Project Risk Management and Project Risk Management Processes
(→The six Ws framework for the roots of uncertainty) |
(→The six Ws framework for the roots of uncertainty) |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
'''6. When''' - when does it have to be done ? (timetable) | '''6. When''' - when does it have to be done ? (timetable) | ||
| − | Answering these questions which are associated with the uncertainty, is fundamental in order to achieve effective identification and management of both theats and opportunities that may occur during the project's life cycle. | + | Answering these questions which are associated with the uncertainty, is fundamental in order to achieve effective identification and management of both theats and opportunities that may occur during the project's life cycle. In figure 3, the flow lines show how the roots of uncertainties influence the project. |
==The Scope of Project Risk Management== | ==The Scope of Project Risk Management== | ||
Revision as of 17:37, 19 September 2015
The Risk Management is a methodology which aims to control the uncertainties that may occur in a project.The methodology started to be studied after the World War II, when large companies with diversified portfolios began to be developped and the need for insurance against the risks started to grow. Project and Risk managers must eliminate the uncertainties, in order to ensure that the project will achieve its goals. The uncertainties and the risks can be related to the duration of activities, to the absence of adequate resources, to the time and cost or other external factors, that can cause undesired effects to the project's performance. In order to manage these risks effectively and efficiently there are processes that can be implemented to deal with risks. The processes include 4 different phases:the 1st phase is the risk management planning which identifies how to plan the activities of the risk management. The 2nd phase is the risk identification which contibutes to the recognition of the risks, the 3rd is the risk analysis that measures the probability and the results of a risk. Finally the 4th step is the risk response planning which enables managers to eliminate the identified risks and establish methods to monitor and control them.
Contents |
History
Risk Management began to be studied after World War II, in order to protect individuals and companies from various losses associated with accidents [1]. Several sources (Crockford 1982, Harrington and Neihaus 2003, Williams and Heins 1995) date the origin of modern risk management to 1955-1964. During the 1950s, new forms of risk management emerged due to the fact that the risk of several new businesses was high and impossible to be insured. Specifically, in the 1960s new planning activities started to be developped such as risk prevention or self-protection and self insurance activities against different kind of losses or risks. Later in the 1970s, financial risk managenent was a first priority for many companies including banks and insurers. The reason was that many companies were exposed to risks that were related to price fluctuations such as interest rates, exchange rates or prices of the raw materials. The next decade, the use of derivatives as risk management tool expanded rapidly as companies intensified their financial risk management. Companies also developped internal risk management models and capital calculations formulas to deal with anticipated risks, as the international risk regulation had already began.
The table below presents some of the most important milestones in the history of risk management.
Fig. 1: Milestones in the history of Risk Management
Uncertainty in Project Management
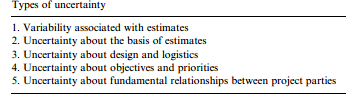
The uncertainties in any project, are the facts that can cause negative or positive effect on the objectives of the project. Most of the project management activities aim to manage the uncertainties that may occur from the earliest stages of the project's life cycle. The lack of available information or knowledge are considered to be some of the basic reasons that cause uncertainties in a project. Although they can affect the project's final performance, uncertainties stem from factors that cannot be anticipated or measured. Some examples include unforseen tasks, unexpected resource requirements and faulty allocations of time. However, uncertainties can be positive as opportunities and negative as threats. Risk Management is considered to be the methodology that undertakes the management of both threats and opportunities. Traditionally, managers focus on identifying, evaluating and managing threats ( or as some call it, risks). Nevertheless, the last decade there has been a stronger focus on how to manage the opportunities facing a project. The uncertainties can occur throughout the project's life cycle, but also in the pre-execution stages when they contribute to uncertainty in five areas.
The table below illustrates the five areas of uncertainty
All these areas are really important and they affect the project's final performance. As the list goes down the areas become fundamentally more important to the project's performance. For instance the variability associated with estimates involves the other four areas and each of them invloves dependencies on later areas in the list.
The six Ws framework for the roots of uncertainty
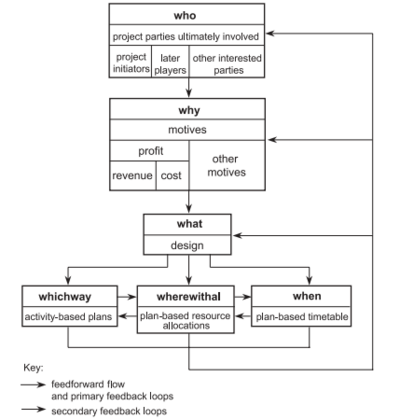
The most important issues that risk management aims to address are related to objectives and relationships between project's parties. Such issues need to be taken into consideration very early in the project and throughout the project's life cycle. For this purpose Chris Chapman[2] and Stephen Ward[3] offer a six Ws framework which is based on the following questions:
1. Who - who are the parties ultimately involved ? (parties)
2. Why - what do the parties want to achieve ? (motives)
3. What - what is it the parties are interested in ? (design)
4. Whichway - how is it to be done ? (activities)
5. Wherewithal - what resources are required ? (resources)
6. When - when does it have to be done ? (timetable)
Answering these questions which are associated with the uncertainty, is fundamental in order to achieve effective identification and management of both theats and opportunities that may occur during the project's life cycle. In figure 3, the flow lines show how the roots of uncertainties influence the project.
The Scope of Project Risk Management
Project Risk Management Processes
Risk Management Planning
Risk Identification
Risk Analysis
Risk Response Planning
Limitations of the methodology
Conclusion
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found