Atkins APPPM
Cloefierri (Talk | contribs) (→SWOT Model) |
Cloefierri (Talk | contribs) (→Description :) |
||
| (59 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
The different tools developed in this article below are divided in categories : | The different tools developed in this article below are divided in categories : | ||
| − | 1. Change Management : - | + | 1. Change Management : - Kotter’s 8-step change model |
| − | - | + | - Lewin’s three-step process |
- PEST Analysis Model | - PEST Analysis Model | ||
| − | - Maslow Hierarchy of needs | + | - Maslow's Hierarchy of needs |
- Managing Change: A process perspective | - Managing Change: A process perspective | ||
- Expectancy theory and the motivation to support or resist change | - Expectancy theory and the motivation to support or resist change | ||
2. Stakeholder Management : - Influence and Interest Stakeholder Matrix | 2. Stakeholder Management : - Influence and Interest Stakeholder Matrix | ||
| − | - | + | - A classification model of stakeholder theory definitions - Miles |
| − | - | + | - Salience Model (Power, Legitimacy, Urgency) |
- Ladder of engagement | - Ladder of engagement | ||
3. Project Management : | 3. Project Management : | ||
| − | + | a) Purpose : - Golden Circle (Why, How and What) | |
- SWOT Model | - SWOT Model | ||
- Key Performance Indicators(KPI) | - Key Performance Indicators(KPI) | ||
- Benefits Realization Management to Maximize Project Effectiveness (BRM) | - Benefits Realization Management to Maximize Project Effectiveness (BRM) | ||
| − | + | b) Uncertainty : - Management of Project Change | |
| − | + | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | === Kotter === | + | === Kotter’s 8-step change model === |
| + | |||
| + | ==== Description : ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | John P. Kotter has created the change model which consist of 8-steps that need to be considered in order to succeed with the implementation of a change. The 8 steps of the model are divided into 3 phases. The first phase concerns the creation of the climate for change. The first step is crucial in order to start the change process as the step concerns the creation of urgency. The first phase also consists of establishing a powerful coalition, who are the ones who play an active part in order to implement the changes. The coalition is most effective if it consists of people from different areas. Furthermore, a clear vision for the change must be created. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The second phase concerns engaging and establishing the organization. This is done through the steps of communicate the vision, empower action and create quick wins. The coalition must communicate the vision. Subsidiary goals can be created in order to motivate involved. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The last phase of the model concerns implementing and sustaining for change. It is at this stage that the changes get fully implemented. It takes time, energy and patience to reach these steps of the model. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Kotter1.png|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kotter, J. P., 1997. I spidsen for forandringer. 1. red. s.l.:Peter Asschenfeldt nye Forlag a/s. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | === Lewin === | + | |
| + | === Lewin’s three-step process === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Description : ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lewin has created a three-step process for understanding individual, group or organizational change. The three steps (from Change management document) are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Unfreeze or unlock the existing level of behaviour | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Move to a new level | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Refreeze behaviour at this new level | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The first step involves the preparing for the acceptance of the change. It involves breaking down the existing status quo in order to build a new one. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The second step is the change stage where people starts moving to a new level, by believe and act in ways that support the new direction. This step can be time consuming because people need to accept the change. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The third step concerns the reinforcement of the new behaviour. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
| + | https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newPPM_94.htm | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | |||
=== PEST Analysis Model === | === PEST Analysis Model === | ||
| + | ==== Description : ==== | ||
The PEST Analysis is a change management tool useful for revealing the direction of change in the business environment and to develop an objective view of this environment. It helps to shape what a company is doing in order to work with change instead of working against the change. To use the pest analysis, and analyse the business environment, the opportunities and the threats, we have to follow the 3 different steps: | The PEST Analysis is a change management tool useful for revealing the direction of change in the business environment and to develop an objective view of this environment. It helps to shape what a company is doing in order to work with change instead of working against the change. To use the pest analysis, and analyse the business environment, the opportunities and the threats, we have to follow the 3 different steps: | ||
