Diversity in teams
(→Annotated bibliography) |
|||
| (221 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ''Written by Gaute Bø Aaløkken'' | |
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
| − | Diversity | + | Diversity in teams is the existence of different individuals with different attributes within a team. This can be surface-level differences such as ethnicity, gender, or age or it can be underlying differences such as functional background, education, or personality. These do all affect a team in different ways and can be challenging for many teams. Studies on the field of diversity in teams are in some areas inconsistent, especially when it comes to the impact diversity has on performance. Where some find that diversity improves the performance of teams, others find a negative impact on performance. Traditionally the effect of diversity has been seen from three perspectives; The Similarity-attraction perspective, The Self-Identity, and Social-Categorization perspective, and the Information Processing perspective. Both Similarity-attraction and Self-Identity and Social-Categorization lead to a more pessimistic view of diversity in teams through social division which again leads to reduced performance. The Information Processing perspective does however offer a positive view, by suggesting that diversity leads to increased creativity, more perspective, and more learning, which in turn can improve performance. |
| − | + | From a manager's perspective, the goal is always to get the best out of the team. With diverse teams, it is therefore important to try to capitalize on the benefits diversity brings and try reducing the negative effects. This can be done by giving diverse teams the right tasks, connecting the team members, and supporting the minority opinions within the team. | |
| − | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Introduction == | ||
| + | In almost all sectors, whether it is government, business, science, health care, diverse groups, and teams are on the rise <ref name="Diversity in Groups"> Fernandes, Catarina R & Polzer, Jeffery T. Diversity in Groups. Available at:https://www.hbs.edu/ris/Publication%20Files/Diversity_in_Groups_EmergingTrends_57796940-b049-43dc-b58b-832eccbcaa80.pdf </ref>. Diversity has many definitions, and one of them is "variation based on any attribute people use to tell themselves that another person is different". <ref name="Effects"></ref>. Diversity is especially connected to projects, programs, and portfolio management through the people perspective. People are critical to the success of projects, programs, and portfolios and as stated in the DS Handbook 185 "Projects are made for people by people" <ref name ="Handbook"> Geraldi, J., Thuesen, C., Oehmen, J., & Stingl, V. (2017). Doing Projects. A Nordic Flavour to Managing Projects: DS-handbook 185:2017. Dansk Standard.</ref>. Even though it sounds obvious, it is only in recent years that people and behaviors have been recognized and incorporated in project management as a profession.<ref name ="Handbook"></ref> An important part of this is to see projects as a collaboration between people, each with their own identities, knowledge, interests, personalities, backgrounds and so on. These are all factors that will make people see and approach the task differently, and requires attention from the manager. It does not help to have the right processes and right systems if the team members do not work effectively together. This has in many ways changed the role of the manager from a technician, an analytical person that schedules meetings and updates budgets, to a leader that also needs to have social skills <ref name ="Handbook"></Ref>. Communication is now recognized as a project success factor, and around 80% of managers' time is spent on communication. <ref name ="Handbook"></Ref>. Identities, knowledge, interests, personalities, and backgrounds are all examples of different types of diversity that can exist in a team. Organizations pay more attention to group compositions and incorporation differences in terms of demographics and functional backgrounds. Managing them is now considered a major challenge to organizations. <ref name="GDHOW"> Seong, J. Y., & Hong, D.-S. (2013). Gender diversity: How can we facilitate its positive effects on teams? Social Behavior and Personality: An international journal, 41(3), 497-508.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Complexity=== | ||
| + | Even though diversity normally is related to the people perspective can also be relevant to the complexity perspectives. There several challenges related to diversity in teams, which can contribute to making the integration of people within the teams harder. This can lead to increased complexity in both projects, programs, or portfolios. Diversity in the interfaces between the stakeholder can also increase the complexity, for example, stakeholders from different cultures are something that could require extra attention from the project manager. Different cultures may do the same type of work in different ways, and expectations for the certain type of work may therefore not always align. As explained in a later section, complexity is also a moderator that can increase the amount of conflict within a culturally diverse team. | ||
==State of subject== | ==State of subject== | ||
