Future workshop method
Marianna89 (Talk | contribs) (→Abstract) |
|||
| (57 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ''Developed by Maria Mamasoula'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Abstract== | ==Abstract== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Future Workshop method is a conceptual tool which is used for decision-making and problem solving, and gives the participants the opportunity to contribute and cooperate in order to draw a desirable future and find a way to implement it . This method focuses on finding new ways to examine a problem and allows the participants to find suitable solutions<ref name="rasmussen"> L. B. Rasmussen, Facilitating change: using interactive methods in organizations, communities and networks. Polyteknisk Forlag, 2011. </ref>. The Future Workshop method is applicable to almost any kind of problem and encourages the participants to use their creativity and imagination. Throughout Future workshop moderating tools like visualizations and open brainstorming are used, which enable out of the box-thinking and the creation of revolutionary ideas. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Future workshop consists of four phases: the preparatory phase, the critique phase, the fantasy phase and last, the implementation phase. During the preparatory phase the problem is introduced to the participants and the main topic is defined. This is followed by the critique phase which is the first phase of the workshop. During this phase the participants express their complaints and negative issues that lead to the problematic situation. Afterwards these complaints are discussed and finally clustered together. During the fantasy phase, the participants come up with ideas without boundaries using their imagination and create a utopian message. Again these ideas are discussed and clustered. Finally, at the last step which is the implementation phase the participants return to the current state putting boundaries. The purpose of this phase is for the participants to try to implement their creative ideas to the present situation and create an action plan. | ||
==Big idea== | ==Big idea== | ||
===History=== | ===History=== | ||
| − | ===Method Description=== | + | The origins of the Future Workshop method go back to the thirties and forties of the last century, although the explicit form of the method took place in the sixties. The father of the Future Workshop method, Robert Jungk, a journalist, activist and researcher, developed Future Workshop as a new tool that would help people to generate and implement creative ideas in order to live better together as a society. |
| + | |||
| + | ''"The Future Workshop is such a way. It helps people to develop creative ideas and projects for a better society. For trying to resist something is just part of the story. It is essential for people to know what they are fighting for, not just what they are fighting against <ref name="rasmussen"/>."'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore, the historical developments of the Future Workshop until the present are listed below as the following: | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''(1950-1960):''' | ||
| + | Action takes place through movement of citizens in the USA, first publication of the method | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''(1960-1970):''' | ||
| + | Future Workshop with five phases using participatory methods such as brainstorming and group work | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''(1970-1980):''' | ||
| + | Future Workshops with three phases with citizens working on actual problems | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''(1980-1990):''' | ||
| + | Recognition of the Future Workshop as a problem solving tool | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''(1990-2000):''' | ||
| + | Future Workshop is established.Organisations and other relevant groups show great interest to the method | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''(2000-present):''' | ||
| + | Future Workshop takes place in textbooks as a method amongst others, used for a big range of problems <ref name="rasmussen"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Phases and Method Description=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Phases==== | ||
| + | The Future Workshop is divided in four phases, a pre-phase and three workshop phases: | ||
| + | |||
| + | #'''Preparatory phase:'''The topic is introduced to the participants. The method and the rules are settled. Logistics such as the time table, space and facilities are also settled. | ||
| + | #'''Critique phase:'''The problem is discussed and the partcicipants express their complaints and negative experiences. Then the complaints are clustered together. | ||
| + | #'''Fantasy phase:'''The participants generate creative ideas without boundaries to create a utopian future. Afterwards these ideas are clustered together. | ||
| + | #'''Implementation phase:'''The participants come back to the current state and try to implement the creative ideas in order to create an action plan that will try to solve the current problem. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Method==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The best way for describing the Future Workshop method is the "funnel-technique" <ref name="rasmussen"/>. The shape of the funnel demonstrates the process of moving from the general part of the problem to the core of it. The funnel technique is used at every phase of the workshop and its purpose is to narrow down the problem and take decisions at the end of each phase. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:funneltechnique.png|frame|caption|Figure 1: The scheme of the Funnel technique <ref name="funnel"> Anne Tanner, “Future Workshop”, lecture presentation, 2017. [online] Available: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1IiLHmxMp3bt5kqf3v85ob5zrdfbkwqfB </ref>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Preparatory phase:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | For the preparatory phase the most important thing is the good planning of the workshop. It is crucial in order to avoid undesirable issues and conflicts and lead to good results. Keys for this phase: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Who are the participants? How will the participants will be divided into teams so equality will exist? | ||
