Management of remote project
(→Remote Project Management) |
(→Key Challenge in the Coordination of dispersed teams) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
= Key Challenge in the Coordination of dispersed teams = | = Key Challenge in the Coordination of dispersed teams = | ||
| − | [[File:challenge.jpg|rigth|thumb|650px|Figure 2:Challenge of remote team<ref name=Monica></ref>]] The key challenge for international NGO's is to deal with geographically dispersed team and all the consequences. They would prefer to be on the field for a more effective action but due to insecurity reasons they have to oversee the activities from another location. Thereby to continue to pursue a humanitarian imperative principle <ref> Once Removed, Stoddard, Lessons and Challenges in remote management of humanitarian operations for insecure area </ref>: getting aid to those in need as the first priority-even if it must be done from a distance. | + | [[File: challenge.jpg|rigth|thumb|650px|Figure 2: Challenge of remote team<ref name=Monica></ref>]] The key challenge for international NGO's is to deal with geographically dispersed team and all the consequences. They would prefer to be on the field for a more effective action but due to insecurity reasons they have to oversee the activities from another location. Thereby to continue to pursue a humanitarian imperative principle <ref> Once Removed, Stoddard, Lessons and Challenges in remote management of humanitarian operations for insecure area </ref>: getting aid to those in need as the first priority-even if it must be done from a distance. Usual companies are practicing remote project more for resourcing and develop new markets. But this lead to coordination problems inside the company. |
| − | This kind of management has several negative side as risk transfer on local team or poor quality and coordination. But those are due to a short-term decision-making attitude. The cluster approach that will be explained latter resolve some of these drawbacks. | + | |
| + | This kind of management has several negative side as risk transfer on local team or poor quality and coordination. But those are due to a short-term decision-making attitude. The cluster approach that will be explained latter resolve some of these drawbacks and can be applied to common companies. | ||
| + | |||
=== Trust === | === Trust === | ||
| − | As local NGO should have trust in their international management, dispersed teams should have the same behavior with the Head Offices. It enforces the formation of cohesiveness between team members. If there is not enough trust between the teams, they will have some difficulties to face challenges and even sometimes blame each other. Moreover, the local | + | As local NGO should have trust in their international management, dispersed teams should have the same behavior with the Head Offices. It enforces the formation of cohesiveness between team members. If there is not enough trust between the teams, they will have some difficulties to face challenges and even sometimes blame each other. Moreover, the local workers have a better understanding of the problem but international headquarters have knowledge from different and previous experiences. Therefore, scattered teams should understand the skills of everyone and use them with trust. So, the manager should |
=== Difference in Time zones, language and cultural barriers === | === Difference in Time zones, language and cultural barriers === | ||
Revision as of 08:36, 24 September 2016
Coordination of Remote Project: a cluster approach
The United Nations (UN) try to be present all over the world and try to response quickly in case of an emergency. However, local aid workers are subject to multiple attacks. Acting in insecure area could mean for the NGO (Non-Governmental Organization) huge expenses in security management. Thereby more of them prefer to use remote management to secure their international staff in a secure place. However, the remote control or remote management can lead to risk transfer to local team, wrong accountability or monitoring. Generally, whole those consequences are due to a bad planning. In addition, remote control is implemented in emergency situation. Though, if it’s executed and correctly planned in the early stage of the project it could really help the NGO to still provide aid to highly insecure area.
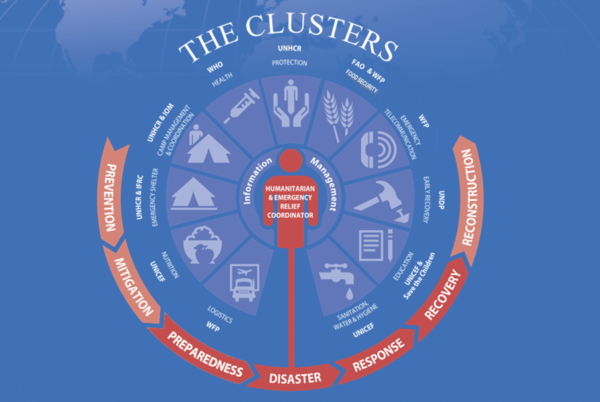
To avoid a lack of coordination they have implemented some years ago a cluster approach (figure 1 shows the UN clusters). The system is composed by a team leader who will coordinate the actions and sectoral teams for each activity. Some notable benefits have been shown through the years as better coordination, less gap and a better information sharing between the members. The theory behind this cluster approach is based on cluster management cycle used also in knowledge cluster (academic and companies). This perpetual cycle is composed by six stages: Define, Design, Implement, Monitor, Evaluate and Revise. It gives a framework and recommendation to correctly implement cluster approach on remote project for example. It highlights the fact that a cluster approach and remote project should be think early before the project otherwise the benefits and objectives could not have been reached. Finally, clusters are a new way to work together. It promotes innovation and is a unit with its own agenda inside a company.
