Managing communication through Network mapping
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
It would often be the project leader but often it is not the case as recognized by Rob Cross and Laurence Prusak ''"In most cases, the central connectors are not the formally designated go-to people in the unit."'' <ref> Cross, R., & Prusak, L. (2002). [http://www.uniroma2.it/didattica/direzioneestrategie/deposito/cross_prusak.pdf The People Who Make | It would often be the project leader but often it is not the case as recognized by Rob Cross and Laurence Prusak ''"In most cases, the central connectors are not the formally designated go-to people in the unit."'' <ref> Cross, R., & Prusak, L. (2002). [http://www.uniroma2.it/didattica/direzioneestrategie/deposito/cross_prusak.pdf The People Who Make | ||
Organizations Go–or Stop] </ref> | Organizations Go–or Stop] </ref> | ||
| − | [[File:Central Connector.PNG|Central Connector]] | + | [[File:Central Connector.PNG|100X100px|Central Connector]] |
Since the central connector is not always the formally go-to person it can be seen as the person most people talk to in the project might not be the project manager at all. | Since the central connector is not always the formally go-to person it can be seen as the person most people talk to in the project might not be the project manager at all. | ||
Revision as of 07:46, 13 September 2016
""" want to change title to "Managing communication through the informal network" how do I do that???""""
Communication and networks are two essential parts of projects that often can be neglected for project planning and project managing. Managing people issues in projects using Network Diagram is a good way of keeping track of whom are the right people to manage in a project. Since a project always concerns different stakeholders and different people who needs to interact with each other it is always important to keep track of whom are linked to whom. This can be done by using a Network Diagram indicating whom are connected to whom and what power does that relationship indicate as well as what power does the individual hold towards the project. And when combining that with the use of the right way of communicating as well as the right communication strategy the likelihood of a successful implementation of a project is way higher than if the communication and the network is not at part of the project plan.
Contents |
Introduction to Network mapping
The network diagram is a way of indicating the connection between people, organizations or other groups or things that might be indicated in a network. The network contains in the basic of nodes and edges. Nodes representing the people, organizations or groups. Edges is then indicating the connection between the people, organizations or groups.
What can then be added as indicators is the size of the node, showing what ever attributes connected to the node. Examples could be turnover of a company, number of employees in a company or age of a person. Then the size of the edge between two nodes can be used to indicate the connection between the two. Examples of that could be the emails between the two, the deals between to companies or the amount of projects they have worked together.
When the network is then drafted there are different roles that can be found in network each of them having a special indication of the importance and abilities of that node.
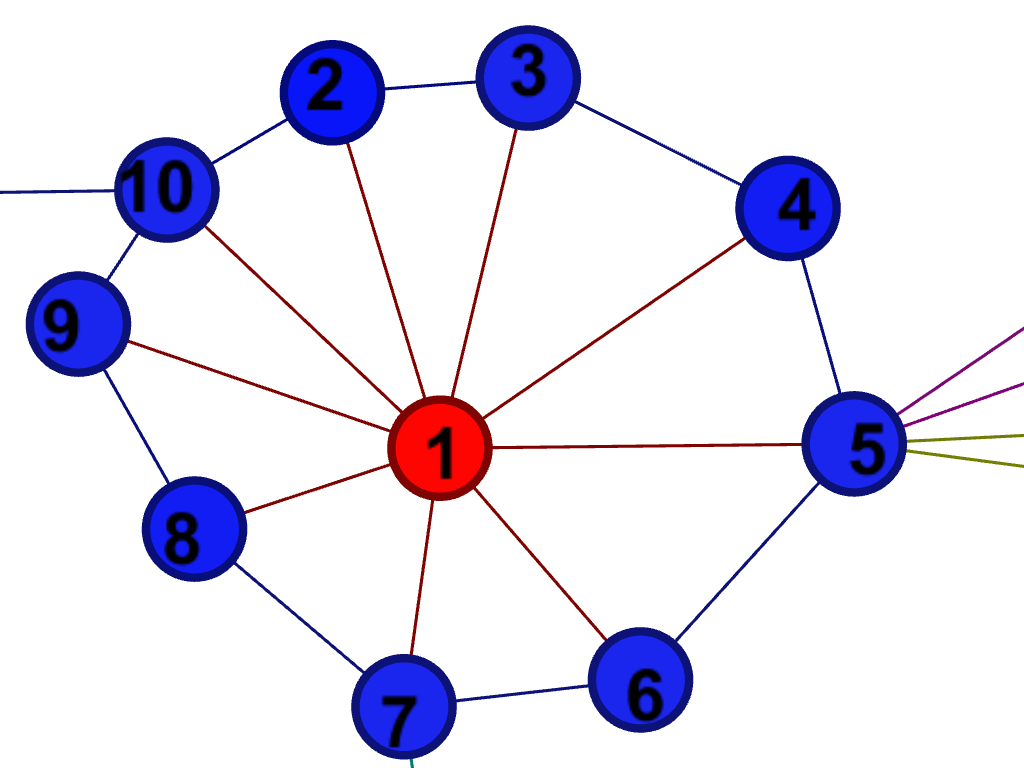
Central connector
The central connector is the type that everyone is talking to, the person or organization that communicates with the most of the others within the project.
