Waterfall vs. Agile Methodology
(→Waterfall Methodology) |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
=Waterfall Methodology= | =Waterfall Methodology= | ||
| − | The | + | The lifecycle model which is today known as traditional or Waterfall model was first described by Royce in 1970.<ref> Sommerville I., "Software process models," ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), vol. 28, pp. 269-271, 1996 </ref> It is called Waterfall model because of its sequential and down-flow characteristic where the phases analysis, design, implementation, testing and release are processed consecutively downwards.<ref name= "Comparative Study"> Dubey A.; Jain A.; Mantri A., "Comparative Study: Waterfall v/s Agile Model", International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research Technology (IJESRT), 2015 </ref> Each phase of the Waterfall model is processed in order without any overlapping and within a specified time period. Once a phase is completed there is no going back to a privious phase as it will be frozen.<ref name= "Waterfall v/s Agile"> Balaji S.; Dr. Sundararajan Murugaiyan M., "Waterfall vs V-Model vs Agile: A Comparative Study on SDLC", International Journal of Information Technology and Business Management (JITBM), 2012 </ref> |
Revision as of 14:46, 26 September 2017
Most software development projects apply either the Waterfall or Agile methodology. A development methodology is the procedure used by an engineering team in order to create the desired product. The Waterfall methodology represents the traditional approach, where the development process is conducted in a linear series of events. On its way toward the conclusion the progress flows continuously through the phases of a project (analysis, design, development, testing, release) like a waterfall. The entire project is planned in advance. Agile is a more recently developed software development methodology, where the linear approach is replaced by an incremental, iterative one. Instead of planning the whole project in advance, Agile enables the adaption of requirements during the whole project. This article provides an introduction of each methodology, a comparison and examples of use, in order to facilitate the decision whether Agile or Waterfall is more suitable for the next project.
Contents |
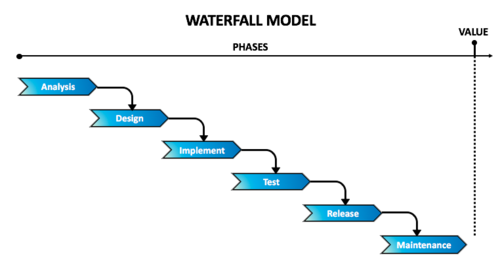
Waterfall Methodology
The lifecycle model which is today known as traditional or Waterfall model was first described by Royce in 1970.[1] It is called Waterfall model because of its sequential and down-flow characteristic where the phases analysis, design, implementation, testing and release are processed consecutively downwards.[2] Each phase of the Waterfall model is processed in order without any overlapping and within a specified time period. Once a phase is completed there is no going back to a privious phase as it will be frozen.[3]
Analysis
In this phase all the requirements and customer needs of the desired system or product are gatherd and recorded in detail in a specification document.[2] This document will be used as input in the design and implementation phase. The requirements of the product should be clear before moving to the next phase as changes in requirement can not be adapted later in the process.[3]
Design
The outcome of the design phase are a specified hardware and a virtual overview of the desired system or software.[3]
Implementation
The actual development of the system starts in the implementation phase. The system is therefor divided in small sub units which are tested by the developers before forwarding them to the testing phase. A quality gate checklist helps to control if there is a deviation from the requirements, planned time-line and product scope.[4]
Testing
In this phase the sub units are integrated to one working system which is tested regarding quality and functional aspects. The collected measures of performance are used for the decision whether the system is ready for the relase. In order to ensure that the outcome of the project meets the customers' requirements the tested system is reviewed according to a checklist. [4]
Release
The product gets prepared for beeing released into the market or delivered to the customer (including installation instructions of the system for customers and user-guides). There is another quality gate in order to check if the final product meets the customer and quality requirements and wheter it is delivered in time. [4]
Maintenance
After releasing the product in the customer environment there can occur problems in the products performance. Hence, the company must provide maintenace in order to solve this issues.[4]
Pros
- All requirements are clearly documented before the development of the product starts
