Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA)
(→The context of CAPA) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
=Abstract= | =Abstract= | ||
| − | Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) are procedures designed to handle nonconformity and other undesirable situations. In this context is corrective actions is defined as actions set in motion to eliminate an occurred nonconformities or unwanted situations, and preventive actions as actions set in motion to eliminate potential nonconformities or unwanted situations <ref name="CAPAFDA">Rodríguez-Pérez, José American Society for Quality 2011, CAPA for the FDA Regulated Industry</ref>. CAPA is a mandatory part of the Quality Management System (QMS) for any pharmaceutical or medical device manufacturer reporting to the U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA). CAPA is also an integrated part of ISO:13485 and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) for medical products. The FDA defines the purpose of a CAPA procedure as: collecting and analyzing information, identifying and investigating product and quality problems, and taking appropriate and effective corrective and/or preventive action to prevent their recurrence <ref name="FDA">FDA website Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) https://www.fda.gov/corrective-and-preventive-actions-capa#page3.</ref> | + | Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) are procedures designed to handle nonconformity and other undesirable situations. In this context is corrective actions is defined as actions set in motion to eliminate an occurred nonconformities or unwanted situations, and preventive actions as actions set in motion to eliminate potential nonconformities or unwanted situations <ref name="CAPAFDA">Rodríguez-Pérez, José American Society for Quality 2011, CAPA for the FDA Regulated Industry</ref>. CAPA is a mandatory part of the Quality Management System (QMS) for any pharmaceutical or medical device manufacturer reporting to the U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA). CAPA is also an integrated part of ISO:13485 and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) for medical products. The FDA defines the purpose of a CAPA procedure as: collecting and analyzing information, identifying and investigating product and quality problems, and taking appropriate and effective corrective and/or preventive action to prevent their recurrence <ref name="FDA">FDA website Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA). Link: https://www.fda.gov/corrective-and-preventive-actions-capa#page3.</ref> |
The purpose of this article is to give the reader an overview on how to perform a CAPA and which risk to be aware of. In this article a 7 step framework is presented. The steps include 1) Identification; 2) Evaluation; 3) Investigation; 4) Analysis; 5) Action Plan; 6) Implementation; 7) Follow-up. | The purpose of this article is to give the reader an overview on how to perform a CAPA and which risk to be aware of. In this article a 7 step framework is presented. The steps include 1) Identification; 2) Evaluation; 3) Investigation; 4) Analysis; 5) Action Plan; 6) Implementation; 7) Follow-up. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
===Project quality management=== | ===Project quality management=== | ||
| − | A project is an unique temporary organizational construction with a defined objective. Projects can operate under different constrains such as time, cost, quality, etc. CAPA projects are related to quality management of a product/system. Quality management is the coordinating of activities to direct and control an organization with regard to quality | + | A project is an unique temporary organizational construction with a defined objective. Projects can operate under different constrains such as time, cost, quality, etc. CAPA projects are related to quality management of a product/system. Quality management is the coordinating of activities to direct and control an organization with regard to quality. The CAPA process can be used as a quality management approach when working with project management. A quality management approach is a procedure that describes how quality will be managed in a given project <ref name="AXELOS">AXELOS, Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition chapter 8</ref>. |
====Continuous improvement==== | ====Continuous improvement==== | ||
| − | CAPA is categorized under the section measurement, analysis and improvement in ISO:13485 and closely related to continues improvement processes. CAPA can be an alternative to processes such as the plan-do-check-act (PDCA) by Shewhart (modified by Deming), or other quality improvement initiatives such as total quality management (TQM), Six Sigma, and Lean | + | CAPA is categorized under the section measurement, analysis and improvement in ISO:13485 and closely related to continues improvement processes. CAPA can be an alternative to processes such as the plan-do-check-act (PDCA) by Shewhart (modified by Deming), or other quality improvement initiatives such as total quality management (TQM), Six Sigma, and Lean <ref name="AXELOS">AXELOS, Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition chapter 8</ref>. |
| − | + | ||
| − | AXELOS, Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
===Regulatory authorities=== | ===Regulatory authorities=== | ||
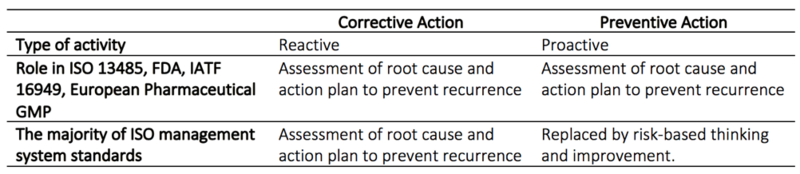