| − | + | There have been conducted substantial amounts of research on the topic of diversity in the past few decades, this has led to mixed, and even contradictory results <ref name="Effects"></ref>. Some studies suggest that diversity brings different perspectives and approaches to problem-solving, which again leads to better quality and performance. Other studies suggest that diversity has negative effects on social integration, communication, and conflict in groups, which in turn will have a negative impact on performance. Among many, there has been a belief that diversity in teams will lead to better quality and higher performance, and diversity has been credited with many positive outcomes in relation to performance<ref name="Effects"></ref>. A qualitative review of the research from the last 50 years on diversity in teams does however show that there are no consistent, positive main effects from diversity<ref name="Effects"></ref>. There have also been conducted several meta-studies, which have found either no correlation between diversity and performance, or even a small negative effect <ref name="CDinTeams"></ref>. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | So why then bother with diverse teams? First of all, there are still ways to manage and benefit from diversity in teams. It can benefit both the team itself, but also the organization where the team exists<ref name="Effects"></ref>. Diversity in teams is also an important step towards equality, and can both reduce discrimination and increase access to career opportunities. <ref name="CDinTeams"></ref>. Equal opportunities can also lead to a larger talent pool, thus more effective utilization of talent in an organization. Finally, as diverse teams are on the rise, it will be inevitable in many project-, program-, and portfolio-teams in the future and therefore something the management should take into consideration. | |
== Effects of diversity == | == Effects of diversity == | ||
| − | The effects of diversity have traditionally been understood trough three different perspectives: <ref name ="Effects"> Mannix, Elizabeth & Neale, Margaret A (2005). What differences make a difference? Psychological Science in the Public Interest. Available at: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/j.1529-1006.2005.00022.x?casa_token=qiXUEAO_nPIAAAAA:77IXwF62pgU5VFPWF6eW7mm2XyX56bgBE-cmFbnMJsl6NTVD1S2u9EEHZIry56F8RPzRaaAfDdyu</ref> | + | The effects of diversity have traditionally been understood trough three different perspectives: <ref name ="Effects"> Mannix, Elizabeth & Neale, Margaret A (2005). What differences make a difference? Psychological Science in the Public Interest. Available at: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/j.1529-1006.2005.00022.x?casa_token=qiXUEAO_nPIAAAAA:77IXwF62pgU5VFPWF6eW7mm2XyX56bgBE-cmFbnMJsl6NTVD1S2u9EEHZIry56F8RPzRaaAfDdyu </ref> <ref name="CDinTeams"></ref> |
'''1. Similarity-attraction.''' | '''1. Similarity-attraction.''' | ||
| − | + | States that "Similarity on attributes such as attitudes, values, and beliefs will facilitate interpersonal attraction and liking, and vice versa".<ref name=CDinTeams></ref>. This applies to both social settings, and to work settings where individuals are attracted to working with those they have something in common with. The perspective shows how individuals can feel drawn toward the validation of homogeneity and comfort of belonging. <ref name="Effects"></ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ''' | + | '''2.Self-Identity and Social-Categorization''' |
| − | Individuals | + | Individuals tend to categorize themselves into specific groups, based on race, gender, values, beliefs among others <ref name="Effects"></ref>. All those that belong to the same group are then seen as outsiders and are treated differently. When categorizing others we tend to focus on the are most distinctive and stand out within the social context. |
| − | Both the similarity-attraction perspective and self-and social categorization perspective tend to lead to the pessimistic view of diversity in teams. Since individuals will be attracted to working with those that are similar to themselves, more homogeneous teams will be more cohesive and the members more socially integrated. It also creates an atmosphere where the outsiders are judged more stereotypically and | + | Both the similarity-attraction perspective and self-and social categorization perspective tend to lead to the pessimistic view of diversity in teams. Since individuals will be attracted to working with those that are similar to themselves, more homogeneous teams will be more cohesive and the members more socially integrated. It also creates an atmosphere where the outsiders are judged more stereotypically and meet different expectations. |
| + | |||
| + | '''3.Information processing''' | ||
| + | Individuals in diverse teams have access to other individuals that have different backgrounds, networks, information, and skills<ref name="Effects"></ref>. The theory stays clear of the typical "demographic proxies", which are typical surface-level differences such as ethnicity or age. Instead, it focuses on the underlying differences such as education, functional background, or expertise and their benefits. In contrast to the other perspectives, the perspective, therefore, offers an offer a more positive view on the effects of diversity. The different members all bring different perspectives and approaches to the table, and also different sources of information and expertise. This can create coordination and integration problems, but it can also improve the group outcome diversity. | ||
== Types of diversity == | == Types of diversity == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | There are several types of diversity that all affect groups and teams differently. Two categories that often are used are: | ||
