Coaching - Project Manager as Change Agent
(→Limitations of coaching) |
(→Limitations of coaching) |
||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
A limitation any Project Manager should be aware of in regards to coaching is the contradict in applying person-centered coaching in a business context which nevertheless is important if a team member is low on motivation or has a wrong attitude. | A limitation any Project Manager should be aware of in regards to coaching is the contradict in applying person-centered coaching in a business context which nevertheless is important if a team member is low on motivation or has a wrong attitude. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A consequence of not framing the business context clearly in a person-centered coaching is that either underlying expected essential prerequisites for a person-centered coaching will be compromised resulting in mistrust and a worsening of a situation or the Project Manager will omit his/her obligations regarding project management. | ||
==Lack of techniques and experience (person-centered and problem-centered)== | ==Lack of techniques and experience (person-centered and problem-centered)== | ||
Revision as of 21:08, 21 February 2018
In the PMI guide, Project Management Body of Knowledge [PMBOK] [1], coaching is mentioned as one out of several interpersonal skill, that a Project Manager is recommended to possess. However, coaching has certain strength when it comes to getting a person 'back on track' if performance is decreasing due to lack of motivation, knowledge or skills. In this perspective, coaching has great potential for Project Managers who are challenged by a decrease in team performance as a result of a change in the project. An important limitation of the use of coaching is seen when a person-centered coaching is applied in a business context, which will be the case if lack of motivation is causing problems for reaching the project objectives. Various recommendations for Project Managers applying coaching is given, one is to get inspiration from a Change Agent and use different modes of intervening to facilitating a change in a demotivated team members mindset or attitude.
Contents |
Introduction
Changes happen in projects. They may be initiated by project team members, stakeholder requests, complaints or a wide range of other factors, however, they can be it is the Project Managers responsibility to manage the change and implement corrective actions [2]
Corrective actions as e.g. re-scheduling, re-planning, and re-budgeting are all covered in the PMI guide, Project Management Body of Knowledge [PMBOK], as opposed to corrective actions ensuring that a team member gets re-motivated and 'back on track' after applying changes to a project. Development of a team members mindset and attitude in case it is unaligned with new project objectives is maybe less tangible than enhancement of skills and knowledge, but nevertheless it very important for regaining high performance.
Coaching is as mentioned, an interpersonal skill that a Project Manager is recommended to possess. Where PMBOK see coaching 'as a means of developing the project team to a higher level of competency and performance', merely by focusing on development or enhancement of specific skills, experience, and knowledge, other literature sees coaching as a process 'unlocking a person’s potential to maximize their own performance'. Where the first has a focus on achieving skills and knowledge the latter has a focus on changing a person's mindset or attitude to tackle a situation. This is called a person-centered coaching approach, as opposed to the first approach which is problem-centered. [3] Applying coaching in a business context demands an upfront framing making it clear that e.g. a project's progression is the coachings highest objective.
Interpersonal skills and competencies of a Project Manager

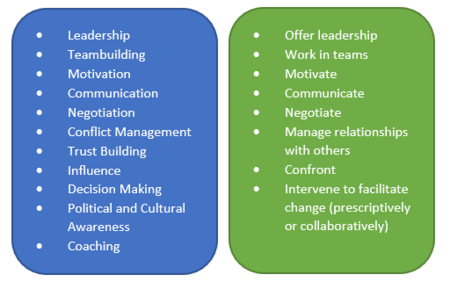
As the Project Manager is assigned to lead a team that is responsible for achieving the project objectives he must possess three specific competencies, in addition to area-specific skills and general management proficiencies required for the project, to be efficient. These three competencies are knowledge of project management, the ability to perform while applying his/her project management skills, and personal competencies such as attitude, core personality characteristics, and leadership.[1]
Keeping the fact in mind, that a project manager accomplishes work through the project team and other stakeholders, interpersonal skills are worth paying attention to as well. Interpersonal skills cannot stand alone, they are to be balanced with other important project management skills such as technical and conceptual skills in the act of analyzing situations and interacting appropriately.[1]
In any situation where a Project Manager needs to implement corrective actions to the project plan, budget or schedule, there is a potential risk that a team member or the entire team will be negatively affected by the change. In a worst-case scenario, the team members will be demotivated, performance will be affected, the progression of the project will decrease and project objective won't be achieved. In such a situation several interpersonal skills are relevant to possess. Communication, trust building, motivation, conflict management, teambuilding and coaching. However, in a situation of change where fear is known as the main reason for people be resistant to changes, coaching skills stand out. Handling a team member's fear - whether it is fear of poor outcomes, fear of the unknown, or fear of realization of faults with change overlooked by management and their fear of resulting problems [5] - requires some kind of dialog with a focus on regaining trust and confidence in the new situation. Two different approaches to coaching can be taken, either a problem-centered or a person-centered.