| + | The background, education, sex, age of the participants are examined. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *How long will the workshop last? | ||
| + | The time table is settled. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The topic is defined. | ||
| + | The specific problem that needs to be solved is examined. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Location and facilities. | ||
| + | The space and the facilities are chosen. The room has to be comfortable for the participants and to create a nice environment. Thus, enough space should be for the required activities that will take place. Last but not least, rest rooms should be available as the workshop last long. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Materials to be used. | ||
| + | For the workshop phases materials such as flipcharts, posters, papers, pens, markers and post-its are required. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Food and drinks. | ||
| + | During the scheduled breaks, water, coffee, tea or other beverages and cake or fruits should be provided to the participants. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Critique phase:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | During the critique phase the participants express their grievances and negative experiences. All the participants should equally contribute and interact with each other. Keys for this phase: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The participants using brainstorming express all their complaints and draw them on paper. For this phase materials like papers, pens and post-its are used in order to visualise the problem. This step of the critique phase is located at the diverging part of the funnel technique, as open brainstorming is used. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The complaints are discussed by the participants to form the key problem and then grouped together according to the topic. The participants evaluate and prioritize the clusters. This step of the phase is located at the converging part of the funnel technique, as the complaints are clustered into groups. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The participants select the most important cluster for the topic and presented to the other groups. | ||
| + | |||
| + | At this phase, the role of the facilitator is really important in order to avoid possible conflicts between the participants. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Fantasy phase:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | During the fantasy face the participants generate creative ideas, without putting boundaries and where everything is possible in order to create an utopian future. The tools that are used for this purpose are meditation, story telling or role playing. Keys for this phase: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The participants using brainstorming and "out of the box" thinking, write down utopian ideas and draw them on paper. This step is placed at the diverging part of the funnel technique. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The participants discuss these ideas and cluster them into groups, evaluate and prioritize them. This step is placed at the converging part of the funnel technique. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The most important cluster of ideas is selected and presented to the other groups. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Again at this phase, the facilitator plays an important role since people have the tendency to put limits to their imagination. The facilitator has to remind them that everything is possible at this phase. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Implementation phase:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | During this phase, the participants choose the most important cluster of ideas from the previous phase and try to adapt these creative ideas to the real world, in order to create value for the current situation. Afterwards they try to implement these ideas by creating an action plan of what, how and where these ideas will take place. Keys for this phase: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The selected cluster of utopian ideas is discussed on how it can be adapted to the existing problem in the real world. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The participants create an action plan and try to implement these ideas. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The action plan is presented to the other groups. | ||
==Application== | ==Application== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Future Workshop method can be applied to almost any kind of problems, as it examines the problematic situation with a wide specter and the participants can actively evolve to find creative solutions to the problem <ref name="rasmussen"/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Due to the broad use of this method, many types of workshops are applied based on the kind of the problems to be solved: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Problem opening up:''' | ||
| + | For a quick opening of a topic or concern. It is used mostly for meetings, conferences and seminars and the participants are usually professionally interested persons. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Problem conferring:''' | ||
| + | For encouraging cooperation and creating prospects. It is used mostly for institutes, staff and working groups and the participants are usually dissatisfied persons. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Problem solving help:''' | ||
