Metrics in Portfolio management
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
===Portfolio Managements=== | ===Portfolio Managements=== | ||
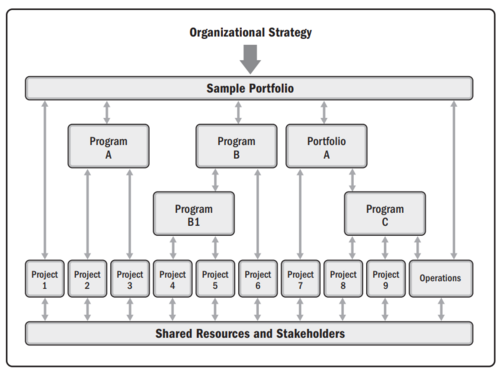
| − | + | As the PMI states <ref name=PMBOOKProject></ref>, portfolio is a collection of projects, programs, subsidiary portfolios, and operations managed as a group to achieve strategic objectives. Notably, those programs or projects within a portfolio may not be directly related or interdependent, they are linked to the organization’s strategic plan by means of the portfolio. | |
[[File:Screenshot 2023-02-19 233453.png|border|500px|right|caption]] | [[File:Screenshot 2023-02-19 233453.png|border|500px|right|caption]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Portfolio management is a crucial organizational capability that enables organizations to effectively manage and balance their portfolio, align projects with their overarching strategy, and ensure the allocation of resources in order to maximize benefits <ref name=PMASA> G. Levin & J. Wyzalek <<Portfolio Management - A strategic approach>> Taylor & Francis Group </ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Portfolio management is a dynamic decision process wherein the list of projects is constantly revised. In this process, new projects are evaluated, selected, and prioritized. Portfolio management is the centralized management of one or more portfolios to achieve strategic objectives. It is the application of portfolio management principles to align the portfolio and its components with the organizational strategy by selecting the best portfolio components, prioritizing the work, providing the needed resources, overseeing or working with portfolio component managers on their implementation, supervising proper transition into the operational environment, and enabling the achievement of portfolio value. <ref name=PMBOOKProject> Project Management Institute (2017) <<The Standard for Portfolio Management>> 4th Edition </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| Line 71: | Line 76: | ||
==Portfolio measurement techniques and metrics== | ==Portfolio measurement techniques and metrics== | ||
| + | As it was mentioned previously, portfolio pursues the strategic objective of the company. This means that decisions (so, metrics) are more than relevant. Portfolio managers should decide what to prioritize between all the opportunities (projects) since the resources are not unlimited. Also, the management of portfolio look for maintain a competitive position of the company. | ||
===Portfolio metrics vs. Project metrics=== | ===Portfolio metrics vs. Project metrics=== | ||
Revision as of 10:11, 9 April 2023
Contents |
Abstract
According to the Project Management Institute (PMI), a metric is a "description of a project or product attribute and how to measure it" [1]. It is, indeed, a quantitative measure of performance or outcome that provides a basis for comparison, evaluation, or improvement.
Peter Drucker famously said, "if you can not measure it, you can not improve it". However, it is not enough just to measure. The ultimate purpose of metrics is, as well, to provide the right information to the right person at the right time, using the correct media and in a cost-effective manner [2]. Notably, building effective metrics is extremely relevant when it comes to decision making at all levels of a company, project or portfolio. Thereby, knowing specifically what to measure when it comes to portfolio management is a must to ensure the future of the organization.
The purpose of this article is to describe the type of metrics needed to evaluate Portfolio performance and outline their differences from the well-known metrics to measure Project performance. Firstly, this article will focus on introducing to general terms. Secondly, the relevant role of the portfolio management will be highlighted. Hereafter, what is needed to create an effective metric will take part in this essay. Lastly, different useful metrics and techniques for portfolio management will be listed and explained in detail.
General terms
Firstly, to understand the topic under study, both the basics of Portfolio Management and Metrics need to be introduced.
Portfolio Managements
As the PMI states [1], portfolio is a collection of projects, programs, subsidiary portfolios, and operations managed as a group to achieve strategic objectives. Notably, those programs or projects within a portfolio may not be directly related or interdependent, they are linked to the organization’s strategic plan by means of the portfolio.
Portfolio management is a crucial organizational capability that enables organizations to effectively manage and balance their portfolio, align projects with their overarching strategy, and ensure the allocation of resources in order to maximize benefits [3].
Portfolio management is a dynamic decision process wherein the list of projects is constantly revised. In this process, new projects are evaluated, selected, and prioritized. Portfolio management is the centralized management of one or more portfolios to achieve strategic objectives. It is the application of portfolio management principles to align the portfolio and its components with the organizational strategy by selecting the best portfolio components, prioritizing the work, providing the needed resources, overseeing or working with portfolio component managers on their implementation, supervising proper transition into the operational environment, and enabling the achievement of portfolio value. [1]
Metrics
The simplest definition of Metric is the one stated by Cambridge: "system for measuring something" [4]. Even though it turns out to be a poorly detailed definition, it lays the foundations of what a metric does. In fact, the core metric function is to measure something. What is being measured and why these measurment are taking place are the components that make metrics relevant. Looking deeper, metrics are tools of quantitative evaluation that can be utilized for the purpose of monitoring and measuring performance or success. At the business or company management level, metrics become even more relevant when they are aggregated to a set of metrics to construct a dashboard that management or analysts regularly consult to ensure that performance assessments and business strategies are maintained.
