Effective Leadership of Cross-functional Project Teams
(→The interactions between the success factors for leading cross-functional teams) |
|||
| (31 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Cross-functional | + | Cross-functional teams break through the “silos” of a traditional organizational structure so that the team is capable of seeing the full picture. Working with individuals who have different perspectives, specialties, and backgrounds allows the team collectively solve challenges and accomplish the project's goals more efficiently. <ref name="ForbesAdvisor"> ''Christine Organ, Cassie Bottorf, 2022, What Are Cross-Functional Teams? Everything you need to know, https://www.forbes.com/advisor/business/cross-functional-teams/'' </ref> This is especially helpful for projects that need to take a broad approach and involve numerous disciplines, such as design, engineering, marketing, and technology. These diverse capabilities can more effectively address challenging issues within the context of project, program, and portfolio management and result in more comprehensive solutions and increased team member satisfaction. |
Human behavior is one of the major sources of rising project complexity, this is due to introducing factors like subjectivity, different cultural and professional backgrounds, or attitudes. Therefore, leading a project team is becoming a challenging task, which requires a combination of technical and interpersonal skills. This leadership is not limited to a designated project leader, as successful project teams often consist of several team members who demonstrate various leadership capabilities. <ref name="PMIGuide"> Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). (2021). A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK ® Guide) – 7th Edition and The Standard for Project Management. Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI) </ref> Nevertheless, the challenge posed by building these teams is significant. To achieve the best possible project outcome it is crucial to create the necessary project environment, enabling all team members to work together and maximize their performance. <ref name="PMIGuide"/> <ref name="Kerzner"> Kerzner, H. (2017). Project Management - A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling (12th Edition). John Wiley & Sons </ref> To create such an environment proper communication, motivation, and taking action when the situation calls for it, is needed. <ref name="PMIGuide"/> | Human behavior is one of the major sources of rising project complexity, this is due to introducing factors like subjectivity, different cultural and professional backgrounds, or attitudes. Therefore, leading a project team is becoming a challenging task, which requires a combination of technical and interpersonal skills. This leadership is not limited to a designated project leader, as successful project teams often consist of several team members who demonstrate various leadership capabilities. <ref name="PMIGuide"> Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). (2021). A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK ® Guide) – 7th Edition and The Standard for Project Management. Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI) </ref> Nevertheless, the challenge posed by building these teams is significant. To achieve the best possible project outcome it is crucial to create the necessary project environment, enabling all team members to work together and maximize their performance. <ref name="PMIGuide"/> <ref name="Kerzner"> Kerzner, H. (2017). Project Management - A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling (12th Edition). John Wiley & Sons </ref> To create such an environment proper communication, motivation, and taking action when the situation calls for it, is needed. <ref name="PMIGuide"/> | ||
| − | This article outlines the key elements of successful cross-functional project team leadership that can be applied to project, program, and portfolio management. These include building a high-performing team, setting clear goals and expectations, managing conflict and overcoming obstacles, and motivating and engaging team members. Followed by a quick look at | + | This article outlines the key elements of successful cross-functional project team leadership that can be applied to project, program, and portfolio management. These include building a high-performing team, setting clear goals and expectations, managing conflict and overcoming obstacles, and motivating and engaging team members. Followed by a quick look at two of the pioneering companies in leveraging cross-functional teams and then discussing the limitations of this article's content. Further, an annotated bibliography is provided for additional reading on the topic. |
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
=== Definition of multidisciplinary/cross-functional team === | === Definition of multidisciplinary/cross-functional team === | ||
| − | "Cross-functional/multidisciplinary teams are groups of people from various departments in an organization—such as marketing, product development, quality assurance, sales, and finance—who work together to achieve a common goal. Oftentimes, cross-functional teams are organized to complete a specific project, but they can also be created with a more ongoing purpose." <ref name="ForbesAdvisor" | + | "Cross-functional/multidisciplinary teams are groups of people from various departments in an organization—such as marketing, product development, quality assurance, sales, and finance—who work together to achieve a common goal. Oftentimes, cross-functional teams are organized to complete a specific project, but they can also be created with a more ongoing purpose."<ref name="ForbesAdvisor"/> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Functional diversity in the context of cross-functional teams refers to the range of skills, knowledge, and expertise that team members from different functional areas bring to the team. On a cross-functional team, it can be beneficial because it brings together individuals with different perspectives, experiences, and knowledge, which can lead to more innovative and effective solutions. For example, a marketing professional might bring a customer-focused perspective, an engineer might bring technical expertise, and a finance professional might bring financial analysis skills. <ref name="FuncDiv"> "Jackson, S.E. (1996). The consequences of diversity in multidisciplinary work teams. In West, M.A. (Ed.) Handbook of work group psychology. John Wiley & Sons Ltd: UK" </ref> | Functional diversity in the context of cross-functional teams refers to the range of skills, knowledge, and expertise that team members from different functional areas bring to the team. On a cross-functional team, it can be beneficial because it brings together individuals with different perspectives, experiences, and knowledge, which can lead to more innovative and effective solutions. For example, a marketing professional might bring a customer-focused perspective, an engineer might bring technical expertise, and a finance professional might bring financial analysis skills. <ref name="FuncDiv"> "Jackson, S.E. (1996). The consequences of diversity in multidisciplinary work teams. In West, M.A. (Ed.) Handbook of work group psychology. John Wiley & Sons Ltd: UK" </ref> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
=== Why cross-functional teams? === | === Why cross-functional teams? === | ||
