Digital Communication in Project Management
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
The team members within any project rely on the ability to collaborate, share, gather and interprete knowledge and information to carry out the objectives of any project - hence, they rely on the ability to communicate | The team members within any project rely on the ability to collaborate, share, gather and interprete knowledge and information to carry out the objectives of any project - hence, they rely on the ability to communicate | ||
| − | <ref name= | + | <ref name="Communication"> ''BG Zulch, |
Communication: The Foundation of Project Management, | Communication: The Foundation of Project Management, | ||
Procedia Technology, Volume 16, 2014, Pages 1000-1009, ISSN 2212-0173, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2014.10.054 (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212017314002813)'' </ref>. | Procedia Technology, Volume 16, 2014, Pages 1000-1009, ISSN 2212-0173, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2014.10.054 (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212017314002813)'' </ref>. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==== Communication processes ==== | ==== Communication processes ==== | ||
| − | Within project management, most communication will follow the ''interactive communication model''; a sender encodes a message that is transmitted through a medium to a receiver that decodes the message and the receiver will in most cases will provide feedback on this message. This process happens both verbally and non-verbally, and it has been argued that the feedback on the message is of key importance to any PM, as it enables the PM to monitor the success of a communication process. The feedback will in this case be a confirmation of understanding from the receiving part <ref name=" | + | |
| + | Within project management, most communication will follow the ''interactive communication model''; a sender encodes a message that is transmitted through a medium to a receiver that decodes the message and the receiver will in most cases will provide feedback on this message. This process happens both verbally and non-verbally, and it has been argued that the feedback on the message is of key importance to any PM, as it enables the PM to monitor the success of a communication process. The feedback will in this case be a confirmation of understanding from the receiving part <ref name="Communication"/>. Some non-verbal communication might, however, take the form of linear communication, where the feedback is not a necessity, i.e. informative e-mails or simple instructive messages. | ||
[[File:Communicationmodel.jpg|center|750px|Interactive Communication Model <ref name=''commodel''> ''Llopis-Lorente, A., Díez, P., Sánchez, A. et al. Interactive models of communication at the nanoscale using nanoparticles that talk to one another. Nat Commun 8, 15511 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15511'' </ref>|thumb]] | [[File:Communicationmodel.jpg|center|750px|Interactive Communication Model <ref name=''commodel''> ''Llopis-Lorente, A., Díez, P., Sánchez, A. et al. Interactive models of communication at the nanoscale using nanoparticles that talk to one another. Nat Commun 8, 15511 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15511'' </ref>|thumb]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | === Planning | + | Characteristic for the interactive communication model is, that both the encoding and the decoding of the message depends on both parties' ''field of experience''. People have different knowledge, behaviors, beliefs, situations, psychological factors, etc., and this might influence the effectivity of the communication. For the sending part, this defines the encoding, i.e. the content of the message, and for the receiving part this shapes the decoding of the message, i.e. the interpretation of the content <ref name=''experience''> '' https://study.com/academy/lesson/interactive-model-of-communication-definition-application.html [online]. Visited on: 16-02-2022 20:00'' </ref>. This is something that a PM with a wish to attain effective communication must take into account when formulating communication. |
| + | |||
| + | The big question in communication within project management is to make sure that it reaches all intended parties with the intended interpretation to avoid misunderstandings. The simple answer as to how to achieve this is simply to plan the communication. However, the reality of this might not be as easily simplified. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Planning project communication <ref name = "Communication"/> === | ||
| + | ===== Communication plan ===== | ||
| + | The PM has the responsibility not only to establish the organisational structure of the project but also the communication plan and lines of communication. Zulch argues that the communication plan should outline the following: | ||
| + | *''Who'': | ||
| + | ::Lines of communication, responsibility and authority and involved parties | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''What'': | ||
| + | ::Communication scope and form | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''When'': | ||
| + | ::Primarily scheduling communication | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''Feedback'': | ||
| + | ::How and when, document control | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''Filing/documentation'': | ||
| + | ::For retrieval, backtracing, storing | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''How'': | ||
