Parkinson's Law in Project Management
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Parkinson describes how work is elastic in its demands on time. Work becomes more complex as to fill the time before completion. He uses the example of how the bureaucracy of the British Civil Service grew unrelated to the amount of work. The growth depended on two factors: (1) The Law of Multiplication of Subordinates and (2) The Law of Multiplication of Work. He formulated a mathematical formula to determine the increase in staff in any public administrative department.<ref name="Essay" /> | Parkinson describes how work is elastic in its demands on time. Work becomes more complex as to fill the time before completion. He uses the example of how the bureaucracy of the British Civil Service grew unrelated to the amount of work. The growth depended on two factors: (1) The Law of Multiplication of Subordinates and (2) The Law of Multiplication of Work. He formulated a mathematical formula to determine the increase in staff in any public administrative department.<ref name="Essay" /> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | Parkinson's Law explains the behavioural aspect of scheduling. According to Parkinson's Law, a person will spent all the available time to complete a task regardless of the tasks size. This results in inefficient use of time and effort. Project managers can use this to understand employees motivation for completing tasks. In project schedule management, this is valuable knowledge when estimating activity duration. The project manager should account for this tendency when scheduling to ensure efficient use of time and effort.<ref> Project Management Institute, Inc. (September 22, 2017). "Chapter 6: Project Schedule Management". ''Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide)'' (6th ed.). Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). pp. 173–230. ISBN 978-1-5231-1232-6. </ref> | + | Parkinson's Law explains the behavioural aspect of scheduling. According to Parkinson's Law, a person will spent all the available time to complete a task regardless of the tasks size. This results in inefficient use of time and effort. Project managers can use this to understand employees motivation for completing tasks. In project schedule management, this is valuable knowledge when estimating activity duration. The project manager should account for this tendency when scheduling to ensure efficient use of time and effort.<ref> Project Management Institute, Inc. (September 22, 2017). "Chapter 6: Project Schedule Management". ''Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide)'' (6th ed.). Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). pp. 173–230. ISBN 978-1-5231-1232-6. </ref> To overcome Parkinson's Law, a project manager must set deadlines to ensure that a task only takes up the necessary time for completion. |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | To overcome Parkinson's Law, a project manager must set deadlines to ensure that a task only takes up the necessary time for completion. | + | |
| − | <br> | + | |
== Theory == | == Theory == | ||
'''Describe the tool, concept or theory and explain its purpose. The section should reflect the current state of the art on the topic''' | '''Describe the tool, concept or theory and explain its purpose. The section should reflect the current state of the art on the topic''' | ||
| + | *The law: work expands to fill the time available for its completion | ||
*Purpose: to explain the behavioural aspect of scheduling | *Purpose: to explain the behavioural aspect of scheduling | ||
*Description: Parkinson's Law is based on Parkinson's own experiences as a British army staff officer during World War II.<ref name="biblo" /> He uses the bureaucracy of the British Civil Service as an example of Parkinson's Law. Parkinson's Law is based on statistical analyses showing that the number of ships and men in the royal navy fell between 1914 and 1928, while the number of employees in administration rose. Parkinson concludes that the growth of bureaucracy is unrelated to the amount of work. The growth depends on two factors: (1) The Law of Multiplication of Subordinates and (2) The Law of Multiplication of Work. | *Description: Parkinson's Law is based on Parkinson's own experiences as a British army staff officer during World War II.<ref name="biblo" /> He uses the bureaucracy of the British Civil Service as an example of Parkinson's Law. Parkinson's Law is based on statistical analyses showing that the number of ships and men in the royal navy fell between 1914 and 1928, while the number of employees in administration rose. Parkinson concludes that the growth of bureaucracy is unrelated to the amount of work. The growth depends on two factors: (1) The Law of Multiplication of Subordinates and (2) The Law of Multiplication of Work. | ||
*Explanation of the factors | *Explanation of the factors | ||
*Parkinson formulated a mathematical formula to determine the increase in staff in any public administrative department.<ref name="Essay" /> | *Parkinson formulated a mathematical formula to determine the increase in staff in any public administrative department.<ref name="Essay" /> | ||
| − | * | + | *Explanation of formula and how to use it |
== Application == | == Application == | ||
'''Provide guidance on how to use the tool, concept or theory and when it is applicable''' | '''Provide guidance on how to use the tool, concept or theory and when it is applicable''' | ||
| − | *Application: Use in project schedule management - to understand how people behave | + | *Application: Use in project schedule management - to understand how people behave, how to schedule to avoid this behaviour and to ensure time is used efficiently - less time more effort instead of long time less effort |
| − | *Use when estimating activity durations | + | *Use when estimating activity durations - determine the length of a task and set a tight and realistic deadline, ensuring that the time to the deadline is only the time it takes to complete it. |
*Use the tools critical path method, gantt chart, milestone planning | *Use the tools critical path method, gantt chart, milestone planning | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
'''Critically reflect on the tool/concept/theory and its application context. What can it do, what can it not do? Under what circumstances should it be used, and when not? How does it compare to the “status quo” of the standards – is it part of it, or does it extent them? Discuss your article in the context of key readings / resources provided in class. Substantiate your claims with literature''' | '''Critically reflect on the tool/concept/theory and its application context. What can it do, what can it not do? Under what circumstances should it be used, and when not? How does it compare to the “status quo” of the standards – is it part of it, or does it extent them? Discuss your article in the context of key readings / resources provided in class. Substantiate your claims with literature''' | ||
