Power, politics and stakeholder management
| (64 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ''Developed by Joachim Schou Larsen'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Abstract== | ==Abstract== | ||
| − | + | When managing any kind of project, programme or portfolio, different issues can occur that have an either positive or negative affect on the total outcome. These issues can be many different internal or external factors, as for example: the economy, natural incidents, people with specific agendas etc. An area of great importance with regard to these issues is stakeholder management, and how to navigate and handle different people, groups and organisations with relation to the project. “''The ability of the project manager to correctly identify and manage these stakeholders in an appropriate manner can mean the difference between success and failure''”.<ref name="PMI">Project Management Institute, ''A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide), Fifth Edition'', 2013</ref> Additionally managers will have to consider different key areas related to stakeholder management if this should be a success. The internal politics within organisations and the power and influence revolving stakeholders is crucial and should be considered with attention to specific factors.<ref name="Hayes">Hayes J. ''The Theory And Practice Of Change Management, Fourth Edition'', 2014</ref> | |
| − | + | In this article stakeholders in relation to power and politics of different kind will be examined and the classic stakeholder-mapping tool is presented as well as an assessment for gaining power/influence in management. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The article comprises the following: | |
| − | + | ||
| + | 1. A description of when the stakeholder mapping is used and in the context it is applicable. Furthermore an explanation of how to acquire and exercising power/influence for management. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. An applications guide of how to perform the stakeholder mapping. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. A consideration of limitations within this topic. | ||
==Big idea== | ==Big idea== | ||
| − | + | Managers need to be able to identify stakeholders that can effect the outcome of a given project or process. This has to be done, to correctly assess and determine how the manager should handle the positive or negative attitudes with regards to the project. Moreover managers need to comprehend and deal with the politics of different organisations and understand that ''“Companies and other institutions are becoming more complex and pluralistic”''.<ref name="Hayes"/> According to John Hayes many organisations ''“can be conceptualized as a collection of constituencies, each pursuing their own objectives”''. <ref name="Hayes"/> It is to be considered that John Hayes looks at organisations as political arenas where individuals and groups will try to obtain their self-orientated goals by affecting others. This political standpoint presented by Hayes will claim that when detecting greater issues and conflicts of interests, the power and influence of different people or groups will decide how the issue is resolved. The standpoint concludes that no rational and logic argument will be the deciding factor, and therefore power and influence cannot be ignored by any sensible manager. | |
| + | |||
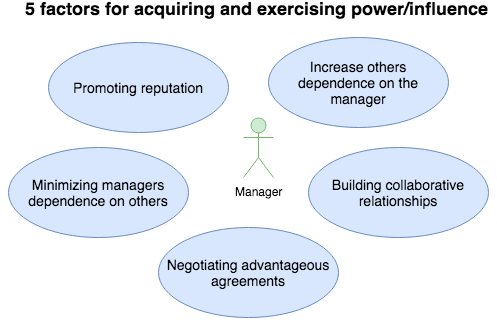
| + | After concluding this an explanation of John Hayes theory “5 factors for acquiring and exercising power/influence” will be described to display how a manager can use these factors in a favourable manner when handling stakeholders. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:5 factor for acquiring power.png|thumb|5 factors for acquiring power, adopted by John Hayes <ref name="Hayes"/>|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Managers and leaders can intensify their ability to influence others and gain power by promoting the five factors shown in the figure. Based on a study made by John Hayes in collaboration with product development engineers from different larger mechanical productions companies it was determined that ''“politically competent managers were those who paid attention to these factors”'' <ref name="Hayes"/> with the aim of making successful deliveries. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Promoting reputation''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | The first factor is promoting the reputation of the manager. Stakeholders will be more likely to accept and follow a manager when he/she is perceived to be competent and deliver the desired benefits. This means the manager not only need the right competencies but also need to be seen as a competent manager. As people, according to Hayes, will pay more attention to managers whom they perceive as competent, motivated and have the ability to affect outcomes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Increase others dependence on the manager''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | The next factor is in regards to the managers’ ability of influencing the targeted stakeholders by increasing their dependence on him/her. A manager can assess ‘others’ dependence by: | ||
| + | |||
| + | • Understanding what the stakeholders seek from the manager, ex. information, resources contacts etc. | ||
| + | |||
| + | • Consider how these recourses are important to the stakeholders. | ||
