EQ and Leadership Effectiveness
(→Succeed as a leader with EQ) |
(→Succeed as a leader with EQ) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
*The four key elements | *The four key elements | ||
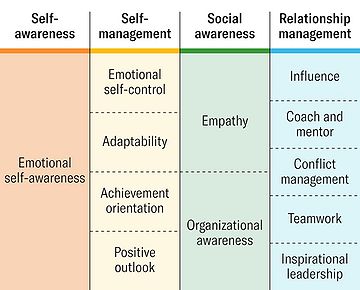
| − | [[File:Wikibilede3.jpg|thumb|upright=2| | + | [[File:Wikibilede3.jpg|thumb|upright=2|The Four Key Elements of Emotional Intelligence]] |
The four key elements of EQ are self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management. These elements are referred to as key in both applying and developing a high EQ. For an individual to experience success working with EQ it is essential to master the elements that involves both internal and external factors. | The four key elements of EQ are self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management. These elements are referred to as key in both applying and developing a high EQ. For an individual to experience success working with EQ it is essential to master the elements that involves both internal and external factors. | ||
Revision as of 13:22, 8 May 2023
Abstract
Emotional Intelligence (EQ) is the ability to understand and manage your own emotions, as well as others’ emotions. EQ is increasingly becoming one of the most important attributes in the field of leadership. The ability to control your emotions as a leader is a crucial part of success and increases the effectiveness of leadership [1].
Emotional intelligence contains four key elements:
- Self-Awareness
- Self-Management
- Social Awareness
- Relationship Management
These four elements relate to different abilities associated with high EQ. The ability to control and apply these elements in leadership can be crucial for managers to increase effectiveness and productivity [2].
Leaders with a high level of EQ are seen to be more effective in achieving organizational goals, creating a positive work environment, and building winning teams. They are both great a developing themselves and others toward the direction of the goals in an organization. To apply EQ in leadership it is important to constantly develop and increase the level of the key elements.
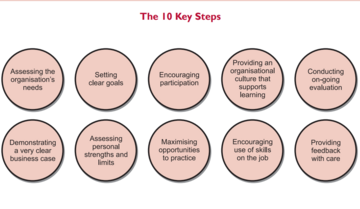
According to the authors behind “EQ and the Bottom Line” they identified 10 key steps to develop EQ in an organization. These steps are in a variety of difficulty to apply within an organization and must be adapted to individual organizations. However, if applied correctly can be a vital driver for increasing organizational EQ and project performance [1] [3] [4].
While EQ is seen as a very valuable tool and the ability of leaders, it is important to acknowledge its limitations. The complexity of the concept and development of EQ requires effort, time, and dedication. Furthermore, all individuals are not equally skilled in EQ, and it can be very difficult to develop these skills for some individuals.
Contents |
Succeed as a leader with EQ
Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
- Theory about EQ
Emotional Intelligence further referred to as EQ, is theoretically described as the ability to manage and understand your own and others’ emotions as an individual person. It is increasingly being acknowledged as one of the most important attributes of a great leader or manager. A person associated with high EQ is often seen as being traditionally better at managing conflicts, connecting with their team members, creating a positive work environment, and building trust.
- The four key elements
The four key elements of EQ are self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management. These elements are referred to as key in both applying and developing a high EQ. For an individual to experience success working with EQ it is essential to master the elements that involves both internal and external factors.
Self-awareness – This is the ability to understand your own emotions, weaknesses, strengths, behavior and rationality. It also includes skills in predicting patterns in behavior and the ability to exclude feelings in a situation of decision-making. Individuals who master self-awareness are excellent in identifying the emotional and rational mind and the triggers associated. They are exceptionally aware of their emotional triggers when they are in stressful situations to avoid making decisions based on their emotions.
Self-management – This is the ability self-manage your emotions and adapt to the a given situation based on your rational mind. It also covers great self-management skills concerning sudden changes in behavior or processes. Individuals with a high level of self-management are extremely good at adapting to negative changes and are very good at keeping a positive mind through stressful or tough situations. They are very good at balancing their emotional and rational mind to make better decisions.
