having these three factors should in some scenarios clarify some misleading suggestions that the EDM would otherwise make. The paper also provides an alternative diagram with the name The Sung Diagram, as well as a clear definition of the three factors and the eight possible actions to take accordingly. By reading this paper, one would be able to use the Sung diagram, which might be preferred in some case.
[edit] References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Bratterud, H., Burgess, M., Fasy, B.T., Millman, D.L., Oster, T., Sung, E. (2020). The Sung Diagram: Revitalizing the Eisenhower Matrix. In: Pietarinen, AV., Chapman, P., Bosveld-de Smet, L., Giardino, V., Corter, J., Linker, S. (eds) Diagrammatic Representation and Inference. Diagrams 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12169. Springer, Cham. https://doi-org.proxy.findit.cvt.dk/10.1007/978-3-030-54249-8_43
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 Covey, Stephen R. (2013). The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: Powerful Lessons in Personal Change, 25th anniversary edn. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-1-4516-3961-2
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Jyothi, N.S., Parkavi, A. (2016) A study on task management system. In: International Conference on Research Advances in Integrated Navigation Systems. Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers Inc. https://doi.org/10.1109/RAINS.2016.7764421
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kennedy, D.R., Porter, A.L. (2022). The Illusion of Urgency. In: American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, vol 86. American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy. https://doi.org/10.5688/ajpe8914