CAPA is most commonly used in highly regulatory industries and is a mandatory part of a Quality Management System (QMS) for any pharmaceutical or medical device manufacturer reporting to the U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or who is compliant with ISO:13485 Medical Devices as well as European Pharmaceutical GMP and IATF. Procedures for corrective actions is also mandatory to include in the QMS for the majority of ISO management systems. | CAPA is most commonly used in highly regulatory industries and is a mandatory part of a Quality Management System (QMS) for any pharmaceutical or medical device manufacturer reporting to the U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or who is compliant with ISO:13485 Medical Devices as well as European Pharmaceutical GMP and IATF. Procedures for corrective actions is also mandatory to include in the QMS for the majority of ISO management systems. | ||
| − | [[File:CAPA.PNG|800px|thumb|centre|Figure 1: Corrective action vs. preventive action </ref>]] | + | [[File:CAPA.PNG|800px|thumb|centre|Figure 1: Corrective action vs. preventive action <ref name="Mark">Hammar, Mark |
| + | Complete guide to corrective action vs. preventive action. Link: https://advisera.com/9001academy/blog/2020/06/22/complete-guide-to-corrective-action-vs-preventive-action/</ref>]] | ||
= The 7 steps of CAPA = | = The 7 steps of CAPA = | ||
Revision as of 18:13, 21 February 2021
Contents |
Abstract
Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) are procedures designed to handle nonconformity and other undesirable situations. In this context is corrective actions is defined as actions set in motion to eliminate an occurred nonconformities or unwanted situations, and preventive actions as actions set in motion to eliminate potential nonconformities or unwanted situations [1]. CAPA is a mandatory part of the Quality Management System (QMS) for any pharmaceutical or medical device manufacturer reporting to the U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA). CAPA is also an integrated part of ISO:13485 and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) for medical products. The FDA defines the purpose of a CAPA procedure as: collecting and analyzing information, identifying and investigating product and quality problems, and taking appropriate and effective corrective and/or preventive action to prevent their recurrence [2]
The purpose of this article is to give the reader an overview on how to perform a CAPA and which risk to be aware of. In this article a 7 step framework is presented. The steps include 1) Identification; 2) Evaluation; 3) Investigation; 4) Analysis; 5) Action Plan; 6) Implementation; 7) Follow-up.
The context of CAPA
Project quality management
A project is an unique temporary organizational construction with a defined objective. Projects can operate under different constrains such as time, cost, quality, etc. CAPA projects are related to quality management of a product/system. Quality management is the coordinating of activities to direct and control an organization with regard to quality. The CAPA process can be used as a quality management approach when working with project management. A quality management approach is a procedure that describes how quality will be managed in a given project [3].
Continuous improvement
CAPA is categorized under the section measurement, analysis and improvement in ISO:13485 and closely related to continues improvement processes. CAPA can be an alternative to processes such as the plan-do-check-act (PDCA) by Shewhart (modified by Deming), or other quality improvement initiatives such as total quality management (TQM), Six Sigma, and Lean [3].
Regulatory authorities
CAPA is most commonly used in highly regulatory industries and is a mandatory part of a Quality Management System (QMS) for any pharmaceutical or medical device manufacturer reporting to the U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or who is compliant with ISO:13485 Medical Devices as well as European Pharmaceutical GMP and IATF. Procedures for corrective actions is also mandatory to include in the QMS for the majority of ISO management systems.
The 7 steps of CAPA
Step 1: Identification
Step 2: Evaluation
Step 3: Investigation
Step 4: Analysis
Step 5: Action plan
Step 6: Implementation
Step 7: Follow-up
CAPA Report and documentation
Limitations
Critically reflect on the tool/concept/theory and its application context. What can it do, what can it not do? Under what circumstances should it be used, and when not? How does it compare to the “status quo” of the standards – is it part of it, or does it extent them? Discuss your article in the context of key readings / resources provided in class. Substantiate your claims with literature
Other relevant Wiki articles
How to create a working CAPA team: Roles and responsibilities in project team.
How to control the scope of the CAPA project: Project Scope Management.
How to ensure control of the CAPA proces: Project Control.
How to improve your CAPA processes: Lessons learned.
Annotated Bibliography
Provide key references (3-10), where a reader can find additional information on the subject. The article MUST make appropriate references to the and reference material provided in class – either incorporating it as a source, or critically discussing aspects that are missing from it but covered by this article. Summarize and outline the relevance of each reference to the topic (around 100 words per reference). The bibliography is not counted in the suggested 3000 word target length of the article.
References
- ↑ Rodríguez-Pérez, José American Society for Quality 2011, CAPA for the FDA Regulated Industry
- ↑ FDA website Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA). Link: https://www.fda.gov/corrective-and-preventive-actions-capa#page3.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 AXELOS, Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition chapter 8
- ↑ Hammar, Mark Complete guide to corrective action vs. preventive action. Link: https://advisera.com/9001academy/blog/2020/06/22/complete-guide-to-corrective-action-vs-preventive-action/