| Line 54: | Line 90: | ||
[[File:PEST 2.png|300px]] | [[File:PEST 2.png|300px]] | ||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMC_09.htm | https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMC_09.htm | ||
---- | ---- | ||
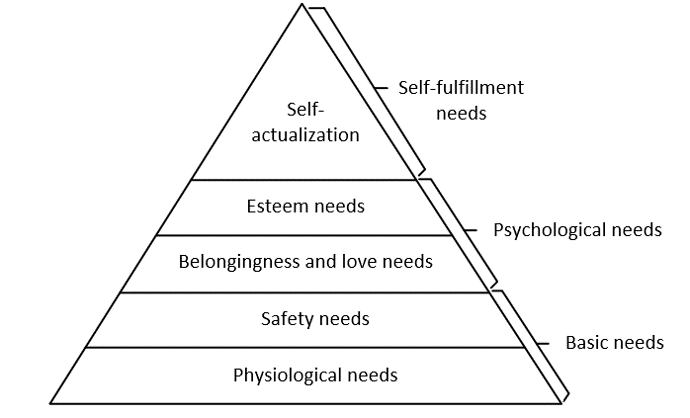
| − | === Maslow Hierarchy of needs === | + | === Maslow's Hierarchy of needs === |
| + | |||
| + | ==== Description : ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to better understand what it takes for the individual to feel secure and satisfied, Maslow’s hierarchy of needs can be used. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The two bottom steps in the pyramid represents the basic needs which is also the needs which have to be maintained when chancing the structure of the company. These needs evolve around having a nice and need environment where it is nice to be, and to create a space where the people feel safe and secure. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The next two steps in the pyramid represents the psychological needs. It is here important to make the individual feel like he or she belongs in the team, so that the individual can create relation to his/her co-workers. It is also in the step of psychological needs that it is important to boost the self-esteem of the individual. In order to get well functioning employees in an organisation, it is important to acknowledge them, give them responsibility over different tasks and in that way ensure that they will feel that they are accomplishing something. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The top step of the pyramid evolves about the self-fulfilment needs. In order to get the most out of the individual it is necessary to make the individual feel that he/she are achieving one’s full potential. This can be a very hard task because it can be necessary to pressure the individual in order to accomplish this, but it is a very fine balance to do this, but not to pressure the individual too much. It is important to give credit when results are achieved. | ||
| + | [[File:Maslow1.png]] | ||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
| + | S. McLeod, “Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs,” SimplePsychology, 2018. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | |||
=== Managing Change: A process perspective === | === Managing Change: A process perspective === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Description : ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following model introduces the conceptual theories and frameworks that define the process of a change from its need’s recognition to its implantation and sustainability. The managers who are leading the change (for example in a form of a large project) can use this framework to identify issues that need to be addressed. This model and its steps may appear obvious to some, but it is the essence of successful change management. Acknowledging the following 5 steps is necessary in order to manage change successfully and to secure a desired outcome. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Process Perspective.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The theory and practise of change management, John Hayes | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | |||
=== Expectancy theory and the motivation to support or resist change === | === Expectancy theory and the motivation to support or resist change === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Description : ==== | ||
| + | This model is based on expectancy theory that considers how expectations influence motivation. The model offers a useful conceptual framework for assessing whether a stakeholder is likely to support or resist an approaching change. The project managers leading the project/change can use the expectancy model to assess and improve the perceived attractiveness of the outcomes and construct relationships between effort and performance and the achievement of outcomes. The first step in the assessment of how stakeholders will react to change is to identify how the change will affect the availability of valued outcomes in the changed situation. When employees are faced with an approaching change, they often fear that they will lose some of the outcomes they value in the existing situation. The expectancy model allows to address those challenges and asses effort-performance and performance-outcome relationships. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Expectancy model.png]] | ||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
| + | The theory and practise of change management, John Hayes | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | |||
=== Influence and Interest Stakeholder Matrix === | === Influence and Interest Stakeholder Matrix === | ||
| + | ==== Description : ==== | ||
Before being able to complete the Influence and Interest stakeholder matrix there are few steps of the Stakeholders analysis to follow (see figure 1). When all the information about the stakeholder are gathered the mapping step can start to get this visual tool. | Before being able to complete the Influence and Interest stakeholder matrix there are few steps of the Stakeholders analysis to follow (see figure 1). When all the information about the stakeholder are gathered the mapping step can start to get this visual tool. | ||
| Line 72: | Line 144: | ||
[[File:Stakeholder Matrix.png|800px]] | [[File:Stakeholder Matrix.png|800px]] | ||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