- Each phase is finished in a specified period of time before moving to the next phase
- Waterfall is simple to implement as it is a linear model
- The amount of resources needed for implementing the waterfall methodology is minimal
- Each phase follows appropriate documentation in order to ensure the quality development [3]
Cons
- You cannot return to a privious phase. If the design phase fails the project might become very complicated in the implementation phase
- If a customer wants to change requirements of the product they cannot be implemented in the current development process
- Even small changes or errors in the finalized product might be very costly and cause a lot of problems [2]
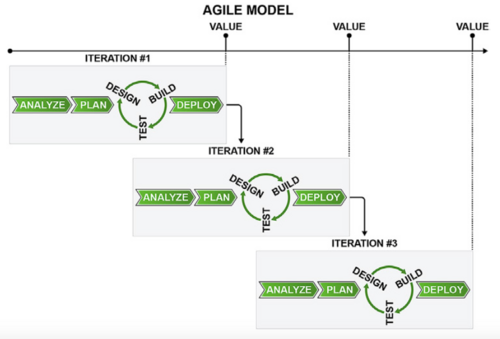
Agile Methodology
The Agile methodology uses an incremental, iterative approach instead of a linear and sequential one. Instead of extensive planning in advance it provides practices, tools and a culture that enable close collaboration of a team in a quick changing environment. During several successive iterations with a predetermined duration the team develops working products in order to get continous feedback from the customer. This procedure enables the team to improve the product with every iteration by adapting the backlog, a list of prioritized requirements for every iteration. An agile approach encourages selforganized cross-functional teams (incorpering planners, designers, developers and testers) with empowered members to create high quality outcomes.[5]
Scrum, Kanban, Lean, Extreme Programming (XP) and Feature Driven Development (FDD) are popular methods of the Agile methodology that provide concrete agile practices and comprise the following characteristics:[6]
- Responsiveness: being able to provide an appropriate response to any changes
- Flexibility: being able to adapt to changes at every time
- Speed: enable rapid and iterative development of a product
- Leannes: focus on cost saving, high quality and a short time frame
- Learning: ability to improve before and after product development
Generally, the different methods of Agile differ slightly one from the other but contain practices that cover the full range of product development. In some cases it is recommendable to combine different practices in order to create a situation-specific method.[6] All Agile Methodologies have in common, that they are driven by Agile values and principles, which are explained in the Agile Manifesto published in 2001:[7]
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
The twelve principles of Agile enlarge on this four value statements.[8]
Pros
- Changing requirements can be implemented at any phase of the process due to short development cycles
- A working product can be developed very quickly [2]
- Continous improvement enables fast and high quality delivery
- Continious dialogue between the customer and the development team ensures immediate user feedback
- The Agile methodology attaches great importance to teamwork as it requires frequent communication and face-to-face interactions. [9]
Cons
- Depends a lot on collaboration with the customer. Especially in long projects that is not allway possible
- Due to lack of documentation there is an increased dependence of interaction between developers [2]
- Compared to linear and sequential models agile methodologies are more difficult to comprehand [9]
- When used in large and complex projects it is difficult to estimate the costs and schedule
- Knowing that changes are possible the team could take hurried decisions without a proper analysis [5]
Comparison of the Waterfall and the Agile Methodology
As already discussed, the Waterfall model is a linear model with a sequential set of processes where the development "flows" from the start point to the delivery of a working product with several stages in between. Waterfall is a plan-driven methodology and hence, the whole project strictly follows a clear plan, that is elaborated in advance. As it requires extensive planning upfront it allows an estimation of costs and timeline, what enables a discussion with the customer. The existence of an ellaborated and clear plan and documentation also results in a more secure project as everyone exactly knows what to do.
Im comparison, the Agile methodology provides flexibel models which enable adaptive planning and development. During each iteration the team works on small packages of the product and receives direct customer feedback at the end of every iteration. Thus, rapid and effective responses to changing customer requirements are possible.
While the product delivery at Waterfall occurs in the very end of the process, Agile methods are divided into small releases and provide the customer with small increments of the final product throughout the process. To be continued...
Waterfall or Agile?
