FMEA – Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
(→Procedure of FMEA) |
(→Procedure of FMEA) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
[[File:Procedure of FMEA.png|frameless|500px|Figure 1: Procedure of FMEA (source: own illustration)]] | [[File:Procedure of FMEA.png|frameless|500px|Figure 1: Procedure of FMEA (source: own illustration)]] | ||
| − | === | + | === Planning and preparation (1) === |
| − | === | + | === Structure Analysis (2) === |
| − | === | + | === Function Analysis (3) === |
| − | === | + | === Failure Analysis (4) === |
| − | === | + | === Risk Analysis (5) === |
| − | === | + | === Optimization (6) === |
| − | === | + | === Results Documentation (7) === |
== Example of the implementation of FMEA == | == Example of the implementation of FMEA == | ||
Revision as of 10:59, 8 April 2023
Contents |
Abstract
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a widely used technique for identifying and mitigating potential failures in products, systems, and processes (Stamatis, 2013). FMEA is used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics, to minimize the risk of product and process failures (Annarelli et al., 2016). The structured approach helps to first identify the potential failure modes, whose influence and probability of occurrence is then evaluated. This information is then further used to prioritize and implement corrective actions that reduce the risk of the failure modes occurring. The benefits of FMEA include identifying potential sources of defects in a product or process, reducing risks and costs through early defect detection and correction, improving the quality and reliability of products and processes, and assisting in decision-making and prioritization of improvement actions. (Schulze et al., 2011). There are several types of FMEA, including Design-FMEA, Process-FMEA, and System-FMEA, each of which targets specific aspects of a product or process. Design FMEA focuses on potential sources of failure in the design process, while process FMEA targets sources of failure in the production process. System FMEA examines the entire system and identifies potential failure sources that can impact the entire system (Vose, 2008).
This article provides a comprehensive overview of FMEA, including its history, the key concepts, the different types of FMEA, the steps involved in conducting FMEA, and the benefits and limitations of FMEA.
Definition and History
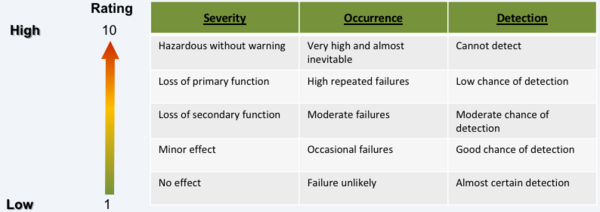
FMEA stands for "Failure Mode and Effects Analysis". The step-by-step approach is a quality management tool for analyzing and identifying possible failure modes in a system as well as their causes and effects (DIN EN 60812:2006-11., 2006). It is used to determine the ways in which a product or process can fail, estimate the risk associated with specific causes and prioritize the actions that should be taken to reduce the risk (Schulze et al., 2011).
FMEA found its beginnings when the U.S. military developed a method called „Procedures for Performing a Failure Mode, Effects and Criticality Analysis” to inspect their equipment in 1949 (Werdich, 2012).
The term itself was created by NASA. The tool was widely used in 1963 when the first moon landing occurred. The application of FMEA contributed to NASA's success (KVP Institut GmbH, 2018). Ford introduced the quality management tool to the automotive industry in 1977. At that time Ford was driven to use FMEA after the gasoline tank of the Ford Pinto model experienced issues with light vibrations. This launched the tool's extensive use in the automotive sector. Manufacturers used various procedures and internal corporate norms at the time because there was no standard guideline (Werdich, 2012, p. 7).
The German Association of the Automobile Industry (VDA) first gathered the various standards together and established a standard that was subsequently applied in the businesses. FMEA was no longer limited to the automotive industry once the German Association for Quality (DGQ) issued a universal and industry-independent explanation of the tool in 1990. Among others, it was then used in the field of services and project management (Werdich, 2012, p. 6-7). Subsequently, the standard was given a more thorough definition. In order to provide a globally consistent standard, the VDA standard and the Automobile Industry Action Group standard were aligned in 2019 (KVP Institut GmbH, 2018).
Types of FMEA: Design-FMEA and Process-FMEA
Among other things, a distinction is made between Design- and Process-FMEA. While the Design-FMEA (DFMEA) is used to find failures in the design of a product, the Process-FMEA (PFMEA) analyzes possible errors in new or existing processes (Brüggemann et al., 2015).
The Design FMEA or DFMEA, is applicable to the development, design and planning of a product, particularly during the early stage or end-stage of the development of a new product. Nevertheless, DFMEA can also be used to correct already existing products. The goal of DFMEA is to uncover potential failures in the design of the individual components of a product and evaluate possible errors on the basis of development specifications which could have a negative impact on health, safety and the environment. The System-FMEA, which is a variant of the DFMEA does not examine individual components but the entire system with regard to the functional interaction of the individual parts (Brüggemann et al., 2015).