Source: Stakeholder matrix - key matrices for stakeholder analysis [[https://www.stakeholdermap.com/stakeholder-matrix.html]] | Source: Stakeholder matrix - key matrices for stakeholder analysis [[https://www.stakeholdermap.com/stakeholder-matrix.html]] | ||
| Line 79: | Line 152: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | === | + | === A classification model of stakeholder theory definitions - Miles === |
| − | - | + | |
| − | === | + | ==== Description : ==== |
| − | -- | + | |
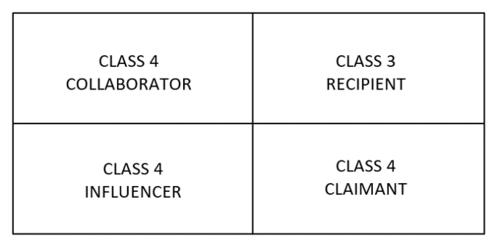
| + | A classification model of stakeholder theory definitions represented by Miles, can be used in order to identify the impact of power, interest and influence of the stakeholder. The model is divided into the four stakeholder classes influencer, collaborator, claimant and recipient. | ||
| + | |||
| + | - An influencer is a stakeholder who has the capacity to influence the actions of an organisation and has an active strategy to do so. | ||
| + | |||
| + | - A collaborator is a stakeholder that cooperates with an organisation but with no active interest to influence the organisation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | - A claimant is a stakeholder who has a claim on an organisation. With this claim the stakeholder has an active strategy to pursue the claim, but no power to guarantee that the claim is attended by the management. | ||
| + | |||
| + | - A recipient is a passive stakeholder, who is a receiver of the impact of organisational activity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | - A stakeholder is not necessarily defined by one of the four categories but can be a combination of two or more stakeholder types. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Miles.png|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
| + | S. Miles, “Stakeholder Theory Classification: A Theoretical and Empirical,” Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht, pp. 437-459, 26 06 2015 | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Salience Model (Power, Legitimacy, Urgency) === | ||
| + | |||
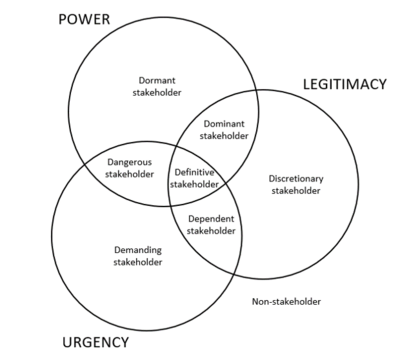
| + | ==== Description : ==== | ||
| + | The model is based upon the three stakeholder attributes: Power, Legitimacy and Urgency. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The stakeholder attribute Power is defined as a relationship among social actors in which one social actor, A, can get another social actor, B, to do something that B would not have otherwise done (Mitchell, Agle, & Wood, 1997). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Legitimacy is defined as a generalized perception or assumption that, the actions of an entity are desirable, proper, or appropriate within some socially constructed system of norms, values, beliefs, definitions (Mitchell, Agle, & Wood, 1997). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Urgency defines the degree to which stakeholder claims call for immediate attention (Mitchell, Agle, & Wood, 1997). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Together the three stakeholder attributes create seven different classifications of stakeholders. The seven classifications are possessing one, two or three of the stakeholder attributes. The stakeholders possessing one stakeholder attributes is characterized as latent stakeholders these are dormant, discretionary, and demanding stakeholders. Expectant stakeholders are those possessing two attributes, and include dominant, dependent, and dangerous. Definitive stakeholders are those possessing all three attributes. Individuals or entities possessing none of the attributes are non-stakeholders or potential stakeholders (Mitchell, Agle, & Wood, 1997). The model forms the basis for categorization of stakeholders in order to obtain a better understanding of how each stakeholder is to be handled. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Salience.png|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
| + | R. K. Mitchell, B. R. Agle and D. J. Wood, “Toward a Theory of Stakeholder Identification and Salience: Defining the Principle of Whoand What Really Counts,” Academy of Management, pp. 853-886, 10 1997. | ||
| + | |||
=== Ladder of engagement === | === Ladder of engagement === | ||
| − | - | + | |
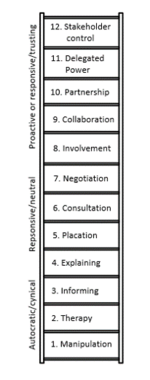
| + | ==== Description : ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File: Ladder.png|150px|thumb|left]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The ladder of stakeholder engagement is a model that intend to illustrate degrees of the quality of stakeholder management from the perspective of the stakeholders (Friedman & Miles, 2006). The ladder can be used in order to describe the relationship between the stakeholders and the organization, as it focuses on the objectives of engagement, tools and communication strategies. The ladder consists of twelve levels. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The lower levels relate to situations where the organization is informing the stakeholders about decisions that have already taken place. There is no engagement and no or limited participation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The lower middle levels involve the offering of some symbolic gestures of participation, where stakeholder’s voices are heard, but not necessarily taken into consideration. The scope is to obtain information of stakeholder concerns and provide response to the concerns. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The higher middle levels involve high level of engagement and involvement but no definitive power. It is an organizational process to enable stakeholder to have influence. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The highest levels concern high level of engagement and involvement and high levels of stakeholder power and control. The stakeholders have at these levels decision-making power and can make decisions independently of the organization. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
