The Double Diamond Framework
(→Discover) |
(→Application of the framework) |
||
| (115 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
Managing design projects has traditionally been understood as preplanned and predefined phases followed in a linear sequential flow. This approach is no longer sufficient as today´s business environment is very dynamic where the technology is advancing rapidly, customers' preferences are everchanging. Organizations are therefore affected by both external and internal factors which increases the complexity and uncertainty in projects. Exploring the right methods to manage the design, innovation, or problem-oriented projects that would speed up the innovation processes and shortening the life cycle of projects is an ongoing challenge for any project manager. Project managers are accountable for the quality and outcome of a project and to produce successful results and meet the stakeholder needs, the project manager must provide the right tools and techniques for the project teams. One widely applied approach for design projects is the Double Diamond framework developed by the Design Council in 2004<ref name="DC"/>. | Managing design projects has traditionally been understood as preplanned and predefined phases followed in a linear sequential flow. This approach is no longer sufficient as today´s business environment is very dynamic where the technology is advancing rapidly, customers' preferences are everchanging. Organizations are therefore affected by both external and internal factors which increases the complexity and uncertainty in projects. Exploring the right methods to manage the design, innovation, or problem-oriented projects that would speed up the innovation processes and shortening the life cycle of projects is an ongoing challenge for any project manager. Project managers are accountable for the quality and outcome of a project and to produce successful results and meet the stakeholder needs, the project manager must provide the right tools and techniques for the project teams. One widely applied approach for design projects is the Double Diamond framework developed by the Design Council in 2004<ref name="DC"/>. | ||
| − | The Double Diamond framework is a graphical representation of a design process. The framework presents four phases: Discover, Define, Develop, and Deliver. The phases are divided into two diamonds where each phase is characterized by either divergent or convergent thinking. It is an iterative design process that helps the design team to understand the customer needs through collaboration with customers, thus developing solutions based on those needs. This article aims to describe the concept of the Double Diamond, elaborate upon why and when project managers | + | The Double Diamond framework is a graphical representation of a design process. The framework presents four phases: Discover, Define, Develop, and Deliver. The phases are divided into two diamonds where each phase is characterized by either divergent or convergent thinking. It is an iterative design process that helps the design team to understand the customer needs through collaboration with customers, thus developing solutions based on those needs. This article aims to describe the concept of the Double Diamond, elaborate upon why and when project managers and design teams could utilize the framework and a description of how to apply the framework in practice as well as providing potential tools and methods that can be applied within each phase to successfully progress the different phases. Moreover, the advantages and limitations will be discussed as well as the opportunity for extending the framework. |
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Introduction to the Double Diamond == | == Introduction to the Double Diamond == | ||
| − | [[File:DDM.png|500px|thumb|The Double Diamond Framework ( | + | [[File:DDM.png|500px|thumb|The Double Diamond Framework (Own illustration inspired from the original framework by the Design Counsil<ref name=" DC"/> ]] |
| − | The double diamond is as mentioned a structured design approach that tackles the design process and challenges in four phases. These are Discover, Define, Develop and Deliver. | + | |
| + | The double diamond is as mentioned a structured design approach that tackles the design process and challenges in four phases. These are Discover, Define, Develop and Deliver<ref name=" DC"/>. | ||
The phases are divided into two diamonds, where the first diamond presents the Problem Space that indicates doing the right thing, and the second diamond focuses on the solution space of doing things right. | The phases are divided into two diamonds, where the first diamond presents the Problem Space that indicates doing the right thing, and the second diamond focuses on the solution space of doing things right. | ||
| − | The phases within the diamonds are changing between divergent and convergent principles which are all about coming up with many ideas and then thinking about what to do with those ideas. The divergent phase, in essence, is to generate as many ideas as possible and exploring possibilities in a broader sense, whereas the convergent phase is about taking the ideas, analyzing, improving, reflecting, and evaluating them. Based on these making decisions and narrowing into one or two key ideas, problems, or | + | The phases within the diamonds are changing between divergent and convergent principles which are all about coming up with many ideas and then thinking about what to do with those ideas. The divergent phase, in essence, is to generate as many ideas as possible and exploring possibilities in a broader sense, whereas the convergent phase is about taking the ideas, analyzing, improving, reflecting, and evaluating them. Based on these making decisions and narrowing into one or two key ideas, problems, or solutions <ref name="DC"/>. |
| − | *'''Discover''' – The first phase is a divergent thinking practice that aims to help the design team to explore and understand the initial problem from a broader perspective. It involves research | + | *'''Discover''' – The first phase is a divergent thinking practice that aims to help the design team to explore and understand the initial problem from a broader perspective. It involves a lot of research, collaboration with potential customers and other stakeholders that are affected by the problem. |