| − | For the team to view the full picture, cross-functional teams remove the "silos" of a typical organizational structure. Working with individuals who have different perspectives, specialties, and backgrounds allows the team as a whole to solve issues more quickly and accomplish project objectives. Because each department is involved throughout the process rather than a project going from department to department, they can foresee obstacles earlier in the process.<ref name="ForbesAdvisor"/> | + | For the team to view the full picture, cross-functional teams remove the "silos" of a typical organizational structure. Working with individuals who have different perspectives, specialties, and backgrounds allows the team as a whole to solve issues more quickly and accomplish project objectives. Because each department is involved throughout the process rather than a project going from department to department, they can foresee obstacles earlier in the process.<ref name="ForbesAdvisor"/> The main reasons for adopting cross-functional teams according to <ref name="Edward"> ''Edward F. McDonough III. (2000). Investigation of Factors Contributing to the Success of Cross-Functional Teams. Elsevier Science Inc'' </ref> are grouped into performance increases and process improvements, which can be seen in the following table. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | The main reasons for adopting cross-functional teams according to <ref name="Edward"> ''Edward F. McDonough III. (2000). Investigation of Factors Contributing to the Success of Cross-Functional Teams. Elsevier Science Inc'' </ref> | + | |
{| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto" | {| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto" | ||
| Line 40: | Line 37: | ||
| − | By bringing together individuals with different skills and perspectives, cross-functional teams can improve problem-solving efforts, resulting in more efficient and effective outcomes. This, in turn, can increase the speed at which projects are completed, leading to faster delivery times and greater agility. Diverse perspectives and expertise enable a more comprehensive evaluation of options and a more informed decision-making process. This | + | By bringing together individuals with different skills and perspectives, cross-functional teams can improve problem-solving efforts, resulting in more efficient and effective outcomes. This, in turn, can increase the speed at which projects are completed, leading to faster delivery times and greater agility. Diverse perspectives and expertise enable a more comprehensive evaluation of options and a more informed decision-making process. This leads to higher customer satisfaction rates, increased success rates, and therefore improves the quality of project outcomes. In addition, facilitating the sharing of knowledge and best practices will result in process improvements and therefore affect the efficiency of the project team. Furthermore, cross-functional teams are promoting ownership, and accountability and thus are leading toward a shared sense of responsibility for project success, resulting in increased motivation and satisfaction among team members. Enabling improved team morale and a greater commitment to achieving goals. |
| − | All those benefits can | + | All those benefits can enhance organizational effectiveness and better business outcomes, making cross-functional teams an indispensable option for organizations looking to achieve more innovative and significant results. |
== Challenges working within cross-functional teams == | == Challenges working within cross-functional teams == | ||
| − | + | Besides the above-mentioned benefits and reasons to utilize cross-functional teams, challenges often arise when working with cross-functional teams because of the inherent functional diversity among team members.<ref name="Webber"> ''Webber.S. (2000). Leadership and trust facilitating cross-functional team success. Journal of Management Development. Emerald'' </ref> The fundamental differences between individuals from different functional areas, such as personality, culture, language, jargon, organizational responsibilities, and reward systems, can create barriers to effective team processes. This diversity can lead to conflicts in priorities and goals, as different departments have different goals and interests. <ref name ="Song"> Song, X.M., Montoya-Weiss, M.M. and Schmidt, J.B. (1997). "Antecedents and consequences of cross-functional cooperation: a comparison of R&D, manufacturing, and marketing perspectives." ''Journal of Product Innovation Management,'' Vol. 14, pp. 35-47. </ref> | |
| − | Other challenges associated with cross-functional teams include time allocation diversity, where team members devote different amounts of time to the project, and multiple reporting relationships, which can lead to role ambiguity and overload. <ref name="Chimneys" /> The different value systems within a cross-functional team can also hinder the development of trust, making it difficult to achieve high-performance potential. <ref> Sitkin, S.B. and Roth, N.L. (1993). "Explaining the limited effectiveness of legalistic remedies for trust/distrust." ''Organization Science,'' Vol. 4 No. 3, pp. 367-92. </ref> | + | Other challenges associated with cross-functional teams include time allocation diversity, where team members devote different amounts of time to the project, and multiple reporting relationships, which can lead to role ambiguity and overload. <ref name="Chimneys" /> The different value systems within a cross-functional team can also hinder the development of trust, making it difficult to achieve high-performance potential. <ref> Sitkin, S.B. and Roth, N.L. (1993). "Explaining the limited effectiveness of legalistic remedies for trust/distrust." ''Organization Science,'' Vol. 4 No. 3, pp. 367-92. </ref> |
| − | + | The earlier mentioned functional diversity is the key difference between cross-functional teams when compared with traditional teams. Traditional teams are designed to accomplish ongoing tasks or goals within a specific department or functional area. On the other hand, cross-functional teams are designed to bring together diverse skills, experiences, and perspectives to achieve a specific goal or project. Most people tend to identify more socially and psychologically with their function and responsibilities than with their organization. This can lead to conflicts between team members, as teams also generate their own identities and loyalties. In addition, cross-functional teams are subject to significant pressure and conflict because they are often temporary task teams, which are created to work on a specific project or goal. Finally, these teams often face high-performance expectations, with ambitious goals to reduce time, create knowledge, and improve organizational learning. <ref name="Chimneys"> ''Denison, D.r., Hart, S.l. , Kahn, J.A (1996). From chimneys to cross-functional teams: Developing and validating a diagnostic model. Academy of Management Journal, 39 1005-1022.'' </ref> <ref name="Holland"> ''Holland.S, Gaston.K, Gomes.J. (2000). Critical success factors for cross-functional teamwork in new product development. International Journal of Management Reviews. Blackwell Publishers'' </ref> Leaders must recognize these challenges and develop strategies to create a climate of trust, promote effective team processes, and ultimately achieve successful performance within cross-functional teams. | |
| − | The earlier mentioned functional diversity | + | |
== Application == | == Application == | ||
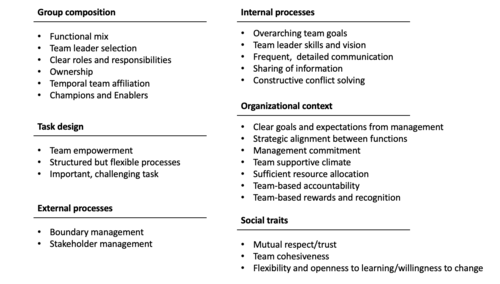