| − | = | + | '''Surface-level differences''' are those that one can see, such as those of race/ethnicity, gender, or age. Research shows that these differences tend to be more likely to have negative effects on the ability of groups to function effectively. <ref name ="Effects"></ref>. |
| + | Surface-level differences are related to the Similarity-attraction perspective and Self-Identity and Social-Categorization perspective, and the negative tendencies, therefore, correlate with the pessimistic views of the perspectives. | ||
| − | + | '''Underlying differences''' are those that are not visible on the surface such as functional background, education, or personality. | |
| + | These are more often related positively to performance through increased creativity or group problem solving, which aligns with the Information processing perspective.<ref name ="Effects"></ref>. They do also require that the process around them is carefully controlled. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The next section will describe some examples of types of diversity: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Cultural Diversity=== | ===Cultural Diversity=== | ||
| − | + | Cultural diversity is defined as "the existence of a variety of cultural or ethnic groups in a society", but can be applied to teams as well. <ref name ="Definition"> Oxford Languages for Google. Cultural diversity definition. Available at: https://www.google.no/search?rls=com.microsoft%3Anb%3A%7Breferrer%3Asource%7D&sxsrf=ALeKk00Aga05cPg7KF2xXvAQudX3lPwCFQ%3A1613070110502&ei=Hn8lYISXHqXnrgTy7L6oAw&q=cultural+diversity+definition&oq=cultural+diversity+definition&gs_lcp=CgZwc3ktYWIQDFAAWABgsCFoAHAAeACAAVWIAVWSAQExmAEAqgEHZ3dzLXdpesABAQ&sclient=psy-ab&ved=0ahUKEwiEnry3wuLuAhWls4sKHXK2DzUQ4dUDCA0</ref>.As the world gets globalized, projects become more international. People are moving between countries, and technology does now allows teams to work together across country borders online. This requires more interaction between people from different cultures, beliefs, and backgrounds than ever before and leads to culturally diverse teams. <ref name="international>Green, K. A., López, M., Wysocki, A., & Kepner, K. (2002). Diversity in the Workplace: Benefits, challenges, and the required managerial tools. EDIS, 2002(2).</ref>. An example of such a project is the [[Hålogaland Bridge]] in northern Norway, where the architect and engineers were Danish, the main contractor Chinese, and some of the subcontractor Norwegian. | |
| − | + | ||
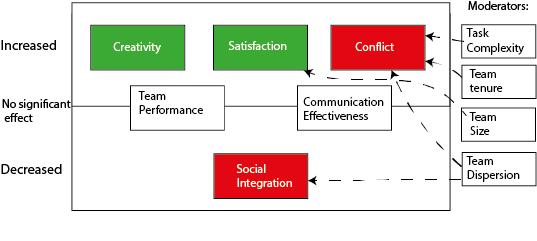
| + | A large meta-study by (Stahl, G., Maznevski, M., Voigt, A. et al) that reconcile past findings in the field, found that cultural diversity is unrelated to team performance.<ref name="CDinTeams"></ref>. What they did find is that it can be both an asset and a liability and that whether a team is able to realize the benefits and reduce the losses associated with cultural diversity, depends both on the context in which the team operates and if they are able to manage the processes effectively. The study found that cultural diversity increases the forces of divergence within teams, and that diverse teams experience increased creativity, more conflict, and less social integration. Contrary to what many may think, culturally diverse teams did not experience less effective communication and actually had higher satisfaction<ref name="CDinTeams"></ref>. There were several moderators to these effects, and the effects may vary, depending on contextual influences. For example, culturally diverse teams have more conflict when the task is complex, the teams were co-located, and if they had more time together. The reason for this could be that teams with longer tenure, often work on more complex projects, end, therefore, has the opportunity to get into deeper and more difficult issues. There is also higher satisfaction in culturally diverse teams, contradictory to the general research on diversity. The rest of these effects and the moderators that increase the effect are shown in the figure below: | ||
| − | + | [[File:CulturalDiversityInTeamsFigure.PNG|thumb|center|600px|Figure 1: Effects of cultural diversity, made with inspiration from <ref name="CDinTeams"></ref>. The effects where strengthened as the moderators increased. ]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Personality diversity=== | ||
| + | Personality diversity in teams is the existence of different personalities within the team and is a typical underlying-difference that is difficult to use. Knowledge of the different types of personalities and how they may influence is crucial for the manager to be able to establish teams that work well together. <ref name ="AXELOS"> AXELOS. Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition, Page 74, The Stationery Office Ltd, 2017.</ref>. It is not possible to change peoples' personalities and characteristics, but knowing the natural roles of the team members can enable the manager to build balanced and effective teams. There are several ways to identify and categorize the natural roles of team members. One way is to do a written test like the Belbin test, this will result in one of [[Belbin's 9 team roles]], which is are 9 essential team roles to a high functioning team. This process can ease the formation of teams and highlights the strengths and weaknesses of all the team roles. Another option is [[The Five-Factor Model (OCEAN)]]-test, where the candidates get scores within five personality traits. | ||
===Gender diversity=== | ===Gender diversity=== | ||