Coaching
Depending on your take on it coaching can be either a means or a process. With reference to PMBOK coaching is seen as a means of developing the project team to a higher level of competency and performance, merely by focusing on development or enhancement of specific skills, experience, and knowledge. With reference to literature by John Whitmore [1] who in the 1970s introduced the sport-individual performance-term coaching to organizations, coaching is seen as a process of 'unlocking a person’s potential to maximize their own performance' which has a high focus on working with mindset and attitude. The latter represents a person-centered approach to coaching because focus primarily is on empowering a person rather than solving a specific problem. This is opposed to the first which has a problem-centered approach by focusing on a person's development of specific skills. [5]
Coaching is based on a dialog between two people, one is conducting the coaching and the other is being coached and is build on the principle 'helping others to learn rather than teaching them a solution'.[add ref]
Coaching can be applied either formally or informally. If informally applied, then the coaching is more likely to be short, focused dialogs applied at any time during a workday. Also called 'corridor-coaching'. In contrast, formal coaching typically involves formal sit-down coaching sessions where e.g. a Project Manager will be conducting the conversation, assisted by a formal structure [e.g. Cooperrider 5F – se Ledelsesbaseret coaching].
A various number of coaching tools such as X,Y,Z can be helpful for the Project Manager applying coaching sessions.
In a specific context
Coaching can be applied in different contexts. With a Project Managers perspective it is relevant to distinguish between two contexts. Personal and business context. [4]
* Coaching a person in a personal context: the person's goals and needs are seen as the highest objective for the coaching. * Coaching a person in a business context: a company's competitive advantage or a project's progression is seen as the highest objective for the coaching.
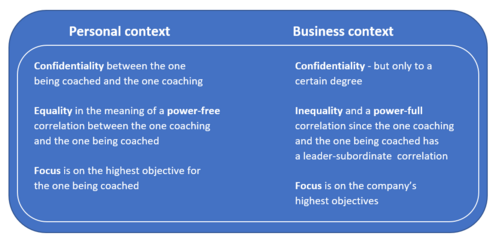
In figure 3 some important differences between coaching in a personal context and a business cóntext is listed.
Personal context
In a personal context essential prerequisites for coaching is: [4]
- confidentiality between the one conducting the coaching and the one being coached
- equality in the meaning of a power-free correlation between the one conducting the coaching and the one being coached
- focus on the highest objective for the one being coached
Both person-centered and problem-centered coaching can be applied in a personal context without reservations.
Business context
In a business context, an essential prerequisite for coaching is to frame the coaching in the business context, upfront, to the one being coached.
In a business context, the highest objective for the business will be in focus which not necessarily is equal the highest objective for the one being coached.
In a business context, there will often be an inequality between the one conducting the coaching and the one being coached and definitely, if its a manager coaching his/her employee e.i. Project Manager coaching a team member.
Both person-centered and problem-centered coaching can be applied in a business context but a claer framing of the context is important due to the underlying belief that coaching in general and especially a person-centered coaching per default is applied in a personal context and in accordance with the essential prerequisites.
PMBOK, which in regards to coaching represents the business context, only addresses problem-centered coaching.
Application
Focusing on a Project Manager with a desire to apply coaching, in practice, aiming to ensure high performance in his/her project team regardless of changes, knowing how to apply problem-centered and person-centered coaching in a business context will be in focus.