| − | + | To overcome the mentioned challenges and enable the full potential of those teams, effective leadership is critical to realizing the full potential of cross-functional teams and driving their success. This section explores the key aspects of leading cross-functional teams based on success factors described by <ref name="PMIGuide" /> <ref name="Kerzner" /> <ref name="Edward" /> <ref name="Holland" />, covering the building of high-performing teams, setting clear goals and expectations, managing conflict, and motivating and engaging team members. An overview of the main factors can be seen in Figure 1. By understanding and implementing these strategies, leaders can ensure that their cross-functional teams are well-equipped to overcome challenges, collaborate effectively, and contribute to the overall success of the organization. | |
[[File:Success_factors_leading_cf_teams.png|thumb|text-bottom|middle|500px|Figure 1: Success factors for leading cross-functional teams described by <ref name="PMIGuide" /> <ref name="Kerzner" /> <ref name="Edward" /> <ref name="Holland" />]] | [[File:Success_factors_leading_cf_teams.png|thumb|text-bottom|middle|500px|Figure 1: Success factors for leading cross-functional teams described by <ref name="PMIGuide" /> <ref name="Kerzner" /> <ref name="Edward" /> <ref name="Holland" />]] | ||
| Line 60: | Line 56: | ||
To build a high-performing team, several factors need to be considered. First, management plays a critical role in setting the team climate, aiming to create an innovative environment by empowering team members and fostering a sense of urgency with a "priority image" that generates commitment. Human resources are another critical aspect, focusing on increasing commitment, trust, communication and collaboration among team members. The skills and functional diversity within the team, along with the right combination of technical expertise, and interpersonal skills, contribute to the team's effectiveness and process performance. Management should therefore set a stage by assembling a team that possesses these qualities. | To build a high-performing team, several factors need to be considered. First, management plays a critical role in setting the team climate, aiming to create an innovative environment by empowering team members and fostering a sense of urgency with a "priority image" that generates commitment. Human resources are another critical aspect, focusing on increasing commitment, trust, communication and collaboration among team members. The skills and functional diversity within the team, along with the right combination of technical expertise, and interpersonal skills, contribute to the team's effectiveness and process performance. Management should therefore set a stage by assembling a team that possesses these qualities. | ||
| − | Enablers, individuals with a vested interest in the project's success, can play | + | Enablers, individuals with a vested interest in the project's success, can play a crucial role by raising awareness and overcoming management resistance. Their indirect influence on the project outcome and their moderating effect on the relationship between stage-setting elements and project performance can be invaluable. Finally, respect among team members is essential for open communication and trust, and team leaders can foster this by modeling the desired behavior and using their interpersonal skills. |
=== Establishing Clear Goals and Expectations === | === Establishing Clear Goals and Expectations === | ||
| Line 69: | Line 65: | ||
=== Managing Conflict and Overcoming Obstacles === | === Managing Conflict and Overcoming Obstacles === | ||
| − | Effectively managing conflict and overcoming obstacles in cross-functional teams are critical aspects of successful team management. Team leaders play a critical role in these processes by acting indirectly as enablers, focusing on facilitating the team's work rather than engaging in developmental tasks themselves. A participative leadership style allows team members the freedom to explore, discuss, and challenge ideas, creating a collaborative environment. By sharing information and knowledge widely, keeping team members challenged, and maintaining a positive climate, team leaders can cultivate cooperation, respect, and open communication within the group. Especially respect is essential to promote open | + | Effectively managing conflict and overcoming obstacles in cross-functional teams are critical aspects of successful team management. Team leaders play a critical role in these processes by acting indirectly as enablers, focusing on facilitating the team's work rather than engaging in developmental tasks themselves. A participative leadership style allows team members the freedom to explore, discuss, and challenge ideas, creating a collaborative environment. By sharing information and knowledge widely, keeping team members challenged, and maintaining a positive climate, team leaders can cultivate cooperation, respect, and open communication within the group. Especially respect is essential to promote open exchange and trust among team members. |
| − | Senior management support is critical to team performance and can take many forms, including demonstrating commitment, helping to overcome obstacles, and providing encouragement. Team leaders should act as a bridge between the project team and senior management, lobbying for resources, protecting the group from outside interference, and managing expectations. By addressing | + | Senior management support is also critical to team performance and can take many forms, including demonstrating commitment, helping to overcome obstacles, and providing encouragement. Team leaders should act as a bridge between the project team and senior management, lobbying for resources, protecting the group from outside interference, and managing expectations. By addressing this, managers can effectively handle conflict and overcome obstacles in cross-functional teams, paving the way for successful project outcomes. |
=== Motivating and Engaging Team members === | === Motivating and Engaging Team members === | ||
| Line 81: | Line 77: | ||
=== Monitoring and Evaluating Team Performance === | === Monitoring and Evaluating Team Performance === | ||
| − | Monitoring and evaluating team performance is | + | Monitoring and evaluating team performance is one of the main aspects of managing cross-functional teams, as it allows leaders to identify areas for improvement and adjust strategies accordingly. It is crucial to establish a set quantitative and qualitative of key performance indicators (KPIs) that are aligned with the project's goals and objectives. These KPIs should include several dimensions, such as schedule, budget, quality, and stakeholder satisfaction. Regular progress reports and team meetings can be used to assess the team's performance against these KPIs, providing managers with valuable insights to address any issues or bottlenecks in a timely manner. <ref name="Kerzner" /> As mentioned earlier it is also important to create an environment that encourages open communication and feedback so that team members can share their concerns, challenges, and suggestions for improvement. By continuously monitoring and evaluating performance, leaders can ensure that cross-functional teams remain focused, engaged, and on track to achieve their project goals and contribute to the success of the organization. |
=== The interactions between the success factors for leading cross-functional teams === | === The interactions between the success factors for leading cross-functional teams === | ||