| − | - | + | Gender diversity in teams is the existence of different genders within teams and is a typical surface-level difference. Traditionally men have higher occupational participation, salaries, and job-positions, so when speaking of gender diversity in teams what's often meant is gender equality. When it comes to management and corporate boards, women are still underrepresented. In the top 300 companies in Europe, only 10 percent of the board seats were held by women. <ref name="impact"></ref> |
| − | - | + | |
| + | Gender equality is often seen as desirable in the popular press, with arguments such as a larger talent pool, improvement of companies' image, better stakeholder relationships, higher employee motivation, and better mutual learning. However, there have not been done many empirical studies on gender diversity in teams, and there is little evidence supporting that gender diversity leads to increased team performance. <ref name="impact">Hoogendoorn, Sander, Hessel Oosterbeek, and Mirjam Van Praag. "The impact of gender diversity on the performance of business teams: Evidence from a field experiment." Management Science 59, no. 7 (2013): 1514-1528.</ref>. There are however some recent studies that suggest that a larger share of women either not have a positive impact and, or may even be harmful.<ref name="impact"></ref> | ||
| + | == How to manage diversity== | ||
| + | Leading a team, whether it is a project team, portfolio teams, or program team, the manager is crucial to reduce the potential negative effects of diversity and capitalize on the positive effects. | ||
| + | Mannix, Elizabeth & Neale, Margaret A has come up with three concrete suggestion on how to do this based on a review of previous research on diversity:<ref name="Effects"></ref> | ||
| − | + | '''1.Task and goals within the teams''' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The first suggestion is to consider the type of task thoroughly for diverse teams. As discussed, diversity can lead to increased creativity and learning in teams. Diverse teams could therefore thrive with tasks and goals that require creation and different perspectives, for example within innovation. Another way to go is to set other success criteria than just performance. Even though diverse teams may not outperform homogeneous teams, the team members may learn from each other in terms of skills and ways of approaching problems and issues. The learning process itself could therefore be a goal and something that could benefit the organization in the long-run. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | '''2.Connceting the team members''' | |
| + | In teams, it can be a challenge for those with other perspectives to be heard. It is important to create an environment that is tolerant of other perspectives, so those with different views are willing to share their viewpoints. Findings from the group-decision-area in recent years show that information exchange in groups typically focuses on the information that is already known among the group members.<ref name="Effects"></ref>. A reason for this because some team members are unwilling to risk the discomfort, potential conflict, and exclusion that deviant behavior might lead to .<ref name="Effects"></ref>. The project manager can try to reduce the effect of this by facilitating social ties, which can lead to trust and social cohesion, effective communication, and improved performance. | ||
| + | Another option could is to connect the team members in a way that is meaningful to the particular team. This can for example be by creating superordinate goals for the teams and can be task-related, organizationally relevant, or focused on work values.<ref name="Effects"></ref>. This creates something that the team members all have in common, and they can "gather around". | ||
| + | '''3.Enhancing the Influence of the Minority''' | ||
| − | == | + | As briefly discussed in the section above, a serious problem in teams is the strain toward conformity, as individuals often try to avoid disagreement and confrontation. Conformity can have its benefits, but can also hinder organizational change and result in less innovation, learning, and even in the detection of errors and decision accuracy. <ref name="Effects"></ref>. Research shows that when an individual is exposed to opposing minority views, they think more about it, see more aspects of the situation, and are more likely to find other solutions or come to new decisions. <ref name="Effects"></ref>. It is therefore important to have these minority opinions and make them heard, as they can lead to divergent thinking and increased performance. To achieve this it is crucial that the manager supports the minority-opinions, and make sure their voices are heard. Finally, the project manager can also facilitate a positive and cooperative team climate, and setting a group norm of openness and learning.<ref name="Effects"></ref><ref name="GDHOW"></ref> |
| + | == Limitations== | ||
| + | The main issue with the topic is that the research is so inconsistent, especially when it comes to performance. The lack of consistency in the research can make it difficult to argue that there is any point in having diverse teams and that it is worth the effort. Mannix, Elizabeth & Neale, Margaret A argue that the studies that do find a positive effect on performance, often do so under very narrow conditions <ref name=Effects>.</ref>. It can be difficult to recreate these conditions, and therefore also to recreate the positive effects. There is also a portion of the studies on the topic, that suggests that diversity can have a negative impact on the performance of a team. They suggest that diversity creates social divisions, which again affects performance negatively. | ||
| − | + | == Annotated bibliography == | |
