Roles and responsibilities of program manager
(→Tools) |
m |
||
| (142 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ''Developed by Nikoleta Kolitsopoulou-Maridaki'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZZZZRCNTDMc|350|right|Video 1: Introduction to the definition of Program Manager|frame}} | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZZZZRCNTDMc|350|right|Video 1: Introduction to the definition of Program Manager|frame}} | ||
| − | '''Roles and responsibilities of program manager''' are very complex | + | '''Roles and responsibilities of program manager''' are very complex and for that reason, it is difficult to define them. They can vary from simple managing multiple projects to managing multiple projects with operational responsibilities and to being accountable for profit or cost targets based on business strategy. Moreover, a program manager has the main supervision of the scope and status of several projects at once which all together consist the program in order to ensure that the program goals are achieved. This accumulation of responsibilities of a diversity of projects and operations means that the program manager should be able to balance business targets and operational performance. Their decisions are both tactical and strategical in nature. The program manager must establish an environment that allows the project managers to complete their projects successfully. In more detail, the main leadership duty is to bring more clarity to the team. Occasionally, the <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Project_management_office Project Management Office (PMO)]</span> may not have sufficient insight regarding design, requirements, risks, issues and their solution. In that case, a program manager may be well placed to accept calculated risk and then to clarify it in their own terms or to seek out such data from the project managers. In large and/or complex programs, a specific role of manager may be required for this specific task. However, the program manager needs this data in order to be confident that the overall program goals are achievable. <ref name="adv">.F.John Reh. November 26, 2017, ''‘The Role and Responsibilities of a Manager’'' [https://www.thebalance.com/what-is-a-manager-2276096]</ref> |
=Big Idea= | =Big Idea= | ||
==Origin of Program Manager== | ==Origin of Program Manager== | ||
| − | Program manager is first and foremost a leader, who delivers a business strategy that requires multiple coordinated projects. Furthermore, | + | Program manager is first and foremost a leader, who delivers a business strategy that requires multiple coordinated projects. Furthermore, they can be considered as a “super” <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Project_manager project manager]</span>. Their roles focus mainly on operational activities, because they are responsible for planning and supervising the successful completion of the program. Last but not least, the program manager should have previously multi-annual experience of being project manager for large and complex projects. <ref name="PMI1">.Zein Omar. January 1, 2010, ''‘Roles, responsibilities and skills in program management’'' / Project Management Institute [https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/roles-responsibilities-skills-program-management-6799]</ref> |
==Roles and responsibilities== | ==Roles and responsibilities== | ||
| − | <ref name="PMI1"></ref> <ref name="PMI2"></ref> <ref name="roles"> ''‘An Roinn Airgeadais’'', ''‘Roles and responsibilities of the Programme Manager’'' [https://www.finance-ni.gov.uk/articles/roles-and-responsibilities-programme-manager]</ref> <ref name="IBM"> .Michael F. Hanford. May 14, 2004,''‘Program management: Different from project management’'' [https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/rational/library/4751.html]</ref> <ref name="tool2"></ref> | + | The major roles and responsibilities of a program manager are listed below. <ref name="PMI1"></ref> <ref name="PMI2"></ref> <ref name="roles"> ''‘An Roinn Airgeadais’'', ''‘Roles and responsibilities of the Programme Manager’'' [https://www.finance-ni.gov.uk/articles/roles-and-responsibilities-programme-manager]</ref> <ref name="IBM"> .Michael F. Hanford. May 14, 2004,''‘Program management: Different from project management’'' [https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/rational/library/4751.html]</ref> <ref name="tool2"></ref> |
'''Planning''' | '''Planning''' | ||
| − | + | Initially, program managers are responsible for planning and scheduling the overall program from different perspectives and supervising the progress of it by creating a road-map, the daily <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Program_management Program Management]</span> throughout the whole program life cycle. In addition, they should be able to manage the main program documents (e.g., the <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Project_management Project Initiation Document - PID]</span>), that means to edit, version and store all management relevant artifacts. To fit all these responsibilities together, there are a lot of program management tools (<span class="plainlinks">[[#Tools|Tools]]</span>) that can be used for assigning tasks, adding comments, organizing dashboards and approvals. | |
'''Management and Assurance''' | '''Management and Assurance''' | ||