The Process FMEA or PFMEA has the goal to uncover risks within a new or an existing process. It is used in particular for the investigation of manufacturing and assembly processes in the context of product development but also in the service and project management area. PFMEA is carried out before a new process is implemented or before changes made to existing processes take effect. Both scenarios for doing PFMEA intend to find any risks that could negatively impact the product, quality, safety, and customer satisfaction (Brüggemann et al., 2015).
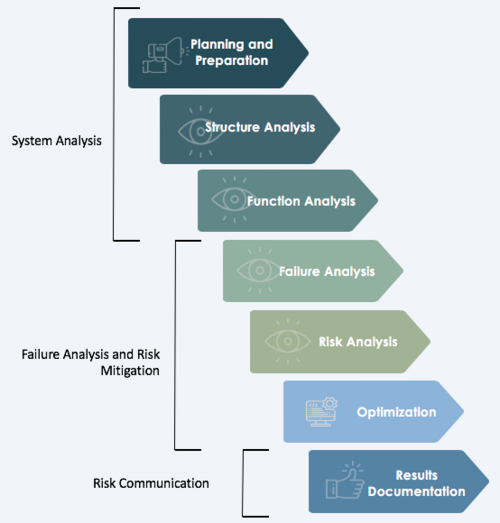
Procedure of FMEA
Planning and preparation (1)
Structure Analysis (2)
Function Analysis (3)
Failure Analysis (4)
Risk Analysis (5)
Optimization (6)
Results Documentation (7)
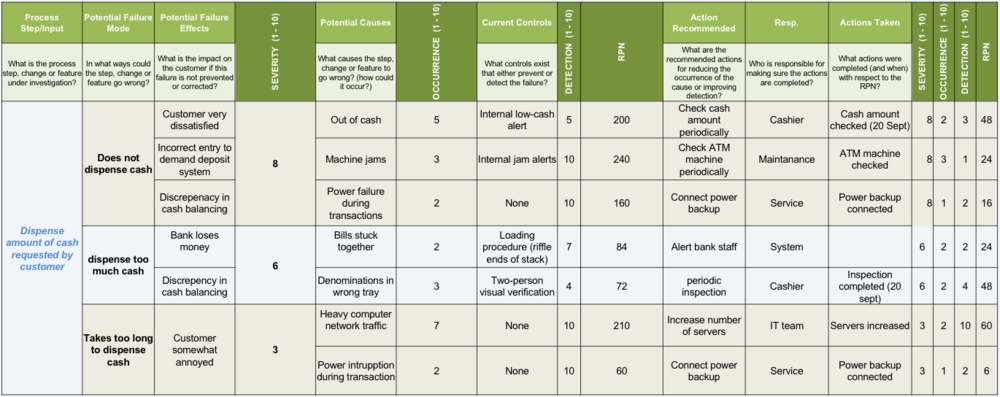
Example of the implementation of FMEA
(Written text with an explanation of implementation will follow)
Project management implications
Benefits and Limitations
(Written text about subsequent points will follow)
Benefits
• Very systematic error analysis down to the cause of the error
• Minimization of error costs, avoidance of complaints
• Easy to transfer to other product variants
• Inclusion of the competences of different departments (Improvement of communication and cooperation)
• Available budget for error correction used optimally, due to focus on essentials
Limitations
• Very time-consuming process due to many individual steps
• Spontaneous suggestions for improvement are rather unlikely
• High personnel and cost-intensive effort higher
• Risk: employees may fear negative consequences when uncovering errors or causes (Do not critically reflect on their own work)
References
Annarelli, A., & Sperandini, A. (2016). FMEA: A practical guide to Failure Mode and Effects Analysis. Springer.
Brüggemann, H., Bremer, P. (2015) Grundlagen Qualitätsmanagement. Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden. p.44-46.
DIN EN 60812:2006-11. (2006). Analysetechniken für die Funktionsfähigkeit von Systemen—Verfahren für die Fehlzustandsart- und -auswirkungsanalyse (FMEA) (IEC 60812:2006); Deutsche Fassung EN 60812:2006. Beuth Verlag. retrieved on 13.02.2023, from https://www.beuth.de/de/norm/din-en-60812/92880886.
Schulze, S, & Schultmann, F. (2011). Falure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) from theory to execution. John Wiley & Sons.
Stamatis, D. H. (2013). Failure mode and effect analysis: FMEA from theory to execution. ASQ Quality Press.
Vose, D. (2008). Risk analysis: A quantitative guide. John Wiley & Sons.
Werdich, M. (2012). FMEA - Einführung und Moderation. Vieweg+Teubner Verlag. p.7.
What is FMEA? Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Explained. (2021, 18. October). Agile in Asia. retrieved on 14.02.2023, from https://www.agileinasia.com/post/what-is-fmea.