PRINCE2, A Project Management Methodology
(→Manage by stages) |
(→Manage by exception) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
== Manage by exception == | == Manage by exception == | ||
| − | + | A PRINCE2 project should have defined tolerances for each project objectives and manage by exception is used in the project organization to manage the level below. The level below should only notify the upper level if there is a big issue that is outside their tolerance. | |
== Focus on products == | == Focus on products == | ||
Revision as of 14:46, 12 September 2015
Project management is a discipline that is indispensable and rapidly expanding as an organization nationally and globally. To implement new strategies and products successfully, an organization needs to select project managers to introduce new products, services with a purpose of gaining competitiveness in the market. However by selecting a project manager and a team, an organization is not guaranteed successful project outcomes.
In past years different methodologies have been developed to help organizations consider all the necessary components of project management, e.g. planning, controlling, communication and finalization of projects. One of the widely used project management methodologies is the PRINCE2 method, this methodology is based on seven principles and seven themes which will be described throughout this article. While this article is going to be used publicly, it is important to know other properties of this methodology, e.g. scalability and advantages, in order to make the right discussion while choosing a project management methodology.
Contents |
PRINCE2
PRINCE (PRoject IN Controlled Environments) is a structured method for effective and efficient project management. The method was developed from an exiting method PROMPTII, which was developed by Simpact Systems Ltd in 1975. In 1979 PROMPTII was adopted by CCTA (The Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency) in UK as the standard for all government projects, mainly for IS (Information Systems) projects. In 1989 Superseded PRINCE the exiting method PROMPTII within government projects. [book]
CCTA continued developing the method and in 1996 launched PRINCE2 in response to user requirements for improved guidance on project management on all projects, not only IS projects. PRINCE2 is based on experiences of European project managements and project teams, who have contributed, some from their successes and others from their mistakes and omissions. [1]
Overview of the method
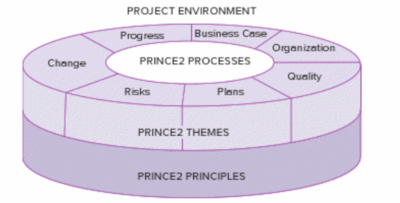
The PRINCE2 method is made of four main parts: The principles, the processes, the themes and the project environment, these elements are shown in figure 1.
Overview of principles
The first integrated element of PRINCE2 is the principles. You can think of this element us a core concept that the rest of PRINCE2 method adheres to. The seven principles are described in details below.
Business justification
The continued business justification principle supports the need for an updated documentation and approved justification at the start and during the project.
Learn from experience
Every project is unique and this uniqueness leads to risk and challenges. The project team should learn from previous projects through log reviewing, in order to avoid the same mistakes.
Roles and responsibilities
Everyone working on a project should know the nature of their involvements, and what they are responsible for. A project should have defined and agreed roles and responsibilities within an organization.
Manage by stages
A PRINCE2 project is controlled, planned and monitored on stage by stage basis. Business case, risk and detailed plan for the next stage should be developed after the previous stages are completed and at the end of every stage the project board should assesses the performance.
Manage by exception
A PRINCE2 project should have defined tolerances for each project objectives and manage by exception is used in the project organization to manage the level below. The level below should only notify the upper level if there is a big issue that is outside their tolerance.
Focus on products
Tailor to suit the environment
Overview of processes
The PRINCE2 structure model, shown in Figure 1, consist of eight management processes, covering activities from starting up of a project, through controlling planning and closing of the project.
These activities are the same for all projects and also in case of implementation of improvement within the organization.
Starting up a project (SU)
Directing a project (DP)
Initiating a project (IP)
Managing stage boundaries (SB)
Controlling a stage (CS)
Managing product delivery (MP)
Closing a project (CP)
Planning (PL)
Overview of themes
The Benefits of PRINCE2
A good project management method will guide the project through a controlled, well-managed and visible sets of activities to archive organization goals. Organizations are aware of the benefits a project management method can bring, and some of the benefits are:
- A repeatable method
- A structured method
- Building on experience
- Ensuring that everyone knows what to expect, where, how and when
- Early warning of problems
Sometimes projects are related to each other or they are a part of a larger program an organization is managing, in all these situations the PRINCE2 method is applicable, it can provide the organization with:
- Active involvement of users and stakeholders in the project
- Controlled management of resources
- Controlled management of risks
- focused on goal of the project, what the project is delivering, why and by whom
PRINCE2 provide the project with:
- Organized start, middle and end of a project
- Regular reviews of the progress
- Good communication between project management team and organization
Project managers are able to:
- Keep meetings in the vital points of the project
- Provide brief reporting about the project
- Divide projects into manageable stages in order to make the goals achievable