| − | Program managers have to focus also on the assessment and assurance of the proper functioning, the productivity, the quality and the progress of the program | + | Program managers have to focus also on the assessment and assurance of the proper functioning, the productivity, the quality and the progress of the program by continuously monitoring and validating it. For that reason, they should coordinate the separate projects and their inter-dependencies and interfaces. To manage this, they have to evaluate in a regular basis the performance of each project that is contained in the program and then to do reviews and reports on it. Specifically, they are responsible for review and then approve the different project plans. Before that, they have to ensure that the project plans are to the appropriate level of quality, on time, within budget and that they meet the requirements of the program scope, plan and governance arrangements. |
'''Alignment and Infrastructure''' | '''Alignment and Infrastructure''' | ||
| − | Program managers should also focus on the internal and external consistency of the program with the infrastructure planning and its interfaces with other programs. It is important because a program consists of several activities which take place at multiple levels and have different goals. Thus, the program manager has to clarify the vision | + | Program managers should also focus on the internal and external consistency of the program with the infrastructure planning and its interfaces with other programs. It is important because a program consists of several activities which take place at multiple levels and have different goals. Thus, the program manager has to clarify the vision and the goals of the program and then to align the separate projects objectives with the business/organizational strategy, in some cases with the aid of the business change manager. Apart from that, program managers are responsible for provision of infrastructure that a program needs for its proper function. This includes the program office technology, and other factors in the work environment that contribute to the development and the completion of the program. |
'''Governance''' | '''Governance''' | ||
| − | One of the most decisive roles of program managers is the creation and confirmation of the separate projects that consist the program with the project managers. They have to define the responsibilities and delegate | + | One of the most decisive roles of program managers is the creation and confirmation of the separate projects that consist the program with the project managers. |
| + | They have to define the responsibilities and delegate the tasks to project managers. In addition, they should track, manage and provide oversight to team activities and their performance throughout the entire program duration. They should be able to assist at any time the project managers if necessary. | ||
'''Improvement and Integration''' | '''Improvement and Integration''' | ||
| − | Another crucial role of program managers is to define the program governance (controls). Particularly, they are responsible for identifying, assessing and managing risks, issues, delays and deviations from required standards. Finally, they should be able decision-making and to resolve performance problems, so they can | + | Another crucial role of program managers is to define the program governance (controls). Particularly, they are responsible for identifying, assessing and managing risks, issues, delays and deviations from required standards. Finally, they should be able to make decisions (<span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision-making decision-making]</span>) and to resolve performance problems, so they can complete the program by improving and optimizing its performance. |
'''Finance''' | '''Finance''' | ||
| − | Managing and utilizing resources across program is also one of the responsibilities of program managers. They are accountable for executive budget and for financial management that means implementation of specific fiscal practices and controls. In more detail they have to track the costs of the program and manage its budget by monitoring expenditure and costs of | + | Managing and utilizing resources across the program is also one of the responsibilities of program managers. They are accountable for executive budget and for financial management that means implementation of specific fiscal practices and controls. In more detail they have to track the costs of the program and manage its budget by monitoring expenditure and costs of the program during its progress. |
'''Communication''' | '''Communication''' | ||
| − | Another role of program manager is to manage the stakeholder's communication | + | Another role of a program manager is to manage the stakeholder's communication, to communicate with the executive sponsors and the program's steering committee and finally to conduct periodic status updates. |
'''Leading''' | '''Leading''' | ||
| − | Finally, the coaching and developing of the employees either the existing or new ones could be a key role of program managers. They should be able to lead project managers and employees through high-level sessions either communicating knowledge about program and schedule development or motivating them. | + | Finally, the coaching and developing of the employees either the existing ones or new ones could be a key role of program managers. They should be able to lead project managers and employees through high-level sessions either communicating knowledge about program and schedule development or motivating them. |
| − | During complex and large programs, sometimes it is required, other managers to be | + | During complex and large programs, sometimes it is required, other type of managers to be hired who will contribute to the completion of the program manager work. They take over some of the program manager responsibilities that are listed above, for instance <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Risk_management Risk Management]</span>, Communication Management or <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benefits_realisation_management Benefits Realisation Management (BRM)]</span>. |
