Concurrent Engineering
Helenasoes (Talk | contribs) (→Process) |
Helenasoes (Talk | contribs) (→People) |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
| − | '''Project manager''' | + | '''Project manager''' |
| − | In | + | In a CE context the project manager is in most cases also the project leader, and their main tasks are to clearly communicate the project’s vision to the team as well as using their “people-skills” to perform activities such as resolve conflicts, make sure all member’s opinions are heard and intrinsically motivate the members in staying focused on the project <ref name="smith"/>. |
| − | + | The project manager is also responsible for making sure that team members are communicating effectively and that the appropriate channels have been established. The same holds true for providing the team with the toolbox of methodologies, technologies, and software required in the project environment, so that everyone on the team is working from the same set of project-related ground rules. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
===Technology=== | ===Technology=== | ||
Revision as of 15:44, 19 February 2023
Written by Helena Svendsen
Contents |
Abstract
The implementation of concurrent engineering in a project management framework will be explained holistically in this article. As concurrent engineering in its nature is highly dependent on the successful collaboration between the project’s organizational parties, this article will look into the following three aspects: the people participating in the project, the project process itself, and the technology and/or tools required to achieve these. The article will focus on how to make the implementation of concurrent engineering approach successful by addressing topics like the need for close communication between team members, the necessity of interdisciplinary teams, effective project planning and what tools are required to support these processes. Finally, the approach's advantages and disadvantages are discussed, and lastly they are paired with the preceding sequential engineering approach to address the situations in which one approach is better to apply than the other.
Big idea
Context
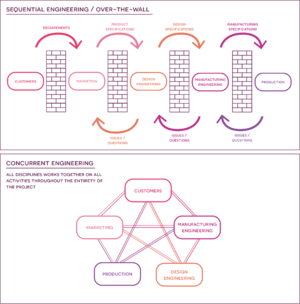
Concurrent engineering (CE) emerged in the 1980s as a result of the need for a more integrated method of operation to keep up with growing competition in the market, respond to a shorter product life-cycle, and meet shifting market and customer demands[1]. Concurrent engineering was thought to be a potential answer to the issues faced by businesses at the time, in order to help them create cheaper goods that could be supplied faster and have higher functionality [2]. Concurrent engineering functioned as a direct response and opposite to the previous traditional "over the wall", sequential engineering (SE) approach, with the overall goals of higher productivity and lower costs by shorter development time and shorter time-to-market.
“Concurrent Engineering is a systematic approach to the integrated, concurrent design of products and their related processes, including manufacturing and support. This approach is intended to cause the developers from the outset to consider all elements of the product life cycle from conception to disposal, including quality, cost, schedule, and user requirements.” - Winner, R.J et al. (1988) [3]
What is Concurrent Engineering?
Concurrent engineering (CE) is neither a technique nor a tool. It is a manner of thinking that calls for a wide range of techniques and methods. The execution of a project's processes simultaneously with the participation of both upstream and downstream functions over the course of the project's life-cycle is the very essence of concurrent engineering [4].
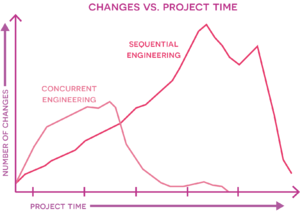
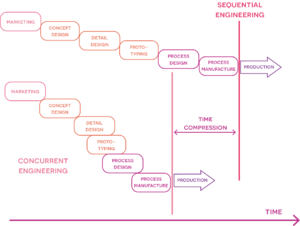
The approach aims to decrease the number of larger iterations further down in the process, where the impact is much greater, by encountering and solving them as they appear in the earlier phases of the project (figure 1). This is made possible by the concurrent nature of the approach, in which integrated, multifunctional teams collaborate and work together simultaneously to address multiple project-related issues at the same time. As the control and responsibility is shared amongst the departments across the project’s phases, and because their activities overlap, they are able to identify potential problems as they appear and are able to address them faster[5]. This is opposite to the traditional sequential engineering (SE) approach, where each activity is handled by one functional organization at a time (marketing, design, manufacturing etc.) and then thrown “over-the-wall” to the next organization (figure 2) without communication. The problem with this approach is that it might be in the very late stages of the process that a problem is identified, because of the lack of communication between organizations, which will result in the activity/product being sent back over-the-wall to fix the issues [6] resulting in a prolonged process time and increased costs. By working concurrently the overall project duration is greatly reduced, as there is constant collaboration and iterations between the teams in the process, ensuring that larger and time-consuming issues will not occur in the final stages, when changes can be both costly and time-consuming. The reduction in time for CE compared to the sequential approach can be seen in figure 3 . And the benefits of the implementation of CE in a project setting can also be deduced from the figure, as it results in an increased productivity and an overall lower cost of the project due to the reduction in duration[5]. Which also means that the time-to-market for the potential product or service is also decreased, providing the company with a competitive advantage on the market compared to their competitors.
