Choosing the right communication network for your project
(→References) |
(→Why the communication network is an important factor of project management) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| − | To make the right decisions, to learn efficiently and to align the work tasks, it is important to coordinate internally. The more coordination that is necessary in an organization, the stronger the communication also has to be to avoid misunderstandings. These misunderstandings can e.g. be regarding crucial information in a project such as the deadline, the work load distribution in terms of who is responsible for what, and even the strategy can be skewed if the communication is not sufficient. The right use of communication can also prevent some amount of conflict associated with the internal organization culture. With more information traveling around the organization, the stronger the culture get, and the better the organization can be resistant to conflicts. The whole basis of the decisions depends on the communication, which means it is important that the necessary information is accessible for the decision maker. | + | To make the right decisions, to learn efficiently and to align the work tasks, it is important to coordinate internally. The more coordination that is necessary in an organization, the stronger the communication also has to be to avoid misunderstandings. These misunderstandings can e.g. be regarding crucial information in a project such as the deadline, the work load distribution in terms of who is responsible for what, and even the strategy can be skewed if the communication is not sufficient. The right use of communication can also prevent some amount of conflict associated with the internal organization culture. With more information traveling around the organization, the stronger the culture get, and the better the organization can be resistant to conflicts. The whole basis of the decisions depends on the communication, which means it is important that the necessary information is accessible for the decision maker. <ref name="dag" /> |
Revision as of 12:58, 4 April 2023
Written by Emilie Lewis Laurberg
Abstract
The purpose of this article is to clarify the importance of choosing a suitable communication network for an organization. There exists several different communication network structures and hierarchies. Each and every one of the network types has benefits and disadvantages in which it is crucial to choose the best type of communication network for an organization im terms of avoiding fatal consequences and archieve the communication goals for the specific organization.
Contents |
Big Idea
Why the communication network is an important factor of project management
- Every project is a temporary organization, in which a communication network will happen automatically
- Emerged communication networks can reflect the hierarchy of the organization and vise vesa, thus it may be relevant to implement a formal communication network in terms of rules and structure
- Why be aware of the type of communication networks that are used?
To make the right decisions, to learn efficiently and to align the work tasks, it is important to coordinate internally. The more coordination that is necessary in an organization, the stronger the communication also has to be to avoid misunderstandings. These misunderstandings can e.g. be regarding crucial information in a project such as the deadline, the work load distribution in terms of who is responsible for what, and even the strategy can be skewed if the communication is not sufficient. The right use of communication can also prevent some amount of conflict associated with the internal organization culture. With more information traveling around the organization, the stronger the culture get, and the better the organization can be resistant to conflicts. The whole basis of the decisions depends on the communication, which means it is important that the necessary information is accessible for the decision maker. [1]
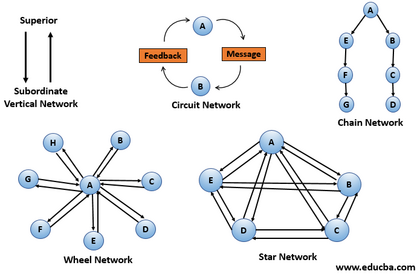
Examples of different types of networks:
- Cetralized and decentralized network structures
- Centralized can make sure everybody knows the same, but information will always have to pass either one person or one media
- Decentralized makes it possible for employees to go directly to their closest leader in smaller groups. This is like in a centralized network, but with several smaller centers instead of just one. This could e.g. be a network structure with one manager, communicating with 5 sub-managers, each communicating with 5 empoyees. This is a hierarchical type of network. Decentralized communication networks comes in deifferent shapes and styles
- Distributed network structures makes it possible for all actors in the network to communicate directly with one another. Pros: The information from one peripheral actor does not have to go through a "central" actor as in the centralized or decentralized networks to get to another peripheral actor. Cons: If one peripheral actor has given a piece of information to another peripheral actor, the other actors will not neccessarily know. This means if a third actor, no matter the "status" in the network, has to find the exact same piece of information, he or she has to search for it to get it without knowing where it is to be found. This is a flat type of network where hierarchical status does not neccessarily matter.
Centralized communication network structure
A centralized communication network is by Oxford Reference described as "A communication network in which one group member has access to more communication channels than any other and therefore tends to process more information than the peripheral group members" [3]
This article will address the possibilities of:
- Keeping the feeling of project ownership at on different levels in an organization due to formal communication networks
- Choosing between vertical and horizontal communication
- Analyzing the type of emerged network in your organization in terms of e.g. number of connections
Key points
- Optimizing the flow of information in a organization
- Making sure the decisions, scope etc. gets around to the people involved
Application
Limitations
Communication network structures [4] Strengths in communication network connections: [5]
References
- ↑ Jacobsen, D.I. & Thorsvik, J. (2014). Hvordan organisationer fungerer, Chapter 8. 3rd edition.
- ↑ https://www.educba.com/types-of-communication-network/
- ↑ https://www.oxfordreference.com/display/10.1093/oi/authority.20110803095558631;jsessionid=57E896C5749F968F524AC78D3AC2A9C3
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedR1 - ↑ Granovetter, M. (1973). The Strength of Weak Ties