*'''Define''' – The second phase is a convergent thinking practice where the focus is to narrow the findings or ideas from the discovery phase, analyze, and evaluate them. Based on the findings and experiences with customers and stakeholders, narrowing the findings and define one or two clear ideas or problems to be solved. | *'''Define''' – The second phase is a convergent thinking practice where the focus is to narrow the findings or ideas from the discovery phase, analyze, and evaluate them. Based on the findings and experiences with customers and stakeholders, narrowing the findings and define one or two clear ideas or problems to be solved. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 26: | ||
*'''Deliver''' – In the fourth and last phase, the focus is on testing and evaluating the solution, and make the concept ready for production and launch. | *'''Deliver''' – In the fourth and last phase, the focus is on testing and evaluating the solution, and make the concept ready for production and launch. | ||
| − | The Double Diamond is a good and simple framework that can guide a design team through the design process and allows them to get from an idea through problem identification, validation, design, and to an ultimate solution. As design processes used to be complex and chaotic, the framework explains that the process can be structured systematically and yet encourages working iteratively. The Design Council's objective was to develop this framework to analyze the designers´ work and to ensure creative outputs. The result of the framework has been evidently successful among a wide range of companies. | + | The Double Diamond is a good and simple framework that can guide a design team through the design process and allows them to get from an idea through problem identification, validation, design, and to an ultimate solution. As design processes used to be complex and chaotic, the framework explains that the process can be structured systematically and yet encourages working iteratively. The Design Council's objective was to develop this framework to analyze the designers´ work and to ensure creative outputs. The result of the framework has been evidently successful among a wide range of companies <ref name="DC"/>. |
== Application of the framework == | == Application of the framework == | ||
The major advantage of the Double diamond framework is that it is flexible and can be adapted to any type of design project where there is a problem that needs to be solved. One can rarely go wrong by applying the framework but taking the steps consciously and utilizing appropriate tools and techniques in the different phases would highly affect the quality and output of a project. | The major advantage of the Double diamond framework is that it is flexible and can be adapted to any type of design project where there is a problem that needs to be solved. One can rarely go wrong by applying the framework but taking the steps consciously and utilizing appropriate tools and techniques in the different phases would highly affect the quality and output of a project. | ||
| − | In the context of project management, the framework helps the project managers | + | In the context of project management, the framework helps the project managers to get a complete overview of the project life cycle and how a team approaches a design project. Starting from the left at the Discover phase and processing through each phase to Deliver phase in a systematic and yet iterative process. Compare to the classic project life cycle approach such as waterfall that requires a lot of planning before applying the model, the Double Diamond includes the planning and initiation which makes it more flexible for project managers to structure the overall work activities, allocate the resources, and estimate a timeline for each phase in a project life cycle. The Double Diamond can be explained based on the standard project management principles of PMBOK Guide where a project life cycle is characterized into four stages: 1)starting the project, 2) Organizing and preparing, 3) Carrying out the work, and 4) Ending the project <ref name="PMBOK"/>. |
| + | |||
| + | The Double Diamond does not focus on time and based on the graphical description phases are equally important, thus should be equally weighted. However, based on experience from a design project developed in close collaboration with a well-known company, the first diamond, Discover and Define, phase would usually take longer time as we are dealing with the beginning of the fuzzy front end where everything is unknown and chaotic. It requires a lot of research, time to reach the appropriate customers and stakeholders, facilitating workshops and interviews, ideating, analyzing, and planning, etc. Once there is a specific problem at the end of the first diamond, things will become more clear, and there will only be one problem to focus on. The design team would also become more confident and expert with what they are doing as they have already tried a similar process during the first diamond but with more than one idea. The second diamond requires more in-depth and specialized work and skillsets. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nevertheless, the weight and timeframe of the double diamond depend on the type of project. It is a graphical framework that organizes the project life cycle into four phases. However, the framework is very flexible and can be adjusted to fit different types of projects in regard to workload and timeframe by "stretching" the diamond in different points where the focus is relying the most upon. For example, if a project is more product and prototype focused than research then the second diamond is going to be very stretched whereas a project that requires very long discovery such as R&D projects then the first diamond is going last a long time and will look very stretched compare to the second diamond. | ||
| + | |||
=== The problem space === | === The problem space === | ||
| − | The first diamond is defined as a problem space where the objective is to | + | The first diamond is defined as a problem space where the objective is to diverge a problem into a range of outputs based on research and discovery and then converging into a focused solution. |
