ISM Principles of Change
(→The Three Aspects) |
(→The Three Aspects) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
== The Three Aspects == | == The Three Aspects == | ||
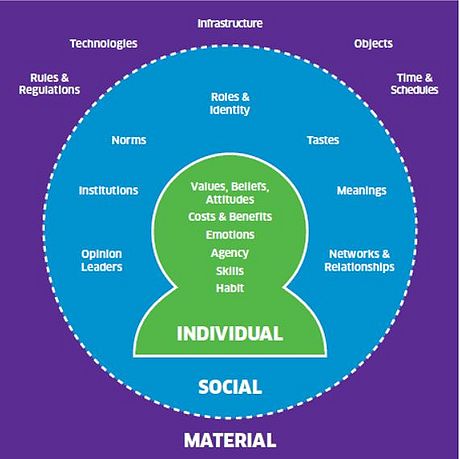
| − | ''The ISM model starts from an understanding of individual behaviour, but sets that within its social and material contexts, | + | ''The ISM model starts from an understanding of individual behaviour, but sets that within its social and material contexts, // |
illustrating how action on multiple levels by multiple actors is required for inclusive and lasting change'' - Andrew Darnton | illustrating how action on multiple levels by multiple actors is required for inclusive and lasting change'' - Andrew Darnton | ||
Revision as of 22:04, 18 February 2021
The ISM - Individual, Social, and Material - model is a multi-disciplinary tool to study the human behavior in the aspects of: behavioral economics, social psychology and sociology [GovScot.]. The model facilitates an integrated, whole-system perspective of the challenges of individuals, organizations, and partnerships. Through the process, stakeholders aim to develop a shared understanding by identifying their respective roles in bringing about change. Hereby, the model draws insight from multiple disciplines to ease the decision-making of complex problems [sustain.]. The result is a shared ownership of solutions. This is a vital part of programme management to successfully transferring ownership to operations in all kind of projects [PMI].
The ISM tool was developed by researcher Andrew Darnton and launched by the Scottish Government in 2013 to evaluate the impact of sustainability challenges in interrelated projects [ISM]. Since, it has found use for policy makers and practitioners to influence people's behaviors and bring about change [Govscot.]. The combination of theoritical and practical aspects of the ISM model is tailored to design or improve programmes, which are utilized in many cases such as waste management, lower carbon emissions, and policy processes [slidsha].
Contents |
Background
The ISM tool was originally created in 2011 at the University of Manchester to map and influence people's behaviour towards sustainability challenges. In this relation, Andrew Darnton further developed and standardized the ISM classification model in 2013 to cover policy interventions and programme management. It was considered to be an all-in-one practical alternative to existing behavioural models by bringing together multiple disciplines as illustrated in Figure XX.
Since, an ISM technical guide has been published by the Scottish Government and nominated as the tool of choice to implement behavioural change. Moreover, the ISM concept has been mandated all public institutions in Scotland in order to meet certain Carbon budgets. The areas include health care, local authorities, DEFRA, the NUS, the Scottish Natural Heritage, and diverse community groups amongst others [ISMtool / scottish government].
The Three Aspects
The ISM model starts from an understanding of individual behaviour, but sets that within its social and material contexts, // illustrating how action on multiple levels by multiple actors is required for inclusive and lasting change - Andrew Darnton
Individual
x
Usage
x
Limitations
x
References
It fosters identification and development of options and shared ownership of solutions, taking account of influences on behaviors and decision-making which ultimately determine the impact of projects and actions.
Further readings: Behavioral economics: Nudge, R. H. Thaler. Social psychology: Influence Science and Practice, R. B. Cialdini. Sociology: The dynamics of social practice, E. Shove.