| − | [[File:Figure_Sucess_framework.png|thumb|text-bottom|right|500px|Figure 2: Model of proposed interactions among stage setters, enablers, team behaviors, and cross-functional team success, own figure adopted from <ref name="Edward" />]] Figure 1 shows the importance and interaction of certain initial conditions and factors which | + | [[File:Figure_Sucess_framework.png|thumb|text-bottom|right|500px|Figure 2: Model of proposed interactions among stage setters, enablers, team behaviors, and cross-functional team success, own figure adopted from <ref name="Edward" />]] Figure 1 underlines the significance of the interplay between crucial success factors for leading cross-functional teams. It shows the importance and interaction of certain initial conditions and factors which were previously discussed. The "stage-setting" elements, such as the establishment of clear goals, empowerment, and a sufficient team climate, indirectly affect project outcomes by influencing team behavior. This behavior, in turn, critically affects project performance. Collaboration, ownership, and commitment are essential to project success, as stage-setting elements alone may not produce sufficient results. <ref name="Edward" /> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | As a result, this model also places a focus on the function of "enablers," such as senior managers, team captains, and champions. These enablers play a crucial role in shaping project performance, primarily by influencing team behavior rather than directly impacting project outcomes. With their actions, attitudes, and the foundation they establish for new projects, they take part in shaping a team environment that encourages collaboration, mutual respect, and a shared understanding of the purpose. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | Additionally, it's important to consider the role of contextual factors in influencing the success of cross-functional teams. Factors such as company size, industry, organizational culture, and the broader business environment can impact the stage-setting elements, enablers, and ultimately the team behavior. <ref name="Edward" /> For example, a startup might benefit from a more flexible and adaptive approach to project management, while a large company might need more structured procedures, standardized communication, and hierarchies. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | In conclusion, strong leadership is crucial to maximizing the potential of cross-functional teams and ensuring their success. Building high-performing teams, setting clear goals and expectations, managing conflict, and motivating and engaging team members are key elements of leading cross-functional teams. Leaders who understand and practice those can ensure their teams are prepared to meet upcoming challenges, work together effectively, and contribute to the overall success of the organization. It is crucial to continually review and reevaluate these success elements, taking into account the always-adapting nature of team dynamics, organizational requirements, and the changing business environment in order to increase the efficiency of managing cross-functional teams. An iterative approach can ensure that team leadership remains aligned with the evolving needs and goals of the organization and the respective team. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | + | By considering the interaction of various success factors, it is possible to create an environment that fosters innovation, productivity, and a shared sense of responsibility. Thus, they are setting the stage for both individual and team-based success. Further, this promotes a culture of continuous learning and improvement, where each project’s challenges and successes serve as lessons for future approaches. | |
| − | + | == Well-known examples in leveraging cross-functional teams == | |
| − | The collaborative environment fostered by Apple's functional structure allowed team members to freely share knowledge and ideas, which is essential for effective cross-functional teamwork. By giving experts the opportunity to lead and mentor others in their areas of expertise, Apple ensured that team members were motivated and engaged, further enhancing the performance of cross-functional teams. Apple has successfully integrated cross-functional teams within every part of its organization to create breakthrough products such as the iPhone. <ref name="Apple" /> | + | === Apple, Inc. === |
| + | |||
| + | To further outline the potential of cross-functional teams, Apple Inc. can be seen as a prime example. Their functional structure breaks down traditional departmental boundaries and fosters deep collaboration across functions. Their organizational structure, based on functional expertise, allows experts to lead other experts in their fields. This breaks down traditional barriers between departments and fosters deep collaboration across functions. In the case of the iPhone, Apple brought together engineers, designers, and marketing professionals to work toward a common goal under the visionary leadership of Steve Jobs. <ref name="Apple"> Joel M. Podolny, Morten T. Hansen. (2020). How Apple Is Organized for Innovation. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2020/11/how-apple-is-organized-for-innovation </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The collaborative environment fostered by Apple's functional structure allowed team members to freely share knowledge and ideas, which is essential for effective cross-functional teamwork. By giving experts the opportunity to lead and mentor others in their areas of expertise, Apple ensured that team members were motivated and engaged, further enhancing the performance of their cross-functional teams. Apple has successfully integrated cross-functional teams within every part of its organization to create breakthrough products such as the iPhone. <ref name="Apple" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Tesla, Inc. === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Another example of successful leadership of cross-functional teams comes from the automobile industry, specifically Tesla, Inc., led by CEO Elon Musk. | ||
| + | Tesla facilitates a philosophy of "anti-silo thinking," which supports cross-disciplinary collaboration and innovation. To develop the Model S, Tesla created a cross-functional team of automotive engineers, software engineers, battery technology experts, and design professionals. This team had to work together to achieve a common goal: to create an electric vehicle that could compete with, and even surpass, gasoline-powered cars in terms of performance, safety, and comfort. Under Musk's leadership, the cross-functional team was encouraged to challenge conventional wisdom and think beyond traditional industry boundaries. <ref name="Tesla"> Ashlee Vance. (2015). Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic Future. HarperCollins. </ref> This approach led to several breakthrough innovations and their current leadership position in the electric vehicle market. | ||
| + | |||
| + | At Tesla, cross-functional teams are a core part of the company's innovation strategy. Musk's open communication, taking calculated risks, and constant learning was a key factor in building a team environment where team members felt empowered and committed to contributing their skills to the overall goal and purpose. | ||
== Limitations == | == Limitations == | ||
