Lean construction
(→LPDS summary) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Construction industries are known for working in projects, and those projects are today complex, uncertain and quick CUQ | + | Construction industries are known for working in projects, and those projects are today complex, uncertain and quick (CUQ) projects (Koskela, 2002). They are also known for having lower productivity and higher wastes than other industries (Forbes and Ahmed, 2011). Lean construction thinking started in the middle of 1990 as a way handle these CUQ-projects. Lean production is well known within manufacturing industries to increase productivity and reduce wastes, but the lean production thinking cannot directly be applied to the construction industry. The reason is that there is a list of factors that differentiates the construction industry from manufacturing industries, e.g. duration of projects, ((Shang and Low, 2014)). |
There are two different interpretations of lean construction. (1) Lean Construction is about how Lean Production methods can be applied to construction, and (2) Lean Construction is a new, theory-based methodology for construction inspired of Lean Production (Koskela, 2002). The second theory is the most common interpretation and also mayor interpretation used within the International Group for Lean Construction. | There are two different interpretations of lean construction. (1) Lean Construction is about how Lean Production methods can be applied to construction, and (2) Lean Construction is a new, theory-based methodology for construction inspired of Lean Production (Koskela, 2002). The second theory is the most common interpretation and also mayor interpretation used within the International Group for Lean Construction. | ||
Revision as of 08:56, 21 November 2014
Construction industries are known for working in projects, and those projects are today complex, uncertain and quick (CUQ) projects (Koskela, 2002). They are also known for having lower productivity and higher wastes than other industries (Forbes and Ahmed, 2011). Lean construction thinking started in the middle of 1990 as a way handle these CUQ-projects. Lean production is well known within manufacturing industries to increase productivity and reduce wastes, but the lean production thinking cannot directly be applied to the construction industry. The reason is that there is a list of factors that differentiates the construction industry from manufacturing industries, e.g. duration of projects, ((Shang and Low, 2014)).
There are two different interpretations of lean construction. (1) Lean Construction is about how Lean Production methods can be applied to construction, and (2) Lean Construction is a new, theory-based methodology for construction inspired of Lean Production (Koskela, 2002). The second theory is the most common interpretation and also mayor interpretation used within the International Group for Lean Construction.
Lean Construction is based on three views in production theory, Transformation, Flow and Value (TFV). These three views do not compete with each other but rather are complementary. All systems that pursue the TFV goals are in a way lean systems, but some are systems are better than others (Koskela, 2002).
Contents |
Development history
The first signs of lean thinking in the construction industry goes back to the 1890s. Frank Gilbreth saw potentials in how to apply manufacturing approaches into construction in order to improve speed and labour efficiency. He saw opportunities in how to reduce what in lean thinking in called wastes. Gilbreth developed a body of knowledge that is considered to be a part of the body of knowledge that formed the field of industrial engineering (Modern Construction Lean Project Delivery and Integrated Practices p52).
The construction industry had a slower productivity growth than other industries in the twentieth century. Historically the industry had build on the Master Builder concept were one entity had responsibility for both design and construction. During the twentieth century the industry converted from Master Building concept to be more fragmented. Designers developed contracts that reduced their construction responsibility which led to more costly and counterproductive behaviors due to adversarial relations and mistrust. Studies from the 1990s and 2000s showed that hours spend productivity were very low and value-added time even lower, there is thus much room for improvement.
In the early 1990s Lauri Koskela looked, like Gilbreth did hundred years earlier, to the manufacturing industry for solutions and directions for the construction industry. Koskela specifically looked at Toyota's successful production system (TPS) and lean production and stated the most successful manufacture methods where based on the Just In Time (JIT) concept (Koskela 1992). Furthermore, Koskela introduced the Transformation, Flow and Value (TFV) theory which is derived from earlier theories regarding production (Koskela 2000).
Koskelas work is the foundation of lean construction, and resulted in a conference in Helsinki, Finland 1993 where the expression "Lean Construction" was decided to be used and the International Group for Lean Construction (IGLC) was founded. Subsequently Glenn Ballard and Greg Howell co-founded the Lean Construction Institute (LCI) in 1997. Studies performed by members from both IGLC and LCI led to Ballard's development of the The Last Planner System (LPS) and The Lean Project Delivery System (LPDS) (Modern Construction Lean Project Delivery and Integrated Practices p53-55).
- Adoption of Relational Contracting
- "Lean Design and Construction is particularly useful on complex, uncertain and quick projects" http://www.leanconstruction.org/about-us/what-is-lean-construction/
What is Lean Construction?
Lean construction is derived from the success of lean thinking within manufacturing industries. There are two slightly different main interpretations of lean construction. The first interpretation, as mentioned above, is about the application of lean production methods to construction. The second interpretation, on the other hand, views lean production as inspiration to the development of a new theory-based methodology for the construction industry (Koskela 2002).
