Dealing with conflicts (sources, escalation, containment)
From DTU ProjectLab
(Difference between revisions)
(→Perspectives on Conflicts) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
==Examples of Sources of Conflicts in Projects== | ==Examples of Sources of Conflicts in Projects== | ||
| − | + | [[File:Types-of-conflicts.JPG|frameless|center|600x240px]] | |
=When Controversy becomes Conflict= | =When Controversy becomes Conflict= | ||
| − | + | [[File:Controversy.JPG|frameless|center|895x385px]] | |
=Balancing Conflicts and Controversies in Groups= | =Balancing Conflicts and Controversies in Groups= | ||
| − | + | [[File:Balancing-controversies.JPG|frameless|center|620x455px]] | |
| − | + | '''Source:''' | |
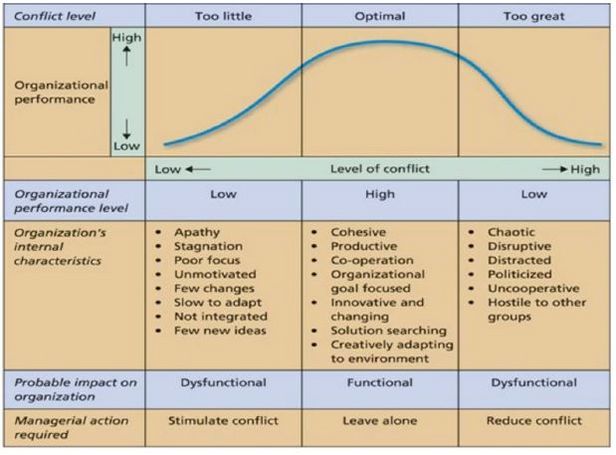
Huczynski & Buchanan (2011), Hatch (1997, p.305); Robbins (1998, p.464) | Huczynski & Buchanan (2011), Hatch (1997, p.305); Robbins (1998, p.464) | ||
Latest revision as of 13:19, 10 August 2017
Contents |
[edit] Definition of Conflict
- Conflict is an escalation of a disagreement, and is characterized by the existence of conflict behavior, in which people inolved are actively trying to damage one another.
(Nicholson, 1992)
- An interactive process manifested in incompatibility, disagreement or dissonance within or between social entities. (Rahim, 2010)
[edit] Perspectives on Conflicts
| Unitary view - conflicts are bad | Pluralist view - conflicts can be constructive if managed |
|---|---|
| Conflicts are negative and destructive | Controversy is a natural and constructive phenomena |
| The organization is a team where the members are expected to work towards a common goal | Organizations consist of different stakeholders who have different values, views, stories and goals |
| The common goal is defined by the management | Conflicts emerge as a consequence of colliding differences (controversies) that are not dealt with |
| Rational behavior is expected and is defined in accordance with company policy |
[edit] Types of Conflicts
[edit] Instrumental
Tangible issues like methods, procedures and semantics.
Approach: Problem solving to find the "best" solution
[edit] Interests
Allocation of resources like time, money, labor and space
Approach: Negotiation to find an agreement - enlarge the cake
[edit] Values
Political, moral and religious values
Approach: Dialogue to reach mutual understanding
[edit] Personal
Identity, self-esteem, loyalty, rejection etc.
Approach: Dialogue to reach mutual understanding
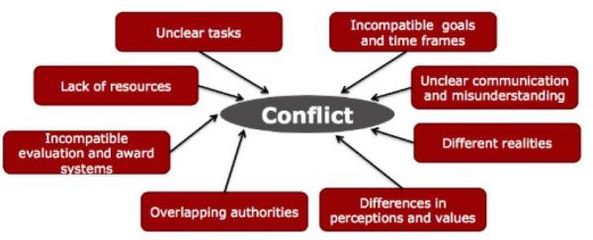
[edit] Examples of Sources of Conflicts in Projects
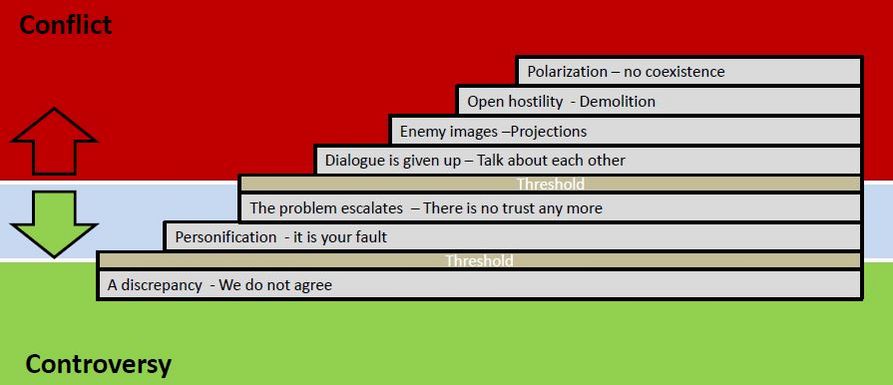
[edit] When Controversy becomes Conflict
[edit] Balancing Conflicts and Controversies in Groups
Source:
Huczynski & Buchanan (2011), Hatch (1997, p.305); Robbins (1998, p.464)