| − | There are limitations to every discussion of leading interdisciplinary project teams. One of these restrictions is that different organizations may have different definitions of what beholds a "cross-functional team | + | There are limitations to every discussion of leading interdisciplinary project teams. One of these restrictions is that different organizations may have different definitions of what beholds a "cross-functional team". Different organizations may interpret the referring concepts in diverse ways, reflecting their unique business structures, strategic goals, and working cultures. This makes it difficult to standardize the approach to this subject. Therefore, it may be more practical to use a different strategy for various businesses or projects, making it challenging to develop a comprehensive manual that covers all possibilities. |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The mentioned success factors are also not only limited to teams with a cross-functional background. Indeed, many of these factors, such as clear communication, conflict resolution, and effective leadership, are universally applicable to team management, regardless of team composition. Moreover, it can be challenging to manage a range of personalities, communication styles, and areas of expertise, and condensing the subject into one condensed article may is not detailed enough for every possible situation. A wide range of topics, including team development, conflict resolution, and project management approaches, are included in the leadership of interdisciplinary project teams. As a result, giving a thorough review that addresses every facet of this complex subject can be to some extent not practicable. Finally, it is essential to consider the unique circumstances and needs of each team and organization. While this article provides a solid foundation for understanding and managing cross-functional teams, leaders are encouraged to further explore additional resources as needed, and adapt the insights to their specific situations. They should also consider supplementing this knowledge with firsthand experiences, professional training, and mentorship to effectively navigate the complexities and nuances of leading interdisciplinary project teams. This adaptive and continuous learning approach can help ensure the successful management and performance of these teams. | ||
== Annotated Bibliography == | == Annotated Bibliography == | ||
Latest revision as of 21:19, 9 May 2023
Cross-functional teams break through the “silos” of a traditional organizational structure so that the team is capable of seeing the full picture. Working with individuals who have different perspectives, specialties, and backgrounds allows the team collectively solve challenges and accomplish the project's goals more efficiently. [1] This is especially helpful for projects that need to take a broad approach and involve numerous disciplines, such as design, engineering, marketing, and technology. These diverse capabilities can more effectively address challenging issues within the context of project, program, and portfolio management and result in more comprehensive solutions and increased team member satisfaction.
Human behavior is one of the major sources of rising project complexity, this is due to introducing factors like subjectivity, different cultural and professional backgrounds, or attitudes. Therefore, leading a project team is becoming a challenging task, which requires a combination of technical and interpersonal skills. This leadership is not limited to a designated project leader, as successful project teams often consist of several team members who demonstrate various leadership capabilities. [2] Nevertheless, the challenge posed by building these teams is significant. To achieve the best possible project outcome it is crucial to create the necessary project environment, enabling all team members to work together and maximize their performance. [2] [3] To create such an environment proper communication, motivation, and taking action when the situation calls for it, is needed. [2]
This article outlines the key elements of successful cross-functional project team leadership that can be applied to project, program, and portfolio management. These include building a high-performing team, setting clear goals and expectations, managing conflict and overcoming obstacles, and motivating and engaging team members. Followed by a quick look at two of the pioneering companies in leveraging cross-functional teams and then discussing the limitations of this article's content. Further, an annotated bibliography is provided for additional reading on the topic.
[edit] Big Idea/Background
[edit] Definition of multidisciplinary/cross-functional team
"Cross-functional/multidisciplinary teams are groups of people from various departments in an organization—such as marketing, product development, quality assurance, sales, and finance—who work together to achieve a common goal. Oftentimes, cross-functional teams are organized to complete a specific project, but they can also be created with a more ongoing purpose."[1]
Functional diversity in the context of cross-functional teams refers to the range of skills, knowledge, and expertise that team members from different functional areas bring to the team. On a cross-functional team, it can be beneficial because it brings together individuals with different perspectives, experiences, and knowledge, which can lead to more innovative and effective solutions. For example, a marketing professional might bring a customer-focused perspective, an engineer might bring technical expertise, and a finance professional might bring financial analysis skills. [4]
[edit] Why cross-functional teams?
For the team to view the full picture, cross-functional teams remove the "silos" of a typical organizational structure. Working with individuals who have different perspectives, specialties, and backgrounds allows the team as a whole to solve issues more quickly and accomplish project objectives. Because each department is involved throughout the process rather than a project going from department to department, they can foresee obstacles earlier in the process.[1] The main reasons for adopting cross-functional teams according to [5] are grouped into performance increases and process improvements, which can be seen in the following table.
| Performance Increase | Process Improvement |
|---|---|
| Speed | Cross-functional interactions |
| Quality | Ownership |
| Customer satisfaction | Improved process |
| Success rate | Motivation and satisfaction |
| Lower Costs | Resource use |
| Improve control |
By bringing together individuals with different skills and perspectives, cross-functional teams can improve problem-solving efforts, resulting in more efficient and effective outcomes. This, in turn, can increase the speed at which projects are completed, leading to faster delivery times and greater agility. Diverse perspectives and expertise enable a more comprehensive evaluation of options and a more informed decision-making process. This leads to higher customer satisfaction rates, increased success rates, and therefore improves the quality of project outcomes. In addition, facilitating the sharing of knowledge and best practices will result in process improvements and therefore affect the efficiency of the project team. Furthermore, cross-functional teams are promoting ownership, and accountability and thus are leading toward a shared sense of responsibility for project success, resulting in increased motivation and satisfaction among team members. Enabling improved team morale and a greater commitment to achieving goals.