| + | A. L. Friedman and S. Miles, Stakeholders: Theory and Pratice, OUP Oxford, 2006 | ||
| + | |||
=== Golden Circle (Why, How and What) === | === Golden Circle (Why, How and What) === | ||
| + | |||
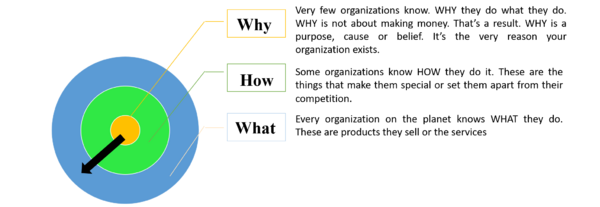
| + | ==== Description : ==== | ||
A key aspect in project management is to establish a strong vision. There are many ways to establish a vision and the Golden Circle Model is one of them. This management tool is based on 3 concentric circles corresponding to three questions: Why, How and What. To use this tool, developed by Simon Sinek, an organization/ a leader/ people must think from inside out to drive projects purposefully. The WHY question starts by identifying the purpose of the project (shall not be answered with something as making money because it’s a consequence), then the HOW question describes how the project is conducted and finally the WHAT is what is being done in the project. | A key aspect in project management is to establish a strong vision. There are many ways to establish a vision and the Golden Circle Model is one of them. This management tool is based on 3 concentric circles corresponding to three questions: Why, How and What. To use this tool, developed by Simon Sinek, an organization/ a leader/ people must think from inside out to drive projects purposefully. The WHY question starts by identifying the purpose of the project (shall not be answered with something as making money because it’s a consequence), then the HOW question describes how the project is conducted and finally the WHAT is what is being done in the project. | ||
| Line 91: | Line 232: | ||
[[File:Golden Circle.png|600px]] | [[File:Golden Circle.png|600px]] | ||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
Wiki APPPM, Why, How, What (The Golden Circle Model), [ONLINE] Available at: [[http://apppm.man.dtu.dk/index.php/Why,_How,_What_(The_Golden_Circle_Model)]] [Accessed 04 March 2020] | Wiki APPPM, Why, How, What (The Golden Circle Model), [ONLINE] Available at: [[http://apppm.man.dtu.dk/index.php/Why,_How,_What_(The_Golden_Circle_Model)]] [Accessed 04 March 2020] | ||
| Line 97: | Line 239: | ||
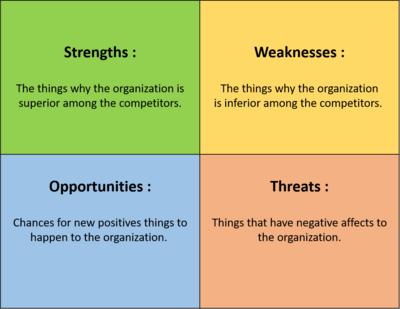
=== SWOT Model === | === SWOT Model === | ||
| − | ====Description==== | + | ====Description :==== |
The SWOT analysis provides information about the current position of an organization. It is an extraordinary useful business tool since gives information about the internal Strengths and Weaknesses of the organization and the external Opportunities and Threats. By applying the SWOT analysis, the organization can take the best advantages and at the same time reduce the chances of failure by understanding the weak points of the organization and avoid risks that they would be fatal for the well-being of the organization. | The SWOT analysis provides information about the current position of an organization. It is an extraordinary useful business tool since gives information about the internal Strengths and Weaknesses of the organization and the external Opportunities and Threats. By applying the SWOT analysis, the organization can take the best advantages and at the same time reduce the chances of failure by understanding the weak points of the organization and avoid risks that they would be fatal for the well-being of the organization. | ||
| Line 103: | Line 245: | ||
[[File:SWOT.png|400px]] | [[File:SWOT.png|400px]] | ||
| − | ====References==== | + | ====References :==== |
https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMC_05.htm | https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMC_05.htm | ||
| Line 114: | Line 256: | ||
=== Key Performance Indicators(KPI) === | === Key Performance Indicators(KPI) === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Description : ==== | ||
| + | While the scope and terms of an organization’s KPIs may differ from project to project, there are various types of data that can be helpful to any organization. Top project management benchmarking measures include return on investment (ROI), productivity, cost performance, cycle time, customer satisfaction, schedule performance, employee satisfaction and alignment with strategic business goals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Examples of KPIs within project management include: | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Project schedule | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Estimate to project completion | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Current development backlog | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Labor costs spent per month | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Current resource allocation | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Too often, organizations blindly adopt industry-recognized KPIs and then wonder why that KPI doesn't reflect their own business and fails to affect any positive change. One of the most important, but often overlooked, aspects of KPIs is that they are a form of communication. As such, they abide by the same rules and best-practices as any other form of communication. Succinct, clear and relevant information is much more likely to be absorbed and acted upon | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.floridatechonline.com/blog/business/key-performance-indicators-in-project-management/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.klipfolio.com/resources/articles/what-is-a-key-performance-indicator | ||
| + | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | |||
=== Benefits Realization Management to Maximize Project Effectiveness (BRM) === | === Benefits Realization Management to Maximize Project Effectiveness (BRM) === | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==== Description : ==== | ||
| − | + | Benefits realization management (BRM) provides organizations with a way to measure how projects and programs add true value to the enterprise. | |
| − | - | + | - IDENTIFY BENEFITS to determine whether projects, programs, and portfolios can produce the intended business results. |
| − | - | + | - EXECUTE BENEFITS management to minimize risks to future benefits and maximize the opportunity to gain additional benefits. |
| − | - | + | - SUSTAIN BENEFITS to ensure that whatever the project or program produces continues to create value. |
| + | |||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
| + | https://www.pmi.org/-/media/pmi/documents/public/pdf/learning/thought-leadership/benefits-realization-management-framework.pdf | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | === Management of Project Change === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Description : ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Changes arise in broad projects across all the different departments. Change management is a wide collective term and could have application into many different types of organization. The most relevant and common approaches are to help, prepare and support individuals, teams, groups, and organization in order to make and establish the changes. The most popular change drivers include technological evolution, process reviews, crisis, and consumer habit changes; pressure from new business entrants, acquisitions, mergers, and organizational restricting. (ref. https://www.hucmi.com/en/hcmbok/ ). The advantages of this tools are that make the organization more flexible and ready for changes, helps the people to understand the kind of change that is required, bring the people closer, and last but not least delivers change that are really effective and efficient for the organization | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==== References : ==== | ||
| − | + | https://www.hucmi.com/en/hcmbok/ | |
| − | - | + | https://www.strategy-business.com/article/rr00006?gko=dab72 |
| − | + | https://the-happy-manager.com/tips/benefits-of-change-management/ | |
| − | + | ||
Latest revision as of 08:48, 10 March 2020
Group name : Lecanaj
[edit] Introduction
Atkins Denmark is an engineering consultancy firm with around 400 employees in Denmark. They provide consultancy primarily on civil engineering work such as road and trail projects. Atkins Denmark's primary resource is delivering their expertise to the client. The aim of this project is to handle the problem that Atkins Denmark are forced to deliver their expertise to the client in a more efficient and better way in order to keep up with the competition on the market. A method for achieving this can be to implement digitisation in the for of internal digital project management practices in the company.
This wiki article is a collection of management tool that our group can use to analyse the digitalization of Atkins.
[edit] Management tools
The different tools developed in this article below are divided in categories :
1. Change Management : - Kotter’s 8-step change model
- Lewin’s three-step process
- PEST Analysis Model
- Maslow's Hierarchy of needs
- Managing Change: A process perspective
- Expectancy theory and the motivation to support or resist change
2. Stakeholder Management : - Influence and Interest Stakeholder Matrix
- A classification model of stakeholder theory definitions - Miles
- Salience Model (Power, Legitimacy, Urgency)
- Ladder of engagement
3. Project Management :
a) Purpose : - Golden Circle (Why, How and What)
- SWOT Model
- Key Performance Indicators(KPI)
- Benefits Realization Management to Maximize Project Effectiveness (BRM)
b) Uncertainty : - Management of Project Change
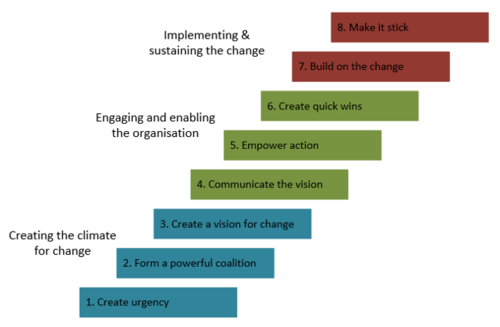
[edit] Kotter’s 8-step change model
[edit] Description :
John P. Kotter has created the change model which consist of 8-steps that need to be considered in order to succeed with the implementation of a change. The 8 steps of the model are divided into 3 phases. The first phase concerns the creation of the climate for change. The first step is crucial in order to start the change process as the step concerns the creation of urgency. The first phase also consists of establishing a powerful coalition, who are the ones who play an active part in order to implement the changes. The coalition is most effective if it consists of people from different areas. Furthermore, a clear vision for the change must be created.
The second phase concerns engaging and establishing the organization. This is done through the steps of communicate the vision, empower action and create quick wins. The coalition must communicate the vision. Subsidiary goals can be created in order to motivate involved.
The last phase of the model concerns implementing and sustaining for change. It is at this stage that the changes get fully implemented. It takes time, energy and patience to reach these steps of the model.
