Project Schedule development
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
==Outputs== | ==Outputs== | ||
| − | At the end of the day, results are the thing that people look at. The goal, that all activities are performed for and all effort done. When it comes to ''time management'' and ''project plan development, | + | At the end of the day, results are the thing that people look at. The goal, that all activities are performed for and all effort done. When it comes to ''time management'' and ''project plan development, "outputs are tangible plans, measurements, tracking processes and status reports that pertain to planning, managing and closing the project itself"<ref>http://asq.org/quality-progress/2008/07/back-to-basics/back-to-basics-outputs-versus-outcomes.html. Retrieved 23 February 2018</ref>. Transparent and clear timetable with task duration and supporting documents are expected. The output, that is a map to follow in terms of keeping project on track, and when necessary, adjustable to the reality of a project environment. |
==Limitation of PSD== | ==Limitation of PSD== | ||
Revision as of 16:27, 23 February 2018
Contents |
Abstract
Soon. Stay tuned.
Motivation
There are many reasons behind Project Schedule development to be taken with appropriate caution, while planning time frame of the project. First of all, it provides in structure way the scheme and toolkit for planned activities. Following the guidelines, it allows to build sufficiently detailed plan of actions with the time-frame for each activity, enable tracking the progress and updating the schedule if necessary. Secondly, transparency and overview of planned action increase efficiency and support maintaining sufficient communication flow. More organized work often benefits in increased motivation, awareness of the project, as well as, gives sense of stability among employees. At last but not the least,PSD implemented correctly decrease the risk of delays, helps allocated resources, which may results in minimizing potential costs of the project.
Introduction
Project Time Management
Project Time Management is defined as set of processes with outputs to ensure all the activities throughout the project are accomplished on time.[1].. It is about increasing both efficiency and effectiveness and to control over the time spent on the particular tasks. As one of the key Project Management areas, the process plays a major role in each out of five project phases. It reflects to the overall performance during the project life cycle as well as the individual task consumption.“Control of time is competitive advantage”[2], wisely used can increase benefits and decrease the costs of a project.
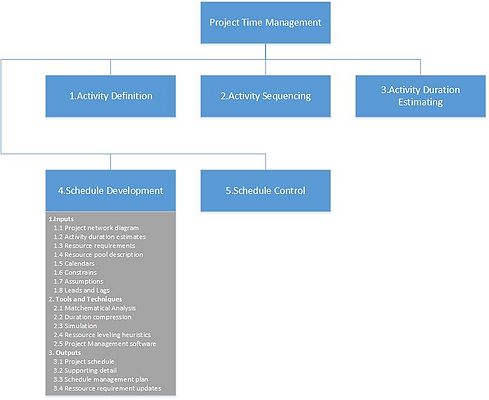
As it is shown in Figure 1. according to PMBOK, The Time Project Management consists of :
- Active Definition- defining particular tasks necessary to accomplished project's goals.
- Activity Sequencing- defining dependencies between project's tasks.
- Activity Duration Estimating- estimating the number of work periods that will be needed to execute individual task.
- Schedule Development- evaluating the sequences of the tasks, its duration and resources requirements in order to prepare the project schedule.
- Schedule Control- monitoring variations to the project schedule.
(different sources: PMI[4] divides it into 4 areas: Time Planning, Time Estimating, Time Scheduling and Time Control).
The overview is meant to be standardized for general purpose of the all project, however based on close connection between Activity Sequencing,Duration Estimating and Development, they may be treated as one process, especially in small projects.[5].
Schedule Development
As the project has starting and finishing date as the project's activities should have them as well. It is essential to define a beginning and a end time of the individual work during life cycle of the project in Project Management. Therefore, Schedule Development as a one of the core processes in Planning Processes[6] should be proceed with details and after analyzing key activities. With its nature to recognize the realistic time and resources limitations, Scheduling takes both into account while preparing the plan. Since the base line of the schedule is affected by many factors, executing this process, PMs should have in mind that the procedure must be iterated.