| − | They take over some of the program manager responsibilities that are listed above, for instance | + | |
=Application= | =Application= | ||
== Skills\Behaviors == | == Skills\Behaviors == | ||
| − | In order a program manager to accomplish all | + | In order a program manager to accomplish all the roles and responsibilities should have some skills and behaviors. A lot of surveys have be carried out to find out which should be the required behaviors of a successful Program Manager and they resulted that although knowledge about business is significant, there is more importance on program management skills. The most crucial of them are the following four policies: <ref name="PMI1"></ref> <ref name="roles"></ref> <ref name="Key"></ref> |
| − | 1. First of all a | + | 1. First of all a program manager has to see the organization strategically and for that are needed: |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | *Strategic/Critical thinking - plan and foresee future implications, thinking broadly, understanding the long term impacts of decisions and the meaningful goals | |
| − | * | + | *The capability to clarify team dynamics and communicate the organizational culture |
| − | * | + | *Effective leadership and management skills - how to set priorities and motivate the team managers, to instigate constructive changes and simultaneously helping the team members to adapt to them through positive feedback and coaching |
| − | + | *The ability to find innovative ways either for solving or forecasting problems | |
| − | + | 2. Another skill is to understand how to lead the organization toward the future: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | *Analyzing cases effectively and making sound decisions | |
| + | *Setting and achieving short and long term goals | ||
| + | *Driving results from two perspectives - delivering results personally by following commitments and requirements of a program and achieving business objectives through others by holding people accountable | ||
| − | + | 3. Working harmoniously with others is a very important feature that the manager needs to have: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | *Communication and collaboration skills - expressing ideas clearly while taking into account the views of others and supporting cross-functional efforts and model collaborative policies to set the example for the team | |
| − | *Good knowledge and handling of project and program management methodology and techniques | + | *The ability to create relationship amongst the members of the program teams which are based on trust and respect, maintaining confidence and keeping commitments |
| − | + | ||
| − | *sound business case | + | 4. Knowledge about specific fields: |
| + | |||
| + | *Good knowledge of finance - understand the way that a firm invests its funds and secure that these investments make a good profit for the company | ||
| + | *Good handling of project and program management methodology - understand and leverage formal project management techniques to ensure timely completion and proper control of initiatives | ||
| + | *The ability to develop a sound business case | ||
== Tools == | == Tools == | ||
| Line 106: | Line 105: | ||
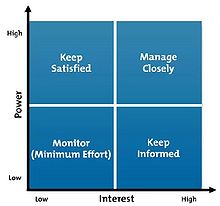
|'''RACI diagram''' | |'''RACI diagram''' | ||
|Governance | |Governance | ||
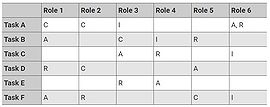
| − | |The RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) diagram is a tool through that the program manager can define the roles and responsibilities of each participant in the program activities | + | |The RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) diagram is a tool through that the program manager can define the roles and responsibilities of each participant in the program activities regarding producing predetermined deliverables. RACI, an acronym which is composed by four participatory program's roles : |
| − | #responsible: those who undertake | + | #responsible: those who undertake tasks or the resources |
| − | #accountable: those who | + | #accountable: those who get the credit for success or responsibility for failure or the activity manager |
| − | #consulted: those whose | + | #consulted: those whose advice and opinion are asked |
| − | #informed: those who are | + | #informed: those who are notified in regular basis of progress |
There is also an expanded version, the RACI-VS that can also be used, adding the following roles: | There is also an expanded version, the RACI-VS that can also be used, adding the following roles: | ||
| − | #verifies: check if the product fulfills the quality criteria that | + | #verifies: those who check if the product fulfills the quality criteria that defined in the product description |
| − | #signs off: those who | + | #signs off: those who approve the verification decision and confirm the product delivery |
| + | |||
|[[File:h.jpg|270px|]] | |[[File:h.jpg|270px|]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
|- | |- | ||
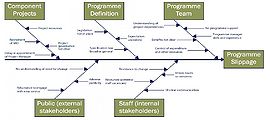
|'''Cause and effect diagram''' | |'''Cause and effect diagram''' | ||
| − | | | + | |Align internal and external consistency of the program |
|The cause and effect diagram is also known as fish-bone diagram. It is diagram which illustrates the causes of various events and the impacts that they have on the examined program. Each diagram consists from several start points (A points) and one or more end points (B points). | |The cause and effect diagram is also known as fish-bone diagram. It is diagram which illustrates the causes of various events and the impacts that they have on the examined program. Each diagram consists from several start points (A points) and one or more end points (B points). | ||