Social awareness – This is known as the ability to understand and emphasize with the emotions of others. Furthermore, you are able to navigate effectively through social situations and deal with other perspectives than you own. Individuals with a high level of social awareness are excellent at listening, felling empathy, communicate effectively and resolve conflicts together with other people. They are great at being aware of social signs and building relationships with people. To build an inclusive and diverse environment, a high degree social awareness among managers is often required.
Relationship management – This is the ability to build and maintain healthy relationships, influence people, motivate others and managing conflicts. This involves communicating effectively, being able to negotiate, and collaborate. Individuals with a high level of relationship management are excellent at building trustful and inclusive relationships. They inspire others and are often seen as trustworthy individuals.
Controlling your emotions
The ability to control your emotions as an individual is a very important aspect of Emotional Intelligence. It enables people to respond to given situations appropriately by effectively managing and balancing their emotions. It indicates a high level of EQ if you are able to be aware of both your positive and negative emotions and regulate them in an appropriate way. In this way, it is also very important to be aware of the aspects of positive emotions that broaden and negative emotions that narrow.
- Positive Emotions - Broadens
Positive emotions are often what broaden our awareness and attention. It makes us more outgoing and driven towards making connections, networking and pursuing opportunities.
Supporting resiliency – Positive emotions strengths our resilience and tend to give the ability to be great at adapting to and overcome new challenges. They are generally better at handling and recovering from difficult situations.
Improving our thinking – Another aspect that positive emotions have a great impact on is our ability to think creative and our problem-solving skills. With positive emotions we reduced silo thinking which can be an obstacle in thinking clearly.
Undoing negative emotions – Negative emotions can be reduced be positive emotions as replace the negative thoughts with feelings of wellbeing and open-mindedness.
Building new skills - As positive emotions give us the curiosity and open-mindedness to explore and pursue opportunities, we are also more likely to learn new skills. Learning new skills requires a growth mindset which is enhanced through positive emotions.
Creating psychological capital - By creating psychological capital we prepare our selves to better handle tough situations. Psychological capital is referred to as internal resources as hope, resilience, efficacy, and optimism. Positive emotions help us building and strength these resources, making individuals more suited for tackling difficult situations.
- Negative emotions – Narrow
Even though negative emotions aren’t seen at as something that can be helpful, there are situations where they come in handy. Where positive emotions broaden, negative emotions tend to narrow our perspective in terms of focus and attention.
An indicator of potential threats - It can help us identifying potential dangers and threats as negative emotions trigger our attention to these. It increases the ability to be quick in decision-making when we are exposed to threats.
Calls attention to an issue – Negative emotions can help us take actions when things aren’t going as they should. They can help pushing towards addressing issues that might be both professionally and personally in our life. Indicating emotions as being angry or disappointed often lead to issues being discussed and addressed instead of being suppressed.
A mechanism of learning – When experiencing negative emotions, they also can affect the desire for change in terms of personal growth and development. They can trigger action towards learning new skills and motivate you to become better.
People who score high in Emotional Intelligence are able to utilize both positive and negative emotions depending on the situation they are in. As mentioned above, there are positive effects of both types of emotions if an individual is aware of the outcomes. However, it can be a very difficult skill not to be too emotionally impacted, but is certainly something to be developed or trained.