| + | |||
| + | • Investigate how easily the stakeholders can obtain the resources from others. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The bullets above will give some understanding of how dependent others are of the manager. But in order to exercise power it is also important that the stakeholders are aware of their dependency and the manager should make this clear more ore less discrete. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Minimizing managers dependence on others''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | After looking at the dependences stakeholders have to the manager, it is also important to consider own dependencies to others and minimize these as much as possible. Therefore the manager needs to identify to whom they have these dependencies and how to change the current situation. This can be done by looking at the following: | ||
| + | |||
| + | • Identify alternative sources of the given assets the manager requires | ||
| + | |||
| + | • Test existing agreements both internal and external where the manager sees stakeholders exercising power on them, and challenge these current dependency relationships. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Building collaborative relationships''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | The fourth factor examines the relationships between managers and those they are dependent on. Building collaborative relationships within this area should improve the manager’s ability to influence other stakeholders, as the relationships should support the agenda from the manager. The bullets below are essential for achieving this: | ||
| + | |||
| + | • Close relationships gives the manager the opportunity to identify resources and information that others may need, but currently does not have. Hereby creating new possible dependencies in favour of the manager to provide. | ||
| + | |||
| + | • Projects can have problems with limited recourses, not because they need more but the problem lies with those handling the resources, not knowing they are needed. Communication improvements facilitated by the manager should improve the problem. | ||
| + | |||
| + | • Improved relationships can also give a possibility of others using the new collaborative networks to impact third parties that elsewise would be unreachable for the management. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Negotiating advantageous agreements''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | The last factor revolves the issue of creating agreements that are of great advantaged for the project or company. It is stated by Hayes that most agreements are more or less based on a level of interdependence. Managers who are good at exercising power/influence on stakeholders should be aware of this statement by Hayes and realistically determine what the project or company can do for the stakeholder and visa versa. This should enable the manager to negotiate favourable working agreements that will support the project. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | When handling stakeholders it was concluded that the five factors presented above is of great importance. Now a guide for how to identify and manage stakeholders will be presented as an assessment tool to understand if and where the manager should exercise power/influence. | ||
==Application== | ==Application== | ||
| + | As stated in the previous section stakeholders or constituents are prone to behave in specific ways that can strengthen their power and ability to make desired outcomes happen. Therefore managers have to be alert with regard to this and identify important stakeholders, categorise them and analyse how to influence them, in order to achieve the desired success for the project. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As a tool for this managing process, the stakeholder map can be used. A guide for how to use the tool will be presented below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | When performing a stakeholder analysis it is important to look at it as a systematically process. Here the manager has to gather and analyse both quantitative and qualitative data and information with regards to those who should be considered having an impact throughout the project. This analysis should identify the interests, expectations and influence of different stakeholders and try to determine how they relate to the project. Furthermore an identification of stakeholder relationships could be developed and used to determine a power/influence strategy as described in the ‘Big idea’ section. | ||
| + | |||
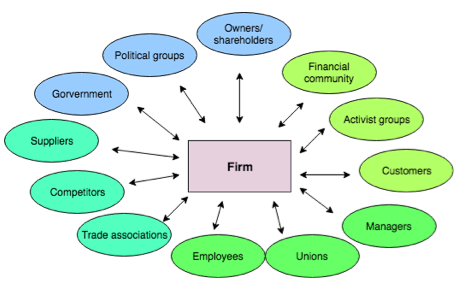
| + | 1. The first step of the analysis is identification of the different stakeholders. This step is sometimes referred to as the ‘Stakeholder brainstorm’ and involves a process where all who is possibly affected or/and could affect the outcome of the project is identified. This identification process is done by using the previous mentioned data and information. To make sure that all relevant stakeholders have been taken into account in this first step, interviews with already identified stakeholders can be an option to ‘search the market’. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Skærmbillede 2018-02-16 kl. 12.47.08.png|thumb|Stakeholders in a large organisation, adopted by ''Fundamentals of strategy'' <ref name="Fun">Johnson G.,Whittington R., Scholes K., Angwin D., Regnér P. ''Fundamentals Of Strategy, Third Edition'', 2015</ref>|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The figure is an illustration of different stakeholders in a large organisation.<ref name="Fun"/> This show how the different groups, people or companies affect the firm leading the project, but on the other hand can also be affected by the project as mentioned in step 1. All these different stakeholders can be a big challenge, especially if the organisation handling the project is large, because many different groups will have conflicting interests and expectations. With this issue taken into account managers will have to analyse the power of the stakeholders. | ||