|[[File:c.jpg|270px|]] | |[[File:c.jpg|270px|]] | ||
| Line 147: | Line 147: | ||
=Comparison with project manager= | =Comparison with project manager= | ||
[[File:2.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Figure 5: Comparison of behaviors between project and program manager. (click to zoom) <ref name="Key">.Lynda Carter, Kristin Tull and Donna VanRooy. ''‘Key Leadership Behaviors Necessary to Advance in Project Management’'', ''‘Project/Program Management Research’'' [file:///C:/Users/nikol/Downloads/Key%20Leadership%20Behaviors%202013%20BW%20PRADCO.pdf]</ref>]] | [[File:2.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Figure 5: Comparison of behaviors between project and program manager. (click to zoom) <ref name="Key">.Lynda Carter, Kristin Tull and Donna VanRooy. ''‘Key Leadership Behaviors Necessary to Advance in Project Management’'', ''‘Project/Program Management Research’'' [file:///C:/Users/nikol/Downloads/Key%20Leadership%20Behaviors%202013%20BW%20PRADCO.pdf]</ref>]] | ||
| − | Program | + | Frequently, the processes of projects and programs are described as being similar in nature due to their close link, although they are different in detailed level. <ref name="PMI2">.Blomquist Tomas, Müller Ralf. January 2004, ''‘Program and portfolio managers’'', ''‘analysis of roles and responsibilities’'' / Project Management Institute [https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/program-portfolio-managers-analysis-roles-responsibilities-8315]</ref> For that reason, the differences of these two concepts are presented in this article. Program managers are often described as the higher organizational hierarchy level over project managers. They are specified as the combination between higher management and operational-level implementation of a company's tasks. <ref name="Pell"></ref> A program is as a set of projects managed together in order to achieve a higher-level common scope, that will be impossible if each of these projects acts alone. <ref name="Pell">.Pellegrinelli, S. 2002, ''‘Shaping context: The role and challenge for programmes. International Journal of Project Management, ch.20, p.229-233’'', </ref> |
| − | + | The main difference between a program manager and a project manager can be described by two actions: creation and compliance. The former one is responsible for creating the business environment culture and the project manager should comply with it. Furthermore, the project manager's responsibilities are based on the triptych of time, cost, and scope of the project. On the other hand, the program manager is judged not only on these three subjects but also on a level that is cumulative for all the projects and operations within the program. This summation of responsibilities for a variety of projects and operations means that the program manager should manage frequent trade-offs between business targets and project/operational performances. Moreover, program management decisions have basically strategic character. The strategy aspects must take into account multidimensional impacts beyond the short-term deliveries of the projects. In contrast to the program manager, the project manager should complete and deliver projects within the time schedule and based on the instructions set by the program manager. To sum up, the project manager should focus on deliveries and execution of the projects whereas the program manager is also responsible for the overall organization and efficacy of the program over the long-term. <ref name="br1">.James T Brown. 2008, ''‘The Handbook of Program Management: How to Facilitate Project Success with Optimal Program Management ’'' </ref> | |
=Example= | =Example= | ||
| − | [[File:3.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[File:3.jpg|thumb|right|170px|Figure 6: Managers in construction. (click to zoom) <ref name="Blog1">.Christopher Dunne. December 2, 2015, ''‘Blog: Drive to Discover’'', ''‘Construction Management, Program Management and Project Management: What's the Difference?’'' [http://www.weareharris.com/blog/archive/difference-between-construction-management-program-management-and-project-management]</ref>]] |
| − | Big construction companies often undertake complicated projects, such the construction of metro. In this case, the program manager has the largest portfolio, which includes multiple projects on multiple sites and the program manager should be responsible for all the metro stations. Program managers have the overarching control, budget and schedule of a program. If the owner is not an expert in facility design and construction, the program manager provides leadership in this field. | + | Big construction companies often undertake complicated projects, such the construction of metro. In this case, the program manager has the largest portfolio, which includes multiple projects on multiple sites and the program manager should be responsible for all these separate projects which in that case are the different metro stations. Program managers have the overarching control, budget and schedule of a program. If the owner is not an expert in facility design and construction, the program manager provides leadership in this field. They cooperate with the stakeholders, including the client, the superintendent, and district officials. Moreover, in this example, the program manager defines the project managers, each of them has to manage the work on one of the metro stations. They are responsible for pre-design, design process, construction, integration and delivery of the project. In recent years, the construction manager has been joined as a member to the project-process. They are the most appropriate to provide important knowledge during the design and construction phase. |
