Situational Leadership II
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:SituationalLeadershipIImodel.jpg|350px|thumb|right|Situational Leadership Model II (Blanchard et al, 1993)]] | [[File:SituationalLeadershipIImodel.jpg|350px|thumb|right|Situational Leadership Model II (Blanchard et al, 1993)]] | ||
| − | The Situational Leadership theory introduced by Paul Hersey and Kenneth H. Blanchard (1974,1982). The idea behind it, is that the most effective leadership style is situational-specific. They argued that when the situation is changing (people involved in the project), the leadership style that it is applicable will have differences from the the one used efficiently before (Ronald K. Hambleton and Ray Gumpert, 1982). The management concept of Situational Leadership is introduced in order to help people be more effective in their everyday interactions. Another ingredient in their theory is that the leadership style needs to differ regarding the given task that needs to be done and the maturity level of the group or the individual. | + | |
| + | As it is widely known many engineers do not receive management education. Based on their technical skills they positioned to lead or manage people and project regarding the work and knowledge that they have. Situational leadership can help engineers become successful managers and enable them diagnose their working environment. | ||
| + | |||
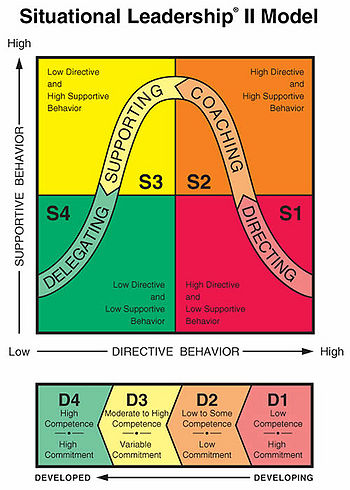
| + | The Situational Leadership theory introduced by Paul Hersey and Kenneth H. Blanchard (1974,1982). The revised model Situational Leadership II appeared was published in January-March 1985. The idea behind it, is that the most effective leadership style is situational-specific. They argued that when the situation is changing (people involved in the project), the leadership style that it is applicable will have differences from the the one used efficiently before (Ronald K. Hambleton and Ray Gumpert, 1982). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The management concept of Situational Leadership is introduced in order to help people be more effective in their everyday interactions. Another ingredient in their theory is that the leadership style needs to differ regarding the given task that needs to be done and the maturity level of the group or the individual. | ||
Situational Leadership is about training managers to identify the advantages and disadvantages of each style, and how they can implemented in different work situations. As Carmen Cirstea and Dumitru Constantinescu mentioned; it is vital for managers to be able to identify their intrinsic leadership style, as intrinsically they return in that style on periods of stress. | Situational Leadership is about training managers to identify the advantages and disadvantages of each style, and how they can implemented in different work situations. As Carmen Cirstea and Dumitru Constantinescu mentioned; it is vital for managers to be able to identify their intrinsic leadership style, as intrinsically they return in that style on periods of stress. | ||
| Line 7: | Line 12: | ||
== Application of Situational Leadership II == | == Application of Situational Leadership II == | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Directive/Supportive Dimensions==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Leadership Styles==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Development Level==== | ||
Revision as of 18:29, 22 September 2017
As it is widely known many engineers do not receive management education. Based on their technical skills they positioned to lead or manage people and project regarding the work and knowledge that they have. Situational leadership can help engineers become successful managers and enable them diagnose their working environment.
The Situational Leadership theory introduced by Paul Hersey and Kenneth H. Blanchard (1974,1982). The revised model Situational Leadership II appeared was published in January-March 1985. The idea behind it, is that the most effective leadership style is situational-specific. They argued that when the situation is changing (people involved in the project), the leadership style that it is applicable will have differences from the the one used efficiently before (Ronald K. Hambleton and Ray Gumpert, 1982).
The management concept of Situational Leadership is introduced in order to help people be more effective in their everyday interactions. Another ingredient in their theory is that the leadership style needs to differ regarding the given task that needs to be done and the maturity level of the group or the individual.
Situational Leadership is about training managers to identify the advantages and disadvantages of each style, and how they can implemented in different work situations. As Carmen Cirstea and Dumitru Constantinescu mentioned; it is vital for managers to be able to identify their intrinsic leadership style, as intrinsically they return in that style on periods of stress.
As leadership is an act from people to the people, it is important to know your people and Paul Hersey and Kenneth H. Blanchard made a model in order to help people, but also, the leaders to successfully deliver a given task. This article will present, review, and also, discuss the implementation of Situational Leadership II in projects.
Contents |