| + | |||
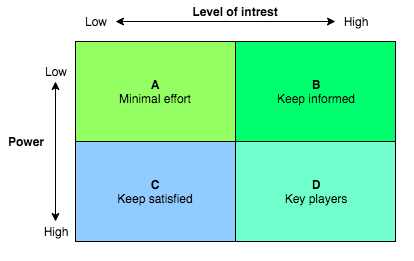
| + | 2. The second stage of the analysis comprises of an assessment of impact or support from each of the different stakeholders. This assessment should be done by classifying all the identified parties with regards to how much power and influence they have on the specific project. This classification should be done by using the power/interest grid in which the manager will categorise the stakeholders ''“based on their level of authority (power) and their level of concern (interest) regarding the project outcomes”'' <ref name="PMI"/> and place them in the matrix as seen below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Stakeholdermatrix.png|thumb|Stakeholder mapping: the power/interest matrix, adopted by ''Fundamentals of strategy'' <ref name="Fun"/>|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Though it might seem fairly easy to do the categorisation of the stakeholders, difficulties in this process can occur.<ref name="Hayes"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Two factors are of great importance when considering these difficulties: | ||
| + | |||
| + | • Individuals or organisations with known support of the project can potentially not be trusted because other groups or people within their organisation undermine their support. | ||
| + | |||
| + | • The second factor is with regards to assessing stakeholders with great power. There may be people or groups with a considerably big power connected to the project, but who has not exercised it in the past. This can be a risk if the stakeholder has drastically more power than expected or lately acquired the power to influence others and is handled inadequately by the manager.<ref name="Hayes"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. As the third and last stage of the stakeholder mapping the manager should evaluate all key stakeholders and determine how they are likely to respond in different situations as foreseen by the manager.<ref name="PMI"/> This should be done to plan how the project/company can influence and enhance potential support from the stakeholders and diminish potential negative effects. | ||
| + | In this stage power acquisition or/and exercising is highly relevant as the stakeholder mapping indicates where the manager should focus with regards to Hayes’ five factors of power. From the mapping process the manager should be able to determine which stakeholders are in the scope of being influenced by the power of the manager. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ex. stakeholders with high power should be approached with the factors regarding “Minimizing managers dependence on others” and “Building collaborative relationships”. With these factors the manager should examine alternatives for stakeholders with a negative approach, as the intention is to minimizing the possible power of the current stakeholder. In some cases this attitude to high power stakeholders can be difficult as some stakeholders is too involved in the project, and therefore the factor of “Building collaborative relationships” will be the more sensible strategy for the manager. With this power strategy, building close relationships should create the possibility of exploiting needed resources for both parties. Creating better and more trusted relationships, with ''“a basis for negotiation and trade”''.<ref name="Hayes"/> | ||
==Limitations== | ==Limitations== | ||
| + | Different issues regarding limitations for the article is presented below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | • '''Context:'''The position of different stakeholders in the power/interest matrix is highly possible to vary from different situations and issues. Therefor it is important to understand the context of which the analysis is performed and not as a manager be blind for new and unseen situations and approaches.<ref name="Fun"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | • '''Understanding of power:''' The five forces do not integrate other parameters of power into its theory. A well renowned research regarding power is the model of national culture and power distance by Geert Hofstede. <ref>Jones G., George J. ''Essentials of Contemporary management, Sixth Edition'', 2015</ref> This study examines more than 100.000 people from 64 different countries and concludes that many different dimensions can have an impact such as: individualism vs. collectivism, power distance, and uncertainty tolerance, etc. Therefore a manager should also consider in which cultural arena he/she is operating in with regards to affect power on stakeholders. | ||
| + | |||