These two interpretations is showed in two different definitions of lean construction. The first definition is from Koskela et al. (2002, p. 211): "Lean construction is a way to design production systems to minimize waste of materials, time, and effort in order to generate maximum possible amount of value." This definition shows that lean construction endeavors for the same goals as lean production which correspond to the first interpretation. On the other hand, The Lean Construction Institute defines lean construction as: "Lean Design and Construction is a production management-based approach to project delivery /.../ Lean Construction extends from the objectives of a lean production system - maximize value and minimize waste - to specific techniques, and applies them in a new project delivery process." This shows that LCI's definition correspond to the first interpretation. It has the same objectives as lean production and applies the techniques into construction.
A New Theory of Production
Transformation, Flow and Value generation (TFV) model is a new theory of production. The model is the cornerstone of lean construction and it is a conceptualization of three theories of production used in the twentieth century; Transformation, Flow and Value generation theories of production (Shao gao). Each of the three theories have introduced their own methods, tools and templates for production. The TFV model is based on the view that Transformation, Flow and Value generation are not competing alternative theories, but rather complement each other (Koskela 2002).
Transformation theory of production
The transformation view of production is the dominant view of production and has its roots in economics. The economist Michael Porter's theory of the value chain is and approach that substantiates the trasformation view. There is three principles in the transformation model that according to Koskela (2000) are most important:
- Production can be divided into sub-processes and tasks and allocate them to specific activities or workstations.
- The cost can be minimized for each sub-process in order to minimize overall costs.
- The value of the output is directly associated with the input. The output value can be raised by better (more costly) inputs.
The transformation view does not recognizes the other value-adding activities within production and only focuses on the transformation itself.
Flow theory of production
The flow view was first introduced by Gilbreth in 1922 and practiced by Henry Ford. However the flow theory did not adhere until the 1980s with the JIT and lean production movement. The two main principles in the flow theory according to Koskela (2000) are:
- Reduce the non-value-adding activities (waste) in production.
- Reduce the lead times and variability in the production processes. Lead time is the total time it takes for a piece inside the production process e.g. waiting, moving and processing time. The variability is the process-time variability (e.g. variability in process time at a workstation) and the flow variability (e.g. variability of arriving jobs to a workstation).
A third principle can be added to the list. It is a set of principles including simplicity (e.g. reduce number of parts and steps in material and information flows) and increase flexibility and transparency in the production processes.
Value generation theory of production
The value generation view of production arose simultaneously with the flow theory as a critique to the transformation concept. As the transformation view focuses on the internal production processes the value generation view focuses more on the costumers' needs. The overall principles of the value generation concept is according to Koskela (2000):
- Capture all costumer requirements.
- The costumer requirements are available in all phases of production (e.g. design solutions and production plans).
- The deliverables are relevant to all different customers roles.
- Ensure that the production system are capable of producing the required products.
Transformation, Flow and Value generation theory
Each theory within the TFV model focuses on specific aspect of the production phenomenon (Koskela, 2000). When they are all integrated into the TFV model, they together strives for the traditional objectives manufacturing businesses strives for; cost, time and quality (Shao and gao).
- The transformation theory strives for the objective of reducing costs through minimizing the costs for each sub-process.
- The flow theory strives for the objective of reducing time through minimizing the non-value-adding activities in the processes.
- The Value generation theory strives for the objective of increasing the quality of the product through focusing on the costumer requirements.
The integration of the three theories is showed in the table below.