| − | + | What differences make a difference? Psychological Science in the Public Interest.<ref name=Effects></ref>. A large study that tries to disentangle what researchers have learned from the last 50 years on the field of diversity in teams and tries to summarize it, and which much of the article is based upon. It also describes how diversity affects teams and how to manage it. | |
| − | |||
| + | Stahl, G., Maznevski, M., Voigt, A. et al. Unraveling the effects of cultural diversity in teams: A meta-analysis of research on multicultural work groups (2010) <ref name ="CDinTeams"> Stahl, Günter & Maznevski, Martha & Voigt, Andreas & Jonsen, Karsten. (2010). Unraveling the effects of cultural diversity in teams: A meta-analysis of research on multicultural workgroups. Journal of International Business Studies. 41. 690-709. 10.1057/jibs.2009.85. </ref> Large meta-study, that tries to summarize previous research on the topic of diversity and cultural diversity. Taken from the report: "Our goals in this study were to take stock of and synthesize the findings from previous research, to reconcile conflicting perspectives and past results, and to propose an agenda for the next stage of research in this field." | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<references> | <references> | ||
Latest revision as of 22:36, 28 February 2021
Written by Gaute Bø Aaløkken
[edit] Abstract
Diversity in teams is the existence of different individuals with different attributes within a team. This can be surface-level differences such as ethnicity, gender, or age or it can be underlying differences such as functional background, education, or personality. These do all affect a team in different ways and can be challenging for many teams. Studies on the field of diversity in teams are in some areas inconsistent, especially when it comes to the impact diversity has on performance. Where some find that diversity improves the performance of teams, others find a negative impact on performance. Traditionally the effect of diversity has been seen from three perspectives; The Similarity-attraction perspective, The Self-Identity, and Social-Categorization perspective, and the Information Processing perspective. Both Similarity-attraction and Self-Identity and Social-Categorization lead to a more pessimistic view of diversity in teams through social division which again leads to reduced performance. The Information Processing perspective does however offer a positive view, by suggesting that diversity leads to increased creativity, more perspective, and more learning, which in turn can improve performance.
From a manager's perspective, the goal is always to get the best out of the team. With diverse teams, it is therefore important to try to capitalize on the benefits diversity brings and try reducing the negative effects. This can be done by giving diverse teams the right tasks, connecting the team members, and supporting the minority opinions within the team.
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
In almost all sectors, whether it is government, business, science, health care, diverse groups, and teams are on the rise [1]. Diversity has many definitions, and one of them is "variation based on any attribute people use to tell themselves that another person is different". [2]. Diversity is especially connected to projects, programs, and portfolio management through the people perspective. People are critical to the success of projects, programs, and portfolios and as stated in the DS Handbook 185 "Projects are made for people by people" [3]. Even though it sounds obvious, it is only in recent years that people and behaviors have been recognized and incorporated in project management as a profession.[3] An important part of this is to see projects as a collaboration between people, each with their own identities, knowledge, interests, personalities, backgrounds and so on. These are all factors that will make people see and approach the task differently, and requires attention from the manager. It does not help to have the right processes and right systems if the team members do not work effectively together. This has in many ways changed the role of the manager from a technician, an analytical person that schedules meetings and updates budgets, to a leader that also needs to have social skills [3]. Communication is now recognized as a project success factor, and around 80% of managers' time is spent on communication. [3]. Identities, knowledge, interests, personalities, and backgrounds are all examples of different types of diversity that can exist in a team. Organizations pay more attention to group compositions and incorporation differences in terms of demographics and functional backgrounds. Managing them is now considered a major challenge to organizations. [4]
[edit] Complexity
Even though diversity normally is related to the people perspective can also be relevant to the complexity perspectives. There several challenges related to diversity in teams, which can contribute to making the integration of people within the teams harder. This can lead to increased complexity in both projects, programs, or portfolios. Diversity in the interfaces between the stakeholder can also increase the complexity, for example, stakeholders from different cultures are something that could require extra attention from the project manager. Different cultures may do the same type of work in different ways, and expectations for the certain type of work may therefore not always align. As explained in a later section, complexity is also a moderator that can increase the amount of conflict within a culturally diverse team.