As it will be explained in this article, the lessons and challenges from the emergency response could be transposed to a companies doing remote project. There are multiples difficulties to implement this kind of project as the difference in time zones, languages, and technology. Moreover, there should be a mutual trust to accomplish the specified task between the members. In brief, this article starts from the case of emergency situation and NGO, shows an approach to correct certain difficulties in the collaboration process, to finally expose the cluster management cycle theory and the definition of common cluster.
Contents |
Remote Project Management
Remote project management or remote control is defined as reducing or restricting movement or withdrawing internationals (or any other staff at particular risk) while shifting responsibilities for program delivery to local staff or local partners. [2]. It was first adopted in the conflict in early 1980s. However, only few documents explained the good practice of this kind of management and how to succeed. ‘Remote control’, ‘remote support’ and ‘remote partnership’ and ‘limited access programming’ are different concepts for remote management that it could be find in the literature [3]
The key element of remote project management is that the project is coordinated from outside: a different city, country, etc. Moreover, one of the consequence is that the team is geographically dispersed. As NGO, some companies have also scattered crews all over the world working on the same project. Thereby, the same challenge must be overcome.
Key Challenge in the Coordination of dispersed teams
This kind of management has several negative side as risk transfer on local team or poor quality and coordination. But those are due to a short-term decision-making attitude. The cluster approach that will be explained latter resolve some of these drawbacks and can be applied to common companies.
Trust
As local NGO should have trust in their international management, dispersed teams should have the same behavior with the Head Offices. It enforces the formation of cohesiveness between team members. If there is not enough trust between the teams, they will have some difficulties to face challenges and even sometimes blame each other. Moreover, the local workers have a better understanding of the problem but international headquarters have knowledge from different and previous experiences. Therefore, scattered teams should understand the skills of everyone and use them with trust. So, the manager should
Difference in Time zones, language and cultural barriers
An example will be taken in order to illustrate this challenge. An American NGO operating in Afghanistan with a local supplier will have some issues with the communication. Indeed,there is a different in time zone, in language, in culture. The different in time zone impose some delays for the response. But in emergency situation this delay is not acceptable. Therefore, there is a significant demand for staff to cover the time difference. Then, the language is also an important barrier. First, which language to use. Then, have all team team members sufficient knowledge to communicate properly? There could be some misunderstanding that can impede the progression and implementation of the emergency response.That is why the remote control should be implemented early and taking into account all these considerations.
Technical issues
First, an easy solution to resolve the different in time zones could be using low bandwidth communication channels, such as emails or documents, which generates large amounts of lost or misunderstood information[4]. Therefore, video and deskopt sharing should be use instead to promote face-to-face communications.
Then, people from different countries use different technologies. Americans will prefer Microsoft Office and the Chinese more open-source software.When the team are in the same building, those problems generally will be resolved by day-to-day communication[4] but for remote project it will be impossible. Therefore, a clear definition of which programs should be used must be done before starting the remote project.
One solution: a cluster approach
As it has been described, remote management can lead to coordination issues. In order to resolve that, the cluster approach was introduced in 2005 [2]. Thereby the lead role was more formalized among the different organisations. The cluster approach is defined by a Cluster lead, the lead coordinator for a specific area of response which is responsible for organizing coordination at global and country level, prepare global planning, guidance and acting as a last resort [6]. Then, there are the lead agencies for each area of activities/clusters: logistics, camp management, etc. The cluster approach is now used in 43 countries to respond to any kind of emergency project [7]
Notable Benefits
Even if this approach is still to be improved, notable benefits have been identified[6] in different fields like gap identification, coordination or information sharing.
Gap identification and Coverage
Thanks to a better collaboration between the agencies, it was possible to reduce the humanitarian efforts on site. Indeed, each of the members rely on each other. Moreover, it was possible to identify the missing services inside the cluster and correct it. [8]. Indeed, the cluster approach allows to have a collective response to a specific problem. The information will be shared in a better way the origin of the different gap and overlap can be identified.
