Agile model
(→Scrum) |
(→Scrum) |
||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
| − | [[File:SCRUM_schem. | + | [[File:SCRUM_schem.jpg|550px|thumb|center|SCRUM process]] |
==== Extreme Programming ==== | ==== Extreme Programming ==== | ||
Revision as of 08:18, 7 March 2022
Contents |
Abstract
Recently, the world has become much more complex and unpredictable, a special acronym has appeared to describe it, “VUCA”, which states for volatile, unpredictable, complex and ambiguous. [1]
The fast pace of changing technology and evolving markets, leads to the need of adaptative and flexible project management approaches. Agile model is an iterative project management approach, that consists of breaking down the development process into small iterations. It also emphasizes the importance of collaborating with the customer and having their feedback though out the process. Requirements and solutions evolve through collaboration between cross-functional teams. It encourages frequent inspection and adaptation for rapid delivery of high-quality solutions that are aligned with customer needs.
Agile first appeared in the early 1990s within the software development industry and is based on the Agile Manifesto, 2001 [2] and its 12 principles. Since then, many agile frameworks have emerged such as SCRUM, Extreme Programming (XP), Kanban and Lean. Nowadays, Agile has become very popular within many organizations.
This article introduces the agile concept and presents the main values and principles of the Agile Manifesto. Next, it describes the different Agile frameworks and its applications. The last part of the article mentions possible limitations of Agile.
Big idea
What is Agile model?
Agile methodology is a project management process that is based on breaking down the project development into more manageable tasks, which are completed in short iterations. It mainly focuses on the collaboration between the development team and their customers, and it requires adaptability and flexibility through the process.[3]
Agile aims to deliver fast solutions that will be tested with the customers in order to get their feedback. This feedback will allow the team to make changes and improvements through a following iteration. It focuses on constantly improve, evolve and respond to changing requirements during the process. It started in the software industry, because of the fast changing and continuously updates of technology.[4]
Mainly, the Agile process could be divided into different phases:
- Scope: define the project scope, analyze concepts and plan requirements.
- Plan: organize teams and tools and plan the iterations.
- Implementation: frequent development delivery through iterations.
- Development
- Test
- Deliver
- Feedback
- Release: release the project.
- Maintenance: follow-up process.
Agile Manifesto
In the 1990’s, because of the fast-changing new technologies, the software development industry realized that it couldn’t move fast enough to meet customers’ demands and requirements. On February 2001, a group of software developers, who formed the Agile Alliance [5], gathered to discuss the main industry practices aiming to find a better approach to the traditional development process, such as Waterfall methodology [6]. They ended up creating the Agile Manifesto, that marked the birth of Agile as a methodology.
This document contains the basic principles that are characteristic of Agile philosophy in project management. It outlines 4 values and 12 principles that guide the Agile philosophy:
Agile main values:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
and 12 principles:
- Satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software.
- Welcome and harness changes for the customer's competitive advantage, even late in development.
- eliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference for shorter timescales.
- Have daily collaboration between business people and developers throughout the project.
- Build projects around motivated individuals. Create the environment and support developers need, and trust them to get the job done.
- Prioritize face-to-face conversation as the most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team.
- Measure progress by the amount of working software completed.
- Maintain a constant and sustainable pace of development indefinitely.
- Enhance agility through continuous attention to technical excellence and good design.
- Keep it simple. Simplicity—the art of maximizing the amount of work not done—is essential.
- Recognize that the best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams.
- Regularly reflect and adapt behavior for continual improvement.
Application
The Agile philosophy can be applied with different frameworks and methodologies, the two most popular are Scrum [7] and Extreme Programming (XP) [8]. Some other Agile methods are Kanban and Lean development.