| TFV model of production (Koskela, 2000) | |||
| Transformation theory | Flow theory | Valu generation theory | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conceptualization of production: | As a transformation of inputs into outputs | As a flow of material, composed of transformation, inspection, moving and waiting | As a process where value for the costumer is created through fulfillment of his/her requirements |
| Main principle: | Getting production realized efficiently | Elimination of waste (non-value-adding activities) | Elimination of value loss (achieved value in relation to best possible value) |
| Methods and practices: | Work breakdown structure, MRP, organizational responsibility chart | Continuous flow, pull production control, continuous improvement | Methods for requirement capture, quality funktion deployment |
| Practical contribution: | Taking care of what has to be done | Making sure that unnecessary things are done as little as possible | Taking care that costumer requirements are met in the best possible manner |
| Suggested name of practical application of the view: | Task management | Flow management | Value management |
Major concepts
- Different views on lean construction
Lean Project Delivery System
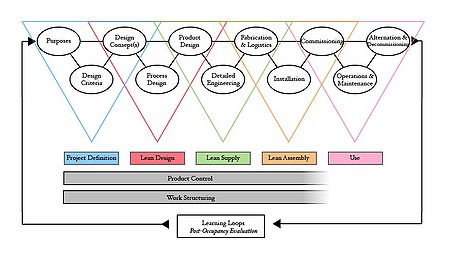
The Lean Project Delivery System (LPDS) is a trademark of the Lean Construction Institute developed in the beginning of 2000s of Glenn Ballard (Ballard, 2000). Projects is defined in terms of phases. The LPDS points out the importance of the relationships between the phases and the involvement stakeholders in each phase (Koskela 2002). The overlapping triangles in the FIGURE represents the five different phases; project definition, lean design, lean supply, lean assembly and use. There is two modules that are embedded in the five phases and extends through the whole project time; Product control and work structuring. A summary of the phases follows:
- Project definition: The project definition phase includes three elements: purpose, design criteria, and design concept(s). The role of this first step is to align and find the costumer and stockholder values and needs. All the elements in this first phase is influencing each other, so there is an importance of good communication between the stakeholders (Koskela 2002). This phase should include representatives from all different stages in the facility's life cycle; from the production team that will design and build the facility to the end user and stakeholders (Ballard 2000). This differs from other project definitions which traditionally only includes the architect and the client (Koskela 2002).
- Lean design: The alignment of the elements in the project definition allows the start of the lean design phase. This phase includes the elements: design criteria(s), design process, and product design. The relationships between the elements are similar with the project definition in the sense that they are developed simultaneously and requires good communication between stakeholders (Koskela 2002). It is important that the project team is observant of opportunities to increase the value for the costumer and expanding the purpose of the facility. If the project allows this opportunity, the project needs to go back to the project definition in order to update the purposes and design criteria (Ballard 2000). Traditional design phases have the tendency to narrow the design phase by focus on one single solution to early in the project with the opportunity for a faster design phase but threat of rework. To lower the risks of rework, the lean design phase should be ended at the last responsible moment using the Last Planner system (which will be described later in the article) and restructuring and streamlining the work and supply chains (Koskela 2002; ballard 2000).
- Lean supply: The lean supply phase includes the three elements: product design, detailed engineering, and fabrication and logistics. The relationship between these three elements are iterative and continuously adjusted (Ballard 2000).
- Lean assembly: The lean assembly phase includes the three elements: fabrication and logistics, installation, and commissioning. This phase starts when the first material and labour is delivered to the site and ends in the commissioning element where the keys is handed over to the client (Ballard 2000).
- Use: The use phase includes the three elements: commissioning, operation and maintenance, and alternation and decommissioning. The elements in this phase are expected and designed for in the previous phases. This last phase of the LPDS is not a part of the project since the facility is delivered during the commissioning phase. However, the project duration expands until the facility is operating to targeted performance (Koskela 2002).
LPDS summary
LPDS is designed and structured with principles and techniques in order to pursue the goals of the TFV model. Such techniques are e.g. involving stakeholders from the whole project life cycle earlier in the project, last responsible moment thinking to prevent reworks, aligning stakeholder interests to increase the end value for the customer and carefully plan buffers to make them more responsive and agile.
TABLE summarizes the Lean Project Delivery System by comparing it to a traditional delivery system.
| Comparison of a traditional and lean project delivery system (Koskela, 2002) | |
| LPDS | Traditional |
|---|---|
| Focus is on the production system | Focus is on transactions and contracts |
| TFV goals | T goals |
| Downstream players are involved in upstream decisions | Decisions are mare sequentially by specialists and "thrown over the wall" |
| Product and process are designed together | Product design is completed, then process design begins |
| All product lice cycle stages are considered in design | Not all product lice cycle stages are considered in design |
| Activities are performed at the las responsible moment | Activities are performed as soon as possible |
| Systematic efforts are made to reduce supply chain lead times | Separate organizations link together through the market, and take what the market offers |
| Learning is incorporated into project, firm, and supply chain management | Learning occurs sporadically |
| Stakeholder interests are aligned | Stakeholder interests are not aligned |
| Buffers are sized and located to perform their function of absorbing system variability | Participants build up large inventories to protect their own interests |
Last planner system
kanban cards
Target Value Design
- Kanban and production smoothing
The LPS was applied to the design process in 1998, representing another milestone. The design process was further improved with the application of target value design (TVD). The first TVD paper was published in 2004.
Key elements
BIM
Används i lean design och lean supply fasen av LPDS
Big Room
Related material
- Comparable standards / recommendations
- Additional related material
Discussion
Strength and weaknesses/criticism
- Controversial points
tabell i lean construction pdf, sidan 59 TFV lean construction sida 39
Integration / relationship to other material
- Sustainable development
Implementation advice
- How can it be implemented in construction industries