[edit] State of subject
There have been conducted substantial amounts of research on the topic of diversity in the past few decades, this has led to mixed, and even contradictory results [2]. Some studies suggest that diversity brings different perspectives and approaches to problem-solving, which again leads to better quality and performance. Other studies suggest that diversity has negative effects on social integration, communication, and conflict in groups, which in turn will have a negative impact on performance. Among many, there has been a belief that diversity in teams will lead to better quality and higher performance, and diversity has been credited with many positive outcomes in relation to performance[2]. A qualitative review of the research from the last 50 years on diversity in teams does however show that there are no consistent, positive main effects from diversity[2]. There have also been conducted several meta-studies, which have found either no correlation between diversity and performance, or even a small negative effect [5].
So why then bother with diverse teams? First of all, there are still ways to manage and benefit from diversity in teams. It can benefit both the team itself, but also the organization where the team exists[2]. Diversity in teams is also an important step towards equality, and can both reduce discrimination and increase access to career opportunities. [5]. Equal opportunities can also lead to a larger talent pool, thus more effective utilization of talent in an organization. Finally, as diverse teams are on the rise, it will be inevitable in many project-, program-, and portfolio-teams in the future and therefore something the management should take into consideration.
[edit] Effects of diversity
The effects of diversity have traditionally been understood trough three different perspectives: [2] [5]
1. Similarity-attraction. States that "Similarity on attributes such as attitudes, values, and beliefs will facilitate interpersonal attraction and liking, and vice versa".[5]. This applies to both social settings, and to work settings where individuals are attracted to working with those they have something in common with. The perspective shows how individuals can feel drawn toward the validation of homogeneity and comfort of belonging. [2]
2.Self-Identity and Social-Categorization
Individuals tend to categorize themselves into specific groups, based on race, gender, values, beliefs among others [2]. All those that belong to the same group are then seen as outsiders and are treated differently. When categorizing others we tend to focus on the are most distinctive and stand out within the social context.
Both the similarity-attraction perspective and self-and social categorization perspective tend to lead to the pessimistic view of diversity in teams. Since individuals will be attracted to working with those that are similar to themselves, more homogeneous teams will be more cohesive and the members more socially integrated. It also creates an atmosphere where the outsiders are judged more stereotypically and meet different expectations.
3.Information processing
Individuals in diverse teams have access to other individuals that have different backgrounds, networks, information, and skills[2]. The theory stays clear of the typical "demographic proxies", which are typical surface-level differences such as ethnicity or age. Instead, it focuses on the underlying differences such as education, functional background, or expertise and their benefits. In contrast to the other perspectives, the perspective, therefore, offers an offer a more positive view on the effects of diversity. The different members all bring different perspectives and approaches to the table, and also different sources of information and expertise. This can create coordination and integration problems, but it can also improve the group outcome diversity.
[edit] Types of diversity
There are several types of diversity that all affect groups and teams differently. Two categories that often are used are:
Surface-level differences are those that one can see, such as those of race/ethnicity, gender, or age. Research shows that these differences tend to be more likely to have negative effects on the ability of groups to function effectively. [2]. Surface-level differences are related to the Similarity-attraction perspective and Self-Identity and Social-Categorization perspective, and the negative tendencies, therefore, correlate with the pessimistic views of the perspectives.
Underlying differences are those that are not visible on the surface such as functional background, education, or personality. These are more often related positively to performance through increased creativity or group problem solving, which aligns with the Information processing perspective.[2]. They do also require that the process around them is carefully controlled.
The next section will describe some examples of types of diversity:
[edit] Cultural Diversity
Cultural diversity is defined as "the existence of a variety of cultural or ethnic groups in a society", but can be applied to teams as well. [6].As the world gets globalized, projects become more international. People are moving between countries, and technology does now allows teams to work together across country borders online. This requires more interaction between people from different cultures, beliefs, and backgrounds than ever before and leads to culturally diverse teams. [7]. An example of such a project is the Hålogaland Bridge in northern Norway, where the architect and engineers were Danish, the main contractor Chinese, and some of the subcontractor Norwegian.