In this perspective, the coaching applied by a Project Manager can be framed as workplace coaching, defined as:
- a dialog between a Project Manager who has the responsibility of achieving project objectives and a team member, in which the Project Manager uses a wide variety of cognitive and behavioral techniques to enhance a coaching dialog with the team member in order to help the team member achieve a mutually defined set of goals or an adjusted mindset or motivation, with the aim of improving his or her work performance and, consequently, the effectiveness and performance of the project team.
As it can be seen, this approach is person-centered and problem-centered, and the context is clearly defined as a business context.
Application of informal coaching: (talk into what is written in Coaching paragraph)
Application of formal Coaching: (talk into what is written in Coaching paragraph) + (Describe some tools, processes, and models that are used in coaching)
[Figure showing the two different coaching approaches (person-focused and problem-focused) in relation to Business context and Personal context]
In terms of applying workplace coaching, a Project Manager can get inspiration from the work of a Change Agent. See Recommendation paragraph.
Limitations of coaching
Due to different factors, coaching applied by a Project Manager has its limitations. First of all, PMBOK does not at any point incite a Project Manager to acquire certain techniques, knowledge or experience within the field of coaching before applying it. This can be risky business due to the following circumstances:
A limitation any Project Manager should be aware of in regards to coaching is the contradict in applying person-centered coaching in a business context which nevertheless is important if a team member is low on motivation or has a wrong attitude.
A consequence of not framing the business context clearly in a person-centered coaching is that either underlying expected essential prerequisites for a person-centered coaching will be compromised resulting in mistrust and a worsening of a situation or the Project Manager will omit his/her obligations regarding project management.
Lack of techniques and experience (person-centered and problem-centered)
(main focus: The mindset/attitude coaching is missing in the PMBOK's way of seeing coaching!)
(Include examples from the PMBOK - Coaching in regards to changing mindset isn’t explicitly mentioned. PMBOK talks about turning a ‘can’t do’-situation into a ‘can do’-situation – not about changing a ‘can’t do’-mindset into a ‘can do’-mindset. PMBOK focuses on coaching the individual, not team coaching. Team-building is mentioned, but there is a big difference between team coaching and team-building even though team cohesiveness and performance may be positively affected by both [TEMO book: balance divergence-cohesiveness for high performance, Factors important for cohesiveness]. PMBOK in some way mentions the benefit from team coaching and/or team-building: ‘as a team develop their skills, abilities, and confidence, their willingness to take a challenging or demanding task in increased’ but if skills can be seen as 1+1+1, ability and confidence is highly influenced by common understanding and team spirit [TEMO book].)
(PMBOK mentions that formal or informal training may be developed to increase technical skills or assist team-building efforts and facilitate consistent interpersonal interactions. It is a little unclear whether the training regards the PM or the team members – or both.=
Lack of attention to the context (personal vs business)
Due to the fact that coaching in its origin was applied in a personal context, there is a risk that there is an underlying belief among people, saying that the essential prerequisites for coaching in a personal context are valid for any coaching and definitely for a person-centered coaching regardless of context. This brings on the risk, that a team member is unclear on the circumstances for a workplace coaching and therefore it is important that a Project Manager is aware of the frequent underlying belief and as a standard, frames the coaching clearly, upfront. If not, a coaching can result in mistrust and a worsening of a situation.
If for instance, a Project Manager chooses to coach a team member with a person-centered focus in a business context, there is a possibility that the Project Manager and the team member will have two different understandings of e.g. confidentiality. If not clearly framed upfront the team member will probably expect that whatever said in the coaching is confidential and that the Project Manager is neutral and equal in regards to power. Contrary, the Project Manager will be aware of his/her responsibility to achieve project objectives why he/she will take any information that compromises a project's progression into consideration and taken action on.[4]
Country, culture or hazard
Other circumstances as power distance in a given country, which paradigm the company corresponds to and the specific situation of change can be a limiting factor for applying coaching.
