Facilitated Work Sessions
Relindqvist (Talk | contribs) |
Relindqvist (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
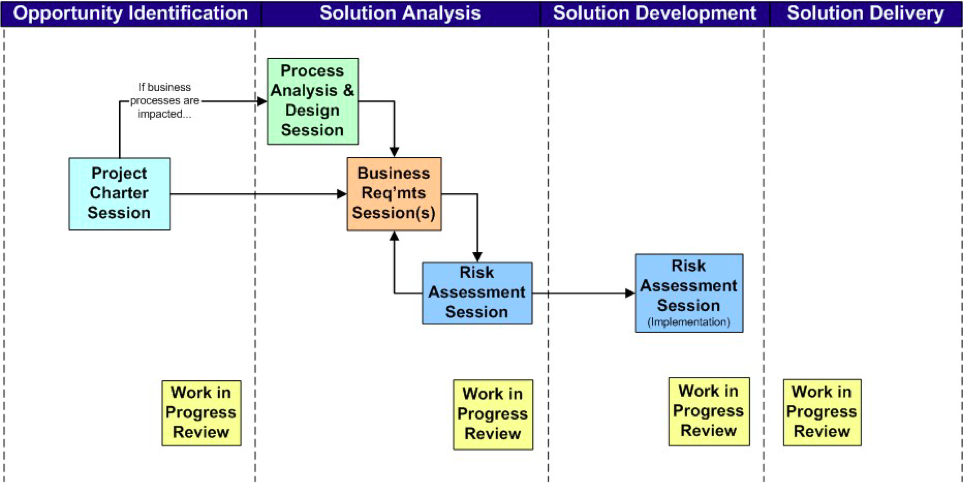
The way to determine when in the project there is a need for a work session is generally when the delivery to be produced is needed. Figure X shows examples of types of work sessions and where they fit in, in generic project phases. | The way to determine when in the project there is a need for a work session is generally when the delivery to be produced is needed. Figure X shows examples of types of work sessions and where they fit in, in generic project phases. | ||
| − | [[File:Phases.png| | + | [[File:Phases.png|Frame|Figure 1: Examples of work session and where they fit into a project.REFERENCE]] |
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
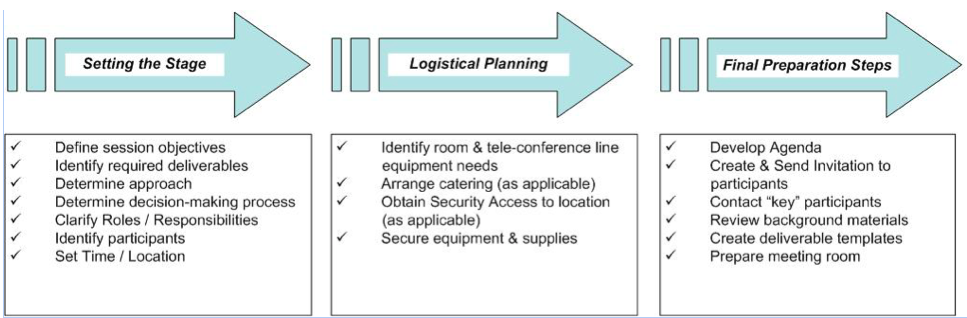
The facilitator plans the work session process, but in order to do so, it will be necessary to talk to the project manager and team. This goes especially for the first part of the planning, where the staging takes place, see Figure XX. Setting the stage is e.g. about defining the objectives for the work session and that should be done together with the project manager and perhaps also the project owner. Setting the stage is about creating the framework where the work session is taking place, what should be done, who should be there and when. Logistical planning covers the practical part of the work session, but is important to plan properly to keep things smooth and professional. The final preparation steps planning is where the design of the process, that is going to make it easy for the group to achieve the objectives, takes place. The facilitator will choose activities that will be appropriate in terms of the objectives, the participants, time and that will be best at bringing the participants’ joint knowledge into play. | The facilitator plans the work session process, but in order to do so, it will be necessary to talk to the project manager and team. This goes especially for the first part of the planning, where the staging takes place, see Figure XX. Setting the stage is e.g. about defining the objectives for the work session and that should be done together with the project manager and perhaps also the project owner. Setting the stage is about creating the framework where the work session is taking place, what should be done, who should be there and when. Logistical planning covers the practical part of the work session, but is important to plan properly to keep things smooth and professional. The final preparation steps planning is where the design of the process, that is going to make it easy for the group to achieve the objectives, takes place. The facilitator will choose activities that will be appropriate in terms of the objectives, the participants, time and that will be best at bringing the participants’ joint knowledge into play. | ||
| − | [[File:Planning.png| | + | [[File:Planning.png|Frame|Figure 2: Planning. REFERENCE]] |
=== Engage a capable facilitator === | === Engage a capable facilitator === | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
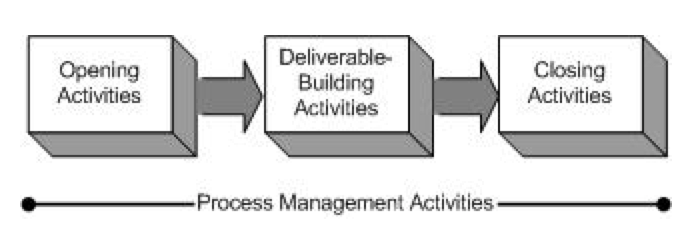
This part is highly context dependent. However, the structure of the work session is typically build by opening activities, delivery-building activities and closing activities as seen in Figure XXX. | This part is highly context dependent. However, the structure of the work session is typically build by opening activities, delivery-building activities and closing activities as seen in Figure XXX. | ||
| − | [[File:Open_Build_Close.png| | + | [[File:Open_Build_Close.png|Frame|Figure 3: Typical work session activities, REFERENCE]] |
==== Opening Activities ==== | ==== Opening Activities ==== | ||
Revision as of 10:53, 21 September 2016
Have you ever heard about projects that struggled to meet deadlines? Or where the quality of the deliverables was not high enough? Or of a project team that struggles with ownership or poor group dynamic? These are all relatively common issues of the project management practice. This article describes a concept for remedy of these issues, facilitated work sessions. Facilitated work sessions exist to speed up projects by producing project deliverables through participatory processes and group dynamics that works, while ensuring ownership of the results and keeping quality up. The general purpose with facilitation is to make it easy for groups to reach a certain goal, and further to make the group achieve more together than the sum of their individual inputs. The article stresses the importance of involving the right people because they are the key to make change happen. The participants are the experts in terms of the content and the facilitator must have the skills to design the process of the work session and lead the people through it.