| + | • '''Research background:''' The five factors by John Hayes are made by conducting a research with some large automotive and aerospace companies. The work was done by collaborating with the product development engineers within these companies and therefore some uncertainties can be stated if the factors are only representable in these mechanical production industries. | ||
| + | |||
| + | • '''The status quo:''' The area described in this article is indented to combine two areas of great relevance to each other. The theory of the stakeholder identification, assessment and management is a part of the standards, but when combining it with the area of assessment, acquisition and execution of power it should extend the topic of stakeholder management further. | ||
==Annotated bibliography== | ==Annotated bibliography== | ||
| − | [1] The book gives an overview of how to identify, and plan for management of stakeholders, as well as manage and control engagement with stakeholders in relation to project management. | + | [1] The book gives an overview of how to identify, and plan for management of stakeholders, as well as manage and control engagement with stakeholders in relation to project management. Furthermore this is a standard book produced by the Project Management Institute and therefor it covers many other topics within project management as project human recourse management, project risk management etc. |
| + | |||
| + | [2] The book is both a theoretical and practical lexicon when looking at change issues, with a wide range of areas covered. It looks at both identification of change, managing the people in regards to the change, and planning and implementation of the new project. Stakeholder management and the fundamentals of power and politics can also be found in this book. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [3] It is a concept book as the title states “Fundamentals of strategy”. This book deals with many different subjects all evolving around different areas of strategy. Among these the basic concepts of stakeholder management along with much more. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:34, 16 November 2018
Developed by Joachim Schou Larsen
Contents |
[edit] Abstract
When managing any kind of project, programme or portfolio, different issues can occur that have an either positive or negative affect on the total outcome. These issues can be many different internal or external factors, as for example: the economy, natural incidents, people with specific agendas etc. An area of great importance with regard to these issues is stakeholder management, and how to navigate and handle different people, groups and organisations with relation to the project. “The ability of the project manager to correctly identify and manage these stakeholders in an appropriate manner can mean the difference between success and failure”.[1] Additionally managers will have to consider different key areas related to stakeholder management if this should be a success. The internal politics within organisations and the power and influence revolving stakeholders is crucial and should be considered with attention to specific factors.[2]
In this article stakeholders in relation to power and politics of different kind will be examined and the classic stakeholder-mapping tool is presented as well as an assessment for gaining power/influence in management.
The article comprises the following:
1. A description of when the stakeholder mapping is used and in the context it is applicable. Furthermore an explanation of how to acquire and exercising power/influence for management.
2. An applications guide of how to perform the stakeholder mapping.
3. A consideration of limitations within this topic.
[edit] Big idea
Managers need to be able to identify stakeholders that can effect the outcome of a given project or process. This has to be done, to correctly assess and determine how the manager should handle the positive or negative attitudes with regards to the project. Moreover managers need to comprehend and deal with the politics of different organisations and understand that “Companies and other institutions are becoming more complex and pluralistic”.[2] According to John Hayes many organisations “can be conceptualized as a collection of constituencies, each pursuing their own objectives”. [2] It is to be considered that John Hayes looks at organisations as political arenas where individuals and groups will try to obtain their self-orientated goals by affecting others. This political standpoint presented by Hayes will claim that when detecting greater issues and conflicts of interests, the power and influence of different people or groups will decide how the issue is resolved. The standpoint concludes that no rational and logic argument will be the deciding factor, and therefore power and influence cannot be ignored by any sensible manager.
After concluding this an explanation of John Hayes theory “5 factors for acquiring and exercising power/influence” will be described to display how a manager can use these factors in a favourable manner when handling stakeholders.
Managers and leaders can intensify their ability to influence others and gain power by promoting the five factors shown in the figure. Based on a study made by John Hayes in collaboration with product development engineers from different larger mechanical productions companies it was determined that “politically competent managers were those who paid attention to these factors” [2] with the aim of making successful deliveries.