Application/Implementation
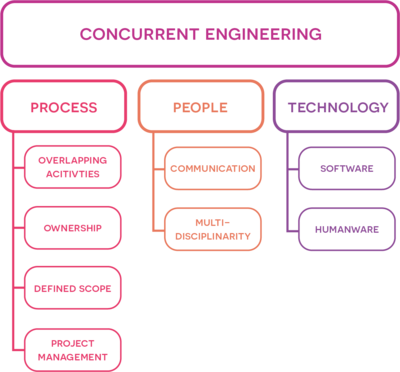
As previously stated, CE requires strong collaboration and communication across the project's numerous phases and disciplines and is fundamentally a socio-technical concept because of the concurrent nature of the method[4]. The organizational capacity to carry out multiple tasks concurrently, to create a multifunctional work team, and to progressively transfer work-in-progress are essential to CE's success. Due to the fact that project planning and leadership have an effect on the entire project, the managerial style of the project manager also significantly affects whether concurrent engineering is successful or unsuccessful. The elements affecting the success of CE and the implementation can be condensed into three categories: Process, People and Technology/Tools. In the following sections these will be explored with focus on what aspects to consider, when attempting to implement CE in a project setting.
Process
- Considering and planning overlapping of activities
- Ensuring that ownership of the process occurs
- Defined, clear and quantitative goals
- Project management activities
Overlapping activities
Defining the process, creating the corresponding schedule of activities, and deciding how to handle the necessary overlapping activities are the first steps in adopting CE. For the project to be completed most effectively and efficiently, this includes how and when the tasks should overlap and where all risks are taken into account early in the process. When there is strong communication and cross-disciplinary teamwork, overlapping activities have been found to shorten development time, but there is also evidence that it is not always advantageous for project governance[6]. This can occur if there are two or more overlapping operations, in which case modifications in the upstream activities necessitate significant changes in the downstream activities, which have already been finished as a result of the overlapping. Therefore, in order to minimize the number of actions that need to be redone, it is crucial to take into account which activities are overlapping and that the downstream impact is taken into account prior to planning overlap.
Ownership and defined scope
Since absence of ownership equates to a lack of project discipline, a process owner must be appointed for the CE process. When an issue arises, the team must be able to turn to the person in charge for guidance. The primary responsibility of the process owner is to ensure that the CE process is correctly implemented and updated as needed. Having a process owner ensures better reactivity to impending changes and better learning for future process improvements, since a process owner is responsible for both the full process and the linked sub-processes[6]. However, for the process owner to be successful in implementing CE, there must be set forth, explicit and measurable project goals. In order for the project team to have a shared knowledge of the objectives when working simultaneously on the project, the scope must be precisely specified. This will help to reduce misconceptions as the project progresses.
Project management
The primary responsibility of the project manager is planning the project, which can be challenging given the simultaneous nature of the approach and the overlapping activities. In order to reduce the project's complexity and create a framework for stage-gate procedures and phase evaluations, the project manager must carefully design the project by dividing it into smaller subphases. All project phases must be taken into account in order to correctly map all the dependencies of the overlapping activities, and then to plan when the parallel and overlapping activities can occur, ensuring the influence on the downstream activities is kept to a minimum [7]. Additionally, planning is done in order to anticipate, identify, and take precautions against any risks related to the various tasks. The project manager uses the milestones and phase reviews to assess whether the project is on track, whether additional resources are required, and whether a delay is occurring. If so, it is the project manager's responsibility to get in touch with the appropriate parties to secure the project's future progress or, if necessary, to put the necessary risk management measures in place to lessen the impact while still staying within budget.