EQ, Leadership, and Stakeholder Engagement
- Leading by being emotional
Emotional Intelligence (EQ) and leadership are closely related, as leaders with high EQ are often seen as more effective and successful. Leaders with high EQ are able to understand and manage their own emotions, as well as the emotions of others, and use this knowledge to build strong relationships and create a positive work environment.[5]
Leadership is essentially concerned with effectiveness, direction, and purpose. It is important for leaders to define a clear direction and being able to communicate this direction to the rest of the team. This includes handling different personality types within the team and make everyone follow the desired direction to be able to deliver and realized value. A clearly defined purpose can strengthen the team's desire to follow the direction of the leader. An important aspect of defining the purpose is through face-to-face communication. Leadership is seen most effective in influencing people when the leader is strong in delivering messages and communicating through face-to-face communication. [6]
High EQ is associated with great leadership qualities for several reasons. Leaders with high EQ are able to empathize with others, build strong relationships, and communicate effectively. They are also able to manage conflict and respond to feedback in a constructive manner. These skills are critical for building a positive work environment, fostering innovation and creativity, and achieving organizational goals.[7]
- The importance of Stakeholder Engagement
How to self-develop EQ
- Never stop developing and learning
Never stop developing and learning is a critical aspect of developing EQ and effective leadership. One methodology to develop EQ is to start by being human. This means not isolating oneself or becoming disconnected from others.
- Self-Management
Apply EQ as a portfolio, program, and project manager
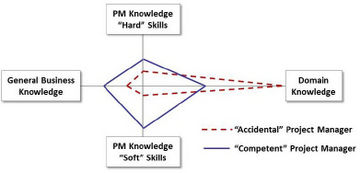
Accidental versus Competent Project Manager
- The Accidental Project Manager
- The Competent Project Manager
The 10 Key Steps
- Key steps to increase EQ in an organization [8]
Going through the key steps of the paper "EQ and the Bottom Line"
- Start simple
Starting by implementing simple goals to slowly increase EQ.
Increase effectiveness and productivity
Leadership effectiveness
- Connecting [9]
- Social awareness
- Engagement
Organizational productivity
- Increasing the bottom line
Increase project performance
- Vulnerability
- Creating a safe environment
- See people as individuals
- Proven studies and results
Conclusion
Limitation
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bharwaney. G, R.Bar-On, A. MacKinlay, EQ and the Bottom Line, pp. 14-16, (EI World, 2011), Available at: http://www.eiconsortium.org/pdf/Bharwaney_BarOn_MacKinlay_EQ_and_Bottom_Line.pdf (Accessed: 12 February 2023).
- ↑ Thompkins. S, Emotional Intelligence and Leadership Effectiveness: Bringing Out the Best, (Center for Creative Leadership, 2022), Available at: https://www.ccl.org/articles/leading-effectively-articles/emotional-intelligence-and-leadership-effectiveness/ (Accessed: 12 February 2023).
- ↑ Rechtfertig. G, Emotional intelligence and key principles to increase your capacity to succeed, (PMI® Global Congress, 2010), Available at: https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/emotional-intelligence-develop-abilities-skills-6628 & https://www.slideshare.net/captsumit/emotional-intelligence-and-key-principles-to-increase-your-capacity-to-succeed (Accessed: 19 February 2023).
- ↑ Casper. C.M, Using emotional intelligence to improve project performance, (Project Management Institute Annual Seminars & Symposium, 2002), Available at: https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/emotional-intelligence-improve-project-performance-1019 (Accessed: 19 February 2023).
- ↑ From the Magazine (January 2004), Leading by Feel, (Harvard Business Review), Available at: https://hbr.org/2004/01/leading-by-feel (Accessed: 4 May 2023).
- ↑ AXELOS and Cabinet Office, Managing Successful Programmes, (The Stationery Office Ltd, 2011 Edition).
- ↑ Berridge. G, High EQ: The Most Desirable Leadership Tenet of Them All, (N2Growth, 2022), Available at: https://www.n2growth.com/high-eq-desirable-leadership-tenet/ (Accessed: 19 February 2023).
- ↑ Burgan. D. S. & Burgan. S. C., Understanding emotional intelligence for project management practitioners, (Project Management Institute Global Congress 2012), Available at: https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/understanding-emotional-intelligence-pm-practitioners-6023 (Accessed: 9 April 2023).
- ↑ El Mokri. M, Emotional intelligence - an appropriate means to enhance team effectiveness?, (Project Management Institute Global Congress 2008), Available at: https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/appropriate-means-enhance-team-effectiveness-neurological-8361 (Accessed: 9 April 2023).