| − | ====Discover==== | + | |
| + | ==== Discover==== | ||
The first stage of the Double Diamond marks the beginning of the design process. The objective is to identify and investigate a broad range of ideas and opportunities within the problem context and diverge to the problem space. | The first stage of the Double Diamond marks the beginning of the design process. The objective is to identify and investigate a broad range of ideas and opportunities within the problem context and diverge to the problem space. | ||
| − | Areas to be investigated are market, user needs, trends, and other sources of information. Different techniques can be used to effectively progress this phase. The Design Council provides a set of tools and techniques that can be utilized: | + | Areas to be investigated are market, user needs, trends, and other sources of information. Different techniques can be used to effectively progress this phase. The Design Council provides a set of tools and techniques that can be utilized <ref name="One"/>: |
| − | * | + | *Creating a project space <ref name="One"/> - Considering a dedicated area to organize project materials, meet for project work, and facilitate workshops can help the design team to have visibility of having a large amount of information and resources and to be able to keep them organized. |
| − | Considering a dedicated area to organize project materials, meet for project work, and facilitate workshops can help the design team to have visibility of having a large amount of information and resources and to be able to keep them organized. | + | |
| − | * | + | *Observation<ref name="One"/> - Considering ethnographic method to observe the customers' reactions towards the idea or their interaction with the product or service. Through observations identifying the areas that the problems occur. |
| − | Considering ethnographic method to observe the customers' reactions towards the idea or their interaction with the product or service. Through observations identifying the areas that the problems occur. | + | |
| − | * | + | *Brainstorming<ref name="One"/> - Brainstorming would enable the design team to generate ideas in regards to the problem effectively. |
| − | Brainstorming would enable the design team to generate ideas in regards to the problem effectively. | + | |
====Define==== | ====Define==== | ||
| + | Moving towards the second phase, the team has to deal with refining the ideas gathered in the Discover phase, to converge to a more specified problem that the project aims to solve. This phase comprises data or ideas analyzing, evaluation, and screening to select the ultimate problem or idea to work on. At the end of this phase, the team has to come up with a specific problem statement<ref name="Two"/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following methods can be used at this phase are: | ||
| + | *Focus groups<ref name="Two"/> - Focus groups can be conducted to generate an overview of user opinion, reactions to ideas, and the general topic. Focus groups usually involve 6-10 participants in a discussion planned and moderated by a skilled facilitator. The length of such a focus group lasts 2-3 hours. | ||
| + | *Assessment Criteria<ref name="Two"/> - This is a selection method that would help the team to select the most promising ideas for further development. A broader range of stakeholders assessing the idea based on criteria would be better. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The Six Thinking Hats <ref name="Hats"/> - The Six Thinking Hats can be conducted to analyze and evaluate an idea's potential from six different perspectives. | ||
=== The solution space === | === The solution space === | ||
| + | After having gained a thorough insight into the problem area and have elected and defined a problem statement, the team moves into the solution space where the focus is on the actual development of the solution or solutions. | ||
| + | |||
====Develop==== | ====Develop==== | ||
| + | As the team has a clear understanding of the problem, they are able to identify different solutions that can solve the problem. The objective of the Develop phase is to look into different solutions and building concepts in form of rapid prototyping and testing through iterative processes <ref name="Three"/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Methods that can be utilized in this phase: | ||
| + | *Agile Development methods | ||
| + | *Persona | ||
| + | *Scrum | ||
| + | *Workshop | ||
| + | |||
====Deliver==== | ====Deliver==== | ||
| + | In the last phase, the process revolves around the final concept where the concept will be tested and finalized for production. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Methods relevant for this phase <ref name="Four"/>: | ||
| + | *Workshop | ||
| + | *Pitch | ||
| + | *Final testing | ||
| + | *Service Blueprint | ||
| + | *Working prototype | ||
| + | *Feedback loop | ||
====Transition from one phase to another==== | ====Transition from one phase to another==== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 88: | ||
== Limitations == | == Limitations == | ||
| + | The Double Diamond framework does not focus on time. It is, therefore the project manager´s responsibility to conduct a timeline over the project period by e.g. using a Gantt chart to list all the activities within each phase and estimate the time for each of those tasks or activities. | ||
| − | + | It can also be argued that the framework is very practical and heavily focuses on the design and development of a solution. It might not be enough to be applied alone for method-oriented projects. A combination of the Double Diamond and the more classical project life cycle models such as the Stage Gates Model can be recommended for complex projects that involve many factors to be taken into consideration than the design and development of one solution. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
== Annotated Bibliography == | == Annotated Bibliography == | ||
| − | + | '''Design Council. 2005. What is the framework for innovation? Design Council's evolved Double Diamond'''. | |