Coordination and leadership
This double managing structure with on one side the Cluster lead ( UN for example) and on the other side the cluster agencies(WHO - World Health organization for instance) responsible for one sector, allows to clearly understand the responsibilities of everyone. This sector agencies are in charge of ’’ ensuring response capacity in place and that assessment, planning and response activities are carried out in collaboration with partners and in accordance with agreed standards and guidelines” [7].What make the cluster approach working is the fact that all the team members are working for the same common humanitarian objectives [7]. The leadership of the coordination is held by the Cluster lead and the leadership on the sector is held by the agencies.
Monitoring, evaluation and information sharing
Before the implementation of cluster approach in the humanitarian response, each member collected information but they are not shared between the agencies. No agency can learn from the other experience and there was no database. Trough cluster they can now share valuable information, analysis, strategic planning and evaluation. <ref=boom></ref>. Thereby this system improves the understanding of an pressing issue and let easy to find an appropriate response. Working processes have been identified and can be so easily implemented.
Cluster management cycle
The cluster approach is a way to implement in aid project but it can be also implemented in conventional companies who are dealing with international partners or teams. Cluster management is defined as a perpetual cyclic activity. It’s a complex, interactive and non-linear process. [9]. There is so a need in an adaptive management structure. Five stages can be looked at:
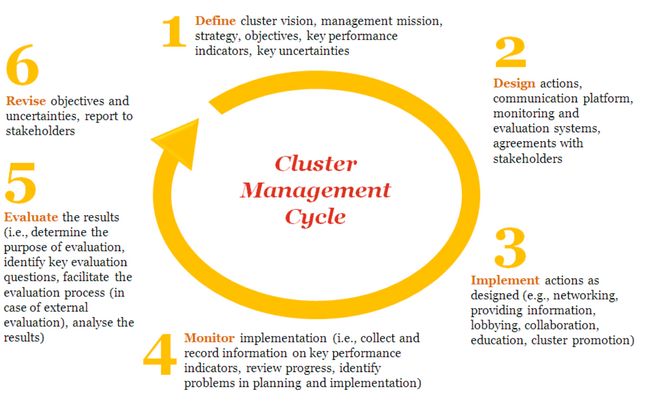
Define
In order to have clearly defined objective, the first step is to define the expected results for the cluster. A clear vision of the long term future of the cluster should be defined. It represents the strategic planning. For example, the WHO (World Health Organisation) cluster defines its vision as promoting health in the world. Another important recommendation is to identifying key uncertainties. As in insecure environment, the cluster manager is working in a highly uncertain environment and should act despite unpredictability. Key uncertainties for NGO or companies could be: [9]
- continuity of commitment of the key stakeholders
- finance instability
- change in technological and regulatory field
In order to succeed in cluster management, the vision and strategy should be developed with all clusters members. Moreover, the goals even in emergency situation should be measurable and feasible. Then, each clusters member should understand what are the benefit of this type of coordination.
Design
After defining objectives, they have to be performed. As it has been seen, one key challenge is to maintain a clear communication between the different stakeholders. Because of the difference in technologies, language it can become a hard task to manage. Therefore, two different plants should be presented.
First, an action plan has to be implemented in order to highlight the activities, the responsibilities related, planning and allocation of the resources [9] For each objective there has to be indicators for success and measurement. Thereby, a data collection could be performed afterwards. However, those indicators should be well chosen in order to avoid an overload of information. Then, a communication plan should be defined in order to promote a positive association, behavior between the members. Several questions should be answered in this plan like “Who are the Stakeholders?” "What are the communication mechanisms", etc. As in emergency situation is important to maintain a regular contact with the local suppliers. The frequency will differ following the role of the cluster member in the crisis as in the project for the companies. However, the communication mechanisms (software, etc) have to be clearly characterize with all the stakeholders. Finally, all the cluster members should accept a governance agreement for the decision making and communication.
Implement
Once the design approved, the implementation has to start. Here also a similarity could be seen between the operational actions of NGO and companies: the networking, providing information, collaboration, training, etc. [10]. The networking activities could be done during workshops or international conferences. The most important step in the implementation is to promote collaboration between the members. If they don't have the goodwill to work together the cluster structure will collapse. However, to have a proper collaboration, it has been shown that some of the key challenge should be mastered. For instance, by providing training in some software, the technical issue could be resolve.
