FMEA
(→General introduction to Risk Management) |
(→General introduction to Risk Management) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
Risk management is the general term for managing unforeseen threats and opportunities. This includes identifying and analyzing risks as well as reacting or preparing appropriately to the identified potential scenarios of a project, program and portfolio. Furthermore, risk management can be applied on a verity of levels and scenarios, but the purpose remains to be a focus on minimizing, eliminating or taking advantage of unknown situations. | Risk management is the general term for managing unforeseen threats and opportunities. This includes identifying and analyzing risks as well as reacting or preparing appropriately to the identified potential scenarios of a project, program and portfolio. Furthermore, risk management can be applied on a verity of levels and scenarios, but the purpose remains to be a focus on minimizing, eliminating or taking advantage of unknown situations. | ||
| − | Managing risk are to some extend essential as a proper risk management strategy can ensure a more optimal resource allocation as well as lowering the effects from an identified situation occurring all of which will improve a company's performance. | + | Managing risk are to some extend essential as a proper risk management strategy can ensure a more optimal resource allocation as well as lowering the effects from an identified situation occurring all of which will improve a company's performance. However, to master risk management, the organization has to structure their approach depending on the particular stage of the project, program, portfolio and importantly use tools and methods of which align with a scope defined by the organization. <ref>[''The Standard of Risk Management in Portfolios, Programs and Projects''] ''Project Management Institute, Inc.'' </ref> An example would be if a company are about to end a construction project. As the risk management is less uncertain, a tool like the Post Project Review (PPR) <ref> [High Voltage Power Network Construction By Keith Harker, Published by The Institution of Engineering and Technology, London, United Kingdom |
| − | <ref>[''The Standard of Risk Management in Portfolios, Programs and Projects''] ''Project Management Institute, Inc.'' </ref> | + | ] "Project Management Procedures" <ref> would become attractive to use as it focusing on structuring the experience within the risk management of the project, for future projects exceed the previous performance with regard to the risks. In other words, the PPR tool is useful to a risk manager who has existing data of an ended project to apply to similar future projects. |
== Introduction to the FMEA tool == | == Introduction to the FMEA tool == | ||
Revision as of 17:04, 7 May 2023
Abstract
The Failure Mode and Effect Analysis.
A tool used for analyzing how potential events can occur doe to failure within the company or project team. The elements analyzed with use of the FMEA tool, can be separated in a matrix and consists of failure events, how they can occur, why they occur and how the failure can be avoided. The different scenarios then get graded with regard to impact-fulness and chance of occurrence, the multiplied score is the used to rank each risk failure event according to their importunateness. The reason for the FMEA tool to have influence on the project management, is because the tool is strictly guiding the PM and his/her team to what topics to focus on in order to get a successful project result. The following report will include:
Contents |
General introduction to Risk Management
Risk management is the general term for managing unforeseen threats and opportunities. This includes identifying and analyzing risks as well as reacting or preparing appropriately to the identified potential scenarios of a project, program and portfolio. Furthermore, risk management can be applied on a verity of levels and scenarios, but the purpose remains to be a focus on minimizing, eliminating or taking advantage of unknown situations. Managing risk are to some extend essential as a proper risk management strategy can ensure a more optimal resource allocation as well as lowering the effects from an identified situation occurring all of which will improve a company's performance. However, to master risk management, the organization has to structure their approach depending on the particular stage of the project, program, portfolio and importantly use tools and methods of which align with a scope defined by the organization. [1] An example would be if a company are about to end a construction project. As the risk management is less uncertain, a tool like the Post Project Review (PPR) Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
What does the tool consists of
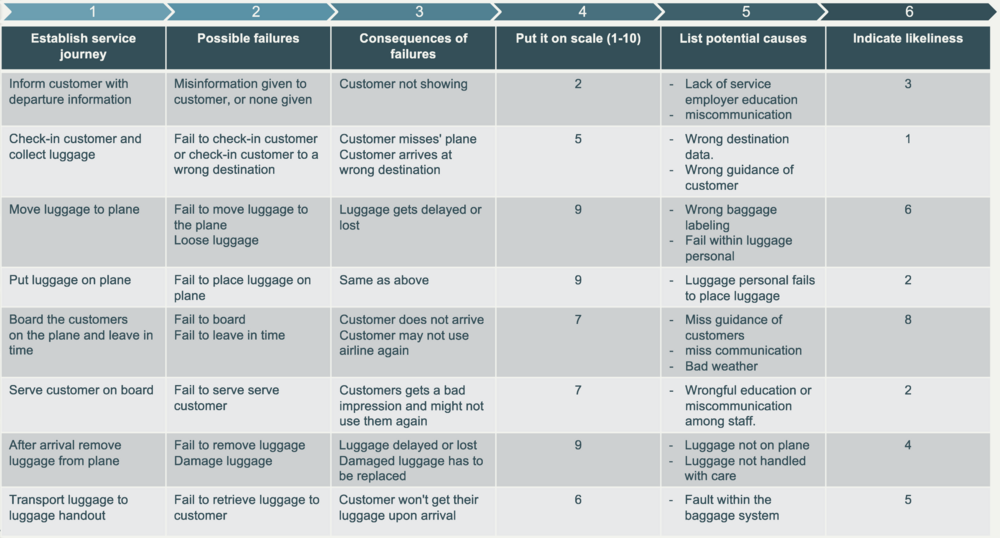
FMEA consists of a matrix with eight rows for a step-by-step approach. First row consists of the stages in the journey. If looking at an example as a flight journey, the different stages would be:
Greed customer in the airport -> receive luggage and print tickets -> ensure that the customer knows of where the plain leves from -> retrieve the ticket at the gate -> seat the customer on the plane -> serve food and beverages -> ensure that the plane lands safely -> retrieve the luggage to the customer.