[edit] References :
Kotter, J. P., 1997. I spidsen for forandringer. 1. red. s.l.:Peter Asschenfeldt nye Forlag a/s.
[edit] Lewin’s three-step process
[edit] Description :
Lewin has created a three-step process for understanding individual, group or organizational change. The three steps (from Change management document) are:
- Unfreeze or unlock the existing level of behaviour
- Move to a new level
- Refreeze behaviour at this new level
The first step involves the preparing for the acceptance of the change. It involves breaking down the existing status quo in order to build a new one.
The second step is the change stage where people starts moving to a new level, by believe and act in ways that support the new direction. This step can be time consuming because people need to accept the change.
The third step concerns the reinforcement of the new behaviour.
[edit] References :
https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newPPM_94.htm
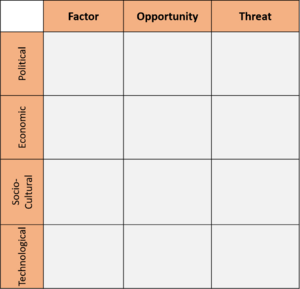
[edit] PEST Analysis Model
[edit] Description :
The PEST Analysis is a change management tool useful for revealing the direction of change in the business environment and to develop an objective view of this environment. It helps to shape what a company is doing in order to work with change instead of working against the change. To use the pest analysis, and analyse the business environment, the opportunities and the threats, we have to follow the 3 different steps:
1. First the PEST model is used to brainstorm the changes. The 4 factors discussed in this phase are explained in figure 1. The questioning will be guided by this figure.
2. After that, a second brainstorm is made dealing with the opportunities arising from each of these changes.
3. Then, a last brainstorm is done about threats/issues caused by opportunities.
The following figure is a document that can be fulfilled during this 3 steps :
[edit] References :
https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMC_09.htm
[edit] Maslow's Hierarchy of needs
[edit] Description :
In order to better understand what it takes for the individual to feel secure and satisfied, Maslow’s hierarchy of needs can be used.
The two bottom steps in the pyramid represents the basic needs which is also the needs which have to be maintained when chancing the structure of the company. These needs evolve around having a nice and need environment where it is nice to be, and to create a space where the people feel safe and secure.
The next two steps in the pyramid represents the psychological needs. It is here important to make the individual feel like he or she belongs in the team, so that the individual can create relation to his/her co-workers. It is also in the step of psychological needs that it is important to boost the self-esteem of the individual. In order to get well functioning employees in an organisation, it is important to acknowledge them, give them responsibility over different tasks and in that way ensure that they will feel that they are accomplishing something.
The top step of the pyramid evolves about the self-fulfilment needs. In order to get the most out of the individual it is necessary to make the individual feel that he/she are achieving one’s full potential. This can be a very hard task because it can be necessary to pressure the individual in order to accomplish this, but it is a very fine balance to do this, but not to pressure the individual too much. It is important to give credit when results are achieved.
[edit] References :
S. McLeod, “Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs,” SimplePsychology, 2018.
[edit] Managing Change: A process perspective
[edit] Description :
The following model introduces the conceptual theories and frameworks that define the process of a change from its need’s recognition to its implantation and sustainability. The managers who are leading the change (for example in a form of a large project) can use this framework to identify issues that need to be addressed. This model and its steps may appear obvious to some, but it is the essence of successful change management. Acknowledging the following 5 steps is necessary in order to manage change successfully and to secure a desired outcome.
[edit] References :
The theory and practise of change management, John Hayes
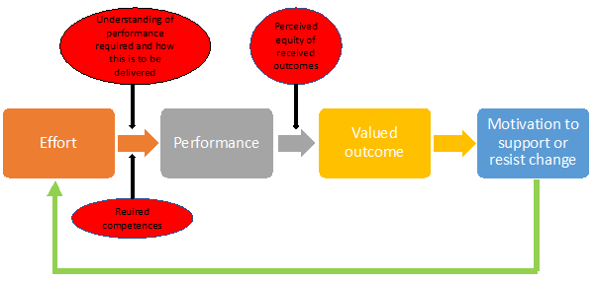
[edit] Expectancy theory and the motivation to support or resist change
[edit] Description :
This model is based on expectancy theory that considers how expectations influence motivation. The model offers a useful conceptual framework for assessing whether a stakeholder is likely to support or resist an approaching change. The project managers leading the project/change can use the expectancy model to assess and improve the perceived attractiveness of the outcomes and construct relationships between effort and performance and the achievement of outcomes. The first step in the assessment of how stakeholders will react to change is to identify how the change will affect the availability of valued outcomes in the changed situation. When employees are faced with an approaching change, they often fear that they will lose some of the outcomes they value in the existing situation. The expectancy model allows to address those challenges and asses effort-performance and performance-outcome relationships.