'''How they can coordinate together:''' | '''How they can coordinate together:''' | ||
| − | + | A big challenge of a construction program is that each manager has a distinct set of responsibilities and they should know exactly what are their roles on a project. That means that the program manager has to define these roles from the beginning of the program and make it clear for all the team members. The clearer is for each of them, even better result will come out. In that case, the responsibilities of a construction manager focus only on site-works, dealing directly with the contractor, project and program managers. The program manager works basically from an office and visits the different sites, if required. About the project manager, he has to be mainly at the construction site to supervise the activities and spend less time at the office to report to the program manager about the program progress. | |
The same philosophy applies to smaller and also larger construction programs involving multiple projects, such as airports. | The same philosophy applies to smaller and also larger construction programs involving multiple projects, such as airports. | ||
=Limitations= | =Limitations= | ||
| + | |||
| + | Although it seems that a program manager contributes for a better development and performance of a program avoiding issues and problems during its process, there are ways in which the program may evolve wrongly. Some of the most common limitations are outlined below: <ref name="lim">.David Goulden. October 10, 2017, ''‘The Advantages and Disadvantages of Project Portfolio Management’'' [https://www.clarizen.com/advantages-disadvantages-project-portfolio-management/]</ref> | ||
| + | *Firstly, the role of a program manager could become too bureaucratic and have a lot of constrains on the program development. That means that the program manager has a more implementing role than assisting essentially the process of the program. | ||
| + | *To clarify the responsibilities for each of the team members seems to be an easy job, especially if the program ranges on a small scale. However, in case that the program is more complex, it is necessary to define the roles, tasks and prioritize them, otherwise it may complicate its evolution. An extension of this limitation could be the wrong allocating of resources, which should distribute evenly according to the program needs in order the program to be accomplished properly. | ||
| + | *Additionally, a program manager can not guarantee that the program will follow the original scope because of constant change. This limitation is one of the main reason why a lot of programs are completed either over their initial budget or with delays. For that reason, Program Management recognizes the formal participation of <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Change_management Change Management]</span> in the program. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =See also= | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Related subjects''' | ||
| + | * <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Project_management_office Project Management Office (PMO)]</span> | ||
| + | * <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Project_management Project Initiation Document - PID]</span> | ||
| + | * <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Project_manager project manager]</span> | ||
| + | * <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Program_management Program Management]</span> | ||
| + | * <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision-making decision-making]</span> | ||
| + | * <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Risk_management Risk Management]</span> | ||
| + | * <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benefits_realisation_management Benefits Realisation Management (BRM)]</span>. | ||
| + | * <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Change_management Change Management]</span> | ||
| + | |||
=Reference= | =Reference= | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
=Annotated Bibliography= | =Annotated Bibliography= | ||
| + | |||
| + | #'''Roles, responsibilities and skills in program management''': ''This paper taken from the PMI web page captures the meanings of program and project management. It aims to clarify the main roles, responsibilities and skills in program and project managers.'' | ||
| + | #'''Program management: Different from project management''''': The purpose of this article is to analyze the main aspects of program management. They are summarized to five categories: governance, management, financial management, infrastructure and planning. Each of these features is explained analytically in this article and simultaneously is compared with those of project management. It also points out for each of these aspects the effort and outcomes needed in order to achieve success.'' | ||
Latest revision as of 18:45, 16 November 2018
Developed by Nikoleta Kolitsopoulou-Maridaki