Monitor
Monitoring is extremely important to gather crucial information on the different projects. To have useful information the participants must know which kind of info should be collected, their form and the involved people. To have a good monitoring it should be done on a systematic way and on a regular basis. [9] There are two ways for monitoring the activities: the first option is on a process-related indicator (that should be defined in step 1), the second one is a continuously collecting of information on the outputs[11]. However, this last method requires a big involvement of the cluster member to share uninterruptedly their information. For emergency case, it could very interesting but in other case it could impede the correct working of the group. The goal of monitoring is to adapt and check if the cluster is acting in the right way. Moreover, it allows to identify problems in planning and/or implementation. The correction should be implemented as soon as possible.
Evaluate
Comparing the actual effects with the decided strategies at a define moment is called evaluation[9]. It differs from monitoring in the way is done. Monitoring is continuous and evaluation is at a precise moment( generally once or twice a year). Moreover, the evaluation report shows if the objectives were reached, the strong and weakness of the cluster. It allows a complete understanding of the cluster organisation. usually, if there is a correct monitoring, the evaluation should be right as well. Two types of evaluation could be highlighted: the formative and the summative. They form together the complete evaluation.
- Formative
The purpose is to analyse the organisation of the cluster.
- Summative
The goal is to look at the improvement of the development of the cluster and its local impact. Then, another purpose of the evaluations is for decision policy. The evaluations are a way to justify certain decisions certainly in difficult contexts liek emergency disaster. Finally, it is extremely important for the experience and the development afterwards. Lessons could be learned and the action plan established in step 2 could be changed
Revise
The final step of this cyclic process is to review objectives and uncertainties taking into account the previous stages. After that the lessons learned and results must be spread with the stakeholders or in the company. At this stage, some report about the different evaluation have to be produce and share to a wider community. This last step closes the cluster management cycle.
Cluster: a new way of teamworking
Over time the effectiveness of a team decrease. [12]. Once the project done and if there is not a real recognition from the company for the well-working team, then the motivation could desappear. Cluster teams are totally the opposite of conventional team. They are by definition outside the company “but are hired and paid by companies as a unit, as a permanent part of the company” [12]. It is like a company unit inside a company. They have their own way of working and divide the remuneration. However, they are not doing consultancy in the way that they are hired for the long term and have their own working tools and methods. This is not always the case for consultancy groups. They are multi-disciplinary, multi-functional collaborative networks to drive optimal outcomes. They come into being to address a particular challenge, and then dissipate to form other networks addressing other challenges[13]
Regardless of the type of cluster (geographically dispersed or not), the following aspects are present[13]:
- Custom-made plan: operational objectives and schedule. It represent the purpose.
- Defined time-frame: when there is a need, the cluster is used. Once the objectives reached, the cluster has no reason to stay.
- Evolving team members: If new skills are required, new members will enter in the cluster.
- Self-organized: Clusters have their own structure and rules. They received the remuneration as an unit and spread it between the participants.
=Benefits and drawbacks
References
- ↑ United Nations Office for humanitarian affairs, http://www.unocha.org/sites/default/files/OCHA_Category/What%20We%20Do/cluster-leads.png
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Once Removed, Stoddard, Lessons and Challenges in remote management of humanitarian operations for insecure area
- ↑ Hansen, 2008; Stoddard, Harmer & Renouf, 2010
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Monica Yap, Successful Distributed Agile Team Working Patterns, https://www.solutionsiq.com/docs/successful-distributed-team-working-patterns.pdf
- ↑ Once Removed, Stoddard, Lessons and Challenges in remote management of humanitarian operations for insecure area
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Logan, BOOM , The Cluster Approach: working towards best practices in Humanitarian Response, 2012]
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Cluster Approach, One Response. http//oneresponse.info/coordination/clusterApproach/pages/ClusterApproach.aspx
- ↑ Steets,Julia.Office of the Coordination for Humanitarian Affairs. Inter-Agency Standing committee. IASC Cluster Approach Evaluation, 2nd Phase. 2010, http://ochanet.unocha.org/p/Documents/Inception_Report_CE2_Final.pdf
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Jan-Hendrik Schretlen, Uncovering excellence in cluster management, 2011, https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/psrc/pdf/cluster_management.pdf
- ↑ Biotechnology Cluster (1999). Report of a team led by Lord Sainsbury, Minister fro Science, United Kingdom
- ↑ Shapiro, J. (2001) Monitoring and Evaluation. CIVICIUS/ World Alliance fro citizen Participation
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 https://hbr.org/2013/02/the-future-of-talent-is-in-clusters
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 https://www.fastcompany.com/3012598/how-talent-clusters-will-help-you-win-a-sustainable-future