| + | The British Design Council provides a continuous update on the Double Diamond framework. The different tools and techniques suggested for each phase of the Double Diamond are described in detail and can be relevant for users to get a better insight as the application of the different tools is not included in this article. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''IDEO.org. 2015. The Field Guide to Human-Centered Design, 1st Edition | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Double Diamond framework represents the principles of Human-Centred Design which is characterized by a non-linear approach that includes phases of inspiration, ideation, and implementation performed iteratively. The Book provides a wide range of tools and methods that can be used to manage the design phases successfully. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Project management institute (2017). A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide). (6th edition) | ||
| + | |||
| + | PMBOK Guide book is the recognized standard of project management that provides rules, guidelines, and characteristics for project management. The stage of the project lifecycle and the project management responsibilities on stage-by-stage are further elaborated in the book that could be useful for the readers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References== | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
| + | |||
<ref name="DC">Design Council. 2021. What is the framework for innovation? Design Council's evolved Double Diamond. [online] Available at: <https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/what-framework-innovation-design-councils-evolved-double-diamond> [Accessed 19 February 2021].</ref> | <ref name="DC">Design Council. 2021. What is the framework for innovation? Design Council's evolved Double Diamond. [online] Available at: <https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/what-framework-innovation-design-councils-evolved-double-diamond> [Accessed 19 February 2021].</ref> | ||
| Line 77: | Line 118: | ||
<ref name="DT">Dam and Siang, R.,.T. 2021. The Field Guide to Human-Centered Design. [Online]. [16 February 2021]. Available from: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/5-stages-in-the-design-thinking-process</ref> | <ref name="DT">Dam and Siang, R.,.T. 2021. The Field Guide to Human-Centered Design. [Online]. [16 February 2021]. Available from: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/5-stages-in-the-design-thinking-process</ref> | ||
| − | <ref name="DD1">Design council. 2014. A study of the design process . [Online]. [17 February 2021]. Available from: https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/sites/default/files/asset/document/ElevenLessons_Design_Council%20(2).pdf</ref> | + | <ref name="DD1">Design council. 2014. A study of the design process. [Online]. [17 February 2021]. Available from: https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/sites/default/files/asset/document/ElevenLessons_Design_Council%20(2).pdf</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="One">Design council. 2015. Design Methods Step 1: Discover. [Online]. [17 February 2021]. Available from: https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-1-discover</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="Two">Design council. 2015. Design Methods Step 2: Define. [Online]. [17 February 2021]. Available from: https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-2-define</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="Three">Design council. 2015. Design Methods Step 3: Develop. [Online]. [17 February 2021]. Available from: https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-3-develop</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="Four">Design council. 2015. Design Methods Step 4: Deliver. [Online]. [17 February 2021]. Available from:https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-4-deliver </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="PMBOK"> Project management institute. 2017. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide). (6th edition). Section 1.2.4 COMPONENT OF THE GUIDE, Page 18-22</ref> | ||
| − | <ref name=" | + | <ref name="Hats">Wells M,. 2015. The six Thinking Hats. [Online]. [17 February 2021]. Available from:http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Six_Thinking_Hats </ref> |
Latest revision as of 23:51, 28 February 2021
[edit] Abstract
Managing design projects has traditionally been understood as preplanned and predefined phases followed in a linear sequential flow. This approach is no longer sufficient as today´s business environment is very dynamic where the technology is advancing rapidly, customers' preferences are everchanging. Organizations are therefore affected by both external and internal factors which increases the complexity and uncertainty in projects. Exploring the right methods to manage the design, innovation, or problem-oriented projects that would speed up the innovation processes and shortening the life cycle of projects is an ongoing challenge for any project manager. Project managers are accountable for the quality and outcome of a project and to produce successful results and meet the stakeholder needs, the project manager must provide the right tools and techniques for the project teams. One widely applied approach for design projects is the Double Diamond framework developed by the Design Council in 2004[1]. The Double Diamond framework is a graphical representation of a design process. The framework presents four phases: Discover, Define, Develop, and Deliver. The phases are divided into two diamonds where each phase is characterized by either divergent or convergent thinking. It is an iterative design process that helps the design team to understand the customer needs through collaboration with customers, thus developing solutions based on those needs. This article aims to describe the concept of the Double Diamond, elaborate upon why and when project managers and design teams could utilize the framework and a description of how to apply the framework in practice as well as providing potential tools and methods that can be applied within each phase to successfully progress the different phases. Moreover, the advantages and limitations will be discussed as well as the opportunity for extending the framework.