| + | ::What type of information for what purpose? | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | After developing this communication plan, Zulch advises that consensus around it is achieved to provide a clear sense of direction to all related parties - and in particular when project complexity rises. Zulch also argues that the primary focal points of the communication plan are; keeping key stakeholders in the loop at all times, and promoting the project. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Lines of communication ===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Zulch divides the lines of communication in two primary categories; formal and informal communication. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Formal communitation:'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Generally speaking, formal communication is any communication with a formal, project-related purpose. It happens in four directions: | ||
| + | |||
| + | #Downward communication: | ||
| + | ::Flows from the top and down through project levels with the purpose of providing information on topics such as strategies, goals, or policies. It is likely to be filtered based on management intention with communication. | ||
| + | #Upward communication: | ||
| + | ::Flows from lower levels and up to supply information. This is crucial to any PM! | ||
| + | #Horizontal communication: | ||
| + | ::Happens between project members at adjacent levels and usually coordinates work efforts. This prevents tunnel vision within departments. | ||
| + | #Diagonal communication: | ||
| + | ::Takes place between project members at different levels usually to provide relevant information on occasion. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The PM must be aware of these when planning the communication, since the positioning within the project authoritative hierarchy defines the method, content and intention with the communication, i.e. the PM must use different communication skills for different levels. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Informal communication:'' | ||
| + | Informal communication is mostly any communication without a formal purpose. It may be project-related but in most cases it constitutes the unofficial communication based on both facts and rumours. It can flow in any direction within the project organisation and uses ''the grapevine'' as its primary channel. Characteristic for this type of communication is that it takes place without the influence of the PM, but it is a fact that it affects the effetiveness of the communication from the PM. | ||
Revision as of 21:01, 16 February 2022
Contents |
Big Idea
Within the field of project management it is estimated, that project managers (PM) on average spend rougly 80% of their time on communication [1]. This explains why some refer to communication as the foundation of project management[2].
Communication is the act of sharing and interpreting information across different project areas and interests. Communication is what holds together the people section of any project, but miscommunication can also be the downfall of any project which otherwise could have turned out successful.
The team members within any project rely on the ability to collaborate, share, gather and interprete knowledge and information to carry out the objectives of any project - hence, they rely on the ability to communicate [3].
However, in recent times, ways of communicating when carrying out projects have undergone severe changes due to the consequences of the concurrent and ongoing pandemic, COVID-19. It is still unclear what all the consequences of these changes are, but patterns are emerging and it seems that at least some of these will be sustained [4].
Although the digital tranformation is something that has been an ongoing trend in many facets of project management since the invention of the internet, COVID-19 has made its impact on the way we communicate within project teams. COVID-19 has not only inducted changes of consequential character. [4] New ways of communicating within projects are emerging and they propose new implementations and applications of existing communication practices. Project team members are experiencing these changes differently and it can be difficult to generalize these perceivings into implementable changes. However, an common emerging pattern is that projects and projects management will have to adjust to an everyday life with more digital communication and PMs will have to adjust to an everyday agenda with a more digital characteristic or at least with the possibility of communicating digitally with some frequency.
Communication in Project Management
When addressing communication in project management, it is relevant to first understand the basic mechanics of this.
"Communication is the process of acquiring all relevant information, interpreting this information and effectively disseminating the information to persons who might need it. Communication is of vital importance to everyone involved in, and influenced by, projects.[5]"
Communication processes
Within project management, most communication will follow the interactive communication model; a sender encodes a message that is transmitted through a medium to a receiver that decodes the message and the receiver will in most cases will provide feedback on this message. This process happens both verbally and non-verbally, and it has been argued that the feedback on the message is of key importance to any PM, as it enables the PM to monitor the success of a communication process. The feedback will in this case be a confirmation of understanding from the receiving part [3]. Some non-verbal communication might, however, take the form of linear communication, where the feedback is not a necessity, i.e. informative e-mails or simple instructive messages.