Roles and responsibilities of program manager are very complex and for that reason, it is difficult to define them. They can vary from simple managing multiple projects to managing multiple projects with operational responsibilities and to being accountable for profit or cost targets based on business strategy. Moreover, a program manager has the main supervision of the scope and status of several projects at once which all together consist the program in order to ensure that the program goals are achieved. This accumulation of responsibilities of a diversity of projects and operations means that the program manager should be able to balance business targets and operational performance. Their decisions are both tactical and strategical in nature. The program manager must establish an environment that allows the project managers to complete their projects successfully. In more detail, the main leadership duty is to bring more clarity to the team. Occasionally, the Project Management Office (PMO) may not have sufficient insight regarding design, requirements, risks, issues and their solution. In that case, a program manager may be well placed to accept calculated risk and then to clarify it in their own terms or to seek out such data from the project managers. In large and/or complex programs, a specific role of manager may be required for this specific task. However, the program manager needs this data in order to be confident that the overall program goals are achievable. [1]
Contents |
[edit] Big Idea
[edit] Origin of Program Manager
Program manager is first and foremost a leader, who delivers a business strategy that requires multiple coordinated projects. Furthermore, they can be considered as a “super” project manager. Their roles focus mainly on operational activities, because they are responsible for planning and supervising the successful completion of the program. Last but not least, the program manager should have previously multi-annual experience of being project manager for large and complex projects. [2]
[edit] Roles and responsibilities
The major roles and responsibilities of a program manager are listed below. [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
Planning
Initially, program managers are responsible for planning and scheduling the overall program from different perspectives and supervising the progress of it by creating a road-map, the daily Program Management throughout the whole program life cycle. In addition, they should be able to manage the main program documents (e.g., the Project Initiation Document - PID), that means to edit, version and store all management relevant artifacts. To fit all these responsibilities together, there are a lot of program management tools (Tools) that can be used for assigning tasks, adding comments, organizing dashboards and approvals.
Management and Assurance
Program managers have to focus also on the assessment and assurance of the proper functioning, the productivity, the quality and the progress of the program by continuously monitoring and validating it. For that reason, they should coordinate the separate projects and their inter-dependencies and interfaces. To manage this, they have to evaluate in a regular basis the performance of each project that is contained in the program and then to do reviews and reports on it. Specifically, they are responsible for review and then approve the different project plans. Before that, they have to ensure that the project plans are to the appropriate level of quality, on time, within budget and that they meet the requirements of the program scope, plan and governance arrangements.
Alignment and Infrastructure
Program managers should also focus on the internal and external consistency of the program with the infrastructure planning and its interfaces with other programs. It is important because a program consists of several activities which take place at multiple levels and have different goals. Thus, the program manager has to clarify the vision and the goals of the program and then to align the separate projects objectives with the business/organizational strategy, in some cases with the aid of the business change manager. Apart from that, program managers are responsible for provision of infrastructure that a program needs for its proper function. This includes the program office technology, and other factors in the work environment that contribute to the development and the completion of the program.
Governance
One of the most decisive roles of program managers is the creation and confirmation of the separate projects that consist the program with the project managers. They have to define the responsibilities and delegate the tasks to project managers. In addition, they should track, manage and provide oversight to team activities and their performance throughout the entire program duration. They should be able to assist at any time the project managers if necessary.
Improvement and Integration
Another crucial role of program managers is to define the program governance (controls). Particularly, they are responsible for identifying, assessing and managing risks, issues, delays and deviations from required standards. Finally, they should be able to make decisions (decision-making) and to resolve performance problems, so they can complete the program by improving and optimizing its performance.
Finance
Managing and utilizing resources across the program is also one of the responsibilities of program managers. They are accountable for executive budget and for financial management that means implementation of specific fiscal practices and controls. In more detail they have to track the costs of the program and manage its budget by monitoring expenditure and costs of the program during its progress.
Communication
Another role of a program manager is to manage the stakeholder's communication, to communicate with the executive sponsors and the program's steering committee and finally to conduct periodic status updates.
Leading
Finally, the coaching and developing of the employees either the existing ones or new ones could be a key role of program managers. They should be able to lead project managers and employees through high-level sessions either communicating knowledge about program and schedule development or motivating them.
