Resource Allocation in Project Management
| (7 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ''Developed by Davide Paganini'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
| − | In project management exists a tight connection between results and resources optimization. An | + | In project management, there exists a tight connection between results and resources optimization. An |
inadequate planning of resource allocation might lead to a non-manageable or non-reasonable budget | inadequate planning of resource allocation might lead to a non-manageable or non-reasonable budget | ||
formulation. | formulation. | ||
| − | Each organization must wisely allocate resources to avoid delays, rework, nonconformity and to ensure | + | Each organization must wisely allocate resources to avoid delays, rework, nonconformity, and to ensure an |
| − | overall company efficiency in the long run. All companies face the same dilemma at one point | + | overall company efficiency in the long run. All companies face the same dilemma at one point: how best to |
allocate resources. Allocating resources to wrong ideas or projects that eventually fail will lead to wastage. | allocate resources. Allocating resources to wrong ideas or projects that eventually fail will lead to wastage. | ||
| − | On the other hand, not allocating resources in the right | + | On the other hand, not allocating enough resources in the right places can lead to even greater opportunity costs. |
Under and over allocation are the main problems that arise in a non-planned resource allocation scenario. | Under and over allocation are the main problems that arise in a non-planned resource allocation scenario. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 18: | ||
final goal of each project manager. | final goal of each project manager. | ||
| − | + | This article will introduce different techniques and approaches used to optimize resource allocation. An explanation will be provided to guide PM's on how to best allocate resources. | |
=Resource Allocation= | =Resource Allocation= | ||
| − | The process of assigning and managing assets | + | The process of assigning and managing assets to support an organization's strategic goals is called resource allocation. In project Management, it is the scheduling of activities and resources required by those activities taking into consideration both the project time and the resource availability. It involves balancing competing commitments and priorities in order to determine the most effective course of action to best utilize a limited pool of resources and maximize the return on investment. |
==Resource Allocation Process & Strategies== | ==Resource Allocation Process & Strategies== | ||
| − | Resource allocation begins with strategic planning. A company | + | Resource allocation begins with strategic planning. A company shall formulate and agree on its vision and goals, and proceed to accomplish them by setting objectives and working through each of them systematically. Once a strategy is drawn, it will be necessary to allocate sufficient resources to accomplish it. Project budgeting comes into play at this stage as each department will use an agreed budgeted fund to allocate resource for specific purposes, such as buying raw materials, hiring employees, etc. Resources must be moved to where they are needed the most. This is why resource allocation is at the core of each project, and why without a proper allocation, a project is destined to fail. |
===Core Resources=== | ===Core Resources=== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 31: | ||
*'''Land''': Natural resource required in production process, land, mineral, forest, oil and water resources. | *'''Land''': Natural resource required in production process, land, mineral, forest, oil and water resources. | ||
| − | *'''Labour''': The aggregate of | + | *'''Labour''': The aggregate of a person's physical and mental effort used to generate goods and services. It is a primary factor in production. The labor force is determined by the adult population of a nation. |
| − | *'''Capital''':Wealth in the form of money or assets | + | *'''Capital''': Wealth in the form of money or assets is a sign of the financial strength of an individual, organization, or nation, and is assumed to be available for development or investment. |
===Allocation Decisions=== | ===Allocation Decisions=== | ||
| − | The basic allocation decisions begin with the choice of what is going to fund the project | + | The basic allocation decisions begin with the choice of what is going to fund the project. It is not only important to avoid allocating resource merely in terms of meeting milestones, but also important in terms of timing and utilization of scarce resources. |
| − | ===Resource Allocation | + | ===Resource Allocation Problems=== |
| − | *'''Time Limited''': Projects must be finished | + | *'''Time Limited''': Projects must be finished by an agreed time, using as few resources as possible. |
| − | *'''Resources Limited''': Projects must be | + | *'''Resources Limited''': Projects must be executed by remaining within specific levels of resource usage or general resource constraints. |