All those benefits can enhance organizational effectiveness and better business outcomes, making cross-functional teams an indispensable option for organizations looking to achieve more innovative and significant results.
[edit] Challenges working within cross-functional teams
Besides the above-mentioned benefits and reasons to utilize cross-functional teams, challenges often arise when working with cross-functional teams because of the inherent functional diversity among team members.[6] The fundamental differences between individuals from different functional areas, such as personality, culture, language, jargon, organizational responsibilities, and reward systems, can create barriers to effective team processes. This diversity can lead to conflicts in priorities and goals, as different departments have different goals and interests. [7] Other challenges associated with cross-functional teams include time allocation diversity, where team members devote different amounts of time to the project, and multiple reporting relationships, which can lead to role ambiguity and overload. [8] The different value systems within a cross-functional team can also hinder the development of trust, making it difficult to achieve high-performance potential. [9]
The earlier mentioned functional diversity is the key difference between cross-functional teams when compared with traditional teams. Traditional teams are designed to accomplish ongoing tasks or goals within a specific department or functional area. On the other hand, cross-functional teams are designed to bring together diverse skills, experiences, and perspectives to achieve a specific goal or project. Most people tend to identify more socially and psychologically with their function and responsibilities than with their organization. This can lead to conflicts between team members, as teams also generate their own identities and loyalties. In addition, cross-functional teams are subject to significant pressure and conflict because they are often temporary task teams, which are created to work on a specific project or goal. Finally, these teams often face high-performance expectations, with ambitious goals to reduce time, create knowledge, and improve organizational learning. [8] [10] Leaders must recognize these challenges and develop strategies to create a climate of trust, promote effective team processes, and ultimately achieve successful performance within cross-functional teams.
[edit] Application
To overcome the mentioned challenges and enable the full potential of those teams, effective leadership is critical to realizing the full potential of cross-functional teams and driving their success. This section explores the key aspects of leading cross-functional teams based on success factors described by [2] [3] [5] [10], covering the building of high-performing teams, setting clear goals and expectations, managing conflict, and motivating and engaging team members. An overview of the main factors can be seen in Figure 1. By understanding and implementing these strategies, leaders can ensure that their cross-functional teams are well-equipped to overcome challenges, collaborate effectively, and contribute to the overall success of the organization.
[edit] Building a High-Performance team
To build a high-performing team, several factors need to be considered. First, management plays a critical role in setting the team climate, aiming to create an innovative environment by empowering team members and fostering a sense of urgency with a "priority image" that generates commitment. Human resources are another critical aspect, focusing on increasing commitment, trust, communication and collaboration among team members. The skills and functional diversity within the team, along with the right combination of technical expertise, and interpersonal skills, contribute to the team's effectiveness and process performance. Management should therefore set a stage by assembling a team that possesses these qualities. Enablers, individuals with a vested interest in the project's success, can play a crucial role by raising awareness and overcoming management resistance. Their indirect influence on the project outcome and their moderating effect on the relationship between stage-setting elements and project performance can be invaluable. Finally, respect among team members is essential for open communication and trust, and team leaders can foster this by modeling the desired behavior and using their interpersonal skills.
[edit] Establishing Clear Goals and Expectations
When managing a cross-functional team, it is essential to set clear goals and expectations to ensure success. Setting well-defined goals provides a common frame of reference that encourages a higher level of cross-functional collaboration. Overarching goals help structure tasks and facilitate collaboration by keeping team members focused on a common outcome. Creating boundaries for the project team prevents constant redefinition of directions and focuses the team's efforts by explicitly stating what to do and what not to do. Ownership, which goes beyond commitment and duty, involves team members tying their identity to the outcome of the project. This sense of ownership can be fostered by establishing a climate, empowering the team, and setting goals. Involving the team in translating goals into specific deliverables is a critical step in cultivating ownership and setting the team up for success. By addressing these factors, cross-functional team management can effectively establish clear goals and expectations, paving the way for successful project outcomes.
[edit] Managing Conflict and Overcoming Obstacles
Effectively managing conflict and overcoming obstacles in cross-functional teams are critical aspects of successful team management. Team leaders play a critical role in these processes by acting indirectly as enablers, focusing on facilitating the team's work rather than engaging in developmental tasks themselves. A participative leadership style allows team members the freedom to explore, discuss, and challenge ideas, creating a collaborative environment. By sharing information and knowledge widely, keeping team members challenged, and maintaining a positive climate, team leaders can cultivate cooperation, respect, and open communication within the group. Especially respect is essential to promote open exchange and trust among team members.
Senior management support is also critical to team performance and can take many forms, including demonstrating commitment, helping to overcome obstacles, and providing encouragement. Team leaders should act as a bridge between the project team and senior management, lobbying for resources, protecting the group from outside interference, and managing expectations. By addressing this, managers can effectively handle conflict and overcome obstacles in cross-functional teams, paving the way for successful project outcomes.
[edit] Motivating and Engaging Team members
Motivating and engaging team members is essential for the team's success. Empowerment is a critical success factor, setting boundaries primarily through clear goals allows the project team to make project-related decisions autonomously. Giving team members more decision-making responsibility leads to increased engagement, satisfaction, and project speed. By pushing decisions down to the lowest level possible, organizations can respond more quickly and reduce the time it takes to solve problems and take action. Empowerment also indirectly affects performance by fostering collaboration among team members. Again enablers as described already above, can play an activating role by raising awareness and overcoming management resistance. Their indirect influence on the project outcome and moderating effect on the relationship between stage-setting elements and project performance can be invaluable in maintaining motivation and dedication. Commitment is another key aspect, as it refers to the sense of duty that team members feel towards achieving the project goals and their willingness to do what is necessary for the project to succeed. Project managers who are successful in gaining commitment from their team are more likely to achieve project goals.