During complex and large programs, sometimes it is required, other type of managers to be hired who will contribute to the completion of the program manager work. They take over some of the program manager responsibilities that are listed above, for instance Risk Management, Communication Management or Benefits Realisation Management (BRM).
[edit] Application
[edit] Skills\Behaviors
In order a program manager to accomplish all the roles and responsibilities should have some skills and behaviors. A lot of surveys have be carried out to find out which should be the required behaviors of a successful Program Manager and they resulted that although knowledge about business is significant, there is more importance on program management skills. The most crucial of them are the following four policies: [2] [4] [7]
1. First of all a program manager has to see the organization strategically and for that are needed:
- Strategic/Critical thinking - plan and foresee future implications, thinking broadly, understanding the long term impacts of decisions and the meaningful goals
- The capability to clarify team dynamics and communicate the organizational culture
- Effective leadership and management skills - how to set priorities and motivate the team managers, to instigate constructive changes and simultaneously helping the team members to adapt to them through positive feedback and coaching
- The ability to find innovative ways either for solving or forecasting problems
2. Another skill is to understand how to lead the organization toward the future:
- Analyzing cases effectively and making sound decisions
- Setting and achieving short and long term goals
- Driving results from two perspectives - delivering results personally by following commitments and requirements of a program and achieving business objectives through others by holding people accountable
3. Working harmoniously with others is a very important feature that the manager needs to have:
- Communication and collaboration skills - expressing ideas clearly while taking into account the views of others and supporting cross-functional efforts and model collaborative policies to set the example for the team
- The ability to create relationship amongst the members of the program teams which are based on trust and respect, maintaining confidence and keeping commitments
4. Knowledge about specific fields:
- Good knowledge of finance - understand the way that a firm invests its funds and secure that these investments make a good profit for the company
- Good handling of project and program management methodology - understand and leverage formal project management techniques to ensure timely completion and proper control of initiatives
- The ability to develop a sound business case
[edit] Tools
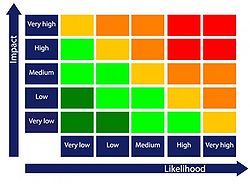
The roles and the responsibilities of a program manager can be performed using a wide set of tools. These techniques can be used to develop ideas and thinking in a program management environment. There are plenty of them and depending on the type of program are differed. On the Table below, the most important tools and techniques that can be used by program managers related to the roles and responsibilities that are referred above, are presented. [6] [8]
[edit] Comparison with project manager
Frequently, the processes of projects and programs are described as being similar in nature due to their close link, although they are different in detailed level. [3] For that reason, the differences of these two concepts are presented in this article. Program managers are often described as the higher organizational hierarchy level over project managers. They are specified as the combination between higher management and operational-level implementation of a company's tasks. [9] A program is as a set of projects managed together in order to achieve a higher-level common scope, that will be impossible if each of these projects acts alone. [9]
The main difference between a program manager and a project manager can be described by two actions: creation and compliance. The former one is responsible for creating the business environment culture and the project manager should comply with it. Furthermore, the project manager's responsibilities are based on the triptych of time, cost, and scope of the project. On the other hand, the program manager is judged not only on these three subjects but also on a level that is cumulative for all the projects and operations within the program. This summation of responsibilities for a variety of projects and operations means that the program manager should manage frequent trade-offs between business targets and project/operational performances. Moreover, program management decisions have basically strategic character. The strategy aspects must take into account multidimensional impacts beyond the short-term deliveries of the projects. In contrast to the program manager, the project manager should complete and deliver projects within the time schedule and based on the instructions set by the program manager. To sum up, the project manager should focus on deliveries and execution of the projects whereas the program manager is also responsible for the overall organization and efficacy of the program over the long-term. [10]
[edit] Example

Big construction companies often undertake complicated projects, such the construction of metro. In this case, the program manager has the largest portfolio, which includes multiple projects on multiple sites and the program manager should be responsible for all these separate projects which in that case are the different metro stations. Program managers have the overarching control, budget and schedule of a program. If the owner is not an expert in facility design and construction, the program manager provides leadership in this field. They cooperate with the stakeholders, including the client, the superintendent, and district officials. Moreover, in this example, the program manager defines the project managers, each of them has to manage the work on one of the metro stations. They are responsible for pre-design, design process, construction, integration and delivery of the project. In recent years, the construction manager has been joined as a member to the project-process. They are the most appropriate to provide important knowledge during the design and construction phase.