Contents |
[edit] Background
The Double Diamond framework is derived from the Design Thinking concept. Some sources are claiming that its origins go back to the “Dynamics of Divergence and Convergence” model introduced in 1996 by Bela Banathy[2]. However, the framework has the same underlying principles as many other design-related models such as Human-Centered Design, by IDEO[3], and the Design Thinking process[4]. The framework is developed by the British Design Council back in 2004. The Design Council´s origin is Industrial Design which is about designing products, devices, objects, and services. The development of the model has been based on qualitative case studies gathered from 11 global companies, amongst other LEGO, Microsoft, Sony, Starbucks, Virgin Atlantic Airways, Xerox[5]. The study specifically looked at the way design was used in these companies, how designers collaborated with staff cross-functionally, and how the design process was managed. The Framework has been revamped incrementally since its publication. These revisions are both done by the Design Council and other companies that have adapted and adjusted the model into their projects. When searching for the Double Diamond on the internet, one can find the model in various shapes and descriptions that are made from different companies and stakeholders based on the type of design projects, however, the standard graphical description is similar to the depicted framework in Figure 1.
[edit] Introduction to the Double Diamond
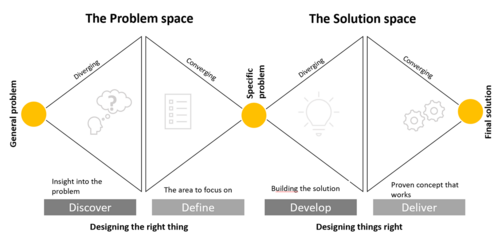
The double diamond is as mentioned a structured design approach that tackles the design process and challenges in four phases. These are Discover, Define, Develop and Deliver[1]. The phases are divided into two diamonds, where the first diamond presents the Problem Space that indicates doing the right thing, and the second diamond focuses on the solution space of doing things right.
The phases within the diamonds are changing between divergent and convergent principles which are all about coming up with many ideas and then thinking about what to do with those ideas. The divergent phase, in essence, is to generate as many ideas as possible and exploring possibilities in a broader sense, whereas the convergent phase is about taking the ideas, analyzing, improving, reflecting, and evaluating them. Based on these making decisions and narrowing into one or two key ideas, problems, or solutions [1].
- Discover – The first phase is a divergent thinking practice that aims to help the design team to explore and understand the initial problem from a broader perspective. It involves a lot of research, collaboration with potential customers and other stakeholders that are affected by the problem.
- Define – The second phase is a convergent thinking practice where the focus is to narrow the findings or ideas from the discovery phase, analyze, and evaluate them. Based on the findings and experiences with customers and stakeholders, narrowing the findings and define one or two clear ideas or problems to be solved.
- Develop – The third phase, focus on developing a solution. The solution would depend on the type of the project whether it is a physical prototype, a service prototype, or an integrated solution.
- Deliver – In the fourth and last phase, the focus is on testing and evaluating the solution, and make the concept ready for production and launch.
The Double Diamond is a good and simple framework that can guide a design team through the design process and allows them to get from an idea through problem identification, validation, design, and to an ultimate solution. As design processes used to be complex and chaotic, the framework explains that the process can be structured systematically and yet encourages working iteratively. The Design Council's objective was to develop this framework to analyze the designers´ work and to ensure creative outputs. The result of the framework has been evidently successful among a wide range of companies [1].