| + | For restructuring business. It is used mostly for organizations and the participants are usually the people that are affected by the problem. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Problem penetrating:''' | ||
| + | For looking into the conflicts and future issues. It is used mostly for institutions and churches and the participants are usually interested people in the situation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Problem sensibilising:''' | ||
| + | For solving problems of common interest. It is used mostly for schools, trainings and professional groups and the participants are usually people interested to the issue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Problem solving personally:''' | ||
| + | For dealing with personal fears and relations. It is used mostly for individuals or families and the participants are people that are affected personally by the issue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Limitations and weaknesses of FW== | ||
| + | |||
| + | As communication and interaction between people is not always easy and simple, Future workshop method have some weaknesses and limitations that are listed below <ref name="chapter6"> René Victor Valqui Vidal, The Future Work Shop. [online] Available: http://www.imm.dtu.dk/~rvvv/CPPS/6Chapter6Thefutureworkshop.pdf [Accessed 15 February 2018] </ref> : | ||
| + | |||
| + | *FW is an interactive method which focuses on problem solving. That means that conflicts may occur during the main phases of the workshop. It is crucial that the participants and the facilitator have the abilities to solve such conflicts. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Fantasy phase requires creativity for the generation of utopian ideas which is not such a simple process. Therefore, it is required that the creative tools will be carefully selected to be used. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The duration of the problem should be adjusted for every single Future Workshop. While sometimes nice ideas can be generated under time pressure, fantasy phase is a more difficult process. Also, long pauses can change the group’s dynamic and not lead to the desirable results. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *As the implementation phase can to an end and an action plan is developed, a question of who is going to carry out the action plan arises. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The role of the facilitator is very crucial. FW requires that the facilitator is experienced, communicative and able to resolve conflicts and issues that may occur. The facilitator should be engaged and motivated by the task. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *During the Future Workshop all the participants are equal. However, sometimes problems may arise due to the differences of the participants according to theis social status, education, sex and age. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Annotated bibliography== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li>'''L. B. Rasmussen, Facilitating change: using interactive methods in organizations, communities and networks. Polyteknisk Forlag, 2011.''' - In this article the tool is described thoroughly and gives insights of how and when the tool is used. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li>'''René Victor Valqui Vidal, The Future Work Shop.''' - In this paper extra useful insights are described for the tool such as the limitations of it. | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:48, 16 November 2018
Developed by Maria Mamasoula
Contents |
[edit] Abstract
The Future Workshop method is a conceptual tool which is used for decision-making and problem solving, and gives the participants the opportunity to contribute and cooperate in order to draw a desirable future and find a way to implement it . This method focuses on finding new ways to examine a problem and allows the participants to find suitable solutions[1]. The Future Workshop method is applicable to almost any kind of problem and encourages the participants to use their creativity and imagination. Throughout Future workshop moderating tools like visualizations and open brainstorming are used, which enable out of the box-thinking and the creation of revolutionary ideas.
The Future workshop consists of four phases: the preparatory phase, the critique phase, the fantasy phase and last, the implementation phase. During the preparatory phase the problem is introduced to the participants and the main topic is defined. This is followed by the critique phase which is the first phase of the workshop. During this phase the participants express their complaints and negative issues that lead to the problematic situation. Afterwards these complaints are discussed and finally clustered together. During the fantasy phase, the participants come up with ideas without boundaries using their imagination and create a utopian message. Again these ideas are discussed and clustered. Finally, at the last step which is the implementation phase the participants return to the current state putting boundaries. The purpose of this phase is for the participants to try to implement their creative ideas to the present situation and create an action plan.
[edit] Big idea
[edit] History
The origins of the Future Workshop method go back to the thirties and forties of the last century, although the explicit form of the method took place in the sixties. The father of the Future Workshop method, Robert Jungk, a journalist, activist and researcher, developed Future Workshop as a new tool that would help people to generate and implement creative ideas in order to live better together as a society.
"The Future Workshop is such a way. It helps people to develop creative ideas and projects for a better society. For trying to resist something is just part of the story. It is essential for people to know what they are fighting for, not just what they are fighting against [1]."
