Design thinking
(→Limitations and Challenges) |
(→Limitations and Challenges) |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
Some of the main limitations of including Design Thinking into Project Management include: | Some of the main limitations of including Design Thinking into Project Management include: | ||
| − | * Not efficient applicable to big organizations because Design Thinking happens in small teams with 6-9 members: direct | + | * Not efficient applicable to big organizations because Design Thinking happens in small teams with 6-9 members: direct and personal discussions, as well as interactions, are part of the process' success |
| − | and personal discussions, as well as interactions, are part of the process' success | + | |
* Not applicable if the approach or the directions for possible solutions are already known: at the starting point of the process it is important to have an unbiased view of the situation to expand creative working | * Not applicable if the approach or the directions for possible solutions are already known: at the starting point of the process it is important to have an unbiased view of the situation to expand creative working | ||
* Misunderstanding of the holistic process: it is not only about being creative to innovate a new product or service, it is also about the execution on the market. The newest and best innovation does not help the company if nobody is willing to buy it. The idea of design needs to be combined with business strategies. | * Misunderstanding of the holistic process: it is not only about being creative to innovate a new product or service, it is also about the execution on the market. The newest and best innovation does not help the company if nobody is willing to buy it. The idea of design needs to be combined with business strategies. | ||
Revision as of 18:05, 18 February 2018
Contents |
Abstract
Due to the global financial and economic crisis, Design Thinking is seen as a key competitive competency for companies to compete in markets. The challenge is to become more innovative in products, services, processes and business management. [1]
Design Thinking is understood as an approach to implement creativity into problem-solving areas and develop new ideas. To address problems, a combination of creative techniques and the consideration of business factors such as the inclusion of stakeholders and the conversion capability of the idea into the company are used. [2] The three main attributes of Design Thinking are Empathy, Invention and Iteration. [3]
Nowadays, Design thinking as an innovation tool itself is not new anymore, but the significance of a novel process in project management is consistently growing. The implementation of design thinking supports project managers with necessary tools and prevent project failures. The difficulty for project managers is to uncover the real customer needs. He needs to receive a better understanding of how the customers think, experience and interact with products or services. Including Design as a soft skill into management processes involve the customer early into the process and therefore improves the ability of project managers to follow the right goal and to target the right customers.[3]
1969, Herbert A. Simon first brought up the idea of design as a way of thinking in his book with the title ‘Sciences of the Artificial’. 1990 the process of design thinking was developed by the design school of Stanford and the design and innovation company IDEO was established to communicate it to the market. [4]
The approach consists of 5-coordinated phases (Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test) where the focus is on the customer and its benefit, well-being and needs.[5] The basis is built by an interdisciplinary team with members out of different fields, departments and hierarchical levels which differs in their experience, background, and point of views. One main method of design thinking is the use of abductive thinking which means that the problem needs to be recognized with observations. Instead of the common way to build up a solution for the problem, it is more about first identifying the problems which disrupt the customer's well-being and as a next step to search for possible solutions. Team members are asked to challenge themselves with thinking outside the box. [6]
The purpose of this article is to focus on the basic concepts of the design thinking process as well as its opportunities and threats. Furthermore, it will indicate how Design Thinking can have an impact on the success of project management and how to implement it successfully into the project management of a company.
The design thinking process
The process developed by IDECO is the 5-step model of Design thinking. It is based on the primary process of Herbert Simon of 1969 with 7 steps.[4]
Empathize
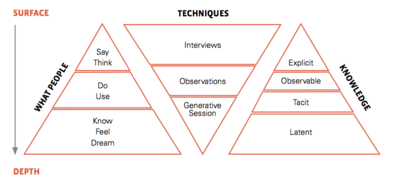
This step is the basis of a human-centred process. It is divided into reframing, exploratory and desk research. After this phase, the project scope and its boundaries, as well as the user profile and stakeholders that need to be addressed, are agreed. The on-site observation is used to gain a deep understanding of the problem and the people. It is essential to analyze their behaviours and interacting with them to build up empathy and to gain insights of how they experience things and the environment. Supported by a research of current trends in this or familiar fields, the designer can come across new ideas and fields of action which he did not have on scope before.It might be challenging for designers to look over the process from an untouched perspective which is fundamental to find new innovations. [5] [6] The three main methods to get in touch with customers, regarding the purpose and the depth of knowledge, can be seen in Figure 2.