| − | The law should be used when scheduling. | + | *The law should be used when scheduling. |
| − | It is part of the standards as the behaviour described by Parkinson's law is to some degree prevented or diminished by schedule management. | + | *It is part of the standards as the behaviour described by Parkinson's law is to some degree prevented or diminished by schedule management. |
| − | + | *Downside: In CPM parkinson's law can show - some will start on late start and possible miss deadline, use all float time | |
| − | + | ||
== Annotated bibliography == | == Annotated bibliography == | ||
'''Provide key references (3-10), where a reader can find additional information on the subject. The article MUST make appropriate references to the and reference material provided in class – either incorporating it as a source, or critically discussing aspects that are missing from it but covered by this article. Summarize and outline the relevance of each reference to the topic (around 100 words per reference). The bibliography is not counted in the suggested 3000 word target length of the article.''' | '''Provide key references (3-10), where a reader can find additional information on the subject. The article MUST make appropriate references to the and reference material provided in class – either incorporating it as a source, or critically discussing aspects that are missing from it but covered by this article. Summarize and outline the relevance of each reference to the topic (around 100 words per reference). The bibliography is not counted in the suggested 3000 word target length of the article.''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 20:55, 14 February 2021
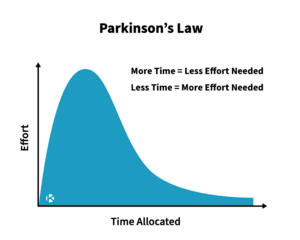
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available for its completion.[2] It was formulated by British historian and author Cyril Northcote Parkinson in an essay for The Economist in 1955.[3]
Parkinson describes how work is elastic in its demands on time. Work becomes more complex as to fill the time before completion. He uses the example of how the bureaucracy of the British Civil Service grew unrelated to the amount of work. The growth depended on two factors: (1) The Law of Multiplication of Subordinates and (2) The Law of Multiplication of Work. He formulated a mathematical formula to determine the increase in staff in any public administrative department.[2]
Parkinson's Law explains the behavioural aspect of scheduling. According to Parkinson's Law, a person will spent all the available time to complete a task regardless of the tasks size. This results in inefficient use of time and effort. Project managers can use this to understand employees motivation for completing tasks. In project schedule management, this is valuable knowledge when estimating activity duration. The project manager should account for this tendency when scheduling to ensure efficient use of time and effort.[4] To overcome Parkinson's Law, a project manager must set deadlines to ensure that a task only takes up the necessary time for completion.
Contents |
Theory
Describe the tool, concept or theory and explain its purpose. The section should reflect the current state of the art on the topic
- The law: work expands to fill the time available for its completion
- Purpose: to explain the behavioural aspect of scheduling
- Description: Parkinson's Law is based on Parkinson's own experiences as a British army staff officer during World War II.[3] He uses the bureaucracy of the British Civil Service as an example of Parkinson's Law. Parkinson's Law is based on statistical analyses showing that the number of ships and men in the royal navy fell between 1914 and 1928, while the number of employees in administration rose. Parkinson concludes that the growth of bureaucracy is unrelated to the amount of work. The growth depends on two factors: (1) The Law of Multiplication of Subordinates and (2) The Law of Multiplication of Work.
- Explanation of the factors
- Parkinson formulated a mathematical formula to determine the increase in staff in any public administrative department.[2]
- Explanation of formula and how to use it
Application
Provide guidance on how to use the tool, concept or theory and when it is applicable
- Application: Use in project schedule management - to understand how people behave, how to schedule to avoid this behaviour and to ensure time is used efficiently - less time more effort instead of long time less effort
- Use when estimating activity durations - determine the length of a task and set a tight and realistic deadline, ensuring that the time to the deadline is only the time it takes to complete it.
- Use the tools critical path method, gantt chart, milestone planning
Limitations
Critically reflect on the tool/concept/theory and its application context. What can it do, what can it not do? Under what circumstances should it be used, and when not? How does it compare to the “status quo” of the standards – is it part of it, or does it extent them? Discuss your article in the context of key readings / resources provided in class. Substantiate your claims with literature
- The law should be used when scheduling.
- It is part of the standards as the behaviour described by Parkinson's law is to some degree prevented or diminished by schedule management.
- Downside: In CPM parkinson's law can show - some will start on late start and possible miss deadline, use all float time
Annotated bibliography
Provide key references (3-10), where a reader can find additional information on the subject. The article MUST make appropriate references to the and reference material provided in class – either incorporating it as a source, or critically discussing aspects that are missing from it but covered by this article. Summarize and outline the relevance of each reference to the topic (around 100 words per reference). The bibliography is not counted in the suggested 3000 word target length of the article.
References
- ↑ Boiser, Lena. "How to Use Parkinson’s Law to Get More Done in Less Time", Kanban Zone. Retrieved 14 February 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Parkinson, C. Northcote (November 19, 1955) "Parkinson’s Law", The Economist. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica "C. Northcote Parkinson", Britannica. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ↑ Project Management Institute, Inc. (September 22, 2017). "Chapter 6: Project Schedule Management". Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) (6th ed.). Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). pp. 173–230. ISBN 978-1-5231-1232-6.