A large meta-study by (Stahl, G., Maznevski, M., Voigt, A. et al) that reconcile past findings in the field, found that cultural diversity is unrelated to team performance.[5]. What they did find is that it can be both an asset and a liability and that whether a team is able to realize the benefits and reduce the losses associated with cultural diversity, depends both on the context in which the team operates and if they are able to manage the processes effectively. The study found that cultural diversity increases the forces of divergence within teams, and that diverse teams experience increased creativity, more conflict, and less social integration. Contrary to what many may think, culturally diverse teams did not experience less effective communication and actually had higher satisfaction[5]. There were several moderators to these effects, and the effects may vary, depending on contextual influences. For example, culturally diverse teams have more conflict when the task is complex, the teams were co-located, and if they had more time together. The reason for this could be that teams with longer tenure, often work on more complex projects, end, therefore, has the opportunity to get into deeper and more difficult issues. There is also higher satisfaction in culturally diverse teams, contradictory to the general research on diversity. The rest of these effects and the moderators that increase the effect are shown in the figure below:
[edit] Personality diversity
Personality diversity in teams is the existence of different personalities within the team and is a typical underlying-difference that is difficult to use. Knowledge of the different types of personalities and how they may influence is crucial for the manager to be able to establish teams that work well together. [8]. It is not possible to change peoples' personalities and characteristics, but knowing the natural roles of the team members can enable the manager to build balanced and effective teams. There are several ways to identify and categorize the natural roles of team members. One way is to do a written test like the Belbin test, this will result in one of Belbin's 9 team roles, which is are 9 essential team roles to a high functioning team. This process can ease the formation of teams and highlights the strengths and weaknesses of all the team roles. Another option is The Five-Factor Model (OCEAN)-test, where the candidates get scores within five personality traits.
[edit] Gender diversity
Gender diversity in teams is the existence of different genders within teams and is a typical surface-level difference. Traditionally men have higher occupational participation, salaries, and job-positions, so when speaking of gender diversity in teams what's often meant is gender equality. When it comes to management and corporate boards, women are still underrepresented. In the top 300 companies in Europe, only 10 percent of the board seats were held by women. [9]
Gender equality is often seen as desirable in the popular press, with arguments such as a larger talent pool, improvement of companies' image, better stakeholder relationships, higher employee motivation, and better mutual learning. However, there have not been done many empirical studies on gender diversity in teams, and there is little evidence supporting that gender diversity leads to increased team performance. [9]. There are however some recent studies that suggest that a larger share of women either not have a positive impact and, or may even be harmful.[9]
[edit] How to manage diversity
Leading a team, whether it is a project team, portfolio teams, or program team, the manager is crucial to reduce the potential negative effects of diversity and capitalize on the positive effects. Mannix, Elizabeth & Neale, Margaret A has come up with three concrete suggestion on how to do this based on a review of previous research on diversity:[2]
1.Task and goals within the teams
The first suggestion is to consider the type of task thoroughly for diverse teams. As discussed, diversity can lead to increased creativity and learning in teams. Diverse teams could therefore thrive with tasks and goals that require creation and different perspectives, for example within innovation. Another way to go is to set other success criteria than just performance. Even though diverse teams may not outperform homogeneous teams, the team members may learn from each other in terms of skills and ways of approaching problems and issues. The learning process itself could therefore be a goal and something that could benefit the organization in the long-run.
2.Connceting the team members
In teams, it can be a challenge for those with other perspectives to be heard. It is important to create an environment that is tolerant of other perspectives, so those with different views are willing to share their viewpoints. Findings from the group-decision-area in recent years show that information exchange in groups typically focuses on the information that is already known among the group members.[2]. A reason for this because some team members are unwilling to risk the discomfort, potential conflict, and exclusion that deviant behavior might lead to .[2]. The project manager can try to reduce the effect of this by facilitating social ties, which can lead to trust and social cohesion, effective communication, and improved performance.
Another option could is to connect the team members in a way that is meaningful to the particular team. This can for example be by creating superordinate goals for the teams and can be task-related, organizationally relevant, or focused on work values.[2]. This creates something that the team members all have in common, and they can "gather around".