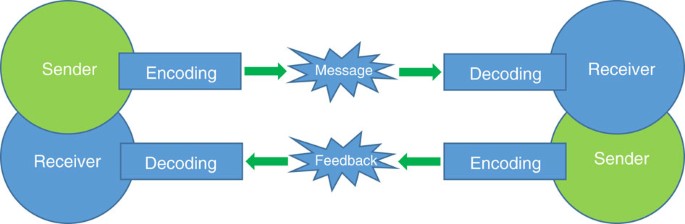
Characteristic for the interactive communication model is, that both the encoding and the decoding of the message depends on both parties' field of experience. People have different knowledge, behaviors, beliefs, situations, psychological factors, etc., and this might influence the effectivity of the communication. For the sending part, this defines the encoding, i.e. the content of the message, and for the receiving part this shapes the decoding of the message, i.e. the interpretation of the content [7]. This is something that a PM with a wish to attain effective communication must take into account when formulating communication.
The big question in communication within project management is to make sure that it reaches all intended parties with the intended interpretation to avoid misunderstandings. The simple answer as to how to achieve this is simply to plan the communication. However, the reality of this might not be as easily simplified.
Planning project communication [3]
Communication plan
The PM has the responsibility not only to establish the organisational structure of the project but also the communication plan and lines of communication. Zulch argues that the communication plan should outline the following:
- Who:
- Lines of communication, responsibility and authority and involved parties
- What:
- Communication scope and form
- When:
- Primarily scheduling communication
- Feedback:
- How and when, document control
- Filing/documentation:
- For retrieval, backtracing, storing
- How:
- What type of information for what purpose?
After developing this communication plan, Zulch advises that consensus around it is achieved to provide a clear sense of direction to all related parties - and in particular when project complexity rises. Zulch also argues that the primary focal points of the communication plan are; keeping key stakeholders in the loop at all times, and promoting the project.
Lines of communication
Zulch divides the lines of communication in two primary categories; formal and informal communication.
Formal communitation:
Generally speaking, formal communication is any communication with a formal, project-related purpose. It happens in four directions:
- Downward communication:
- Flows from the top and down through project levels with the purpose of providing information on topics such as strategies, goals, or policies. It is likely to be filtered based on management intention with communication.
- Upward communication:
- Flows from lower levels and up to supply information. This is crucial to any PM!
- Horizontal communication:
- Happens between project members at adjacent levels and usually coordinates work efforts. This prevents tunnel vision within departments.
- Diagonal communication:
- Takes place between project members at different levels usually to provide relevant information on occasion.
The PM must be aware of these when planning the communication, since the positioning within the project authoritative hierarchy defines the method, content and intention with the communication, i.e. the PM must use different communication skills for different levels.
Informal communication:
Informal communication is mostly any communication without a formal purpose. It may be project-related but in most cases it constitutes the unofficial communication based on both facts and rumours. It can flow in any direction within the project organisation and uses the grapevine as its primary channel. Characteristic for this type of communication is that it takes place without the influence of the PM, but it is a fact that it affects the effetiveness of the communication from the PM.
- ↑ Geraldi, Joana; Thuesen, Christian; Oehmen, Josef; Sting, Verena (2017), Doing Projects. A Nordic Flavour to Managing Projects, Engineering Systems Division, Management Engineering Department, Technical University of Denmark.
- ↑ Zulch, B. (2014):Communication: The Foundation of Project Management. Procedia Technology, 16, 1000–1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2014.10.054.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 BG Zulch, Communication: The Foundation of Project Management, Procedia Technology, Volume 16, 2014, Pages 1000-1009, ISSN 2212-0173, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2014.10.054 (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212017314002813)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Encinas, E., Simons, A., & Sattineni, A. (2021). Impact of COVID-19 on Communications within the Construction Industry. 2(Cdc), 165–156. https://doi.org/10.29007/lhs4
- ↑ Egeland, B. Project communication series: PM communication skills. [online]. Available from: <http://pmtips.net/project-communication-series-pm-communication-skills/>.; 2010.
- ↑ Llopis-Lorente, A., Díez, P., Sánchez, A. et al. Interactive models of communication at the nanoscale using nanoparticles that talk to one another. Nat Commun 8, 15511 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15511
- ↑ https://study.com/academy/lesson/interactive-model-of-communication-definition-application.html [online]. Visited on: 16-02-2022 20:00