Define
The outcome is the formulation of the problem statement as a challenge for the innovation based on the discoveries of the previous phase combined with the observer's point of view as a unique design vision. This step is really important because it defines a specific customer need which the solution needs to satisfy. A beneficial point of view needs to give the project a design frame, a guideline for the innovation effort and captures people which are involved in the project.[5]
Ideate
At this stage, the user's needs are understood and the human-centered problem statement is defined. Next step is to think 'outside the box' and generate ideas to solve the problem. At the beginning, it is important to find as many ideas as possible with a varied range: any idea which first seems to be absurd needs to be reflected. The tool which is often used to collect ideas, is the Brainstorming.[4] There are also several other methods but the crucial criterion is that the collection and the evaluation of ideas need to be separated from each other. The widening of mindset can be enhanced by working with an interdisciplinary team of workers that have lots of ideas in mind and that are willing to build upon an other's idea. This increases the innovation potential of the collection of the solution.[5]
Prototype
The aim of this phase is to bring the developed ideas at an early stage into a physical form to make them more tangible and to see if the theory can work in reality. Uncovering a failure of an idea at an early stage saves valuable resources. IDECO recommends, for instance, a wall of post-it notes, a role-play, an object, or also a storyboard as potential prototypes. The prototype itself changes during the project time. At the beginning, it is simply designed to allow the creation of multiple prototypes. With the growth of the idea over the time period, the prototype becomes more detailed. However, the prototype should represent the situation to receive feedback from future customers and stakeholders as well as to uncover possible weaknesses of the ideas, reduce risks and decrease the range of possible solutions. Other than testing, it is also used to gain empathy for the customer's point of view, to explore alternative options for solutions and to inspire people for the idea.[5]
Test
Testing is understood as the evaluation of the best solutions found within the prototyping. As well as during the previous phases, the future customer shall be included. Although if its the last stage, it is an iterative process meaning the result does not necessarily need to be the final product. The outcome can be refinements of the solution by including the feedback of the customer or even to redefine the problem if the wrong goal was reached.[5]
The iterative nature of Design Thinking
The process is more flexible and does not need to be passed sequentially. Usually, the next step can only be determined as soon as the outcomes of the previous step are available. In order to gain the deepest insights into customer's behaviour, needs and requirements, it might be helpful in many cases to use the outcomes of later stages for an earlier one. Therefore, it is allowed to jump between the phases, run them simultaneously and repeat them.[4]
Design Thinking within Project Management
Three main fields can be identified where Design Thinking is well suited within Project Management: exploration, stakeholder involvement and strategizing. Design Thinking perfectly suits to projects with high uncertainty and ambiguity due to its characteristics. At the beginning of the project, the final solution is not known. First, the situation needs to be analyzed and a problem statement needs to be defined. Then, many solutions are collected and the project manager can test selected ones effectively. The project manager and the project team learn continuously about the situation by moving iteratively between the several steps.[9]
Design Thinking as a user-centred process contributes to Stakeholder Management.[9] Stakeholder Management is a key challenge in Project Management and covers the identification people and groups which are affected by the project, defining their needs and requirements as well as their degree of involvement.[10] To move the user in the fore, followed by other stakeholders, he is involved at an early stage and frequently interacting with the project during the process. In combination with a multidisciplinary project team, the process allows a better understanding of human needs, behaviour and preferences.[9]
Design thinking encourages project strategy orientation and formulation. The deep development of the problem directly at the beginning of the process illustrates this. Furthermore, the process takes a large scope of possible solutions into account which is an efficient way to identify a strategy formulation. Also, the gained knowledge after a phase can be implemented immediately due to the process' iterative characteristic.[9]
Key Factors for successful implementation
Personality of a Design Thinker
Next, to other major factors, the project manager can contribute to the success of the project by selecting a team out of individuals due to their professional experiences and also by their personal characteristics.[10] In order to find the right team members for a project including Design Thinking, the project manager should look for members with particular features such as well developed empathy to realize particular features within the environment, optimism and experimentalism. Moreover, integrated thinking as the ability to find a unique and novel solution in consideration of many, sometimes also inconsistent variables, plays a major role. Also, members with a wide range of experiences within different fields are beneficial for the project.[11]
Advantages, Limitations and Challenges
Advantages
There are numerous advantages associated with Design Thinking. The 6-step process is easy comprehensive and applicable. It comprises a holistic approach from the problem definition to suitable solutions. The progress of the project can be traced at any time by means of the prototypes. Discovered errors are directly implemented. Besides those, there are also far-reaching positive influences.
