Implementing SWOT
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
- What cooperations and relationships do we have with others? | - What cooperations and relationships do we have with others? | ||
| − | Weaknesses | + | '''Weaknesses''' |
| − | + | ||
| + | You can say weakness is when an element in the strength tends to fail. In other words, the weakness can be seen as a barrier for the organization to achieve its business goals and objectives. | ||
| + | Examples of weaknesses in an organization could be: Bad reputation, poor communication, inexperienced in the field or poor quality. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Key questions for the organization to go through its weaknesses, is by asking questions like: | ||
| + | |||
| + | - what is something we are not good at in the company? | ||
| + | - what kinds of cooperations and alliances should we have (but dont have)? | ||
| + | - does our workforce lack anything when it comes to training or competencies? | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Revision as of 11:38, 19 February 2021
Contents |
Abstract
This article is going to have focus on the SWOT Analysis. There will be an introduction to the SWOT and how to implement the tool. Furthermore, there will be a focus on the strenghts and weaknesses of the SWOT analysis which is something that is very beneficial and relevant when working with this tool. In relation to project management, the SWOT analysis can be applied in several different fields like research, strategy or marketing in both public and private organizations and companies.
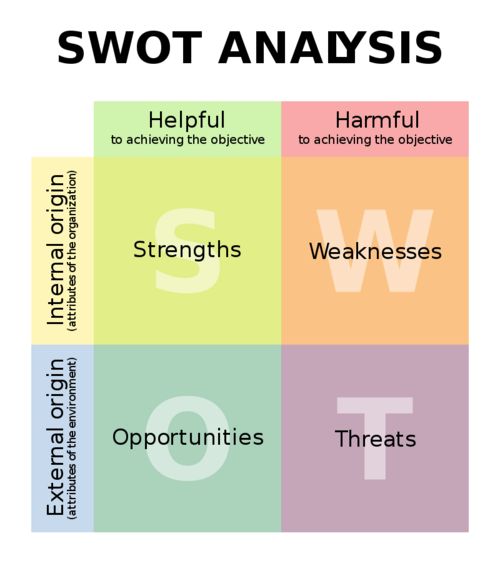
Many companies apply SWOT to get an overview of the potential risks and the obstacles and difficulties there can be. The aforementioned can be for both internal and external problems and purposes. The abbreviation, SWOT, derives from Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats. So the main purpose of the SWOT is to be an analytical device for defining the four aforementioned factors in a specific organization or establishment.
Both the Weaknesses and strenghs can be viewed as internal factors which could be something like ressources or skills that the company possesses. Oppurtunities and threats are viewed as external factors where the company or organization's influence is mainly indirect, which is a correlation to it being called "external" factors or conditions.
Overall, SWOT is designed to give a fact-based and realistic look into an organization, project or any other initiative that is being set in motion. The result may not be a definite action plan but is a very good benchmark and indicator which can give a good point of orientation.
If the SWOT is used well and with a relatively broad base of both external and also internal input, it will lead to a strong analysis that qualifies and enhances the potential for all or parts of a an organizations projects or other initiatives.
Introduction of the SWOT
Implementation of the SWOT
Strength
Strenghs of the company refers typically to the internal skills and resources.It can also be defined as the key factors which plays a role in the company doing well. Examples of strengths could be: trusted brand, high quality, great communication and a good location.
Key questions for the organization to go through it, is by asking questions like:
- What is the things we are very good at, which is better than others? - what is the specific competencies that leads to our success? - What cooperations and relationships do we have with others?
Weaknesses
You can say weakness is when an element in the strength tends to fail. In other words, the weakness can be seen as a barrier for the organization to achieve its business goals and objectives. Examples of weaknesses in an organization could be: Bad reputation, poor communication, inexperienced in the field or poor quality.
Key questions for the organization to go through its weaknesses, is by asking questions like:
- what is something we are not good at in the company? - what kinds of cooperations and alliances should we have (but dont have)? - does our workforce lack anything when it comes to training or competencies?