After identifying all stages of the journey, the second step in the FMEA tool is to describe the potential failure mode for each state. Then the consequences for each failure is added, then the severity of impact, then potential cause, frequency of occurrence, then process controls/recovery actions and lastly the sum-score of the impact and frequency for the ranking of importance.
Here is an example of how the FMEA matrix would look
This example shows how a FMEA could be visualized and importantly, how to fill the matrix it self.
The only real change that one might want to add, could be an extra column with the score sum, in order to clearly identify the modes of at most importance.
How does the tool work
Before using the FMEA matrix, it is important for the project manager to clearly understand if his/hers project is a system, product or process. To get the most from the tool, it is however important to apply it in an early stage of a project, this could be in the initialization of the risk assessments of a project or particular part of the project. This means that what ever result made from the assessment can potentially help avoiding a potential failure, before it happens.
Limitations of the tool
The FMEA has some clear limitations. Firstly, when using the tool, the output is very much defined by the quality of the input. To get the absolut bedst from the FMEA, the project manager needs to gather a lot of information, data and experience. However, if the quality of the out put is not as important as the result of the ranking, then the FMEA might still be a genuinely good tool for a project manager to manage risks and potential risks.
Theory and purpose
The FMEA tool is considered a part of a risk assessment. The tool is considered a "what could happen" or "What would happen" situation assessment tool and is useful after gathering an overview of risks from I.e. a risk matrix assessment or similar tools. [2] The purpose of the tool is to avoid biased decisions based on limited analysis of dept or assumptions based assessments. The methodology consists of assessing each and every element of identified risks fully from the initial defined risks and trough to the absolute end of potential secondary impacts. This helps to create a more accurate assessment of the impact in particular the impact of a potential risk occurring with regard to the side effects and rebound effects depending on the particular usage. Furthermore, the tool does not exceed in assessing the probability of an instance occurring as this is out side the scope of the tool. This can however be assessed with a simulation approach, depending of the event of topic.
Application of the tool in practice
Application in general
The step by step approach of the FMEA tool can be considered more circular with regard to the general risk assessment of a project, system or service. In this application description, the tool will be considered in combination with a classic risk matrix used by many companies when assessing the impact and chance of occurrence of risks on projects.
Risk Matrix
The risk matrix consists of two axis. One tells the probability of occurrence and the other tells the magnitude of the impact when occurring. the x,y coordinates are then used for plotting the identified risks. Here is an example of how on could apply the risk matrix.
identifying the risks:
- Misinformation given to customers
- Fail to check in customers
- Losing a customer's luggage
- Fail to place luggage on the plane
- Fail to leave on time (air port)
- Fail to serve customers in flight
- Damaging luggage
- Fail to retrive luggage to customer
Placing risk in a risk matrix:
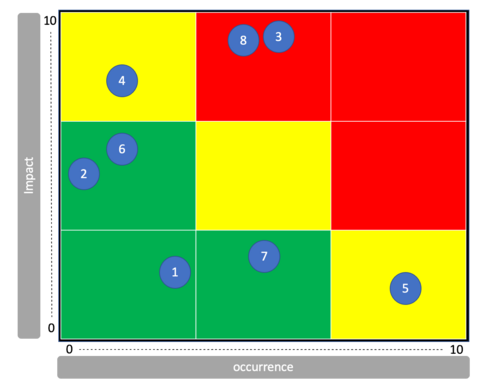
These placements would typically be allocated based on simple based decisions and even though they can be realistic at first glimt, the reality is typically much different. This makes for the benefit of using the FMEA tool.
FMEA and Risk Matrix
The application of the FMEA is useful for assessing the initial risk assessment from the Risk Matrix, and can be further investigated trough data quantitative or qualitative investigations depending on the particular element. Here is an example of how the FMEA tool is applied in combination with the Risk Matrix and its initial identified risks.
As seen, some of the initial rankings might have changed due to more thorough investigations and the result from the FMEA model can then be re applied to the Risk Matrix, as well as used for ranking the importance of addressing for each risk.
Application by PM on a project
The FMEA tool would be applied by a project manager when looking into new projects. The PM should then gather the most experienced team within the project team and maybe even some prominent stakeholders, in order to get as many failure modes as possible. Then the PM could prioritise due to different sets of focuses on the project result. For instance, if a particular stakeholder has highly important needs from what the project delivers, then the potential failure modes affecting those needs would become relevant to encounter. [3]
Alternative applications
On an existing project, then the Project Manager could use the FMEA as an evaluation tool for current as well as previous incidents. The important difference here is that the tool would now be used with a focus on solutions to the failure modes rather than a pinpointing of which failure modes to analyze.
Final notes
References
- ↑ [The Standard of Risk Management in Portfolios, Programs and Projects] Project Management Institute, Inc.
- ↑ [http://www.innovation-portal.info/] Innovation Portal
- ↑ [http://asq.org/learn-about-quality/process-analysis- tools/overview/fmea.html/] General about FMEA