Context element
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
| − | === 1. The project context === | + | ==== 1. The project context ==== |
Maybe something about life cycles? [2 p12] | Maybe something about life cycles? [2 p12] | ||
| − | ===2. The temporal context === | + | ====2. The temporal context ==== |
| − | ===3. Organisational context === | + | ====3. Organisational context ==== |
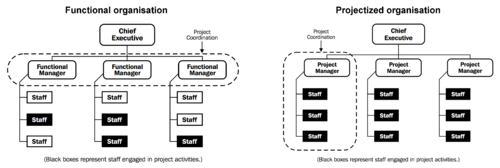
[[File:FunctAndProject.png|thumb|500x500px|right|Figure 1: Organisational structure of a functional (left) and a projectized organisation (right). Source: Guide to Body..]] | [[File:FunctAndProject.png|thumb|500x500px|right|Figure 1: Organisational structure of a functional (left) and a projectized organisation (right). Source: Guide to Body..]] | ||
All projects, except rare cases, exists within a organisational environment and a corporate context. Classically organisations that undertake projects can be described as being functional or projectized organisations. It should be noted that the classification is a spectrum and many organisations lie somewhere between the to classifications. | All projects, except rare cases, exists within a organisational environment and a corporate context. Classically organisations that undertake projects can be described as being functional or projectized organisations. It should be noted that the classification is a spectrum and many organisations lie somewhere between the to classifications. | ||
| − | In traditional functional organisations the staff is organised by their type of work and their are clear reporting lines to the respective management of each work function. When projects are undertaken in functional they are often separated into phases corresponding to the responsibilities of the functional groups. For example in product development, the first phase is often the design phase and will be undertaken as a individual project by the design/engineering department. Subsequently the manufacturing department undertakes the next phase as an individual project. This means that questions and challenges related to their other phases of the project often are communicated to the department head, who consults the associated department head who then contacts the relevant staffing [2]. | + | In traditional functional organisations the staff is organised by their type of work and their are clear reporting lines to the respective management of each work function. When projects are undertaken in functional they are often separated into phases corresponding to the responsibilities of the functional groups. For example in product development, the first phase is often the design phase and will be undertaken as a individual project by the design/engineering department. Subsequently the manufacturing department undertakes the next phase as an individual project. This means that questions and challenges related to their other phases of the project often are communicated to the department head, who consults the associated department head who then contacts the relevant staffing [2]. Another issue that project managers in functional organisations should be aware of is if functional managers are rewarded for assigning staff time to projects. In these cases it is important for the project manager to control that assigned staff is being used effectively. |
| + | When cross-functional projects are undertaken in functional organisations some challenges might arise for the project manager if the overall leadership is not clearly defined. One solution is to define clear project controls at the start of the project, and agreeing these with the project board. This will help to "ensure that the project manager understands the level of interaction and support to expect during the project and is given appropriate exposure to other areas of the corporate organization" [3]. | ||
| − | In projectized organisations the project members are typically co-located regardless of their functional group and reporting is typically done directly to the project manager. For projects undertaken in these organisations, the project management often have a greater deal of independence and authority over the allocated project staff [2]. | + | |
| + | Project based organisations are typically companies that derive their primary revenue from projects (engineering firms, government contractors, consultants etc.). In projectized organisations the project members are typically co-located regardless of their functional group and reporting is typically done directly to the project manager. For projects undertaken in these organisations, the project management often have a greater deal of independence and authority over the allocated project staff. These organisations often have systems in place that support the project management such as financial systems for accounting and reporting of projects [2]. | ||
| − | |||
| Line 49: | Line 50: | ||
Mention internal stakeholders (source and ref for further reading) | Mention internal stakeholders (source and ref for further reading) | ||
| − | |||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
| − | ===4. External context === | + | ====4. External context ==== |
Mention external stakeholders. | Mention external stakeholders. | ||
| − | === Prince2 === | + | ==== Prince2 ==== |
Prince2 uses different distinctions between the context of projects as wether they are stand alone or part of either a program or portfolio. | Prince2 uses different distinctions between the context of projects as wether they are stand alone or part of either a program or portfolio. | ||
Revision as of 12:08, 22 February 2019
Contents |
WORK IN PROGRESS
This article is under construction as part of the wiki article assignment.