[edit] Monitoring and Evaluating Team Performance
Monitoring and evaluating team performance is one of the main aspects of managing cross-functional teams, as it allows leaders to identify areas for improvement and adjust strategies accordingly. It is crucial to establish a set quantitative and qualitative of key performance indicators (KPIs) that are aligned with the project's goals and objectives. These KPIs should include several dimensions, such as schedule, budget, quality, and stakeholder satisfaction. Regular progress reports and team meetings can be used to assess the team's performance against these KPIs, providing managers with valuable insights to address any issues or bottlenecks in a timely manner. [3] As mentioned earlier it is also important to create an environment that encourages open communication and feedback so that team members can share their concerns, challenges, and suggestions for improvement. By continuously monitoring and evaluating performance, leaders can ensure that cross-functional teams remain focused, engaged, and on track to achieve their project goals and contribute to the success of the organization.
[edit] The interactions between the success factors for leading cross-functional teams
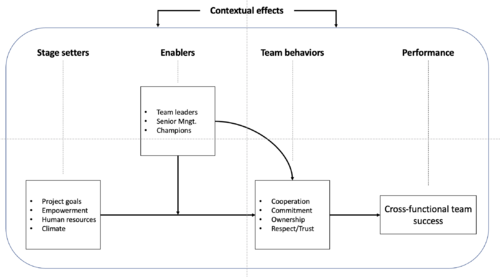
As a result, this model also places a focus on the function of "enablers," such as senior managers, team captains, and champions. These enablers play a crucial role in shaping project performance, primarily by influencing team behavior rather than directly impacting project outcomes. With their actions, attitudes, and the foundation they establish for new projects, they take part in shaping a team environment that encourages collaboration, mutual respect, and a shared understanding of the purpose.
Additionally, it's important to consider the role of contextual factors in influencing the success of cross-functional teams. Factors such as company size, industry, organizational culture, and the broader business environment can impact the stage-setting elements, enablers, and ultimately the team behavior. [5] For example, a startup might benefit from a more flexible and adaptive approach to project management, while a large company might need more structured procedures, standardized communication, and hierarchies.
In conclusion, strong leadership is crucial to maximizing the potential of cross-functional teams and ensuring their success. Building high-performing teams, setting clear goals and expectations, managing conflict, and motivating and engaging team members are key elements of leading cross-functional teams. Leaders who understand and practice those can ensure their teams are prepared to meet upcoming challenges, work together effectively, and contribute to the overall success of the organization. It is crucial to continually review and reevaluate these success elements, taking into account the always-adapting nature of team dynamics, organizational requirements, and the changing business environment in order to increase the efficiency of managing cross-functional teams. An iterative approach can ensure that team leadership remains aligned with the evolving needs and goals of the organization and the respective team.
By considering the interaction of various success factors, it is possible to create an environment that fosters innovation, productivity, and a shared sense of responsibility. Thus, they are setting the stage for both individual and team-based success. Further, this promotes a culture of continuous learning and improvement, where each project’s challenges and successes serve as lessons for future approaches.
[edit] Well-known examples in leveraging cross-functional teams
[edit] Apple, Inc.
To further outline the potential of cross-functional teams, Apple Inc. can be seen as a prime example. Their functional structure breaks down traditional departmental boundaries and fosters deep collaboration across functions. Their organizational structure, based on functional expertise, allows experts to lead other experts in their fields. This breaks down traditional barriers between departments and fosters deep collaboration across functions. In the case of the iPhone, Apple brought together engineers, designers, and marketing professionals to work toward a common goal under the visionary leadership of Steve Jobs. [11]
The collaborative environment fostered by Apple's functional structure allowed team members to freely share knowledge and ideas, which is essential for effective cross-functional teamwork. By giving experts the opportunity to lead and mentor others in their areas of expertise, Apple ensured that team members were motivated and engaged, further enhancing the performance of their cross-functional teams. Apple has successfully integrated cross-functional teams within every part of its organization to create breakthrough products such as the iPhone. [11]
[edit] Tesla, Inc.
Another example of successful leadership of cross-functional teams comes from the automobile industry, specifically Tesla, Inc., led by CEO Elon Musk. Tesla facilitates a philosophy of "anti-silo thinking," which supports cross-disciplinary collaboration and innovation. To develop the Model S, Tesla created a cross-functional team of automotive engineers, software engineers, battery technology experts, and design professionals. This team had to work together to achieve a common goal: to create an electric vehicle that could compete with, and even surpass, gasoline-powered cars in terms of performance, safety, and comfort. Under Musk's leadership, the cross-functional team was encouraged to challenge conventional wisdom and think beyond traditional industry boundaries. [12] This approach led to several breakthrough innovations and their current leadership position in the electric vehicle market.
At Tesla, cross-functional teams are a core part of the company's innovation strategy. Musk's open communication, taking calculated risks, and constant learning was a key factor in building a team environment where team members felt empowered and committed to contributing their skills to the overall goal and purpose.
[edit] Limitations
There are limitations to every discussion of leading interdisciplinary project teams. One of these restrictions is that different organizations may have different definitions of what beholds a "cross-functional team". Different organizations may interpret the referring concepts in diverse ways, reflecting their unique business structures, strategic goals, and working cultures. This makes it difficult to standardize the approach to this subject. Therefore, it may be more practical to use a different strategy for various businesses or projects, making it challenging to develop a comprehensive manual that covers all possibilities.