Agile methodologies
Scrum
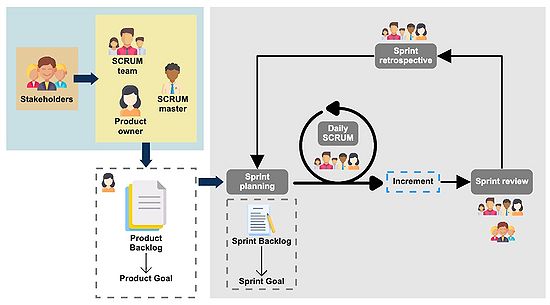
Scrum is an agile development method which concentrates specifically on the project management point of view. As the Agile philosophy indicates, it employs an iterative and incremental approach and aims to understand customer needs and deliver value to them in short cycles, prioritizing the most valuable features. It is mainly used in product management.
Each iteration of Scrum is known as Sprint. At the end of each Sprint, the team delivers a product functionality. Sprints have fixed lengths, typically maximum one month, and a new Sprint starts immediately after the conclusion of the previous one. Each Sprint could be considered as a short project.
The requirements and attributes of the product are defined in the Product Backlog. It is a repository of what needs to be done and improve the product and is continuously updated during the development of the project. It defines the Product Goal, which is the long-term objective for the Scrum team.
The items in the Product Backlog are grouped into Sprint Backlogs. Each Sprint has a Sprint Backlog which defines the Sprint Goal, the set of selected items from the Product Backlog that would be implemented in the Sprint, as well as the actionable plan for delivering. It is also updated throughout the process by the developers.
The goal of each Sprint is to add value and functionalities to the project, which are called Increments. Increments are concrete steps towards the Product Goal. Each increment is additive, so that all the increments should work together. Multiple increments can be created within a Sprint.
The team working with Scrum is formed by three main roles:
- Scrum master: responsible for organizing the team, removing obstacles to progress and establishing the Scrum methodology.
- Product owner: responsible for maximizing the value of the product resulting from the work of the Scrum team and for the delivery of the functionality at each iteration. It also creates and updates the Product Backlog and prioritizes the tasks.
- Scrum team: small cross-functional team of people developing the project. It consists of one Scrum Mater, one Product owner and Developers. There aren’t hierarchies within the team and it is typically formed by 10 or fewer people.
The Scrum process is divided into four different stages. First, the Sprint planning, is the beginning of the Sprint where the work to be done is defined and planned. It is created by the entire Scrum team and the outcome is the Sprint Backlog, that includes the items from the Product Backlog selected to be implemented in the Sprint and the plan for delivering them.
During the Sprint, the team participates in Daily scrum, 15 mins daily meetings where the Scrum team tracks the progress towards the Sprint Goal and adapt the Sprint Backlog as necessary. The goal is to improve the communication and promote quick decision-making.
When the Sprint is coming to its end, the Scrum team, reviews, together with the stakeholders, what was accomplished in the Sprint and what has changed in the environment. The Product Backlog may be also adjusted to meet new opportunities. These events can take up to four hours for a one-month Sprint and are called Sprint review.
Finally, the Sprint retrospective is the last event in the Sprint that focuses on planning a way to increase the quality and effectiveness of the Sprint. It can last up to three hours for a one-month Sprint. The Scrum team inspects how the last Sprint went with regards to individuals, interactions, processes and tools.
This process is repeated for each of the Sprints.
Extreme Programming
Extreme Programming (XP) is one of the most specific agile methodologies for software development. It consists of delivering higher quality software and empathizes team work. It is very helpful when there is constantly changing demands or requirements from the customers. It also consists of frequent releases of the product and short development cycles.
It improves the software development process based on five main values:
- Communication: communication between all team members, from customers to programmers and managers.
- Simplicity: keep the design simple and clean.
- Feedback: get feedback by testing their software from day one and deliver the system to the customers as early as possible and implement changes as suggested.
- Respect: every small success deepens their respect for the unique contributions of each and every team member.
- Courage: courageously respond to changing requirements and technology.
Extreme Programmings is a way of work based on these values that lead to the XP rules:
- Planning:
It all starts with user stories, things that the user aims the system needs to do for them. They are written by the customer in the format of about three sentences and are used to plan the release schedule through a release planning meeting. The release plan lays out the overall project and is used to create iteration plans. Iterations also consist of frequent small releases. And projects are mainly divided into iterations of one to three weeks length. They are planned through the iteration planning meetings at the beginning of each iteration to determine the iteration programming tasks.