| − | *'''Resource Over-allocation''': | + | *'''Resource Over-allocation''': Assigning more tasks than what resources can handle within the standard work week. A company with multiple projects and a limited pool of resources often face this issue, which leads to overtime and overspending on financial resources. |
=Resource Allocation Techniques= | =Resource Allocation Techniques= | ||
| − | “The schedule produced for a project assumes that enough manpower and equipment is available to get the activities done as scheduled. This is not always the case, and in a large | + | “The schedule produced for a project assumes that enough manpower and equipment is available to get the activities done as scheduled. This is not always the case, and in a large, complex project, it might not be obvious that a deficiency exists.” <ref> The Associated General Contractors of America(AGC) (1976). The Use of CPM In Construction.</ref> |
“Resources required by activities are unlimited, while some resources are highly limited in practice. In most real construction projects, scheduling without considering resource limitations may result in a non-credible schedule, since the start-ability of activities is affected by resource availability.” <ref> Kim, Kyunghwan (2003). “A Resource-constrained CPM (RCPM) Scheduling and Control Technique with Multiple Calendars” - Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University PHD. Dissertation. - https://theses.lib.vt.edu/theses/available/etd-06272003-143644/unrestricted/ETD.pdf. </ref> | “Resources required by activities are unlimited, while some resources are highly limited in practice. In most real construction projects, scheduling without considering resource limitations may result in a non-credible schedule, since the start-ability of activities is affected by resource availability.” <ref> Kim, Kyunghwan (2003). “A Resource-constrained CPM (RCPM) Scheduling and Control Technique with Multiple Calendars” - Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University PHD. Dissertation. - https://theses.lib.vt.edu/theses/available/etd-06272003-143644/unrestricted/ETD.pdf. </ref> | ||
| − | There are different solutions and techniques to tackle the problem of resource allocation, | + | There are different solutions and techniques to tackle the problem of resource allocation, and identifying the right one for a specific business is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the procedure. |
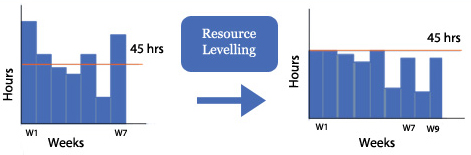
==Resource Leveling== | ==Resource Leveling== | ||
| Line 56: | Line 59: | ||
The aim of leveling resources is to minimize the variations in resource loading by "Shifting tasks within their slack allowances". <ref> Schwalbe, Kathy (2007). Information Technology Project Management 5th Edition.</ref> | The aim of leveling resources is to minimize the variations in resource loading by "Shifting tasks within their slack allowances". <ref> Schwalbe, Kathy (2007). Information Technology Project Management 5th Edition.</ref> | ||
| − | The technique is applied to resolve conflicts and to create a smoother distribution of resources, determine the correct resource requirements to ensure availability at any given time and | + | The technique is applied to resolve conflicts and to create a smoother distribution of resources, determine the correct resource requirements to ensure availability at any given time, and to schedule the activities in order to secure the most fluid achievable transition across usage levels. In other words, resource leveling operates to allocate resource efficiently to complete a project in in the given time period. |
| − | In resource leveling, resources | + | In resource leveling, resources should be assigned to those activities with: |
*Minimum slack <ref> Scheduling projects: How to determine the critical path using activity slack calculations? - http://www.pmknowledgecenter.com/dynamic_scheduling/baseline/scheduling-projects-how-determine-critical-path-using-activity-slack-calculations - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016 </ref> | *Minimum slack <ref> Scheduling projects: How to determine the critical path using activity slack calculations? - http://www.pmknowledgecenter.com/dynamic_scheduling/baseline/scheduling-projects-how-determine-critical-path-using-activity-slack-calculations - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016 </ref> | ||
*Shortest duration | *Shortest duration | ||
| Line 72: | Line 75: | ||
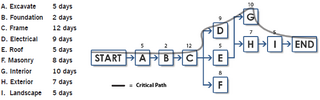
[[File:Activity-Network-Diagram-Example-Chart-2.png|thumb|320px|sub|Figure 1 - Activity Network Diagram - Construction Building Example]] | [[File:Activity-Network-Diagram-Example-Chart-2.png|thumb|320px|sub|Figure 1 - Activity Network Diagram - Construction Building Example]] | ||
*1- Create a project activity network diagram. (Figure 1) | *1- Create a project activity network diagram. (Figure 1) | ||