[edit] References :
The theory and practise of change management, John Hayes
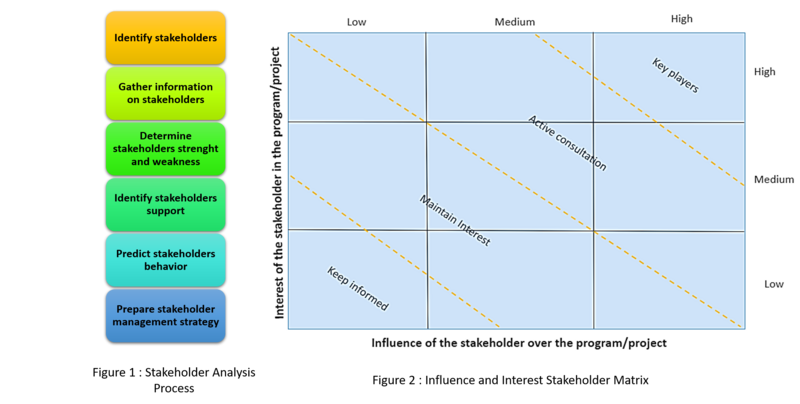
[edit] Influence and Interest Stakeholder Matrix
[edit] Description :
Before being able to complete the Influence and Interest stakeholder matrix there are few steps of the Stakeholders analysis to follow (see figure 1). When all the information about the stakeholder are gathered the mapping step can start to get this visual tool.
The Influence/interest matrix suggested in Managing Successful programme is based on a matrix of nine squares. After having listed all the stakeholders it’s important to evaluate their interest and influence which can be measured on a scale of high, medium or low. Where the interest can be defined as the potential interest in the project of the stakeholder. So the position of the stakeholder in the matrix is set by this two parameter (x,y) where x = level of inluence and y = level of interest. In addition to the nine squares, it is possible to split the matrix into four diagonal bands as shown below : Key players, Active consultation, Maintain interest and Keep informed.
[edit] References :
Source: Stakeholder matrix - key matrices for stakeholder analysis [[1]]
Wiki APPPM, Stakeholder Analysis, [ONLINE] Available at:
[[2]] [Accessed 04 March 2020]
[edit] A classification model of stakeholder theory definitions - Miles
[edit] Description :
A classification model of stakeholder theory definitions represented by Miles, can be used in order to identify the impact of power, interest and influence of the stakeholder. The model is divided into the four stakeholder classes influencer, collaborator, claimant and recipient.
- An influencer is a stakeholder who has the capacity to influence the actions of an organisation and has an active strategy to do so.
- A collaborator is a stakeholder that cooperates with an organisation but with no active interest to influence the organisation.
- A claimant is a stakeholder who has a claim on an organisation. With this claim the stakeholder has an active strategy to pursue the claim, but no power to guarantee that the claim is attended by the management.
- A recipient is a passive stakeholder, who is a receiver of the impact of organisational activity.
- A stakeholder is not necessarily defined by one of the four categories but can be a combination of two or more stakeholder types.
[edit] References :
S. Miles, “Stakeholder Theory Classification: A Theoretical and Empirical,” Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht, pp. 437-459, 26 06 2015
[edit] Salience Model (Power, Legitimacy, Urgency)
[edit] Description :
The model is based upon the three stakeholder attributes: Power, Legitimacy and Urgency.
The stakeholder attribute Power is defined as a relationship among social actors in which one social actor, A, can get another social actor, B, to do something that B would not have otherwise done (Mitchell, Agle, & Wood, 1997).
Legitimacy is defined as a generalized perception or assumption that, the actions of an entity are desirable, proper, or appropriate within some socially constructed system of norms, values, beliefs, definitions (Mitchell, Agle, & Wood, 1997).
Urgency defines the degree to which stakeholder claims call for immediate attention (Mitchell, Agle, & Wood, 1997).
Together the three stakeholder attributes create seven different classifications of stakeholders. The seven classifications are possessing one, two or three of the stakeholder attributes. The stakeholders possessing one stakeholder attributes is characterized as latent stakeholders these are dormant, discretionary, and demanding stakeholders. Expectant stakeholders are those possessing two attributes, and include dominant, dependent, and dangerous. Definitive stakeholders are those possessing all three attributes. Individuals or entities possessing none of the attributes are non-stakeholders or potential stakeholders (Mitchell, Agle, & Wood, 1997). The model forms the basis for categorization of stakeholders in order to obtain a better understanding of how each stakeholder is to be handled.
[edit] References :
R. K. Mitchell, B. R. Agle and D. J. Wood, “Toward a Theory of Stakeholder Identification and Salience: Defining the Principle of Whoand What Really Counts,” Academy of Management, pp. 853-886, 10 1997.