Within strategic management, there is a huge debate going on. As Roger L. Martin a professor in strategic management at the University of Toronto, who is one of the well-known supporters of Design Thinking, said in an interview that the era of shareholder capitalism is overtaken by the customer capitalism. He states that if a company wants to satisfy its shareholders they first need to start with putting effort into maximizing customers' happiness. By doing so, it needs Design Thinking. This strategic orientation also positively effects the corporate level. It leads to an inspired working environment with a higher motivation of employees. Employees know precisely for whom the product is designed. Customers are more feasible in contrast to shareholders which can change from day today.[1]
Moreover, Design Thinking is needed to compete in markets with short product-life-cycles. The fundamental competitive advantage is to develop a completely new product or service within the shortest time frame compared to others. With its human-centered approach, valuable knowledge about key elements that conduct to customer satisfaction can be created as a competitive advantage. The process also supports the development of creative and innovative solutions. [1]
Current researches of the School of Engineering and Technology at the Central Queensland University have demonstrated that project managers acquire soft skills such as empathy, collaboration, creativity, and non-linear problem solving by using Design thinking within their work. The topic of adapting the curriculum of Project Management Education to the changing environment was already placed during a Global Working Party organized by the International Project Management Association (IPMA) in 1999. In contrast to traditional project manager competencies, the ability to cultivate empathy for customers cannot be learned. But empathy is an important element which influences the project's success. It is mentioned that 51% lessons learned from project failures refer to the planning phase, communication, resource planning and control. The core problems within the project start result from a misunderstanding of the customers and the stakeholders as well as missing empathy. Using Design Thinking allows to decrease project failures. [3]
Limitations and Challenges
Some of the main limitations of including Design Thinking into Project Management include:
- Not efficient applicable to big organizations because Design Thinking happens in small teams with 6-9 members: direct and personal discussions, as well as interactions, are part of the process' success
- Not applicable if the approach or the directions for possible solutions are already known: at the starting point of the process it is important to have an unbiased view of the situation to expand creative working
- Misunderstanding of the holistic process: it is not only about being creative to innovate a new product or service, it is also about the execution on the market. The newest and best innovation does not help the company if nobody is willing to buy it. The idea of design needs to be combined with business strategies.
- Not all kind of industries can benefit from the idea of Design Thinking: there are always industries which are more customer focused than others, for example, the deep technical robot industry
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Leavy, B. (2011):Roger Martin explores three big ideas: customer capitalism, integrative thinking and design thinking", Strategy & Leadership (Vol. 39 Issue: 4, pp.19-26)
- ↑ Johansson-Sköldberg, U.; Woodilla, J.; Çetinkaya, M.(2013): Design Thinking: Past, Present and Possible Futures.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Design Thinking: Get a Quick Overview of the History website of International Design Foundation. Last access on 5.Feb
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Plattner, H.bootcamp bootlegInstitute of Design at Stanford
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Vianna, M.; Vianna, Y.; Adler, I.K.; Lucena, B.; Russo, B.(2012)Design Thinking - Business Innovation
- ↑ http://taniacruz.com/save-time-with-design-thinking/
- ↑ name=DesignThinking
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Ben Mahmoud-Jouini, S.; Midler, C.; Silberzahn, P. (2016): ‘’Contributions of design thinking to project management in an innovation context.’’ Project Management Journal, 47(2)
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 [Project Management Institute (2013):’’A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge’’]
- ↑ Brown, T. (2008): Design Thinking,Harvard Business Review