| − | It is the sequence of project activities that shows the sequential | + | It is the sequence of project activities that shows the sequential relationship between them with arrows and nodes. This tool is widely used in project management and is required to identify a project’s critical path (used to determine the expected completion time of the project). The nodes represent the nine activities required to build a construction and the arrows that connect the different nodes show the process flow. [Figure 1] It is possible to identify different types of activities like an A,B,C run in series. I.e. is not possible to proceed with the activity B if A is not completed. D,E,F run in parallel, so they must all be completed before G or H can be executed. A network diagram is also essential in identify the critical path, which is the path which has the longest completion time. <ref> Six Sigma Daily (2012). “The Activity Network Diagram” - http://www.sixsigmadaily.com/the-activity-network-diagram/ - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016</ref> |
*2- Create a table showing resource requirements, duration and available slack for each activity. | *2- Create a table showing resource requirements, duration and available slack for each activity. | ||
| − | In order to allocate resources optimally and identify project resource gap it is important to have create a complete overview of each | + | In order to allocate resources optimally and identify project resource gap it is important to have create a complete overview of each activity's requirements. This will help in identify the difference between available and required resources. This stage is crucial as different approaches can be taken, e.g. adding more resources, prolonging the schedule, hiring more labor forces,etc. |
<ref> I.T. Toolkit. “How to Use Resource Leveling for Project Planning and Scheduling” - https://www.ittoolkit.com/how-to-it/projects/resource-leveling.html - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016</ref> | <ref> I.T. Toolkit. “How to Use Resource Leveling for Project Planning and Scheduling” - https://www.ittoolkit.com/how-to-it/projects/resource-leveling.html - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016</ref> | ||
| Line 85: | Line 88: | ||
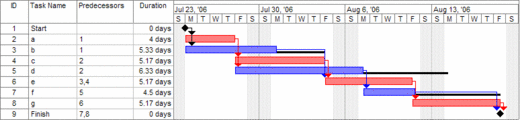
*3-Develop a resource loading table or Gantt chart. (Figure 2) | *3-Develop a resource loading table or Gantt chart. (Figure 2) | ||
| − | "Is | + | "Is an instrument that addresses the determination of realistic due dates and other important milestones for new customer orders, as well as the resource capacity levels that are a result of the actual set of orders in the system" <ref> Willem Hans, Elias (2001). “Resource Loading by branch-and-price Techniques” - Twente University Dissertation - https://www.utwente.nl/bms/iebis/staff/hans/phdhans.pdf - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016</ref> |
| − | Gantt chart, as | + | A Gantt chart, as seen in Figure 2, is a project planning tool used in project management. It is used to show the timing of tasks necessary to fulfill project's requirements. Each line represent a different task, and they are represented on a time-phased scheme. The expected time is represented by a horizontal bar whose left end represents the expected beginning of the task and the right end, the expected completion date. In the network diagram, tasks may run in sequence, parallel or overlap. <ref> Durfee, W. (2008). “Project Planning and Gantt Charts” - University of Minnesota - http://www.me.umn.edu/courses/me2011/handouts/proj_planning.pdf - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016</ref> |
| Line 98: | Line 101: | ||
"A prioritization matrix, as can be seen in Figure 3, is a simple tool that provides a way to sort a diverse set of items into an order of importance." <ref> Gosenheimer, Carol. (2012). “Project Prioritization, A Structured Approach to Working on What Matters Most” - Office of Quality Improvement, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Division of Enrollment Management - https://oqi.wisc.edu/resourcelibrary/uploads/resources/Project_Prioritization_Guide_v_1.pdf - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016</ref> | "A prioritization matrix, as can be seen in Figure 3, is a simple tool that provides a way to sort a diverse set of items into an order of importance." <ref> Gosenheimer, Carol. (2012). “Project Prioritization, A Structured Approach to Working on What Matters Most” - Office of Quality Improvement, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Division of Enrollment Management - https://oqi.wisc.edu/resourcelibrary/uploads/resources/Project_Prioritization_Guide_v_1.pdf - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016</ref> | ||
| − | A Prioritization matrix bring different benefits: | + | A Prioritization matrix bring different benefits such as: |
| − | * | + | *Quantifying decisions with numeric rankings. |
| − | * | + | *Facilitating agreement on priorities. |
| − | * | + | *Providing a quick and reliable image to evaluate options. |
| − | * | + | *Aiding in the prioritization of complex issues. |
====Steps==== | ====Steps==== | ||
| Line 119: | Line 122: | ||
*1- Agree on the objectives to be reached and identify the key project stakeholders | *1- Agree on the objectives to be reached and identify the key project stakeholders | ||
| − | It is necessary to ensure that the | + | It is necessary to ensure that the entire team working on the matrix is fully aligned on the ultimate objective. |
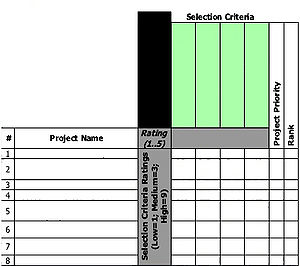
*2- Identify which projects should be evaluated for prioritization. (Figure 4) | *2- Identify which projects should be evaluated for prioritization. (Figure 4) | ||