[edit] Application of the framework
The major advantage of the Double diamond framework is that it is flexible and can be adapted to any type of design project where there is a problem that needs to be solved. One can rarely go wrong by applying the framework but taking the steps consciously and utilizing appropriate tools and techniques in the different phases would highly affect the quality and output of a project.
In the context of project management, the framework helps the project managers to get a complete overview of the project life cycle and how a team approaches a design project. Starting from the left at the Discover phase and processing through each phase to Deliver phase in a systematic and yet iterative process. Compare to the classic project life cycle approach such as waterfall that requires a lot of planning before applying the model, the Double Diamond includes the planning and initiation which makes it more flexible for project managers to structure the overall work activities, allocate the resources, and estimate a timeline for each phase in a project life cycle. The Double Diamond can be explained based on the standard project management principles of PMBOK Guide where a project life cycle is characterized into four stages: 1)starting the project, 2) Organizing and preparing, 3) Carrying out the work, and 4) Ending the project [6].
The Double Diamond does not focus on time and based on the graphical description phases are equally important, thus should be equally weighted. However, based on experience from a design project developed in close collaboration with a well-known company, the first diamond, Discover and Define, phase would usually take longer time as we are dealing with the beginning of the fuzzy front end where everything is unknown and chaotic. It requires a lot of research, time to reach the appropriate customers and stakeholders, facilitating workshops and interviews, ideating, analyzing, and planning, etc. Once there is a specific problem at the end of the first diamond, things will become more clear, and there will only be one problem to focus on. The design team would also become more confident and expert with what they are doing as they have already tried a similar process during the first diamond but with more than one idea. The second diamond requires more in-depth and specialized work and skillsets.
Nevertheless, the weight and timeframe of the double diamond depend on the type of project. It is a graphical framework that organizes the project life cycle into four phases. However, the framework is very flexible and can be adjusted to fit different types of projects in regard to workload and timeframe by "stretching" the diamond in different points where the focus is relying the most upon. For example, if a project is more product and prototype focused than research then the second diamond is going to be very stretched whereas a project that requires very long discovery such as R&D projects then the first diamond is going last a long time and will look very stretched compare to the second diamond.
[edit] The problem space
The first diamond is defined as a problem space where the objective is to diverge a problem into a range of outputs based on research and discovery and then converging into a focused solution.
[edit] Discover
The first stage of the Double Diamond marks the beginning of the design process. The objective is to identify and investigate a broad range of ideas and opportunities within the problem context and diverge to the problem space. Areas to be investigated are market, user needs, trends, and other sources of information. Different techniques can be used to effectively progress this phase. The Design Council provides a set of tools and techniques that can be utilized [7]:
- Creating a project space [7] - Considering a dedicated area to organize project materials, meet for project work, and facilitate workshops can help the design team to have visibility of having a large amount of information and resources and to be able to keep them organized.
- Observation[7] - Considering ethnographic method to observe the customers' reactions towards the idea or their interaction with the product or service. Through observations identifying the areas that the problems occur.
- Brainstorming[7] - Brainstorming would enable the design team to generate ideas in regards to the problem effectively.
[edit] Define
Moving towards the second phase, the team has to deal with refining the ideas gathered in the Discover phase, to converge to a more specified problem that the project aims to solve. This phase comprises data or ideas analyzing, evaluation, and screening to select the ultimate problem or idea to work on. At the end of this phase, the team has to come up with a specific problem statement[8].
The following methods can be used at this phase are:
- Focus groups[8] - Focus groups can be conducted to generate an overview of user opinion, reactions to ideas, and the general topic. Focus groups usually involve 6-10 participants in a discussion planned and moderated by a skilled facilitator. The length of such a focus group lasts 2-3 hours.
- Assessment Criteria[8] - This is a selection method that would help the team to select the most promising ideas for further development. A broader range of stakeholders assessing the idea based on criteria would be better.
- The Six Thinking Hats [9] - The Six Thinking Hats can be conducted to analyze and evaluate an idea's potential from six different perspectives.
[edit] The solution space
After having gained a thorough insight into the problem area and have elected and defined a problem statement, the team moves into the solution space where the focus is on the actual development of the solution or solutions.