Promoting reputation
The first factor is promoting the reputation of the manager. Stakeholders will be more likely to accept and follow a manager when he/she is perceived to be competent and deliver the desired benefits. This means the manager not only need the right competencies but also need to be seen as a competent manager. As people, according to Hayes, will pay more attention to managers whom they perceive as competent, motivated and have the ability to affect outcomes.
Increase others dependence on the manager
The next factor is in regards to the managers’ ability of influencing the targeted stakeholders by increasing their dependence on him/her. A manager can assess ‘others’ dependence by:
• Understanding what the stakeholders seek from the manager, ex. information, resources contacts etc.
• Consider how these recourses are important to the stakeholders.
• Investigate how easily the stakeholders can obtain the resources from others.
The bullets above will give some understanding of how dependent others are of the manager. But in order to exercise power it is also important that the stakeholders are aware of their dependency and the manager should make this clear more ore less discrete.
Minimizing managers dependence on others
After looking at the dependences stakeholders have to the manager, it is also important to consider own dependencies to others and minimize these as much as possible. Therefore the manager needs to identify to whom they have these dependencies and how to change the current situation. This can be done by looking at the following:
• Identify alternative sources of the given assets the manager requires
• Test existing agreements both internal and external where the manager sees stakeholders exercising power on them, and challenge these current dependency relationships.
Building collaborative relationships
The fourth factor examines the relationships between managers and those they are dependent on. Building collaborative relationships within this area should improve the manager’s ability to influence other stakeholders, as the relationships should support the agenda from the manager. The bullets below are essential for achieving this:
• Close relationships gives the manager the opportunity to identify resources and information that others may need, but currently does not have. Hereby creating new possible dependencies in favour of the manager to provide.
• Projects can have problems with limited recourses, not because they need more but the problem lies with those handling the resources, not knowing they are needed. Communication improvements facilitated by the manager should improve the problem.
• Improved relationships can also give a possibility of others using the new collaborative networks to impact third parties that elsewise would be unreachable for the management.
Negotiating advantageous agreements
The last factor revolves the issue of creating agreements that are of great advantaged for the project or company. It is stated by Hayes that most agreements are more or less based on a level of interdependence. Managers who are good at exercising power/influence on stakeholders should be aware of this statement by Hayes and realistically determine what the project or company can do for the stakeholder and visa versa. This should enable the manager to negotiate favourable working agreements that will support the project.
When handling stakeholders it was concluded that the five factors presented above is of great importance. Now a guide for how to identify and manage stakeholders will be presented as an assessment tool to understand if and where the manager should exercise power/influence.
[edit] Application
As stated in the previous section stakeholders or constituents are prone to behave in specific ways that can strengthen their power and ability to make desired outcomes happen. Therefore managers have to be alert with regard to this and identify important stakeholders, categorise them and analyse how to influence them, in order to achieve the desired success for the project.
As a tool for this managing process, the stakeholder map can be used. A guide for how to use the tool will be presented below:
When performing a stakeholder analysis it is important to look at it as a systematically process. Here the manager has to gather and analyse both quantitative and qualitative data and information with regards to those who should be considered having an impact throughout the project. This analysis should identify the interests, expectations and influence of different stakeholders and try to determine how they relate to the project. Furthermore an identification of stakeholder relationships could be developed and used to determine a power/influence strategy as described in the ‘Big idea’ section.
1. The first step of the analysis is identification of the different stakeholders. This step is sometimes referred to as the ‘Stakeholder brainstorm’ and involves a process where all who is possibly affected or/and could affect the outcome of the project is identified. This identification process is done by using the previous mentioned data and information. To make sure that all relevant stakeholders have been taken into account in this first step, interviews with already identified stakeholders can be an option to ‘search the market’.
The figure is an illustration of different stakeholders in a large organisation.[3] This show how the different groups, people or companies affect the firm leading the project, but on the other hand can also be affected by the project as mentioned in step 1. All these different stakeholders can be a big challenge, especially if the organisation handling the project is large, because many different groups will have conflicting interests and expectations. With this issue taken into account managers will have to analyse the power of the stakeholders.