| Line 130: | Line 133: | ||
*4- Compare criteria importance by allocating a value to each criterion on a agreed scale. (Figure 6) | *4- Compare criteria importance by allocating a value to each criterion on a agreed scale. (Figure 6) | ||
| − | Judge the importance of each criteria comparing it with the other. These number will | + | Judge the importance of each criteria comparing it with the other. These number will be arbitrary to an extent. However, by keeping them constant and applying them in a prioritization matrix, it is possible to reach an accurate standard. |
| − | *5- Compare each project's impact on each criterion by rating them | + | *5- Compare each project's impact on each criterion by rating them on the agreed scale. (Figure 7) |
*6- Compare the projects against the weighted criteria (Figure 8) | *6- Compare the projects against the weighted criteria (Figure 8) | ||
| − | Once the importance of each criterion and project is stated is possible to evaluate how they | + | Once the importance of each criterion and project is stated, it is possible to evaluate how they relate with each other. By multiplying each project rating with each criterion rating it is possible to retrieve the score for each project and each criterion. |
*7- Compare the final result | *7- Compare the final result | ||
| Line 149: | Line 152: | ||
*Rank 8- Project 4 | *Rank 8- Project 4 | ||
| − | It's | + | It's immediately obvious at this point to evaluate which projects to work on first. The most important project is Project 2, with a score of 69, and the least important is Project 4, with a score of 17. During resource allocation it will be possible to distribute resources based on the priority of each projects compared to the others. |
<ref> Jain, Ankur. “Using a Criteria-Based Matrix to Prioritize IT Projects” - I, Six Sigma - https://www.isixsigma.com/operations/information-technology/applying-criteria-based-matrix-prioritize-it-projects/ - Online, Checked on 16/09/2016</ref> | <ref> Jain, Ankur. “Using a Criteria-Based Matrix to Prioritize IT Projects” - I, Six Sigma - https://www.isixsigma.com/operations/information-technology/applying-criteria-based-matrix-prioritize-it-projects/ - Online, Checked on 16/09/2016</ref> | ||
<ref> Bonacorsi, Steven. (2011). “7 Steps to Using Prioritization Matrices” - PEX, Process Excellence Network - http://www.processexcellencenetwork.com/lean-six-sigma-business-transformation/articles/process-excellence-methodologies-using-prioritizat - Online, Checked on 16/09/2016</ref> | <ref> Bonacorsi, Steven. (2011). “7 Steps to Using Prioritization Matrices” - PEX, Process Excellence Network - http://www.processexcellencenetwork.com/lean-six-sigma-business-transformation/articles/process-excellence-methodologies-using-prioritizat - Online, Checked on 16/09/2016</ref> | ||
| Line 155: | Line 158: | ||
==Contingency== | ==Contingency== | ||
| − | In resource allocation is often critical to have a contingency plan. Contingency is a way to cope with uncertainty | + | In resource allocation is often critical to have a contingency plan. Contingency is a way to cope with uncertainty. When estimating resources, it is important to set aside a fund of the project to be used in case of an emergency. The amount of the funds should be determined based on the level of risk that the project faces, and on the project budget itself. |
| − | This contingency fund will be used to cover unforeseen increases in costs by absorbing impacts of project uncertainty. Contingency shouldn't be used as primary alternative in mitigating risk, it should only be part of a complete and | + | This contingency fund will be used to cover unforeseen increases in costs by absorbing the impacts of project uncertainty. Contingency shouldn't be used as primary alternative in mitigating risk, it should only be part of a complete and structured risk mitigation plan. |
| − | + | Determining the contingency fund requires an agreement between the project manager and the project owner. The first usually wants the contingency to be set high in order to permit greater flexibility, and be protected from uncertainty. on the other hand, the latter wants the contingency to be set low to maintain more control over the project. If the contingency is set too high, PMs may not be sufficiently involved, on the contrary, and if set too low, it will eventually bring managers to micromanage the project. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | As stated above, determining the right amount of contingency is not simple. If a project belongs to a category that the company knows well it is possible to use historical data to calculate it. If a project is brand new with new technologies and innovative procedures, it is more probable that it would come with a higher risks, which would generate great uncertainty, and might require a more structured approach to define the amount of contingency. To overcome such problems, contingency can be calculated at a major task level instead of project level. Defining the amount to allocate this way would be easier as riskier tasks would require more money.<ref> National Research Council of the National Academies. “The Owner's Role in Project Risk Management” - Page 52</ref> | ||
