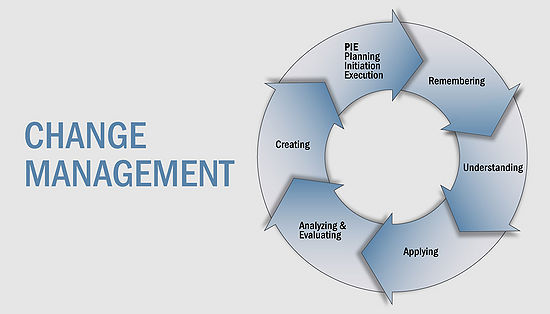
Symbiosis of change and project management
(→Abstract) |
(→Introduction to the VUCA model) |
||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
==Change management in practice== | ==Change management in practice== | ||
===Introduction to the VUCA model=== | ===Introduction to the VUCA model=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | People constantly encounter a change in their daily work, more precisely there's only one sure thing and that is change. In international practice this phenomenon is expressed in a mosaic word: VUCA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | VUCA expanded includes: | ||
| + | * '''Volatility''' | ||
| + | * '''Uncertainty''' | ||
| + | * '''Complexity''' | ||
| + | * '''Ambiguity''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Managers and employees in companies need to cope with these four circumstances on a day-to-day basis and provide appropriate answers and solutions to questions related to these categories. Under such circumstances, it is essential to have a top leadership that is ready, able, and motivated towards change. The hardest task for a manager is to overcome resistance against change. The shorter the time, while resistance is present in a company's management the more effective, is the management of the change process. | ||
Revision as of 19:02, 25 March 2022
Abstract
In the last few decades, the value of project management was a bit misunderstood. We have got to a point where we label as project management different processes or activities that are actually not in this field. Projects can be really different in terms of their scale, their funding, and it really depends on what happens within their corporate framework. We can safely assume that the success of a project rests on how well it is prepared, how receptive are the ones who try to achieve it, and how positive or negative is the attitude towards the specific project. A lot of times these properties are more important, than the actual professional competence of the worker, employee, or manager. In this article, I would like to investigate the necessities and needs of change management in relation to project management, since in practice these too cannot exist without each other's logical background.
If we look back 10-15 years in the past, in the operation of big companies changing to new IT systems and computers was great challenge management wise. And change happened under the umbrella of project management. How did this actually happen?
The CEOs of the companies had big expectations regarding the use of computers instead of human-centered work. They wanted shorter intervals between the ordering and payment processes, a decrease of the administrational staff, or better customer service. However to implement these technologies they needed to link the introduction of IT systems to a wide range of organizational changes (Bingi – Sharma – Godla, 1999). Although the employees of the companies looked at this conversion in a bad way, they felt that this is an obstacle to their daily work habits or as a restriction to it. At this point, we can see how the management of change is as equally important as the project itself.
Contents |
The success criteria of projects
Reasons why a project could fail
Since in practice, the realization of a lot of projects fails, we should clarify what's the success criteria of a typical project. A project is successful if:
- It's considered finished within a specified time frame
- Uses a budget from within a specified spending limit
- Fulfills the intended purpose
At the same time, a project is considered unsuccessful if:
- Before or during the implementation phase, it is interrupted or stopped
- It reaches the implementation phase but doesn't fulfill its purpose
(Fitz-Gerald – Carol, 2003)
Because of the high number of unsuccessful projects, we should look at the reasons behind it more deeply:
- The strategic goals of the project weren't clearly defined, Not just the goals, but the expectations of the project weren't clear enough.
- The top of the management is not working with the defined system of the project, the responsible leaders do not see the essential and key changes which are introduced and are not actively monitoring the implementation process.
- The project management underestimates the scope, size, and complexity of the project:
- Unrealistic timelines are made, and communication is not sufficient for the amount of the expectations
- There is no consistency between business expectations and the chosen system
- The organization is not behind the change:
- Employees naturally seek the status quo and do not feel the need for change
- Workers are afraid of the new system, maybe it can make their work more difficult, or maybe reduces the place and value in the company, or even makes their work obsolete or unnecessary.
- The project team is not skilled enough
- Users are unable to operate the new system properly, due to a poor design or insufficient training
- Data quality is not ensured, inaccurate data leads to loss of confidence towards the project. Employees set aside the new system and get back to the old, reliable one.
- After organizational changes, performance indicators are not fitted properly
- The involvement of different supply sites for the project has not been adequately addressed
- Technical problems with implementation difficulties
(Umble - 2003)
Success criteria
Because most of the studies and articles overlap or sometimes complement each other in identifying the critical success factors, six higher categories have been developed, that contain different success criteria.