[edit] Develop
As the team has a clear understanding of the problem, they are able to identify different solutions that can solve the problem. The objective of the Develop phase is to look into different solutions and building concepts in form of rapid prototyping and testing through iterative processes [10].
Methods that can be utilized in this phase:
- Agile Development methods
- Persona
- Scrum
- Workshop
[edit] Deliver
In the last phase, the process revolves around the final concept where the concept will be tested and finalized for production.
Methods relevant for this phase [11]:
- Workshop
- Pitch
- Final testing
- Service Blueprint
- Working prototype
- Feedback loop
[edit] Transition from one phase to another
It is essential to be aware that the Double Diamond is not a linear approach where a team has to completely finish one phase before starting with another phase, and that there is no chance for going back and adjust things as it is known from the traditional project life cycle approaches such as Stage Gates Model. However, the transition from one phase to another requires reporting and evaluation from the project manager, project owner, and relevant stakeholders. This can be done by presenting the idea or solution, preferably in form of pretotypes and prototypes. If the idea or the solution is approved, the team can move to the next phase but if not, then there should be put some time to revise. However, the transition should be smooth and since the double diamond is an iterative process, the designers iterate their ways forward.
[edit] Limitations
The Double Diamond framework does not focus on time. It is, therefore the project manager´s responsibility to conduct a timeline over the project period by e.g. using a Gantt chart to list all the activities within each phase and estimate the time for each of those tasks or activities.
It can also be argued that the framework is very practical and heavily focuses on the design and development of a solution. It might not be enough to be applied alone for method-oriented projects. A combination of the Double Diamond and the more classical project life cycle models such as the Stage Gates Model can be recommended for complex projects that involve many factors to be taken into consideration than the design and development of one solution.
[edit] Annotated Bibliography
Design Council. 2005. What is the framework for innovation? Design Council's evolved Double Diamond.
The British Design Council provides a continuous update on the Double Diamond framework. The different tools and techniques suggested for each phase of the Double Diamond are described in detail and can be relevant for users to get a better insight as the application of the different tools is not included in this article.
IDEO.org. 2015. The Field Guide to Human-Centered Design, 1st Edition
The Double Diamond framework represents the principles of Human-Centred Design which is characterized by a non-linear approach that includes phases of inspiration, ideation, and implementation performed iteratively. The Book provides a wide range of tools and methods that can be used to manage the design phases successfully.
Project management institute (2017). A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide). (6th edition)
PMBOK Guide book is the recognized standard of project management that provides rules, guidelines, and characteristics for project management. The stage of the project lifecycle and the project management responsibilities on stage-by-stage are further elaborated in the book that could be useful for the readers.
[edit] References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Design Council. 2021. What is the framework for innovation? Design Council's evolved Double Diamond. [online] Available at: <https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/what-framework-innovation-design-councils-evolved-double-diamond> [Accessed 19 February 2021].
- ↑ Zamarrón. 2020. Iteration and divergence-convergence are not alternative approaches. [Online]. [16 February 2021]. Available from: https://medium.com/@albertozamarron
- ↑ Ideo. 2015. The Field Guide to Human-Centered Design. [Online]. [16 February 2021]. Available from: https://bestgraz.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/Field-Guide-to-Human-Centered-Design_IDEOorg.pdf
- ↑ Dam and Siang, R.,.T. 2021. The Field Guide to Human-Centered Design. [Online]. [16 February 2021]. Available from: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/5-stages-in-the-design-thinking-process
- ↑ Design council. 2014. A study of the design process. [Online]. [17 February 2021]. Available from: https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/sites/default/files/asset/document/ElevenLessons_Design_Council%20(2).pdf
- ↑ Project management institute. 2017. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide). (6th edition). Section 1.2.4 COMPONENT OF THE GUIDE, Page 18-22
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Design council. 2015. Design Methods Step 1: Discover. [Online]. [17 February 2021]. Available from: https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-1-discover
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Design council. 2015. Design Methods Step 2: Define. [Online]. [17 February 2021]. Available from: https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-2-define
- ↑ Wells M,. 2015. The six Thinking Hats. [Online]. [17 February 2021]. Available from:http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Six_Thinking_Hats
- ↑ Design council. 2015. Design Methods Step 3: Develop. [Online]. [17 February 2021]. Available from: https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-3-develop
- ↑ Design council. 2015. Design Methods Step 4: Deliver. [Online]. [17 February 2021]. Available from:https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-4-deliver