==Other Techniques== | ==Other Techniques== | ||
| Line 167: | Line 169: | ||
===Linking Tasks=== | ===Linking Tasks=== | ||
| − | Linking similar task between different projects. If a resource have been allocated to a task which is similar across different projects it is possible to link these task. In this way a resource that appears to be over-allocated with tasks, can actually work | + | Linking similar task between different projects. If a resource have been allocated to a task which is similar across different projects, it is possible to link these task. In this way a resource that appears to be over-allocated with tasks, can actually work simultaneously with activities that shares common similarities. |
===Leaving Breathing Room=== | ===Leaving Breathing Room=== | ||
| − | + | Anticipating challenges is important when it comes to allocating resources. Project managers should carefully think ahead in order to foresee obstacles and constraints. It is then vital to leave breathing room between tasks to avoid unexpected expenses. When facing strict deadlines, it is necessary to focus energy on time management and in creating a clear timetable to achieve goals. However, in order not to under-allocate resources that could lead to a budget loss, a balance between breathing room and a quick approach to task must be achieved. | |
=Conclusions= | =Conclusions= | ||
| − | The process | + | The process of resource allocation can be described as the company activity of placing its scarce resources in the best possible way. The strategy is to bring to customers, goods and services, who fully satisfy the expressed request, by matching their preferences to utilize the lowest possible production cost. Resource allocation is an ongoing process throughout a project's lifetime, and must be monitored to ensure an efficient use of resources and to identify all problems. |
| − | + | =Annotated Bibliography= | |
* Schwalbe, Kathy (2007). Information Technology Project Management 5th Edition. | * Schwalbe, Kathy (2007). Information Technology Project Management 5th Edition. | ||
| − | * | + | **''A comprehensive manual of project management, containing different concepts, tools and techniques. The contribution to this article are mostly from Chapter 6,7 and 9.'' |
| − | * | + | |
| + | *Gosenheimer, Carol. (2012). “Project Prioritization, A Structured Approach to Working on What Matters Most” - Office of Quality Improvement, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Division of Enrollment Management | ||
| + | **''A clear an concise overview of what is Project Prioritization and how to set priorities.'' | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:47, 18 December 2018
Developed by Davide Paganini
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
In project management, there exists a tight connection between results and resources optimization. An inadequate planning of resource allocation might lead to a non-manageable or non-reasonable budget formulation.
Each organization must wisely allocate resources to avoid delays, rework, nonconformity, and to ensure an overall company efficiency in the long run. All companies face the same dilemma at one point: how best to allocate resources. Allocating resources to wrong ideas or projects that eventually fail will lead to wastage. On the other hand, not allocating enough resources in the right places can lead to even greater opportunity costs. Under and over allocation are the main problems that arise in a non-planned resource allocation scenario.
Is critical to have a planned approach in RA to manage a project portfolio effectively. Being able to allocate the correct resources, in terms of skills and quantity, to the right ideas, projects and products should be the final goal of each project manager.
This article will introduce different techniques and approaches used to optimize resource allocation. An explanation will be provided to guide PM's on how to best allocate resources.
[edit] Resource Allocation
The process of assigning and managing assets to support an organization's strategic goals is called resource allocation. In project Management, it is the scheduling of activities and resources required by those activities taking into consideration both the project time and the resource availability. It involves balancing competing commitments and priorities in order to determine the most effective course of action to best utilize a limited pool of resources and maximize the return on investment.
[edit] Resource Allocation Process & Strategies
Resource allocation begins with strategic planning. A company shall formulate and agree on its vision and goals, and proceed to accomplish them by setting objectives and working through each of them systematically. Once a strategy is drawn, it will be necessary to allocate sufficient resources to accomplish it. Project budgeting comes into play at this stage as each department will use an agreed budgeted fund to allocate resource for specific purposes, such as buying raw materials, hiring employees, etc. Resources must be moved to where they are needed the most. This is why resource allocation is at the core of each project, and why without a proper allocation, a project is destined to fail.