3.Enhancing the Influence of the Minority
As briefly discussed in the section above, a serious problem in teams is the strain toward conformity, as individuals often try to avoid disagreement and confrontation. Conformity can have its benefits, but can also hinder organizational change and result in less innovation, learning, and even in the detection of errors and decision accuracy. [2]. Research shows that when an individual is exposed to opposing minority views, they think more about it, see more aspects of the situation, and are more likely to find other solutions or come to new decisions. [2]. It is therefore important to have these minority opinions and make them heard, as they can lead to divergent thinking and increased performance. To achieve this it is crucial that the manager supports the minority-opinions, and make sure their voices are heard. Finally, the project manager can also facilitate a positive and cooperative team climate, and setting a group norm of openness and learning.[2][4]
[edit] Limitations
The main issue with the topic is that the research is so inconsistent, especially when it comes to performance. The lack of consistency in the research can make it difficult to argue that there is any point in having diverse teams and that it is worth the effort. Mannix, Elizabeth & Neale, Margaret A argue that the studies that do find a positive effect on performance, often do so under very narrow conditions [2]. It can be difficult to recreate these conditions, and therefore also to recreate the positive effects. There is also a portion of the studies on the topic, that suggests that diversity can have a negative impact on the performance of a team. They suggest that diversity creates social divisions, which again affects performance negatively.
[edit] Annotated bibliography
What differences make a difference? Psychological Science in the Public Interest.[2]. A large study that tries to disentangle what researchers have learned from the last 50 years on the field of diversity in teams and tries to summarize it, and which much of the article is based upon. It also describes how diversity affects teams and how to manage it.
Stahl, G., Maznevski, M., Voigt, A. et al. Unraveling the effects of cultural diversity in teams: A meta-analysis of research on multicultural work groups (2010) [5] Large meta-study, that tries to summarize previous research on the topic of diversity and cultural diversity. Taken from the report: "Our goals in this study were to take stock of and synthesize the findings from previous research, to reconcile conflicting perspectives and past results, and to propose an agenda for the next stage of research in this field."
- ↑ Fernandes, Catarina R & Polzer, Jeffery T. Diversity in Groups. Available at:https://www.hbs.edu/ris/Publication%20Files/Diversity_in_Groups_EmergingTrends_57796940-b049-43dc-b58b-832eccbcaa80.pdf
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 2.18 2.19 Mannix, Elizabeth & Neale, Margaret A (2005). What differences make a difference? Psychological Science in the Public Interest. Available at: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/j.1529-1006.2005.00022.x?casa_token=qiXUEAO_nPIAAAAA:77IXwF62pgU5VFPWF6eW7mm2XyX56bgBE-cmFbnMJsl6NTVD1S2u9EEHZIry56F8RPzRaaAfDdyu
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Geraldi, J., Thuesen, C., Oehmen, J., & Stingl, V. (2017). Doing Projects. A Nordic Flavour to Managing Projects: DS-handbook 185:2017. Dansk Standard.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Seong, J. Y., & Hong, D.-S. (2013). Gender diversity: How can we facilitate its positive effects on teams? Social Behavior and Personality: An international journal, 41(3), 497-508.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 Stahl, Günter & Maznevski, Martha & Voigt, Andreas & Jonsen, Karsten. (2010). Unraveling the effects of cultural diversity in teams: A meta-analysis of research on multicultural workgroups. Journal of International Business Studies. 41. 690-709. 10.1057/jibs.2009.85.
- ↑ Oxford Languages for Google. Cultural diversity definition. Available at: https://www.google.no/search?rls=com.microsoft%3Anb%3A%7Breferrer%3Asource%7D&sxsrf=ALeKk00Aga05cPg7KF2xXvAQudX3lPwCFQ%3A1613070110502&ei=Hn8lYISXHqXnrgTy7L6oAw&q=cultural+diversity+definition&oq=cultural+diversity+definition&gs_lcp=CgZwc3ktYWIQDFAAWABgsCFoAHAAeACAAVWIAVWSAQExmAEAqgEHZ3dzLXdpesABAQ&sclient=psy-ab&ved=0ahUKEwiEnry3wuLuAhWls4sKHXK2DzUQ4dUDCA0
- ↑ Green, K. A., López, M., Wysocki, A., & Kepner, K. (2002). Diversity in the Workplace: Benefits, challenges, and the required managerial tools. EDIS, 2002(2).
- ↑ AXELOS. Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition, Page 74, The Stationery Office Ltd, 2017.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Hoogendoorn, Sander, Hessel Oosterbeek, and Mirjam Van Praag. "The impact of gender diversity on the performance of business teams: Evidence from a field experiment." Management Science 59, no. 7 (2013): 1514-1528.