PIMS Novo Nordisk 2020
(→Situational leadership model) |
(→Situational leadership model) |
||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
Leadership style in terms of the amount of task behavior and relationship behavior (3) | Leadership style in terms of the amount of task behavior and relationship behavior (3) | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4leaderbehaviour.png | ||
Revision as of 19:31, 3 March 2020
Contents |
TWO PEOPLE CANNOT EDIT AT THE SAME TIME
Tools
Part of PIMS Work Breakdown Structure
Abstract
Quick introduction to tools collected
Tools
Purpose
Project charter
The project charter lays the foundation of the project this can be divided into 4 different areas. (1)
- The project charter is used to define the scope, objective and vision of a project. This is done by describing the specific outcomes and how these will be achieved.
- In the organizing part the project team is defined along with the responsibility for the different participants. It also defines the relevant stakeholders.
- The implementation plan describes how the organization is going to succeed in fulfilling the objective described in 1. This usually involves timeline marking the different tasks and milestones during the project, the dependency among the different tasks and resousceplan.
- The last part is budgeting and risks. Here the high level risks that apply to the project should be listed. Whit these information a budget can be made.
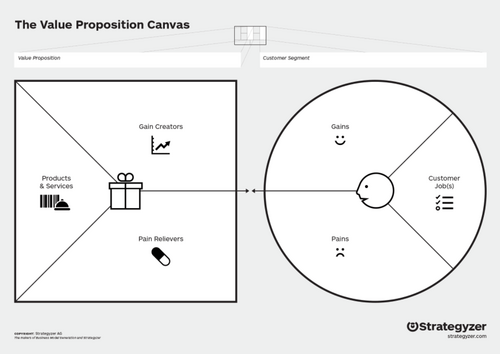
Value Proposition Canvas
The Value Proposition Canvas, a part of Osterwalder and Pigneur’s Business Modell Canvas (1), can be used to clarify the project objectives and fully understand the customer needs. The right side of the model, the customer segment is sub dividable in
- Pains – unwanted things the customer could experience while getting the job done, e.g. extra cost, risks, and negative feelings towards the project
- Gains – positive outcomes the customer wishes to achieve
- Customer Jobs – all tasks the customer tries to perform and the problems they intend to solve
and used to exploit the project owners’ indentations, whereas the left side, the value proposition with its three subcategories, strives to describe the customer requirements.
- Pain Relivers – how the project solves specific customer pains
- Gain Creators – how the project creates the intended gains for the customer
- Product and Services – the services and products the project provides for the customer (2)
1( http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Use_of_Business_Model_Canvas_to_Kickstart_the_project_management
2( http://www.orange.ngo/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/value-proposition-design.pdf, http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Value_proposition_canvas
3( https://www.strategyzer.com/canvas/value-proposition-canvas
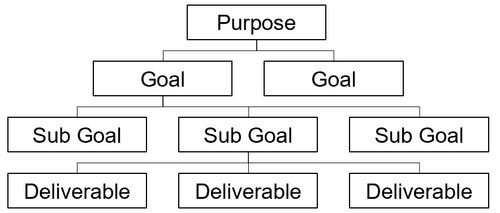
Goal Breakdown structure
Goal Breakdown Structure The purpose states why a project exists. However, the purpose needs to be translated in a strategy in order to achieve its benefits. Therefore, the Goal Breakdown Structure (GBS) intends to divide projects, programs and portfolios overall purposes into manageable goals, sub-goals, and deliverables while maintaining the link to the overall objective. Whereas the Work Break Down Structure (1) strives to translate purpose by the completion of tasks, the GBS is taking a different approach and is structuring the company by goals and objectives that may have measurable elements such as cost, time, etc. (2) This goal hierarchy ensures the permanent alignment with the overall intention of the company. (3)
1( http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Work_Breakdown_Structure
2( https://ebookcentral-proquest-com.proxy.findit.dtu.dk/lib/dtudk/reader.action?docID=5180851#
3( http://apppm.man.dtu.dk/index.php/Goal_hierarchy_or_Goal_Breakdown_Structure
People
Situational leadership model
Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard developed the theory of ‘situational leadership’ (1) . The theory describes four different leadership styles and four levels of individual or team maturity or readiness. Depending on these two factors, suggest which style of leadership best suits which level of maturity. (2)
The leadership styles are: S1: Telling: one-way communication where the manager defines roles and is very directive about how work will be performed. S2: Selling: two-way communication. The team or individual is now encouraged to buy into the decisions being made by the manager. S3: Participating: shared decisions between individuals and the manager. S4: Delegating: manager delegate to individuals but retains responsibility for monitoring progress.
Leadership style in terms of the amount of task behavior and relationship behavior (3)
4leaderbehaviour.png
(1) Hersey, P. & Blanchard, K. H. (1969). "Life cycle theory of leadership". Training and Development Journal. 23 (5): 26–34
(2) https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-the-situational-theory-of-leadership-2795321
(3) Graph based on Hersey, P. & Blanchard, K. H. (1969). "Life cycle theory of leadership".
