SWOT Analysis 101
(→Definition and explanation of SWOT analysis as a tool for strategic planning) |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
'''Strengths''' | '''Strengths''' | ||
| − | + | Strengths are internal attributes that give an organization a competitive advantage. | |
| + | An example of strengths could be skilled personnel, strong brand reputation, unique products or services, or efficient processes. | ||
| + | By identifying these strengths, it is possible to help an organization to capitalize on advantages and develop new or better strategies to either maintain or increase market position for the organisation. | ||
'''Weaknesses''' | '''Weaknesses''' | ||
Revision as of 13:41, 7 April 2023
Contents |
Abstact
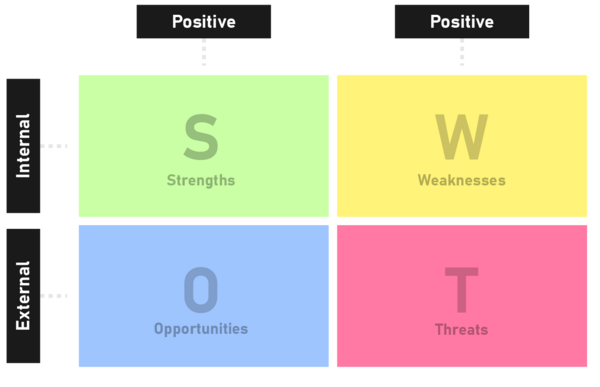
The SWOT analysis categorized as “Uncertainty” under how to anticipate if something happens is a versatile strategic planning tool used to assess an organization's internal and external factors. The SWOT analysis is a method of anticipating uncertainty, as it evaluates the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
The four elements of SWOT analysis include strengths, which are internal factors that give a competitive advantage, weaknesses, which are internal factors that hinder performance, opportunities, which are external factors that can improve performance, and threats, which are external factors that could negatively impact a business.
Using the SWOT analysis can be useful in many ways, the method can be good for identifying areas in need of improvement, making key strategic decisions, performance overhauls, development of products, market competition overview, and more. Using the SWOT analysis requires one to identify both the internal and external factors and to evaluate them based on the four elements: strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. These four elements are then used to create a strategic plan. Furthermore, the method is a tool to be used alongside other strategic planning tools.
Despite the SWOT analysis being a popular tool, it is not without limitations and criticisms. The downsides of the tool include its oversimplifying of key factors and its subjective nature. Nonetheless, SWOT analysis remains a useful tool for organizations to inform and plan their strategic decisions for improved performance.
Introduction
Origin
The SWOT analysis is from the 1960s, the man who was recognised for the analysis was a business consultant named Albert S. Humphrey. Albert Humphrey developed the SWOT analysis framework during a project at Stanford Research Institute (SRI), where over 500 companies funded a project to identify and find reasons behind the success and failure of corporate planning. Over the decades the analysis tool has matured and evolved even more making it the tool widely used today for business strategy and management. Cite(2)
Definition and explanation of SWOT analysis as a tool for strategic planning
The SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to assess internal and external environments, mainly in organisations. The tool is segmented up into four sections that revolve around identifying and evaluating strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats regarding an organisation and the environment it currently resides in both externally and internally. This way the tool is used to achieve objectives by analysing these four factors to gain key insight into the current competitive position and to what strategy is currently needed to take to grow/improve the organisation's current standing. In summary, by evaluating the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, informed decisions can be made to capitalize on the company's strengths, exploit opportunities, and minimize threats that could impact the organization. Cite(1) Cite(2)
The four elements of SWOT analysis: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats
Strengths Strengths are internal attributes that give an organization a competitive advantage. An example of strengths could be skilled personnel, strong brand reputation, unique products or services, or efficient processes. By identifying these strengths, it is possible to help an organization to capitalize on advantages and develop new or better strategies to either maintain or increase market position for the organisation.
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Threats
Discussion
Discussion of the purpose and benefits of conducting a SWOT analysis Explanation of how to conduct a SWOT analysis, including identifying internal and external factors, evaluating the elements, and developing a plan based on the findings of the analysis.
Advantages
Disadvantages & Limitations
Examples of use
Examples of how businesses and organizations can use SWOT analysis to make strategic decisions and improve performance
Comparison
Comparison of SWOT analysis to other strategic planning tools, furthermore a discussion of the limitations and criticisms of SWOT analysis as a tool for decision-making.
References
Investopedia “SWOT Analysis: How To With Table and Example” (1) https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/swot.asp (February 12, 2023) (2) https://www.bl.uk/business-and-ip-centre/articles/what-is-swot-analysis (April 07, 2023)