Metrics require a need or purpose and, not least, they need a target and/or baselines as reference points. On the one hand, it is necessary to specify what is intended to be measured in order to determine why this metric have to be conceived. On the other hand, the definition of targets: if there is no point of comparions, what is going to be measured against? The metric would not have a raison d'être [2].
Roles and responsibilities of a portfolio management PMO
The PMO generally establishes the metrics needed to validate the performance of the overall portfolio of projects. To be effective, the PMO needs to define the success metrics it will use in context to determining how well each project and the overall PMO organization is delivering value within and across the performance domain framewok. The PMO might also want to weight each Performance Domain (PD) in terms of how important it is in determining the PMO’s (and each project’s) success. Each metric should directly align with each domain’s intended outcomes to support efficient oversight. [5]
The current eight performance domains are:
- Stakeholders (relationship, engagement and expectation management)
- Teams (health and performance)
- Development Approach & Life Cycle (process of building)
- Planning (defining what needs to be done)
- Project Work (assignments and tasks)
- Delivery (deploying the project into operations/use)
- Measurement (ways to quantify, monitor and track progress and outcomes)
- Uncertainty (identifying and mitigating risk/dealing with unknowns)
Effective metrics
Gold rules
Efficient use of time and resources is crucial in portfolio management, and progress measurement is no exception. Consequently, it is relevant for portfolio managers to point to the development of metrics that only measure relevant and useful insights for decision-making. According to the PMI Standard [1] and George T. Doran [6], the SMART criteria is one of the golden rules to be followed in order to create effective metrics. Specifically, the acronym SMART stands for:
- Specific: Measurements are specific as to what to measure. define what you are going to accomplish answer the What is measuring
- Meaningful: metrics ought to be linked to the business case, baselines, or requirements. Evaluating project achievement that do not contribute to meeting objecvives or enhancing performance is ineffective. Besides, metrics' meaningfulness is commonly related to their nature of being quantifiable or "measurable" against the baseline and stated requirements.
- Achievable: it is meaningless to establish unfeasible or out-of-reach targets. Targets defined need to be attainable given the people, technology, and environment considered.
- Relevant: the information provided by the measure should represent value and allow actionable information.
- Time-bound: metrics have to be associated to an specific time frame. Creating these boundaries allows to keep the measurements on track and accountable.
Value based metrics vs. Traditional metrics
"Project Management Metrics, KPIs, and Dashboards" by Harold Kerzner [2] highlights the key differences between traditional metrics and value-based metrics and explains how each type of metric can be useful. It is argues that traditional metrics are useful for tracking project performance and ensuring that it is completed within the constraints of the triple constraint model (time, cost, and scope) called Iron triangle. However, these metrics may not necessarily provide a comprehensive view of the projects' overall value to the organization.
On the other hand, value-based metrics are centered on the strategic objectives and intended benefits. They help to ensure that the projects are aligned with the organization's strategic objectives and that it generates the expected benefits. However, value-based metrics may be more difficult to measure and track than traditional metrics. The definition of value and how it is measured can differ depending on the industry, company, and the characteristics of the business. Different stakeholders may have their own ideas of what value means to them, such as job security, profitability, reputation, or the creation of intellectual property. It can be challenging to meet the needs and expectations of all stakeholders at once
Notably, while traditional metrics have as primarily audience the project manager and the team, value (or value reflective) metrics are more useful for the clients/stakeholders.
The importance of the value component in the definition of success cannot be overstated. When management makes poor decisions managing project portfolios, companies end up working on the wrong projects. For example, the deliverable requested can be produced but either there is no market for the product or stakeholders may be displeased with management’s performance.
In any case, Kerzner suggests that the use of value-based metrics and traditional metrics in combination can provide a more accurate and comprehensive assessment of the project's performance. The traditional metrics can be used to monitor the performance of the project and ensure that it is completed within the constraints of the triple constraint model. The value-based metrics can be used to measure the project's overall impact on the organization and assess its contribution to the organization's strategic objectives.
Portfolio measurement techniques and metrics
As it was mentioned previously, portfolio pursues the strategic objective of the company. This means that decisions (so, metrics) are more than relevant. Portfolio managers should decide what to prioritize between all the opportunities (projects) since the resources are not unlimited. Also, the management of portfolio look for maintain a competitive position of the company.
Portfolio metrics vs. Project metrics
Measurement techniques and metrics
Application
Limitations
It is relevant to note that advances in project metrics have been rapid, but advances in portfolio metrics have been slow because not all companies maintain a project management office (PMO) dedicated to portfolio management activities. This leads to changes in the role of the project manager, the metrics used, and the dashboard displays [2].
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Project Management Institute (2021) <<Project Management: A guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge and The Standard for Project Management>> PMBOK guide 7th Edition
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Harold, Kerzner (2017) <<Project Management Metrics, KPIs, and Dashboards>>, Wiley & Sons
- ↑ G. Levin & J. Wyzalek <<Portfolio Management - A strategic approach>> Taylor & Francis Group
- ↑ Cambridge dictonary, Cambridge University Press & Assessment 2023
- ↑ Michael Wood (2021) <<Are You Effectively Measuring the Right Success Metrics?>> Project Management Institute
- ↑ Doran, G.T. (1981) <<There's a S.M.A.R.T. way to write management's goals and objectives>>