It would often be the project leader but often it is not the case as recognized by Rob Cross and Laurence Prusak "In most cases, the central connectors are not the formally designated go-to people in the unit." [1]
Boundary spanner
Boundary spanner is a person whom are connecting two different groups these groups can be direct departments within a company or the crane operators on a building site. The person or organization having such contact and being the only one with that direct contact is of vital importance for the project because without that person there is no direct contact and therefore often no trust bounds between the project and the individual group, department or company.
Information broker
The information broker is the one who connects a large number of individuals or organizations and often between the main group and sub groups. The difference from the central connector is that the information broker is not only defined by the number of contacts but also the importance of the contacts.
Peripheral specialist
Peripheral specialist is the outsider. The person or company that do not have as many contacts as everyone else but whom are often a specialist and is therefore important because of the know-how. The link between that organization or person and the main group is very important because without that the organization or group might not have access to the know-how provided by the peripheral specialist.
Communication
The way of communicating is an important aspect of how the project will be conceived by the once whom are supposed to listen. It is not regardless how the project manager communicates to up to the clients who set the assignment, out to the other internal or external stakeholders or down to the project group all of them various stakeholders. The classification of stakeholders and more on stakeholder management can be found on the Wiki page Stakeholder Management[2] The importance of communication is also reinforced in the book Power i projekter & portefølje p. 269 where it is stated that when asked what the management could do better in change projects the main improvements should be better communication as answered by 67% of the group asked [3]. It is first very important to consider the channel that is chosen for the communication.
Communication plan
It is important to make at communication plan this will reduce the resistance in the project and at the same time create knowledge to the project. A good communication plan contains the steps shown in figure XX.
- Who is the target audience
The target audience is often part of the stakeholders especially the important stakeholder as have been found in a stakeholder analysis [2] but the most important stakeholders and the effect of what they can do comes by making a Risk Identification Risk Identification [4].
- What is the message
It is very important that the message is thought through before it ends up at the receiver. In one sentence it shall be clear what the message is to the receiver and what kind of experience should the message bring. The motivation is a important part, is it a burning platform or a golden wish that should be the motivation for the project?
- The channel of communication
The media could be as examples email, sms, face to face or other ways of getting the the message across. By using email it might seem very efficient but it will often get to the point where nobody is really taken notice to what is really said in the mail. The more effective way is face to face but that can be very time consuming and therefore it is not relevant to do it in order to deliver every message. The trade off by the two means of communicating is further discussed by Hayes [5] If there is an interest in changing the opinion of an stakeholder there is a need for communicating through a personal dialogue and involve the stakeholder so that it becomes clear why the stakeholder should change their opinion.
- The effect of the message
The goal should be clear from the start in order say what is it that the stakeholder should provide to the project or what the project should bring the stakeholder.
- New knowledge?
- Changed opinion?
- Changed conduct?
It is clear that it demands way more effort to change the opinion and the conduct of a stakeholder then is takes to just provide the stakeholder with new information about the project or the risk at hand in the project.
- Timing
Timing is everything, and it demands a plan in order to time the communication. There should be a communication plan for the project or at least in the project plan be marked out when and how the communication should take place in order for the project to be on track. It is of cause very hard to know in projects when to communicate what but at least it should be clear what is expected to be communicated and after what events it is necessary to communicate.
- Responsibility
It is very important to appoint somebody whom are responsible for communicating at the right time and to the right people. This way there is no uncertainty of whom to ask if there is any questions and there will come the normal question of whom are supposed to tell it. The responsible person should also be in charge of the communication plan, updating it whenever there is a change in project plan and being responsible for communicating unforeseen events.