- Managing:
It is important to provide the team a dedicated and open space that enables communication between team members and avoid physical barriers that divide people. Organize daily stand up meetings and set a sustainable, measurable and predictable pace. The measure of how much work is getting done in the project is also called project velocity.
In order to avoid serious knowledge loss and coding bottle necks, it is important to consider to move people around and cross training activities. A good idea is to encourage everyone to try to work on a new section of the system, at least part of each iteration. Pair programming makes it possible without losing productivity and ensuring continuity of thoughts. It consists of two team members working together on a single computer. Although it is a difficult skill to learn, it increases the software quality without compromising the delivery time.
- Designing:
As mentioned in the values, keep the design simple and structure it in a way that helps new people begin contributing quickly. Use system metaphor to be able to explain the system design to new people without the need of providing huge documents on them.
CRC (Class, Responsibilities and Collaboration) cards are a useful method to design the system as a team and involve entire project teams to contribute to the design. CRC sessions allow people to break away from the procedural mode of thought and more fully appreciate object technology. [REF]
Create spike solutions, simple program to explore potential solutions, to figure out answers to technical or design problems. Refactor throughout the entire project life cycle to avoid complexity, try remove redundancy, eliminate unused functionalities and rejuvenate obsolete designs.
- Coding:
The customer should always be available, not only to help the development team, but to be part of it as well. And, the code must follow the agreed coding standards.
As mentioned in the managing section, it is interesting to practice pair programming, as it increases software quality without impacting time to deliver.
Keep continuously integrating the code to avoid possible future integration issues. Developers should be integrating and commiting code into the code repository every few hours, when ever possible.
Encourage collective ownership, so that everyone can contribute with new ideas to all segments of the project. Any developer should be able to change any line of code to add a functionality, fix bugs, improve designs or refactor. No one should become a bottle neck for progress.
Testing: All code must have a unit test, which are automated tests written by the developers to test functionality as they write it, that build confidence that the code works correctly. And all the code must pass the unit test before it can be released.
When bugs are found in the code, acceptance test should be created. Acceptance tests are created form the user stories, the customer defines scenarios that should be tested when a user story has been correctly implemented.
Limitations
Overall, Agile has demonstrated to be a very useful methodology in the current times when everything is so volatile and unpredictable. It has shown to be a realistic approach that results in efficient processes to develop projects that better meet the customer needs.
As mentioned in previous sections, the main strength of Agile is the ability to adapt to frequent changes. However, it doesn’t always make sense to follow Agile methodology. For instance, one of the main values of Agile focuses on customer collaboration, so in cases where the customer is not prepared or is not willing to be part of the project development that could result in a difficulty.
One of the Agile benefits is the customer satisfaction, because of the rapid and frequent deliveries. Nevertheless, it is important that the team is used to work in a fast-paced and changing environment, so it might be key to educate teams in Agile before starting to apply the methodology. Furthermore, Agile team members should be highly qualified and experienced, so that they can make fast and relevant decisions. Dealing with strict delivery management and meeting the frequent deadlines could also be a challenge when working with Agile.
On the other hand, the fact that the work is split into many short iterations, where requirements change and evolve during the process, also lead to a lack of documentation. The shortage of formal documents could create confusion and crucial decisions taken throughout different phases could be misinterpreted by the team members. Therefore, transferring work between teams for further development or maintenance could also become a difficulty. So, it drives to a high dependency to the individuals in the Agile teams.
References
- ↑ Bennis, Warren; Nanus, Burt (1987) "VUCA"
- ↑ Beck, K., et al (2001) "Manifesto for Agile Software Development"
- ↑ Pimonova S. (2020) Agile Methodology in Education of IT Students, Application of. In: Tatnall A. (eds) Encyclopedia of Education and Information Technologies. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-10576-1_214
- ↑ da Silva, Tiago Silva; Estácio, Bernardo (2017) Agile Methods. Springer International Publishing.
- ↑ Agile Alliance [1]
- ↑ Waterfall model [2]
- ↑ Schwaber, Ken; Sutherland, Jeff (2020) "The Scrum Guide"
- ↑ Wells, Don (2013) "Extreme Programming"