[edit] Core Resources
- Land: Natural resource required in production process, land, mineral, forest, oil and water resources.
- Labour: The aggregate of a person's physical and mental effort used to generate goods and services. It is a primary factor in production. The labor force is determined by the adult population of a nation.
- Capital: Wealth in the form of money or assets is a sign of the financial strength of an individual, organization, or nation, and is assumed to be available for development or investment.
[edit] Allocation Decisions
The basic allocation decisions begin with the choice of what is going to fund the project. It is not only important to avoid allocating resource merely in terms of meeting milestones, but also important in terms of timing and utilization of scarce resources.
[edit] Resource Allocation Problems
- Time Limited: Projects must be finished by an agreed time, using as few resources as possible.
- Resources Limited: Projects must be executed by remaining within specific levels of resource usage or general resource constraints.
- Resource Over-allocation: Assigning more tasks than what resources can handle within the standard work week. A company with multiple projects and a limited pool of resources often face this issue, which leads to overtime and overspending on financial resources.
[edit] Resource Allocation Techniques
“The schedule produced for a project assumes that enough manpower and equipment is available to get the activities done as scheduled. This is not always the case, and in a large, complex project, it might not be obvious that a deficiency exists.” [1]
“Resources required by activities are unlimited, while some resources are highly limited in practice. In most real construction projects, scheduling without considering resource limitations may result in a non-credible schedule, since the start-ability of activities is affected by resource availability.” [2]
There are different solutions and techniques to tackle the problem of resource allocation, and identifying the right one for a specific business is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the procedure.
[edit] Resource Leveling
The aim of leveling resources is to minimize the variations in resource loading by "Shifting tasks within their slack allowances". [3]
The technique is applied to resolve conflicts and to create a smoother distribution of resources, determine the correct resource requirements to ensure availability at any given time, and to schedule the activities in order to secure the most fluid achievable transition across usage levels. In other words, resource leveling operates to allocate resource efficiently to complete a project in in the given time period.
In resource leveling, resources should be assigned to those activities with:
- Minimum slack [4]
- Shortest duration
- Earlier start
- Most amount of successor tasks
- Highest resources requirement
[edit] Steps
- 1- Create a project activity network diagram. (Figure 1)
It is the sequence of project activities that shows the sequential relationship between them with arrows and nodes. This tool is widely used in project management and is required to identify a project’s critical path (used to determine the expected completion time of the project). The nodes represent the nine activities required to build a construction and the arrows that connect the different nodes show the process flow. [Figure 1] It is possible to identify different types of activities like an A,B,C run in series. I.e. is not possible to proceed with the activity B if A is not completed. D,E,F run in parallel, so they must all be completed before G or H can be executed. A network diagram is also essential in identify the critical path, which is the path which has the longest completion time. [5]
- 2- Create a table showing resource requirements, duration and available slack for each activity.
In order to allocate resources optimally and identify project resource gap it is important to have create a complete overview of each activity's requirements. This will help in identify the difference between available and required resources. This stage is crucial as different approaches can be taken, e.g. adding more resources, prolonging the schedule, hiring more labor forces,etc. [6]
- 3-Develop a resource loading table or Gantt chart. (Figure 2)
"Is an instrument that addresses the determination of realistic due dates and other important milestones for new customer orders, as well as the resource capacity levels that are a result of the actual set of orders in the system" [7]
A Gantt chart, as seen in Figure 2, is a project planning tool used in project management. It is used to show the timing of tasks necessary to fulfill project's requirements. Each line represent a different task, and they are represented on a time-phased scheme. The expected time is represented by a horizontal bar whose left end represents the expected beginning of the task and the right end, the expected completion date. In the network diagram, tasks may run in sequence, parallel or overlap. [8]
[edit] Prioritize Projects
Organizations often struggle to balance a growing list of incoming projects while the need for core services continues. Prioritizing projects avoid pressure on individuals or teams in presence of over-allocation or task conflict. It is essential to decide how to prioritize projects and separate high priority projects from lower ones. A prioritization matrix can overcome such problems.
[edit] Prioritization Matrix
"A prioritization matrix, as can be seen in Figure 3, is a simple tool that provides a way to sort a diverse set of items into an order of importance." [9]
A Prioritization matrix bring different benefits such as:
- Quantifying decisions with numeric rankings.