[edit] Ladder of engagement
[edit] Description :
The ladder of stakeholder engagement is a model that intend to illustrate degrees of the quality of stakeholder management from the perspective of the stakeholders (Friedman & Miles, 2006). The ladder can be used in order to describe the relationship between the stakeholders and the organization, as it focuses on the objectives of engagement, tools and communication strategies. The ladder consists of twelve levels.
The lower levels relate to situations where the organization is informing the stakeholders about decisions that have already taken place. There is no engagement and no or limited participation.
The lower middle levels involve the offering of some symbolic gestures of participation, where stakeholder’s voices are heard, but not necessarily taken into consideration. The scope is to obtain information of stakeholder concerns and provide response to the concerns.
The higher middle levels involve high level of engagement and involvement but no definitive power. It is an organizational process to enable stakeholder to have influence.
The highest levels concern high level of engagement and involvement and high levels of stakeholder power and control. The stakeholders have at these levels decision-making power and can make decisions independently of the organization.
[edit] References :
A. L. Friedman and S. Miles, Stakeholders: Theory and Pratice, OUP Oxford, 2006
[edit] Golden Circle (Why, How and What)
[edit] Description :
A key aspect in project management is to establish a strong vision. There are many ways to establish a vision and the Golden Circle Model is one of them. This management tool is based on 3 concentric circles corresponding to three questions: Why, How and What. To use this tool, developed by Simon Sinek, an organization/ a leader/ people must think from inside out to drive projects purposefully. The WHY question starts by identifying the purpose of the project (shall not be answered with something as making money because it’s a consequence), then the HOW question describes how the project is conducted and finally the WHAT is what is being done in the project.
[edit] References :
Wiki APPPM, Why, How, What (The Golden Circle Model), [ONLINE] Available at: [[3]] [Accessed 04 March 2020]
[edit] SWOT Model
[edit] Description :
The SWOT analysis provides information about the current position of an organization. It is an extraordinary useful business tool since gives information about the internal Strengths and Weaknesses of the organization and the external Opportunities and Threats. By applying the SWOT analysis, the organization can take the best advantages and at the same time reduce the chances of failure by understanding the weak points of the organization and avoid risks that they would be fatal for the well-being of the organization.
[edit] References :
https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMC_05.htm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SWOT_analysis
https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/4245-swot-analysis.html
[edit] Key Performance Indicators(KPI)
[edit] Description :
While the scope and terms of an organization’s KPIs may differ from project to project, there are various types of data that can be helpful to any organization. Top project management benchmarking measures include return on investment (ROI), productivity, cost performance, cycle time, customer satisfaction, schedule performance, employee satisfaction and alignment with strategic business goals.
Examples of KPIs within project management include:
- Project schedule
- Estimate to project completion
- Current development backlog
- Labor costs spent per month
- Current resource allocation
Too often, organizations blindly adopt industry-recognized KPIs and then wonder why that KPI doesn't reflect their own business and fails to affect any positive change. One of the most important, but often overlooked, aspects of KPIs is that they are a form of communication. As such, they abide by the same rules and best-practices as any other form of communication. Succinct, clear and relevant information is much more likely to be absorbed and acted upon
[edit] References :
https://www.floridatechonline.com/blog/business/key-performance-indicators-in-project-management/
https://www.klipfolio.com/resources/articles/what-is-a-key-performance-indicator
[edit] Benefits Realization Management to Maximize Project Effectiveness (BRM)
[edit] Description :
Benefits realization management (BRM) provides organizations with a way to measure how projects and programs add true value to the enterprise.
- IDENTIFY BENEFITS to determine whether projects, programs, and portfolios can produce the intended business results.
- EXECUTE BENEFITS management to minimize risks to future benefits and maximize the opportunity to gain additional benefits.
- SUSTAIN BENEFITS to ensure that whatever the project or program produces continues to create value.
[edit] References :
[edit] Management of Project Change
[edit] Description :
Changes arise in broad projects across all the different departments. Change management is a wide collective term and could have application into many different types of organization. The most relevant and common approaches are to help, prepare and support individuals, teams, groups, and organization in order to make and establish the changes. The most popular change drivers include technological evolution, process reviews, crisis, and consumer habit changes; pressure from new business entrants, acquisitions, mergers, and organizational restricting. (ref. https://www.hucmi.com/en/hcmbok/ ). The advantages of this tools are that make the organization more flexible and ready for changes, helps the people to understand the kind of change that is required, bring the people closer, and last but not least delivers change that are really effective and efficient for the organization
[edit] References :
https://www.hucmi.com/en/hcmbok/
https://www.strategy-business.com/article/rr00006?gko=dab72
https://the-happy-manager.com/tips/benefits-of-change-management/