How they can coordinate together:
A big challenge of a construction program is that each manager has a distinct set of responsibilities and they should know exactly what are their roles on a project. That means that the program manager has to define these roles from the beginning of the program and make it clear for all the team members. The clearer is for each of them, even better result will come out. In that case, the responsibilities of a construction manager focus only on site-works, dealing directly with the contractor, project and program managers. The program manager works basically from an office and visits the different sites, if required. About the project manager, he has to be mainly at the construction site to supervise the activities and spend less time at the office to report to the program manager about the program progress.
The same philosophy applies to smaller and also larger construction programs involving multiple projects, such as airports.
[edit] Limitations
Although it seems that a program manager contributes for a better development and performance of a program avoiding issues and problems during its process, there are ways in which the program may evolve wrongly. Some of the most common limitations are outlined below: [12]
- Firstly, the role of a program manager could become too bureaucratic and have a lot of constrains on the program development. That means that the program manager has a more implementing role than assisting essentially the process of the program.
- To clarify the responsibilities for each of the team members seems to be an easy job, especially if the program ranges on a small scale. However, in case that the program is more complex, it is necessary to define the roles, tasks and prioritize them, otherwise it may complicate its evolution. An extension of this limitation could be the wrong allocating of resources, which should distribute evenly according to the program needs in order the program to be accomplished properly.
- Additionally, a program manager can not guarantee that the program will follow the original scope because of constant change. This limitation is one of the main reason why a lot of programs are completed either over their initial budget or with delays. For that reason, Program Management recognizes the formal participation of Change Management in the program.
[edit] See also
Related subjects
- Project Management Office (PMO)
- Project Initiation Document - PID
- project manager
- Program Management
- decision-making
- Risk Management
- Benefits Realisation Management (BRM).
- Change Management
[edit] Reference
- ↑ .F.John Reh. November 26, 2017, ‘The Role and Responsibilities of a Manager’ [1]
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 .Zein Omar. January 1, 2010, ‘Roles, responsibilities and skills in program management’ / Project Management Institute [2]
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 .Blomquist Tomas, Müller Ralf. January 2004, ‘Program and portfolio managers’, ‘analysis of roles and responsibilities’ / Project Management Institute [3]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 ‘An Roinn Airgeadais’, ‘Roles and responsibilities of the Programme Manager’ [4]
- ↑ .Michael F. Hanford. May 14, 2004,‘Program management: Different from project management’ [5]
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 .Jason Westland. May 30, 2017, ‘Best Program Management Tools for Managers’, ‘6 Tools That Help Manage Programs’ / Project Manager [6]
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 .Lynda Carter, Kristin Tull and Donna VanRooy. ‘Key Leadership Behaviors Necessary to Advance in Project Management’, ‘Project/Program Management Research’ [file:///C:/Users/nikol/Downloads/Key%20Leadership%20Behaviors%202013%20BW%20PRADCO.pdf]
- ↑ ‘An Roinn Airgeadais’, ‘Programme and project management tools and techniques’ [7]
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 .Pellegrinelli, S. 2002, ‘Shaping context: The role and challenge for programmes. International Journal of Project Management, ch.20, p.229-233’,
- ↑ .James T Brown. 2008, ‘The Handbook of Program Management: How to Facilitate Project Success with Optimal Program Management ’
- ↑ .Christopher Dunne. December 2, 2015, ‘Blog: Drive to Discover’, ‘Construction Management, Program Management and Project Management: What's the Difference?’ [8]
- ↑ .David Goulden. October 10, 2017, ‘The Advantages and Disadvantages of Project Portfolio Management’ [9]
[edit] Annotated Bibliography
- Roles, responsibilities and skills in program management: This paper taken from the PMI web page captures the meanings of program and project management. It aims to clarify the main roles, responsibilities and skills in program and project managers.
- Program management: Different from project management: The purpose of this article is to analyze the main aspects of program management. They are summarized to five categories: governance, management, financial management, infrastructure and planning. Each of these features is explained analytically in this article and simultaneously is compared with those of project management. It also points out for each of these aspects the effort and outcomes needed in order to achieve success.