Contents |
About Facilitated Work Sessions
Facilitated work sessions can be described by defining facilitation and work sessions separately.
Facilitation is essentially about helping a group of people reaching a goal and that involves planning or designing the process that does this together with leading or guiding during the process itself. The purpose of facilitation is also to get the knowledge of the participants into play in order to obtain a higher level of knowledge that lets the group achieve more than the sum of what the individuals could achieve.
A work session is basically a meeting that is characterised by being very structured and its purpose is to bring about a specific work product contributing to the project. The work being solving issues, making decisions and documenting the outcomes.
The participants are people with a stake in the specific work to be done. These could be the project owners, experts on the subject, customers, end-users, and suppliers if it makes sense.
- Cross-functional, 12-20 people, 2-3-day working session
- The Facilitator
- A Skillset and a Mindset – shortly describe what it generally requires to be a facilitator, e.g. specific values and human skills
Application
The application of facilitated work sessions will be context dependent, but a way to approach facilitated work sessions, including finding out whether they are relevant in your project, are provided guidelines for in this section. The recommended approach consists of six steps:
- Assess the need
- Plan effectively
- Engage a capable facilitator
- Engage the right participants
- Use the right work session approach and techniques
- Distribute quality results
Each of them are further described in the following:
Assess the need
Facilitated work sessions are first and foremost relevant to use when collaboration is required or believed to be the most value adding way to achieve the objective. However, there are other factors to take into account when deciding to or not to go with a work session.
- If the project involve multiple lines of companies or multiple departments in one company.
- If time is very limited and even small delays in the critical path will have a big impact.
- If the project is among the most important strategic initiatives in the company.
- If the project is trying to do something that is new in the company.
- If the project is trying to do something that has been tried before, but failed.
- If the project needs experts to participate who are not allocated full-time to the project.
- If the project result in changes that need group consensus or broad socialisation.
- If scope creep happens or if it is hard to acquire a specification of requirements from the team.
- If the project operates in a geographically dispersed environment.
The way to determine when in the project there is a need for a work session is generally when the delivery to be produced is needed. Figure X shows examples of types of work sessions and where they fit in, in generic project phases.
Plan effectively
The facilitator plans the work session process, but in order to do so, it will be necessary to talk to the project manager and team. This goes especially for the first part of the planning, where the staging takes place, see Figure XX. Setting the stage is e.g. about defining the objectives for the work session and that should be done together with the project manager and perhaps also the project owner. Setting the stage is about creating the framework where the work session is taking place, what should be done, who should be there and when. Logistical planning covers the practical part of the work session, but is important to plan properly to keep things smooth and professional. The final preparation steps planning is where the design of the process, that is going to make it easy for the group to achieve the objectives, takes place. The facilitator will choose activities that will be appropriate in terms of the objectives, the participants, time and that will be best at bringing the participants’ joint knowledge into play.