Abstract
The topic of this article is the context element of project management. The context element is a concept in project management, that provides an understanding of how outside factors and environment impact a certain project. The environment in which a project is determines many the limitations, requirements and possibilities of the project. This article will provide a theoretical understanding of the context element and describe different contexts. Furthermore the article will present the relevant models that can be used to understand and manage the context element, and lastly it will present the limitations of the context element and the related models.
- Abstract bør opsummere alt hvad der er skrevet i artiklen, gen-skriv til slut*
Background
The context element is a concept in project management that describes how the outside environment influences a project. [a defintion of it]. The context element is a wide concept and covers a wide range of different factors of different importance that influence the limitations, the resources and many other apsects. In order to get a better overview of the concept, it can be organised into the different categories, the project context, the temporal context, the organisational context and the external context [1].
1. The project context
Maybe something about life cycles? [2 p12]
2. The temporal context
3. Organisational context
All projects, except rare cases, exists within a organisational environment and a corporate context. Classically organisations that undertake projects can be described as being functional or projectized organisations. It should be noted that the classification is a spectrum and many organisations lie somewhere between the to classifications.
In traditional functional organisations the staff is organised by their type of work and their are clear reporting lines to the respective management of each work function. When projects are undertaken in functional they are often separated into phases corresponding to the responsibilities of the functional groups. For example in product development, the first phase is often the design phase and will be undertaken as a individual project by the design/engineering department. Subsequently the manufacturing department undertakes the next phase as an individual project. This means that questions and challenges related to their other phases of the project often are communicated to the department head, who consults the associated department head who then contacts the relevant staffing [2]. Another issue that project managers in functional organisations should be aware of is if functional managers are rewarded for assigning staff time to projects. In these cases it is important for the project manager to control that assigned staff is being used effectively.
When cross-functional projects are undertaken in functional organisations some challenges might arise for the project manager if the overall leadership is not clearly defined. One solution is to define clear project controls at the start of the project, and agreeing these with the project board. This will help to "ensure that the project manager understands the level of interaction and support to expect during the project and is given appropriate exposure to other areas of the corporate organization" [3].
Project based organisations are typically companies that derive their primary revenue from projects (engineering firms, government contractors, consultants etc.). In projectized organisations the project members are typically co-located regardless of their functional group and reporting is typically done directly to the project manager. For projects undertaken in these organisations, the project management often have a greater deal of independence and authority over the allocated project staff. These organisations often have systems in place that support the project management such as financial systems for accounting and reporting of projects [2].
The matrix orgnisation.
Mention internal stakeholders (source and ref for further reading)
4. External context
Mention external stakeholders.
Prince2
Prince2 uses different distinctions between the context of projects as wether they are stand alone or part of either a program or portfolio.
Projects can exist as stand-alone entities within an organization and outside the governance structures introduced by programmes or portfolios, or where an organization has been set up solely for the purpose of undertaking the project.
Projects within programmes are typically mandated by the program manager. The goal of the project is then to realise the benefits and strategic target of the programme. The project will as such be impacted by the programme’s approach to governace, structure and reporting requirements.
Every project must be viewed in the context of it's environment. Every project has limitations set by it's environment, this could be rules and standards set. Also time, money, technologyor knowlegde sets limitations (known as resources).
It is important to take the context into account, so the project can be planned and adjusted accordingly to the limitations sets by factors outside the project.
– What are the current barriers or limitations to the project? – Which restrictions a ect the project development?
In program management the context element can both be seen as the context between projects in the program, and between the program and the outside (source)
In the project canvas[x], the context element is a part of the uncertainty aspect. what is it here and how to use it...
Application
The context element is a concept, and can therefore not be applied in itself, but in the scientific literature there exist a range of models and tools that can help understand, manage and (..) the contextual element of a project. In Prince2 ...
How should a project manager use the context element.
-Triple constraint model
- Matrix - Co-location of teams (Project-half double) - The four levels of management recomended by Prince2 - Stakeholder management
Limitations
Annotated bibliography (3-5)
1. Prince2 about projcts in commercial environment. As mentioned, projects in commercial environments for example joint venture and collaborative research can be complicated. Further reading can be done in Prince 2 project guide page ??.
2. PRINCE2 appendix C describes porject boards.
References (5-8)
[1] How to DO Porjects [2] Guide to the body of knowledge [3] Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition [x] Project canvas manuel