- Facilitating agreement on priorities.
- Providing a quick and reliable image to evaluate options.
- Aiding in the prioritization of complex issues.
[edit] Steps
Here a simple example to help understand the process of creating a Prioritization Matrix.
- 1- Agree on the objectives to be reached and identify the key project stakeholders
It is necessary to ensure that the entire team working on the matrix is fully aligned on the ultimate objective.
- 2- Identify which projects should be evaluated for prioritization. (Figure 4)
The expertise and the knowledge of the involved participants are required to outline which projects should be compared on the prioritization matrix.
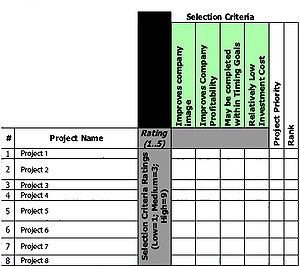
- 3- Identify the criteria required to meet the goal (Figure 5)
Create a list containing all the characteristics needed to achieve the prefixed objective. Through brainstorming and discussion the team should align on these criteria. Few examples:
-Ease of implementation, Customer satisfaction, Improves Company image, Use of Technology, Improves Company Profitability, May be completed within timing goals, Investment Cost
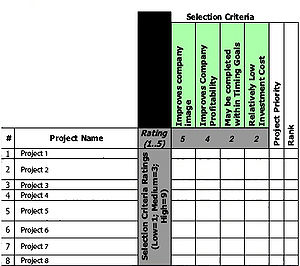
- 4- Compare criteria importance by allocating a value to each criterion on a agreed scale. (Figure 6)
Judge the importance of each criteria comparing it with the other. These number will be arbitrary to an extent. However, by keeping them constant and applying them in a prioritization matrix, it is possible to reach an accurate standard.
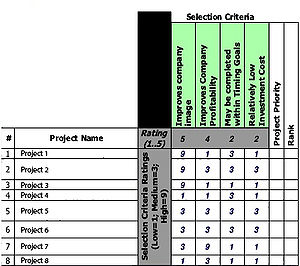
- 5- Compare each project's impact on each criterion by rating them on the agreed scale. (Figure 7)
- 6- Compare the projects against the weighted criteria (Figure 8)
Once the importance of each criterion and project is stated, it is possible to evaluate how they relate with each other. By multiplying each project rating with each criterion rating it is possible to retrieve the score for each project and each criterion.
- 7- Compare the final result
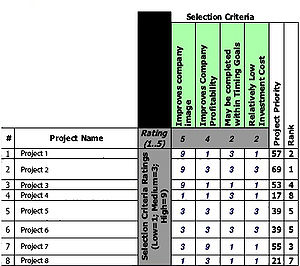
Once all the scores are added up for each project is possible to outline which ones should be prioritize. In the given example the result is:
- Rank 1- Project 2
- Rank 2- Project 1
- Rank 3- Project 7
- Rank 4- Project 3
- Rank 5- Projects 5 & 6
- Rank 7- Project 8
- Rank 8- Project 4
It's immediately obvious at this point to evaluate which projects to work on first. The most important project is Project 2, with a score of 69, and the least important is Project 4, with a score of 17. During resource allocation it will be possible to distribute resources based on the priority of each projects compared to the others. [10] [11]
[edit] Contingency
In resource allocation is often critical to have a contingency plan. Contingency is a way to cope with uncertainty. When estimating resources, it is important to set aside a fund of the project to be used in case of an emergency. The amount of the funds should be determined based on the level of risk that the project faces, and on the project budget itself. This contingency fund will be used to cover unforeseen increases in costs by absorbing the impacts of project uncertainty. Contingency shouldn't be used as primary alternative in mitigating risk, it should only be part of a complete and structured risk mitigation plan.
Determining the contingency fund requires an agreement between the project manager and the project owner. The first usually wants the contingency to be set high in order to permit greater flexibility, and be protected from uncertainty. on the other hand, the latter wants the contingency to be set low to maintain more control over the project. If the contingency is set too high, PMs may not be sufficiently involved, on the contrary, and if set too low, it will eventually bring managers to micromanage the project.