People
- Need for close communication between team members
- Need for multidisciplinarity
- The role of the project manager in a CE setting
Communication
A few prerequisites must be met for a CE team to succeed in order for the project to get off to the best potential start. These requirements suggest that an effective team should have no more than 10 members, and that each member must choose to work on the project of their own free will and be driven by their intrinsic motivation to continue working on it until completion [5]. In addition, for the team to be able to successfully execute the project, it must have at least one representative from each of the major disciplines involved. Since strong communication between the phases/disciplines is necessary to reap the benefits of a CE strategy, it is crucial to keep this in mind before embarking on the project since this might necessitate some changes to function properly.
This includes colocation [5], in which the project team is physically situated in close proximity to one another. This has demonstrated to considerably enhance both problem-solving and decision-making since they have constant access to both the people and the information related to the project. By physically putting the team members close to one another, they are more likely to talk about issues and assist one another in solving them. It also helps to strengthen the team's bond by ensuring that the group views itself as a team rather than a group of individuals sharing knowledge, which in turn strengthens communication [8]. Due to the overlapping nature of CE, the team members' sensitivity [5] to each other's tasks, is also an important factor in the need for communication. For example, if one team member is working on an upstream task, the other team members are highly sensitive to the outcome of that task because it affects their downstream tasks, and as a result, they are more eager to keep each other updated to streamline the process.
Multidisciplinary teams
The usage of multidisciplinary teams, which in this context means that the project team is made up of experts from all the various stages of the project's life-cycle, is the most important component of CE. Depending on the project's scope and objectives, this may comprise individuals from the marketing, design, manufacturing, and programming departments, for example. The inclusion of the client and the supplier in the team has also demonstrated to be a valuable contribution, as their skills can decrease the number of iterations and lead time over the course of the project[1].
The idea behind multidisciplinary teams is that all departments collaborate from the start of the project in order to foresee potential issues and solve them quickly before they have a chance to cause expensive delays. The project manager facilitates communication by setting up these multidisciplinary teams so that all parties involved in the project can communicate directly and promptly with one another across departments to submit their inputs before the project is completed and reach decisions quicker [9]. The departments can gain greatly from this form of communication by utilizing one another's skills and experience to minimize the number of time-consuming adjustments by discussing problems as they arise and solves them as a team [1]. For instance, can manufacturing begin estimating costs based on the early designs, allowing them to begin ordering the necessary machinery, which subsequently can minimize the lead time of waiting for the machines to start manufacturing the product.
Project manager
In a CE context the project manager is in most cases also the project leader, and their main tasks are to clearly communicate the project’s vision to the team as well as using their “people-skills” to perform activities such as resolve conflicts, make sure all member’s opinions are heard and intrinsically motivate the members in staying focused on the project [8].
The project manager is also responsible for making sure that team members are communicating effectively and that the appropriate channels have been established. The same holds true for providing the team with the toolbox of methodologies, technologies, and software required in the project environment, so that everyone on the team is working from the same set of project-related ground rules.
Technology
- Software: Information and communications technologies
- Humanware: Training to utilize tools and approach
- Metrics: To measure progress and improve performance
Software
If integrated communication and information technologies are not put into place, the collaboration between department becomes difficult
- Communication tools that can be used to support CE
- Information sharing tools that can help the team in collaborating across disciplines [10] [9]
Humanware
- The people involved must also be considered in this aspects, as they need extensive training in both using the tools and understanding the approach of CE - and everything that comes with it. [8]
Metrics
- Needs goal-oriented metrics in order to keep the project on track in regards to deadlines and budget [6]
Can be left out...
Implementation approach
When is it applicable? How to implement? When to implement?