Therefore, the historical developments of the Future Workshop until the present are listed below as the following:
(1950-1960): Action takes place through movement of citizens in the USA, first publication of the method
(1960-1970): Future Workshop with five phases using participatory methods such as brainstorming and group work
(1970-1980): Future Workshops with three phases with citizens working on actual problems
(1980-1990): Recognition of the Future Workshop as a problem solving tool
(1990-2000): Future Workshop is established.Organisations and other relevant groups show great interest to the method
(2000-present): Future Workshop takes place in textbooks as a method amongst others, used for a big range of problems [1]
[edit] Phases and Method Description
[edit] Phases
The Future Workshop is divided in four phases, a pre-phase and three workshop phases:
- Preparatory phase:The topic is introduced to the participants. The method and the rules are settled. Logistics such as the time table, space and facilities are also settled.
- Critique phase:The problem is discussed and the partcicipants express their complaints and negative experiences. Then the complaints are clustered together.
- Fantasy phase:The participants generate creative ideas without boundaries to create a utopian future. Afterwards these ideas are clustered together.
- Implementation phase:The participants come back to the current state and try to implement the creative ideas in order to create an action plan that will try to solve the current problem.
[edit] Method
The best way for describing the Future Workshop method is the "funnel-technique" [1]. The shape of the funnel demonstrates the process of moving from the general part of the problem to the core of it. The funnel technique is used at every phase of the workshop and its purpose is to narrow down the problem and take decisions at the end of each phase.
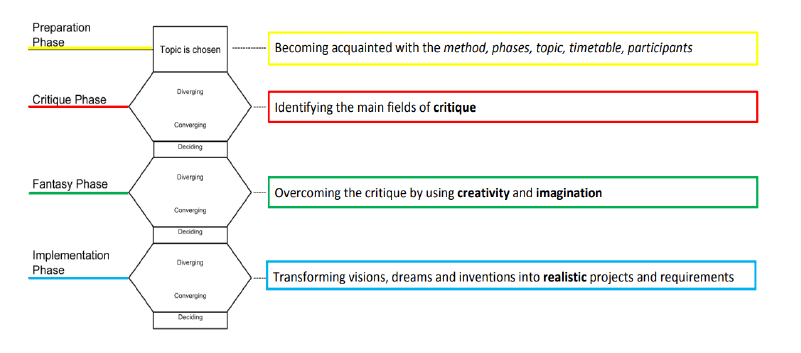
Preparatory phase:
For the preparatory phase the most important thing is the good planning of the workshop. It is crucial in order to avoid undesirable issues and conflicts and lead to good results. Keys for this phase:
- Who are the participants? How will the participants will be divided into teams so equality will exist?
The background, education, sex, age of the participants are examined.
- How long will the workshop last?
The time table is settled.
- The topic is defined.
The specific problem that needs to be solved is examined.
- Location and facilities.
The space and the facilities are chosen. The room has to be comfortable for the participants and to create a nice environment. Thus, enough space should be for the required activities that will take place. Last but not least, rest rooms should be available as the workshop last long.
- Materials to be used.
For the workshop phases materials such as flipcharts, posters, papers, pens, markers and post-its are required.
- Food and drinks.
During the scheduled breaks, water, coffee, tea or other beverages and cake or fruits should be provided to the participants.
Critique phase:
During the critique phase the participants express their grievances and negative experiences. All the participants should equally contribute and interact with each other. Keys for this phase:
- The participants using brainstorming express all their complaints and draw them on paper. For this phase materials like papers, pens and post-its are used in order to visualise the problem. This step of the critique phase is located at the diverging part of the funnel technique, as open brainstorming is used.
- The complaints are discussed by the participants to form the key problem and then grouped together according to the topic. The participants evaluate and prioritize the clusters. This step of the phase is located at the converging part of the funnel technique, as the complaints are clustered into groups.
- The participants select the most important cluster for the topic and presented to the other groups.
At this phase, the role of the facilitator is really important in order to avoid possible conflicts between the participants.
Fantasy phase:
During the fantasy face the participants generate creative ideas, without putting boundaries and where everything is possible in order to create an utopian future. The tools that are used for this purpose are meditation, story telling or role playing. Keys for this phase:
- The participants using brainstorming and "out of the box" thinking, write down utopian ideas and draw them on paper. This step is placed at the diverging part of the funnel technique.