2. The second stage of the analysis comprises of an assessment of impact or support from each of the different stakeholders. This assessment should be done by classifying all the identified parties with regards to how much power and influence they have on the specific project. This classification should be done by using the power/interest grid in which the manager will categorise the stakeholders “based on their level of authority (power) and their level of concern (interest) regarding the project outcomes” [1] and place them in the matrix as seen below.
Though it might seem fairly easy to do the categorisation of the stakeholders, difficulties in this process can occur.[2]
Two factors are of great importance when considering these difficulties:
• Individuals or organisations with known support of the project can potentially not be trusted because other groups or people within their organisation undermine their support.
• The second factor is with regards to assessing stakeholders with great power. There may be people or groups with a considerably big power connected to the project, but who has not exercised it in the past. This can be a risk if the stakeholder has drastically more power than expected or lately acquired the power to influence others and is handled inadequately by the manager.[2]
3. As the third and last stage of the stakeholder mapping the manager should evaluate all key stakeholders and determine how they are likely to respond in different situations as foreseen by the manager.[1] This should be done to plan how the project/company can influence and enhance potential support from the stakeholders and diminish potential negative effects. In this stage power acquisition or/and exercising is highly relevant as the stakeholder mapping indicates where the manager should focus with regards to Hayes’ five factors of power. From the mapping process the manager should be able to determine which stakeholders are in the scope of being influenced by the power of the manager.
Ex. stakeholders with high power should be approached with the factors regarding “Minimizing managers dependence on others” and “Building collaborative relationships”. With these factors the manager should examine alternatives for stakeholders with a negative approach, as the intention is to minimizing the possible power of the current stakeholder. In some cases this attitude to high power stakeholders can be difficult as some stakeholders is too involved in the project, and therefore the factor of “Building collaborative relationships” will be the more sensible strategy for the manager. With this power strategy, building close relationships should create the possibility of exploiting needed resources for both parties. Creating better and more trusted relationships, with “a basis for negotiation and trade”.[2]
[edit] Limitations
Different issues regarding limitations for the article is presented below:
• Context:The position of different stakeholders in the power/interest matrix is highly possible to vary from different situations and issues. Therefor it is important to understand the context of which the analysis is performed and not as a manager be blind for new and unseen situations and approaches.[3]
• Understanding of power: The five forces do not integrate other parameters of power into its theory. A well renowned research regarding power is the model of national culture and power distance by Geert Hofstede. [4] This study examines more than 100.000 people from 64 different countries and concludes that many different dimensions can have an impact such as: individualism vs. collectivism, power distance, and uncertainty tolerance, etc. Therefore a manager should also consider in which cultural arena he/she is operating in with regards to affect power on stakeholders.
• Research background: The five factors by John Hayes are made by conducting a research with some large automotive and aerospace companies. The work was done by collaborating with the product development engineers within these companies and therefore some uncertainties can be stated if the factors are only representable in these mechanical production industries.
• The status quo: The area described in this article is indented to combine two areas of great relevance to each other. The theory of the stakeholder identification, assessment and management is a part of the standards, but when combining it with the area of assessment, acquisition and execution of power it should extend the topic of stakeholder management further.
[edit] Annotated bibliography
[1] The book gives an overview of how to identify, and plan for management of stakeholders, as well as manage and control engagement with stakeholders in relation to project management. Furthermore this is a standard book produced by the Project Management Institute and therefor it covers many other topics within project management as project human recourse management, project risk management etc.
[2] The book is both a theoretical and practical lexicon when looking at change issues, with a wide range of areas covered. It looks at both identification of change, managing the people in regards to the change, and planning and implementation of the new project. Stakeholder management and the fundamentals of power and politics can also be found in this book.
[3] It is a concept book as the title states “Fundamentals of strategy”. This book deals with many different subjects all evolving around different areas of strategy. Among these the basic concepts of stakeholder management along with much more.
[edit] References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide), Fifth Edition, 2013
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Hayes J. The Theory And Practice Of Change Management, Fourth Edition, 2014
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Johnson G.,Whittington R., Scholes K., Angwin D., Regnér P. Fundamentals Of Strategy, Third Edition, 2015
- ↑ Jones G., George J. Essentials of Contemporary management, Sixth Edition, 2015