- Define the scope and make sure there are measurable goals for the team to work towards.
- Staff the CE team with people from all the involved departments, including suppliers and customers. And employ a process owner to keep track of the CE process.
- Consider their soft-skills like conflict-solving-skills and ability to work with other people.
- Decide in what degree to utilize specialists over generalists, by considering the end goal of the project.
- Make colocation a priority
- Plan the project
- Divide the project into sub-tasks and map the task’s dependencies to figure out which activities can overlap without having too much impact on the downstream activities.
- Plan/figure out what tools/technologies to use to further support the communication between the team members
- Start the project and follow the progress.
- Be an available project manager, but someone who is also an authority figure, who can assign tasks, set milestones and make sure that the project is on schedule by stating deadlines to the team.
Benefits & Limitations
Intro text to chapter...
Benefits
- Shorter time-to-market
- Larger modifications occur in the early phases. Problems are addresses as they appear, so they will not have a major impact later on
- Minimized risks of loss in terms of information between departments when handing over a task, due to the overlapping activities
- More innovative solutions due to the implementation of the multidisciplinary teams
Limitations
- Require extensive organizational changes in order to implement, which can be costly
- All participants in CE need extensive training in CE for it to work
- Need for willing team members to collaborate
- Difficult to plan the entire project when little information is known in the early stages
Concurrent vs. sequential engineering
When to choose one or the other?
- CE: no need for a defined output (only scope) in the beginning - SE: need for at defined goal/output
- For simpler projects that do not require extensive collaboration between departments or across disciplines, SE works. In cases of more complex projects, where there is a possibility of a department making a mistake in the later phases, that can result in costly delays, CE is the best approach.
- In SE progress is easier to track compared to CE due to the overlapping activities
Bibliography
Concurrent Engineering in the 21st Century: Foundations, Developments and Challenges
The newest advancements and industry-best practices for the guiding principles of the framework are covered in-depth in this book's presentation of concurrent engineering. It delves deeply into CE procedures and practices, as well as practical applications and experiences. The book offers a thorough overview of CE from many different viewpoints and industries since it is a compilation of research by numerous professors and scholars.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Trygg, L. (1993). “Concurrent Engineering practices in selected Swedish companies: a movement or an activity of the few?” in Journal of Product Innovation Management, 10(5), pp. 403–415. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/0737-6782(93)90098-B
- ↑ Clark, K.B. & Fujimoto, T. (1991). Product development performance: strategy, organization, and management in the world auto industry. Harvard Business School Press, Boston
- ↑ Winner, R.J. et al. (1988). The role of concurrent engineering in weapons system acquisition. IDA R-338. USA: Institute for Defense Analyses.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Stjepandić J., et al. (eds) (2015) Concurrent engineering in the 21st Century: foundations, developments and challenges. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Swink, M.L. (1998). “A tutorial on implementing concurrent engineering in new product development programs,” in Journal of Operations Management, 16(1), pp. 103-116. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-6963(97)00018-1.'
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Bhuiyan, N. et al. (2006). “Implementing Concurrent Engineering” in Research-Technology Management, 49(1), pp. 38-43. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1080/08956308.2006.11657357
- ↑ Ainscough, M. & Yasdani, B. (2000) "Concurrent Engineering within British Industry" in Concurrent Engineering 8(1), pp. 2-11. Available at: https://doi-org.proxy.findit.cvt.dk/10.1177/1063293X0000800
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Smith, P.G. (1998) “Concurrent Engineering Teams,” in D.I. Cleland (ed.) Field Guide to Project Management. John Wiley & Sons, pp. 439–450, chapter 32.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Ebrahimi M., S. (2011). Concurrent Engineering Approaches within Product Development Processes for Managing Production Start-up phase (Dissertation), pp. 45-86. Tekniska Högskolan i Jönköping.
- ↑ Paashuis, V. & Boer, H. (1997). "Organizing for concurrent engineering: an integration mechanism framework" in Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 8(2), pp. 79-89. Available at: https://doi-org.proxy.findit.cvt.dk/10.1108/09576069710165765.