Meetings management and strategy
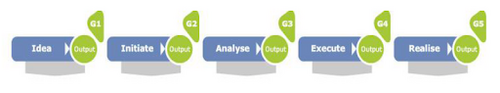
Project execution model (PEM)
The Project Execution Model is a five staged model used to guide the project manager in the activity. Each stage is followed by a gate where stakeholder such as project owners, project managers, steering groups and project sponsors review the completion of the previous stage in order to continue with the next phase or demand rework. The stages are:
- Idea – brief description of project objectives, stakeholders, resources (time, cost, personnel etc.), and risks to generate a basic understanding of the project
- Initiate – establishment of steering group to evaluate and give direction regarding project objective plus scope and further detailization of stage one topics.
- Analyze – placement of key project team based on selected scope in stage two. Furthermore, creation of Work Breakdown Structure (1), refinement of risk management, and finalization of cost budget.
- Execute –main project work carried out including preparations for transition from project phase to daily operation.
- Realise – realization of benefits. (2)
| Stakeholders | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Project Owner | Owns benefits and deliverables and appoints project manager |
| Project Manager | Day-to-day management of project execution |
| Steering Group (StG.) | Support during scoping and stage approval plus smoothening of project environment |
| Project Sponsor | Head of steering group, final approver of gate completion and overall investment cost |
| Project Team | Execution of project according to personal expertise |
| Line of Business | Internal corporate business unit to negotiate how to meet targets and resources with project manger |
(1) http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Work_Breakdown_Structure (2) http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Project_Execution_Model_(PEM)#PEM_-_a_five_gate_model (3) http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/File:Image001.png (4) http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Project_Execution_Model_(PEM)#Roles_and_responsibilities
Expectations management
Project sponsor
Stakeholder map
After identifying the relevant stakeholders, they can be mapped in various ways. For example in a power vs interest matrix(1) or mapping stakeholder benefits(2). Using the tools as above or similar, gives a very good idea of what stakeholders interest are and how they can achieve them. In addition also how the stakeholders interests differentiate from each other. Different positions in the power vs interest matrix corresponds to different managerial behaviour towards the specific stakeholder. Using this, paired with a stakeholder benefits analysis, gives a solid picture of the current stakeholder state.
1 https://www.brighthubpm.com/resource-management/80523-what-is-the-powerinterest-grid/
2 https://project-management.com/what-is-stakeholder-analysis/
Challenges in cross-cultural project management
Complexity
Project control
Risk management
All projects involve risks. Successful managing and identification of risks therefore plays a big role in any project. To map and categorize prior identified risk, a popular method is the risk matrix. (1) A typical risk matrix consist of two dimensions. How severe the consequences are if the risk occurs and how likely they are to occur. Using a matrix shows the project manager or controllers what risk’s to focus on. Thus makes it possible to decide if the risk is acceptable or it has to somehow be reduced to “as low as reasonably practicable” (ALARP)(2) As the project goes on, the landscape of risk may change. New risk’s may occur and probabilities can in- or decrease. It is therefore necessary to review the risk matrix and update it to show the current risk situation.
(1) https://www.cgerisk.com/knowledgebase/Risk_matrices
(2) https://www.hse.gov.uk/risk/theory/alarpglance.htm#
Change agent theory
Uncertainty
Risk identification
To manage risks, it is important to have identified and planned for as many risks as possible. If an unidentified risk occurs, the consequences may be much severe, as no actions are planned. To identify risks, a starting point can be to conduct a SWOT analysis or draw analogies and do research of other similar projects.(5) Later on, a more detailed identification can take place, for example assumptions analysis or interviews. To analyze root causes, a fishbone diagram or similar may be used. It is very difficult to ensure that all risks are taken into account. As projects usually include things that are unknown, some risks are also impossible to identify from the start. It is therefore very important to update and review the list of risks and their impact/frequency during the duration of the project.
(1) https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/risk-identification-life-cycle-tools-7784
Guide
subheading
subsubheading
Tricks
bold text is done by 3 apostrophes on each side. Check code
Every time you press enter to go to next line, press it twice.
Headings are done by equal signs. Check code
Test picture
Click "upload file" to the left, under "toolbox". Upload your favorite picture and remember the exact name.
The code for the figure below is(Enter filename and desired figurename);
File:Novosixtest.jpeg |500px|thumb|center|Figure 1 Test picture
How to do a reference
References
- ↑ (1) http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Use_of_Business_Model_Canvas_to_Kickstart_the_project_management
- ↑ (1) http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Use_of_Business_Model_Canvas_to_Kickstart_the_project_management
- ↑ Project Management Institute, Inc.. (2017). Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) (6th Edition). (pp. 513). Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). Retrieved from https://app-knovel-com.proxy.findit.dtu.dk/web/view/khtml/show.v/rcid:kpGPMBKP02/cid:kt011DXO32/viewerType:khtml//root_slug:13-project-stakeholder-management/url_slug:project-stakeholder-management?kpromoter=federation&b-toc-cid=kpGPMBKP02&b-toc-root-slug=&b-toc-url-slug=project-stakeholder-management&b-toc-title=Guide%20to%20the%20Project%20Management%20Body%20of%20Knowledge%20(PMBOK%C2%AE%20Guide)%20(6th%20Edition)&page=11&view=collapsed&zoom=1