These six higher categories consist of:
- Top leadership: - which has to have total commitment and vision as critical success criteria
- Project management: - clear project goals, consistent team members, enough and correct data, planning and control
- Organization: - optimization of business processes
- Stakeholders: - communication, cooperations, and involvement, information, and education
- Technology: - choosing a program or project package, implementing that into the used system, data handling
- Performance: - performance limit and criteria, descriptive and incentive system
(Umble - 2003)
We can see that the success of different projects depends on lots of different factors. However, to what extent they are related to change management we need to look a little deeper into the importance of change management at different project phases.
Change management in a project
The basis of change management
The concept of change management is difficult to determine because it is used for different situations and the scale ranges from general change to change in the preparation phase or maybe change in the sales. Also, the literature on the topic is dominated by practical experiences and an integrative, theoretical frame is missing.
This problem also exists in the context of change management related to project management. In order to have a uniform interpretation of the concept, the following definition is considered relevant: Under change management, we mean the management of in-depth planned changes in a company. It is primarily about people, while the aspects of the subject are covered by project management. Change management targets the change process, from start to the final evaluation, and does not make statements about possible contents.
(Kohnke - Bungard - Madukanya, 2005).
Moving forward with the ideas from the Success criteria chapter, the critical success factors for "Organization" and "Technology" are clearly in the content/subject level in the purpose of implementing a project. Meanwhile the "Top leadership", "Stakeholders" and "Performance" categories represent the people oriented side of the process.The importance of change management in relation to project success
Studies have shown that change management has significant importance in the implementation of projects. In the following sections, I would like to summarize the key findings related to three people-oriented categories of success factors.
Top leadership
Different studies have rated top management as the most important of the critical success factors. In project implementations, usually not just a large area of the company's assets are affected, but also the ones who want the integrate the change. To make the necessary changes the support of the senior management is essential. Support is not just about providing the needed resources for the project, but also for the change process itself. It is not enough to be a member of the top management, you have to have the responsibility and possibility of decision approval, covering all areas concerned. According to Nah's (2003) study, the vision of the project, compared to the other success factors only is in the middle importance-wise. But vision plays a very important role, as it gives direction to change. (Nah's, 2003) In addition, vision provides a long-term perspective. Implementing projects are usually long-term plans, that can take up several years, especially if there are cultural changes that come with it. A high problem area is also the short-term perspective of the management and their focus on quick solutions which can hinder the success of the project. Deep changes take time, and this time must be given to the company by the top management. (Kohnke, 2005)
Stakeholders
A really common problem area is that the need to manage a change was not recognized at all or in time. The implementation of new systems leads to deep changes within a company's affected sectors. The affected employees perceive this differently, leading to insecurity, fear, and resistance, which all could negatively affect the success of the project (Aladwani,2001, 2005).
In practice, this resistance leads to diversion from the necessary changes, and in the end, only the old processes are mapped into the "new system". (Aladwani, 2005).
Dismantling this resistance and applying a new way of working and system acceptance is the most important task of change management. In a company where employees share common values and goals and are open to change, the project is more likely to succeed. (Nah- Zuckweiler - Lau, 2003).
Performance
Performance as an aspect of success is hard to measure, this way in the referenced studies they gave rather low importance to it regarding success factors. It is mentioned that the introduction of appropriate performance targets and properties is difficult, and the tendency shows that they rather focus on quantifiable measurements than take into account people-oriented "soft" success factors. Like individual or group behavior and motivation. Change management is not applied in these cases at all or only insufficiently. In practice, projects usually start without change management, and sooner or later they reach a point where the lack of identifying a needed change or the resistance from the stakeholders significantly hampers the continuation of the project. In this case, a cry for help is made towards change management, a framework is needed to save the situation.
Change management in practice
Introduction to the VUCA model
People constantly encounter a change in their daily work, more precisely there's only one sure thing and that is change. In international practice this phenomenon is expressed in a mosaic word: VUCA.
VUCA expanded includes:
- Volatility
- Uncertainty
- Complexity
- Ambiguity
Managers and employees in companies need to cope with these four circumstances on a day-to-day basis and provide appropriate answers and solutions to questions related to these categories. Under such circumstances, it is essential to have a top leadership that is ready, able, and motivated towards change. The hardest task for a manager is to overcome resistance against change. The shorter the time, while resistance is present in a company's management the more effective, is the management of the change process.