- The participants discuss these ideas and cluster them into groups, evaluate and prioritize them. This step is placed at the converging part of the funnel technique.
- The most important cluster of ideas is selected and presented to the other groups.
Again at this phase, the facilitator plays an important role since people have the tendency to put limits to their imagination. The facilitator has to remind them that everything is possible at this phase.
Implementation phase:
During this phase, the participants choose the most important cluster of ideas from the previous phase and try to adapt these creative ideas to the real world, in order to create value for the current situation. Afterwards they try to implement these ideas by creating an action plan of what, how and where these ideas will take place. Keys for this phase:
- The selected cluster of utopian ideas is discussed on how it can be adapted to the existing problem in the real world.
- The participants create an action plan and try to implement these ideas.
- The action plan is presented to the other groups.
[edit] Application
Future Workshop method can be applied to almost any kind of problems, as it examines the problematic situation with a wide specter and the participants can actively evolve to find creative solutions to the problem [1].
Due to the broad use of this method, many types of workshops are applied based on the kind of the problems to be solved:
- Problem opening up:
For a quick opening of a topic or concern. It is used mostly for meetings, conferences and seminars and the participants are usually professionally interested persons.
- Problem conferring:
For encouraging cooperation and creating prospects. It is used mostly for institutes, staff and working groups and the participants are usually dissatisfied persons.
- Problem solving help:
For restructuring business. It is used mostly for organizations and the participants are usually the people that are affected by the problem.
- Problem penetrating:
For looking into the conflicts and future issues. It is used mostly for institutions and churches and the participants are usually interested people in the situation.
- Problem sensibilising:
For solving problems of common interest. It is used mostly for schools, trainings and professional groups and the participants are usually people interested to the issue.
- Problem solving personally:
For dealing with personal fears and relations. It is used mostly for individuals or families and the participants are people that are affected personally by the issue.
[edit] Limitations and weaknesses of FW
As communication and interaction between people is not always easy and simple, Future workshop method have some weaknesses and limitations that are listed below [3] :
- FW is an interactive method which focuses on problem solving. That means that conflicts may occur during the main phases of the workshop. It is crucial that the participants and the facilitator have the abilities to solve such conflicts.
- Fantasy phase requires creativity for the generation of utopian ideas which is not such a simple process. Therefore, it is required that the creative tools will be carefully selected to be used.
- The duration of the problem should be adjusted for every single Future Workshop. While sometimes nice ideas can be generated under time pressure, fantasy phase is a more difficult process. Also, long pauses can change the group’s dynamic and not lead to the desirable results.
- As the implementation phase can to an end and an action plan is developed, a question of who is going to carry out the action plan arises.
- The role of the facilitator is very crucial. FW requires that the facilitator is experienced, communicative and able to resolve conflicts and issues that may occur. The facilitator should be engaged and motivated by the task.
- During the Future Workshop all the participants are equal. However, sometimes problems may arise due to the differences of the participants according to theis social status, education, sex and age.
[edit] Annotated bibliography
- L. B. Rasmussen, Facilitating change: using interactive methods in organizations, communities and networks. Polyteknisk Forlag, 2011. - In this article the tool is described thoroughly and gives insights of how and when the tool is used.
- René Victor Valqui Vidal, The Future Work Shop. - In this paper extra useful insights are described for the tool such as the limitations of it.
[edit] References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 L. B. Rasmussen, Facilitating change: using interactive methods in organizations, communities and networks. Polyteknisk Forlag, 2011.
- ↑ Anne Tanner, “Future Workshop”, lecture presentation, 2017. [online] Available: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1IiLHmxMp3bt5kqf3v85ob5zrdfbkwqfB
- ↑ René Victor Valqui Vidal, The Future Work Shop. [online] Available: http://www.imm.dtu.dk/~rvvv/CPPS/6Chapter6Thefutureworkshop.pdf [Accessed 15 February 2018]