The mentioned success factors are also not only limited to teams with a cross-functional background. Indeed, many of these factors, such as clear communication, conflict resolution, and effective leadership, are universally applicable to team management, regardless of team composition. Moreover, it can be challenging to manage a range of personalities, communication styles, and areas of expertise, and condensing the subject into one condensed article may is not detailed enough for every possible situation. A wide range of topics, including team development, conflict resolution, and project management approaches, are included in the leadership of interdisciplinary project teams. As a result, giving a thorough review that addresses every facet of this complex subject can be to some extent not practicable. Finally, it is essential to consider the unique circumstances and needs of each team and organization. While this article provides a solid foundation for understanding and managing cross-functional teams, leaders are encouraged to further explore additional resources as needed, and adapt the insights to their specific situations. They should also consider supplementing this knowledge with firsthand experiences, professional training, and mentorship to effectively navigate the complexities and nuances of leading interdisciplinary project teams. This adaptive and continuous learning approach can help ensure the successful management and performance of these teams.
[edit] Annotated Bibliography
To dive further into the methods and topics regarding the leadership of cross-functional teams, the following references are highly recommended:
- Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). (2021). A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK ® Guide) – 7th Edition and The Standard for Project Management. Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI) - This guide from the Project Management Institute provides comprehensive coverage of project management best practices, standards, and frameworks. It includes methodologies, tools, and techniques for effective project management, making it a valuable resource for understanding the principles and practices of leading cross-functional project teams.
- Kerzner, H. (2017). Project Management - A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling (12th Edition). John Wiley & Sons - Kerzner's Project Management textbook provides a practical approach to planning, scheduling, and controlling projects. It covers a wide range of topics, including cross-functional team management, and provides insight into the challenges and opportunities associated with leading cross-functional teams in various project environments.
- Edward F. McDonough III. (2000). Investigation of Factors Contributing to the Success of Cross-Functional Teams. Elsevier Science Inc - The article by McDonough examines the factors that contribute to the success of cross-functional teams, focusing on elements such as collaboration, ownership, and commitment. The study provides valuable insights into the role of these factors in the effectiveness of cross-functional project teams and offers a deeper understanding of the dynamics at play in successful team management.
- Holland.S, Gaston.K, Gomes.J. (2000). Critical success factors for cross-functional teamwork in new product development. International Journal of Management Reviews. Blackwell Publishers - The article examines the critical success factors for cross-functional teamwork in new product development. The authors provide a detailed analysis of the elements that contribute to effective team management, such as communication, collaboration, and trust, and highlight the importance of these factors in the successful execution of cross-functional projects.
- Christine Organ, Cassie Bottorf, 2022, What Are Cross-Functional Teams? Everything you need to know, https://www.forbes.com/advisor/business/cross-functional-teams/ - Forbes Advisor is a trusted online source of expert advice and information on a wide range of topics, including finance, investing, business, and technology. It is an extension of Forbes, a well-established media company with a long history of producing reliable, high-quality content. Forbes Advisor features articles written by industry experts and professionals to ensure that the information provided is accurate, up-to-date, and useful.
- Joel M. Podolny, Morten T. Hansen. (2020). How Apple Is Organized for Innovation. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2020/11/how-apple-is-organized-for-innovation - Harvard Business Review (HBR) is a highly credible source of information on business, management, and leadership. Published by Harvard Business Publishing, a subsidiary of Harvard University, HBR features articles written by academics, business leaders, and management experts. The content is well-researched, evidence-based, and often includes insights from cutting-edge research and real-world case studies.
Further, the following wiki articles are recommended for more in-depth information about related methods and topics connected with leading cross-functional teams:
- Effective Communication in Project Management by Alessandro Palmerini, http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Effective_Communication_in_Project_Management
- How to successfully go through the Five Stages of Team Development by Natacha Leduc, http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/How_to_successfully_go_through_the_Five_Stages_of_Team_Development
- Leadership vs. management, http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Leadership_vs._management
- SMART Goals (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time-bound) by Nicolai Mossing Madsen, http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/SMART_Goals_(Specific,_Measurable,_Attainable,_Relevant,_Time-bound)
- Dealing with conflict in project management by Sebastian Graff Daugaard, http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Dealing_with_conflict_in_project_management
[edit] References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Christine Organ, Cassie Bottorf, 2022, What Are Cross-Functional Teams? Everything you need to know, https://www.forbes.com/advisor/business/cross-functional-teams/
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). (2021). A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK ® Guide) – 7th Edition and The Standard for Project Management. Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Kerzner, H. (2017). Project Management - A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling (12th Edition). John Wiley & Sons
- ↑ "Jackson, S.E. (1996). The consequences of diversity in multidisciplinary work teams. In West, M.A. (Ed.) Handbook of work group psychology. John Wiley & Sons Ltd: UK"
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Edward F. McDonough III. (2000). Investigation of Factors Contributing to the Success of Cross-Functional Teams. Elsevier Science Inc
- ↑ Webber.S. (2000). Leadership and trust facilitating cross-functional team success. Journal of Management Development. Emerald
- ↑ Song, X.M., Montoya-Weiss, M.M. and Schmidt, J.B. (1997). "Antecedents and consequences of cross-functional cooperation: a comparison of R&D, manufacturing, and marketing perspectives." Journal of Product Innovation Management, Vol. 14, pp. 35-47.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Denison, D.r., Hart, S.l. , Kahn, J.A (1996). From chimneys to cross-functional teams: Developing and validating a diagnostic model. Academy of Management Journal, 39 1005-1022.
- ↑ Sitkin, S.B. and Roth, N.L. (1993). "Explaining the limited effectiveness of legalistic remedies for trust/distrust." Organization Science, Vol. 4 No. 3, pp. 367-92.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Holland.S, Gaston.K, Gomes.J. (2000). Critical success factors for cross-functional teamwork in new product development. International Journal of Management Reviews. Blackwell Publishers
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Joel M. Podolny, Morten T. Hansen. (2020). How Apple Is Organized for Innovation. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2020/11/how-apple-is-organized-for-innovation
- ↑ Ashlee Vance. (2015). Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic Future. HarperCollins.