- In countries with high power distance a coaching approach can be non-applicable since the coaching attitude implies and certain employee autonomy. [6]
- In a company or department corresponding with 'command and control' paradigm coaching can tend to be less successful since coaching is a natural part of the 'interactive learning' paradigm and thus requires a less hierarchical structure, more a fare more value-based motivation than the command and control paradigm supports.[7]
- In situations where a change causes a hazard and an immediate corrective action is needed, coaching will not be applicable since coaching is based on dialog it tends to be
Recommendations
(Short intro stating the context of the recommendations - ensure to show that the recommendations are relevant in regards to the limitations ) A recommendation for Project Managers is to apply informal workplace coaching rather than formal coaching sessions, and always to frame the coaching in a business context, upfront.
Apply Change Agent mindset
A way to get started with workplace coaching is to get an understanding of what it takes to facilitate a change or said with other words 'to move people from current state to a desired future state' [ref Facilitating change]. As seen in figure 2 Change Agent skills are very similar to the interpersonal skills a Project Manager is recommended to possess. This argues for the possibilityLooking into the fact that a Project Manager no matter what will be comparable to an internal Change Agent, it is relevant to ensure that the recommended circumstances for applying an internal Change Agent are present. In accordance with literature [5] the main arguments for choosing an internal Change Agent is as follows:
- the person responsible for managing the unit or subsystem that is to be the (initial) target for change is committed to acting as change agent
- It is agreed that a particular insider has the time, knowledge and commitment to manage the change more effectively than an outsider
- the system does not have the resources to employ an outsider
- issues of confidentiality and trust prohibit the use of an outsider
- it proved impossible to identify a suitable outside consultant.
As seen, in general, no prerequisites are contradictory to a Project Managers role and responsibility in regards to project management.
In terms of facilitating change in a project team, a Project Manager can be inspired by the intervening modes that a Change Agent uses. (include:...facilitating and developing the capabilities of those involved [5])
Apply different intervening modes for facilitating change
Using four different ways of collaborative intervening – depending on the situation, the individual or the team.
Theorizing approach The theorizing mode of intervening is problem-centered. It involves Project Manger identifying theories and conceptual models that are pertinent to the team members problem situation, presenting these to the team member and helping them learn to use them to facilitate a better understanding of their situation in an analytical cause-and-effect fashion. The Project Manager then build on this understanding and use it to help clients identify what they can do to move towards a more desirable state of affairs. This mode of intervening might be adopted when Project Managers feel that some kind of theoretical framework could help a team member to organize their thoughts and provide the basis for a fresh appraisal of their predicament. Project Managers can also use theories to facilitate the discussion of potentially delicate or sensitive issues. [MoC text - rewrite]
Supportive approach The supportive mode of intervening is a person-centred, as opposed to a problem-centred, approach to helping. It involves the Project Manager working with the team member to help them clarify their views and express feelings and emotions that impede objective thinking about a problem or opportunity. Project Managers adopting a supportive mode of intervening listen empathetically, withhold any judgement and help clients develop for themselves a more objective view of the situation. [from MoC] Supportive tends to be person-centred!
Challenging approach The challenging mode of intervening is problem-centered. It involves the Project Manager confronting the foundations of the team members thinking in an attempt to identify beliefs, values, and assumptions that may be distorting the way situations are viewed. An assumption underlying this challenging mode of intervening is that effective action can be undermined by team members inability or unwillingness to face up to reality. Challenging interventions are designed to call attention to contradictions in action and attitude or challenge precedents or practices that seem inappropriate. The aim of this approach is not only to challenge values and assumptions but also identify alternatives that might facilitate the exploitation of opportunities, or lead to the development of more effective solutions to problems. [MoC text - rewrite]
Information-gathering approach The information-gathering mode of intervening is problem-centered. It involves Project Managers assisting team members to collect data they can use to evaluate and reinterpret a problem situation. The assumption underlying this approach is that information deficiencies are an important cause of malfunctioning. Project Managers objectives are to guide a team member so that they arrive at a better level of awareness of the underlying causes of a problem and to help them to identify what action is required to resolve it. An assumption to this approach is that any information presented by the Project Manager will be less acceptable and less likely to be understood than information that a team member or the team generate for themselves. As well as a team member will be less resistant to proposals and action plans they generate for themselves.[MoC text - rewrite]
Change Management theory also present a fifth way to intervene with team members in a situation of change. This approach is prescriptive, as opposed to the other approaches which are collaborative. Given its nature, it is not to be seen as a recommendable approach in coaching, but it is presented here, as it is important for Project Managers who prefer a coaching attitude towards team members, to be aware of the need for clear leadership in situations where immediate action is needed. Furthermore, PMBOK distinguishes between coaching and counseling (to be considered: Is there a correlation between won’t do and can’t do and can different intervening approaches be used in coaching in ‘won't’ do situations? [Modes of intervening – prescriptive (advising) versus Collaborative (Theorizing approach, supportive approach, challenging approach, information-gathering approach)??)