The flow of Schedule Development is determined by the steps (see Figure 1.) :
1.Inputs
1.1 Project network diagram- visual overview of the sequence and dependency(relation) between the activities.
1.2 Activity duration estimates- estimating the number of work periods that will be needed to execute individual task.
1.3 Resource requirements- Quantity and type of resources required for each activities from Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
1.4 Resource pool description- Quantitative and type availability of resources during project.
1.5 Calendars- Defining periods when work is allowed
1.6 Constrains- Limitations that affects project's team work. There are two main types :
1.6.1 Imposed dates,
1.6.2 Key events and major milestones.
1.7 Assumptions- hypothesis and beliefs, which are taken for granted for the purpose of the project
1.8 Leads and Lags- Dependencies between predecessor and successor activities
2. Tools and Techniques
2.1 Mathematical Analysis- based on theoretical calculations of starts and finishes of the activities (without taking under consideration any constrains) it provides the time windows where particular activity should be proceed. As most known methods includes:
2.1.1 Critical Path Method (CPM)
2.1.2 Graphical Evaluation and Review Technique (GERT)
2.1.3 Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
2.2 Duration compression- Process used to shorten duration of the activities without interfering into the scope of the project. Methods included in the process :
2.2.1 Craching
2.2.2 Fast Tracking
2.3 Simulation- Based on assumptions multiple duration of the activities are calculated. The most known simulation is Monte Carlo Analysis.
2.4 Resource leveling heuristics- based on resources constrains and limitation, starts and ends date of the activities are adjusted.
2.5 Project Management software- These products allows to speed up above calculation by automating the processes
3. Outputs
3.1 Project schedule- Plan of the start and finish of each planned activity. It is shown either as table or more often as a graph like :
3.1.1 Project Network Diagrams
3.1.2 Gantt Charts
3.1.3 Milestone Charts
3.1.4 Time-scaled Network Diagrams.
3.2 Supporting detail- All assumptions and constrains related to the project,plus additional details differ on project type.
3.3 Schedule management plan- Description how the changes in the schedule are managed.
3.4 Ressource requirement updates- see point 1.4
Outputs
At the end of the day, results are the thing that people look at. The goal, that all activities are performed for and all effort done. When it comes to time management and project plan development, "outputs are tangible plans, measurements, tracking processes and status reports that pertain to planning, managing and closing the project itself"[7]. Transparent and clear timetable with task duration and supporting documents are expected. The output, that is a map to follow in terms of keeping project on track, and when necessary, adjustable to the reality of a project environment.
Limitation of PSD
Methodology described above allows in clear and convenient way schedule the activities for the the project, however as every process it has its weakness and limitations:
1.Changing the scope: Activities defined before scheduling are simply based on the scope of the project in terms of delivering desire deliverable. Nonetheless, it is unhightly likely that the scope remains the same through the whole life cycle of the project. Changing the scope means also defining new or re-defining existing activities, which in results affects the outputs out of Schedule Development.
2. Decreased budget: For the Schedule Developments means that duration of some activities need to be shorten and resources reallocated.
3. Since projects environment is dynamic and in constant change, there is no Schedule Development tool or method , which can build 100% accurate time-frame. Projects are affected and influence by multiple factors, which ends up with readjusting or iterating the plan.
Glossary
References
- ↑ Page 59, 1996 ed. PMBOK® Guide.
- ↑ https://www.pmi.org/learning/featured-topics/time. Retrieved 11 February 2018
- ↑ Page 60, 1996 ed. PMBOK® Guide.
- ↑ https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/time-management-project-functions-schedules-5283. Retrieved 11 February 2018
- ↑ Page 60, 1996 ed. PMBOK® Guide.
- ↑ Page 47, 1996 ed. PMBOK® Guide
- ↑ http://asq.org/quality-progress/2008/07/back-to-basics/back-to-basics-outputs-versus-outcomes.html. Retrieved 23 February 2018