Stakeholder Analysis and Matrices
(→Stakeholder Analysis) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
=Stakeholder Analysis= | =Stakeholder Analysis= | ||
| − | + | The stakeholder analysis can be useful in the way that policymakers and managers can identify key players and assess their knowledge, interest, position, alliance, and importance to the project or policy. By using the analysis, managers can interact more effectively with key stakeholders and increase their support. The stakeholder analysis is conducted before a program is implemented. This allows managers or policymakers to prevent potential misunderstandings about and/or oppositions to the program or policy. <ref> http://www.eestum.eu/voorbeelden/Stakeholders_analysis_guidelines.pdf </ref> | |
| + | The analysis characterizes stakeholders and provides the information that is needed for a manager to know where his focus should be during the program or policy. The analysis includes the stakeholders’ interests in the project, positions for or against it, potential alliances with other stakeholders, and also their ability to affect the process | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:6830-pf-8.gif]] | ||
=Stakeholder Matrix= | =Stakeholder Matrix= | ||
Revision as of 14:16, 15 September 2015
Stakeholders are referred to as actors (persons or organizations) with a vested interest in the decision or policy that is being promoted. Stakeholder analysis is the method or process used to identify these actors or key individuals/groups that will have an affect on a project, and how to win them over. Stakeholder analysis allows policy and/or decision makers to interact more effectively with key stakeholders; detect and act to prevent potential misunderstandings about and/or opposition to the policy or program; and increase support for a given policy or program.
Contents |
Background
Process
Stakeholder Analysis
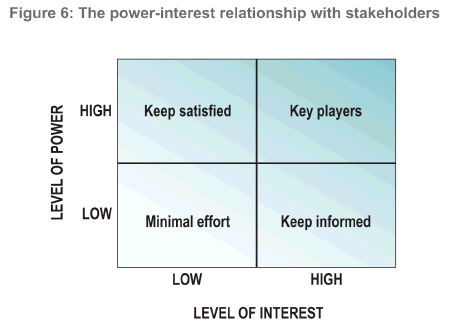
The stakeholder analysis can be useful in the way that policymakers and managers can identify key players and assess their knowledge, interest, position, alliance, and importance to the project or policy. By using the analysis, managers can interact more effectively with key stakeholders and increase their support. The stakeholder analysis is conducted before a program is implemented. This allows managers or policymakers to prevent potential misunderstandings about and/or oppositions to the program or policy. [1]
The analysis characterizes stakeholders and provides the information that is needed for a manager to know where his focus should be during the program or policy. The analysis includes the stakeholders’ interests in the project, positions for or against it, potential alliances with other stakeholders, and also their ability to affect the process
Stakeholder Matrix
How to make a Stakeholder Analysis Matrix
Benefits
Challenges and Uncertainty
Conclusion
References
Further Readings
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found