Advising approach - (prescriptive) The advising way of intervening is prescriptive, as opposed to the four collective modes described above. Project Managers intervene by giving advice and telling team members what to do in order to rectify problems or develop opportunities. The underlying assumption is that the Project Manager has a greater level of relevant expertise or competence to make a sound diagnosis and plan corrective actions for the team member than the team member has for themselves. In many circumstances, Project Managers can see a solution because they are more experienced than their team members, but if they intervene by offering advice and telling team members what to do, they deprive them of the opportunity to learn how to solve the problem for themselves. [MoC text - rewrite]
Apply problem-centered AND person-centered coaching
(Describe why there is a need for both approaches (motivation/attitude) and (skills, knowledge and experience) for a Project Manager in regards to managing a project team in a situation of change.)
Apply informal workplace coaching on a daily basis - and formal when needed
(Reason: Informal workplace coaching provided on a daily basis e.g. as 'corridor coaching' will in most cases help the Project Manager to early recognition and immediate action when a change causes trouble in the mindset or attitude of a team member. A formal coaching with a sit-down coaching session is necessary for situations ....... xxxxxxxx)
Other ways to prevent or handle decrease in team performance
(Elaborate a little on this - since given in TA-feedback) (1) High-Performance Teams, (2) Project governance, (3) Self-managed work teams, (4) Teams motivation.
Conclusion
(Ensure that conclusion is only based on things that is written earlier in this wiki)
Project Manager can preferably apply a coaching approach in the day-to-day dialog with team members, teams, and stakeholders to help them to a new level of understanding that can clarify their thinking about a problem. The Project Manager can beneficially use one or more of three problem-centered, collaborative intervening modes , typically uses by change agents, in his/her dialog with team members and stakeholders.
Annotated bibliography
Peterson, David B. (1996). Executive Coaching at work: The art of one-on-one change. Consulting Psychology Journal: Practice and Research — 1996, Volume 48 (2), pp. 78-86 Abstract Outlines the 5 research-based strategies that guide one-on-one coaching by a management consulting firm: forge a partnership, inspire commitment, grow skills, promote persistence, and shape the environment.
Kilburg, R. R. (1996). Toward a conceptual understanding and definition of executive coaching. Consulting Psychology Journal, 48(2), pp. 134-144. A review of the literature on coaching reveals that very little empirical research has focused on the executive coaching methods used by consultants with managers and leaders in organizations. Within the framework of a 17-dimensional model of systems and psychodynamic theory, the author provides an overview of a conceptual approach to coaching activities that incorporates 5 identifiable components plus an emphasis on goal setting, intervention methods, and hypothesized factors in negative consulting outcomes.
References
(Must fix: the same reference is shown multiple times)
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Committee, P. M. I. S. (2004). A guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute. Inc.
- ↑ Great Britain. Office of Government Commerce. (2009). Managing successful projects with PRINCE2. TSO.
- ↑ Whitmore, J. (2009). Coaching for performance: GROWing human potential and purpose: the principles and practice of coaching and leadership. Nicholas Brealey.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Molly-Søholm, T., & Jacob Storch. (2013). Ledelsesbaseret coaching. Ledelsesbaseret Coaching. L & R Business. Retrieved from https://findit.dtu.dk/en/catalog/2192969265
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedChange - ↑ Home - Hofstede Insights. (n.d.). Retrieved February 15, 2018, from https://www.hofstede-insights.com/
- ↑ Baungård Rasmussen, L. (2011). Facilitating change: using interactive methods in organizations, communities and networks. Polyteknisk Forlag. Retrieved from https://findit.dtu.dk/en/catalog/2395961761