Engage a capable facilitator
Choosing the right facilitator is critical to success. Choose first and foremost a facilitator with the skills that it takes. The person can be internal, and employee or even the project manager or she/he can be external. Besides the skills it is crucial that the facilitator can be neutral concerning the subject or professional content of the project and work session. It means that the facilitator must be completely un-biased while guiding and supporting the participant group and this can be difficult if one has a stake in the project as for example the project manager does. Try to match the facilitator with the work session and consider the requirements in terms of the work session, but also think about group dynamics between the participants.
Engage the right participants
Every work session needs participants, and it is important to engage the participants who together are able to produce the needed outputs and meet the objectives. They may include:
- People with knowledge within the subject of interest who understand the business
- Project and process owners plus project sponsor to make sure the output is implemented and measured
- Support partners that will be able to identify the impacts of the proposed change (technology, finance, law)
- Customers who can validate whether the outputs matches their requirements
- Suppliers with knowledge to determine possibilities regarding implementation of the product/service
Use the right work session approach and techniques
This part is highly context dependent. However, the structure of the work session is typically build by opening activities, delivery-building activities and closing activities as seen in Figure XXX.
Opening Activities
A good opening phase creates a good foundation for the following phase, when the actual work is going to be done. Therefore this phase is just as important to facilitate well as the rest. This is where the participants meet each other and the facilitator and create a common starting point. Generally with facilitated processes a nice way to begin is by opening content, relations and process by answering WHAT, WHO and HOW? When a work session starts everyone should be able to answer the WHY? But explain the purpose of the work session and make sure everyone confirms it. After that, proceed to activities and somehow answer the other questions, not necessarily in the order described below.
WHAT: What is the work session about?
- Explain objectives of the work session.
- Have a presentation bring everyone up to speed on the project, e.g. by the project manager.
WHO: Who are we and what can each of us contribute with?
- Let the participants know that they are welcomed and valued. Could be by project sponsor/manager to make sure that they feel important.
- Have an introductory round and it should be made clear, by him/herself or the facilitator, why they are there.
- Clarify roles in the work session. The facilitator is going to lead the process and participants contribute with expertise.
HOW: How are we going to work?
- Make clear what the ground rules are, and ask the participants to confirm them.
- Explain the overall process and take them through the agenda. Make sure the agenda is visible during the work session.
Also, give practical information about restrooms, coffee availability and other information that they will need in the location.
Delivery-building Activities
These are the activities, which together are supposed to bring about the deliverable(s) one step at a time. It requires active participation and collaboration from the participants and guidance from the facilitator. It is important to provide clear instructions and explain how the activity contributes to achieving the objectives. The facilitator must
- Ask questions to dig deeper, sometimes get more specific – sometimes more abstract.
- Use active listening, and listen in order to understand and hence ask the right questions that will take the team further.
- Take the stage when it is needed - as well as taking a step back when needed.
- Document during the process, especially when the team has come to a conclusion or made a decision.
- Make sure that the dialogue does not die.
- Make sure the work and atmosphere stays constructive and professional.
- Keep time – the agenda can be reviewed and changed if fitting, but the team must reach meet the objectives by the end of the work session.
Closing Activities
Closing activities should be included at the end of every day and at the end of the entire work session. They exist to close what have been opened to avoid people leaving with unfinished business as well as for ensuring ownership and making the next steps in the project.
WHAT: What have been achieved through the day/whole work session?
- Sum up what the team has achieved
- Make sure that each participant knows what to do next (overnight assignment/after the work session)
- Are there any issues or actions left? If any, by the end of the work session make sure that the right person gets ownership and a deadline. Facilitate any discussions in this matter.
WHO: Who learned what and how did the participants experience the collaboration?
- A nice way of closing relations is to have everyone say something at the end; it could be an (brief) evaluation of the day/entire work session regarding the group collaboration.
HOW: How was it done, and how do we move forward?
- Take a look at the agenda together and go through it, perhaps while summing up achievements.
- Quickly go through the agenda of the following day.
- Evaluate the activities with focus on the process (at end of work session).
Distribute quality results
Limitations
Not good if there is actual conflicts in the team – they should be handled, but not using facilitated work sessions
- maybe some reflections on what problems facilitated work sessions cannot solve (reasonable) and in general reflect on the concept and its application and it’s effect on projects.
Bibliography
Adams, Tammy and Means, Jan. Accelerating Your Projects Using Facilitated Work Sessions. PMI Global Congress Proceedings. 2005.
Adams, Tammy and Means, Jan, Facilitating the Project Lifecycle: Skills & Tools to Accelerate Progress for Project Managers, Facilitators, and Six Sigma Project Teams, 2005.
Hogan, Christine. Understanding Facilitation. Kogan Page Publishers. 2002.
Rasmussen, Lauge Baungaard. Facilitating Change. Polyteknisk Forlag. 2011.