Example of Use
The following examples demonstrate the different approaches of each methodology.[10] [11] The project goal is the development of a customer adress book.
Waterfall Model
Product Requirements
First, the Product Manager has to create a document of requirements:
• Enable user to create new contacts
• Enable user to see his contacts
• Enable user to import contacts from other applications
• Enable user to email his contacts from the adress book
• Enable user to add pictures to represent his contacts
The created document will comprise detailed requirements, user scenarios and potential layouts
Timeframe: 2 weeks
Analysis
Engineering team takes these requirements and analyzes them, asking questions as needed. Product manager updates documents as questions are resolved.
Timeframe: 1 week
Design Engineering team creates a design for functionality, including database design, mock-ups and workflows.
Timeframe: 3 weeks
Implementation Engineering team develops functionality and prepares it for testing.
Timeframe: 1 week
Testing Product team tests entire functionality.
Timeframe: 2 weeks
Release The product functionality is released.
TOTAL elapsed time: 9 weeks
Agile Model
Product Requirements
The product manager creates a document of requirements:
• Enable user to create new contacts
• Enable user to see his contacts
• Enable user to import contacts from other applications
• Enable user to email his contacts from the adress book
• Enable user to add pictures to represent his contacts
These requirements documents will be simple, and will include user scenarios. As each item is worked on, questions will arise, and there will be opportunities to discuss them as they occur. From this list, the requirements for the first iteration are chosen (starting with the highest priority items).
Timeframe: 1 week
Iteration Nr.1 The team works on the functionality to create new contacts and to view contacts. This includes the design, development and tes ting for these items. At the end of the iteration, the team demonstrates the functionality to the product manager, where he or she can provide feedback.
Timeframe: 2 weeks
Iteration Nr.2 Team works on the functionality to import contacts, to email and to add pictures to the contacts. This includes the design, development and testing for these items. At the end of the iteration, the team demonstrates the functionality to the product manager, where he or she can provide feedback.
Timeframe: 2 weeks
Iteration Nr.3 Team conducts a regression test and prepares to release the product.
Timeframe: 1 week
Release The product functionality is released.
Total elapsed time: 6 weeks
Note that if any changes to the requirements occur during this project, each iteration would adjust accordingly.
Conclusion
References
- ↑ Sommerville I., "Software process models," ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), vol. 28, pp. 269-271, 1996
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Dubey A.; Jain A.; Mantri A., "Comparative Study: Waterfall v/s Agile Model", International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research Technology (IJESRT), 2015
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Balaji S.; Dr. Sundararajan Murugaiyan M., "Waterfall vs V-Model vs Agile: A Comparative Study on SDLC", International Journal of Information Technology and Business Management (JITBM), 2012
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Bomarius F. et al., "Product-Focused Software Process Improvement", 10th International Confernce, Springer, 2009
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Boral S.,"Domain I: Agile Principles and Mindset", Ace the Pmi-acp pp. 1-27, 2016
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Von Rosing M. et al., "Applying Agile Principles to BPM", Complete Business Process Handbook: Body of Knowledge From Process Modeling To Bpm — 2014, Volume 1, pp. 553-577
- ↑ Schwaber K. et. al., "Manifesto for Agile Management", 2001, Retrieved from http://agilemanifesto.org/ 22.09.2017
- ↑ K. Schwaber et. al., "Twelve principles of agile software", 2001. Retrieved from http://agilemanifesto.org/principles.html 22.09.2017
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Shiotsu Y., "Agile vs. Waterfall: A Side-by-Side Comparison", Retrieved from https://www.upwork.com/hiring/development/agile-vs-waterfall/, 22.09.2017
- ↑ "Product development: The Waterfall methodology (model) in software development", 2009, Retrieved from https://www.marsdd.com/mars-library/product-development-the-waterfall-methodology-model-in-software-development/, 22.09.2017
- ↑ "Product development: Using Agile methodology for software development", 2009, Retrieved from https://www.marsdd.com/mars-library/product-development-using-agile-methodology-for-software-development/, 22.09.2017