As stated above, determining the right amount of contingency is not simple. If a project belongs to a category that the company knows well it is possible to use historical data to calculate it. If a project is brand new with new technologies and innovative procedures, it is more probable that it would come with a higher risks, which would generate great uncertainty, and might require a more structured approach to define the amount of contingency. To overcome such problems, contingency can be calculated at a major task level instead of project level. Defining the amount to allocate this way would be easier as riskier tasks would require more money.[12]
[edit] Other Techniques
[edit] Linking Tasks
Linking similar task between different projects. If a resource have been allocated to a task which is similar across different projects, it is possible to link these task. In this way a resource that appears to be over-allocated with tasks, can actually work simultaneously with activities that shares common similarities.
[edit] Leaving Breathing Room
Anticipating challenges is important when it comes to allocating resources. Project managers should carefully think ahead in order to foresee obstacles and constraints. It is then vital to leave breathing room between tasks to avoid unexpected expenses. When facing strict deadlines, it is necessary to focus energy on time management and in creating a clear timetable to achieve goals. However, in order not to under-allocate resources that could lead to a budget loss, a balance between breathing room and a quick approach to task must be achieved.
[edit] Conclusions
The process of resource allocation can be described as the company activity of placing its scarce resources in the best possible way. The strategy is to bring to customers, goods and services, who fully satisfy the expressed request, by matching their preferences to utilize the lowest possible production cost. Resource allocation is an ongoing process throughout a project's lifetime, and must be monitored to ensure an efficient use of resources and to identify all problems.
[edit] Annotated Bibliography
- Schwalbe, Kathy (2007). Information Technology Project Management 5th Edition.
- A comprehensive manual of project management, containing different concepts, tools and techniques. The contribution to this article are mostly from Chapter 6,7 and 9.
- Gosenheimer, Carol. (2012). “Project Prioritization, A Structured Approach to Working on What Matters Most” - Office of Quality Improvement, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Division of Enrollment Management
- A clear an concise overview of what is Project Prioritization and how to set priorities.
[edit] References
- ↑ The Associated General Contractors of America(AGC) (1976). The Use of CPM In Construction.
- ↑ Kim, Kyunghwan (2003). “A Resource-constrained CPM (RCPM) Scheduling and Control Technique with Multiple Calendars” - Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University PHD. Dissertation. - https://theses.lib.vt.edu/theses/available/etd-06272003-143644/unrestricted/ETD.pdf.
- ↑ Schwalbe, Kathy (2007). Information Technology Project Management 5th Edition.
- ↑ Scheduling projects: How to determine the critical path using activity slack calculations? - http://www.pmknowledgecenter.com/dynamic_scheduling/baseline/scheduling-projects-how-determine-critical-path-using-activity-slack-calculations - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016
- ↑ Six Sigma Daily (2012). “The Activity Network Diagram” - http://www.sixsigmadaily.com/the-activity-network-diagram/ - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016
- ↑ I.T. Toolkit. “How to Use Resource Leveling for Project Planning and Scheduling” - https://www.ittoolkit.com/how-to-it/projects/resource-leveling.html - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016
- ↑ Willem Hans, Elias (2001). “Resource Loading by branch-and-price Techniques” - Twente University Dissertation - https://www.utwente.nl/bms/iebis/staff/hans/phdhans.pdf - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016
- ↑ Durfee, W. (2008). “Project Planning and Gantt Charts” - University of Minnesota - http://www.me.umn.edu/courses/me2011/handouts/proj_planning.pdf - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016
- ↑ Gosenheimer, Carol. (2012). “Project Prioritization, A Structured Approach to Working on What Matters Most” - Office of Quality Improvement, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Division of Enrollment Management - https://oqi.wisc.edu/resourcelibrary/uploads/resources/Project_Prioritization_Guide_v_1.pdf - Online, Checked on 15/09/2016
- ↑ Jain, Ankur. “Using a Criteria-Based Matrix to Prioritize IT Projects” - I, Six Sigma - https://www.isixsigma.com/operations/information-technology/applying-criteria-based-matrix-prioritize-it-projects/ - Online, Checked on 16/09/2016
- ↑ Bonacorsi, Steven. (2011). “7 Steps to Using Prioritization Matrices” - PEX, Process Excellence Network - http://www.processexcellencenetwork.com/lean-six-sigma-business-transformation/articles/process-excellence-methodologies-using-prioritizat - Online, Checked on 16/09/2016
- ↑ National Research Council of the National Academies. “The Owner's Role in Project Risk Management” - Page 52