Communication strategies
In order to get the right message across it is important to use the right communication strategy and each strategy have its own benefits and disadvantages.
Spray and pray
The strategy involves letting as much information out as possible to as many people as possible trusting that they might be able to sort through what is relevant and what is not. It gives the receiver the impression of being well informed but they might drown in information and not be able to get the important information out. The strategy is partially criticized inPower i projekter & portefølje p. 275 [3] . Because of as it is pointed out There is a high risk that communication to everyone do not hits anyone
Tell and sell
This strategy involves being prepared at selling the argument, the problem is though that there is a need for a lot of time to prepare the argument and "wrap it up nicely".
Underscore and explore
Underscore and explore attempts to make interesting and make the receiver come to the project manager for more information getting them hook by interest. On the other hand it can be time consuming and the receiver in not interested at all it is a waste.
Identify and reply
Identify and reply tries identify what issues the receiver might have with the project and then getting them to understand the necessity or the need. It will often demand some information about what the receiver dislikes and likes about the project and that might be hard to get.
Withhold and uphold
Simply keeping the information until absolutely necessary before telling. It can be difficult to keep the information for that long and it is rarely appreciated by the receiver.
Mistakes in communication
Communication is an art and even though it takes place all the time and some would argue more at this day then in the past there is still some critical mistakes that happens when communicating in a project. Some of those mistakes are here summed up by the given examples in [3] There is a good example saying that 41% says that to little, late or bad communication is the main reason for the negative feelings towards the project [3] p. 272
- Silence
We all know it, the sound of silence in a project or when we have raised a question. There is nothing more frustrating than wanting an answer and no answer is given and often we what to have the answer right away and can not really wait until tomorrow. The same is relevant in projects where the stakeholder often ask "what does it mean for me". Building a highway next to some houses is an example where the questions might rise about the noise, the time, the value of the house. A stakeholder whom are kept in the dark is probably more likely to be unwilling to cooperate.
- Big Bang, followed up by silence
Imagine that the project is started and you told that the department will be moved from Copenhagen to Aarhus, then nothing. That must be one of the must unpleasantness situations to be in. There is missing a notice about the consequences as well as the time and duration. In some cases there might even come a time where the stakeholder starts to think about whether or not the project have started or if it have been cancelled.
- Abstract and extraneous language
If there is no communication specific for the stakeholder then they might miss the point. One example could be if the project communication responsible communicates in the same way to the layer as well as the mason. The mason will probably not think that the subject is relevant for him/her. And might be left thinking if it is something they should carer about or if it is none of his/her business.
- It is forgotten that there should be two to a complete a dialogue
When it is always one way communication then there is a problem. There is nothing being discussed by one party always being the one giving orders but not opening up for any answers or dialogue. This instance can easily be contributing to important information not being delivered back to sender.
- Action speaks louder than words
This is a classic mistake where one thing is said but the opposite is shown. If one hand the company should cut down on the expenses but the sales team gets a team building trip to Aspen, Colorado in USA. Then the people on floor might be a bit sceptical about the idea. It is classical that the leader should lead and there be the first to take on the cut down on the expenses. Otherwise there is probably not much support to gain from the workforce.
- The wrong messenger
It is often more important who delivers the message instead of what the message really is. In many cases it is not ideal that it is the new coming head of department that delivers the message instead of the owner whom everyone trust and respect.
The examples given is just some of the main mistakes that happens when communicating.
Network Mapping as an communication tool
Conclusion
References
- ↑ Cross, R., & Prusak, L. (2002). [http://www.uniroma2.it/didattica/direzioneestrategie/deposito/cross_prusak.pdf The People Who Make Organizations Go–or Stop]
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Stakeholder Management, The Wiki page is concentrated about the importance of the stakeholders and the classification of the stakeholder. It then goes on to defining the influence and visualizing it though the stakeholder matrix.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Attrup, M. L., & Olsson, J. R. (2008). Power i projekter & portefølje (2nd ed.). DJØF Forlag.
- ↑ Risk Identification, This Wiki page gives a good overview of how to identify the risk and classify the risk at hand
- ↑ Hayes, J. (2014). The Theory and Practice of Change Management (4th ed.). Palgrave Macmillan Limited (Marts 2014).